Aspen is a home rule municipality that is the county seat and the most populous municipality of Pitkin County, Colorado, United States. The city population was 7,004 at the 2020 United States Census. Aspen is in a remote area of the Rocky Mountains’ Sawatch Range and Elk Mountains, along the Roaring Fork River at an elevation just below 8,000 feet (2,400 m) above sea level on the Western Slope, 11 miles (18 km) west of the Continental Divide. Aspen is now a part of the Glenwood Springs, CO Micropolitan Statistical Area.
Founded as a mining camp during the Colorado Silver Boom and later named Aspen for the abundance of aspen trees in the area, the city boomed during the 1880s, its first decade. The boom ended when the Panic of 1893 led to a collapse of the silver market. For the next half-century, known as “the quiet years”, the population steadily declined, reaching a nadir of fewer than 1000 by 1930. Aspen’s fortunes recovered in the mid-20th century when neighboring Aspen Mountain was developed into a ski resort, and industrialist Walter Paepcke bought many properties in the city in the 1950s and redeveloped them. Today it is home to three institutions, two of which Paepcke helped found, that have international importance: the Aspen Music Festival and School, the Aspen Institute, and the Aspen Center for Physics.
In the late 20th century, the town became a popular retreat for celebrities. Gonzo journalist Hunter S. Thompson worked out of a downtown hotel and ran unsuccessfully for county sheriff. Singer John Denver wrote two songs about Aspen after settling there. Both figures popularized Aspen among the counter-cultural youth of the 1970s as an ideal place to live, and the city continued to grow even as it gained notoriety for some of the era’s hedonistic excesses (particularly its drug culture).
Aspen remains popular as a year-round destination for locals, second-home buyers and tourists. Outdoor recreation in the surrounding White River National Forest serves as a summertime counterpart to the city’s four ski areas. Prime residential real estate in Aspen is the most expensive of any ski resort in the world on a per-square-foot basis, according to a study of 44 global ski resorts. Aspen is the world’s second-highest-rated ski resort in terms of “the quality and reliability of their conditions and their capacity to withstand climate change.”
| Name: | Aspen city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Colorado |
| County: | Pitkin County |
| Total Area: | 3.858 sq mi (9.992 km²) |
| Land Area: | 3.858 sq mi (9.992 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.000 sq mi (0.000 km²) |
| Total Population: | 7,004 |
| Population Density: | 1,815/sq mi (701/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 81611, 81612 (PO Boxes) |
| Area code: | 970 |
| FIPS code: | 0803620 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0204686 |
| Website: | aspen.gov |
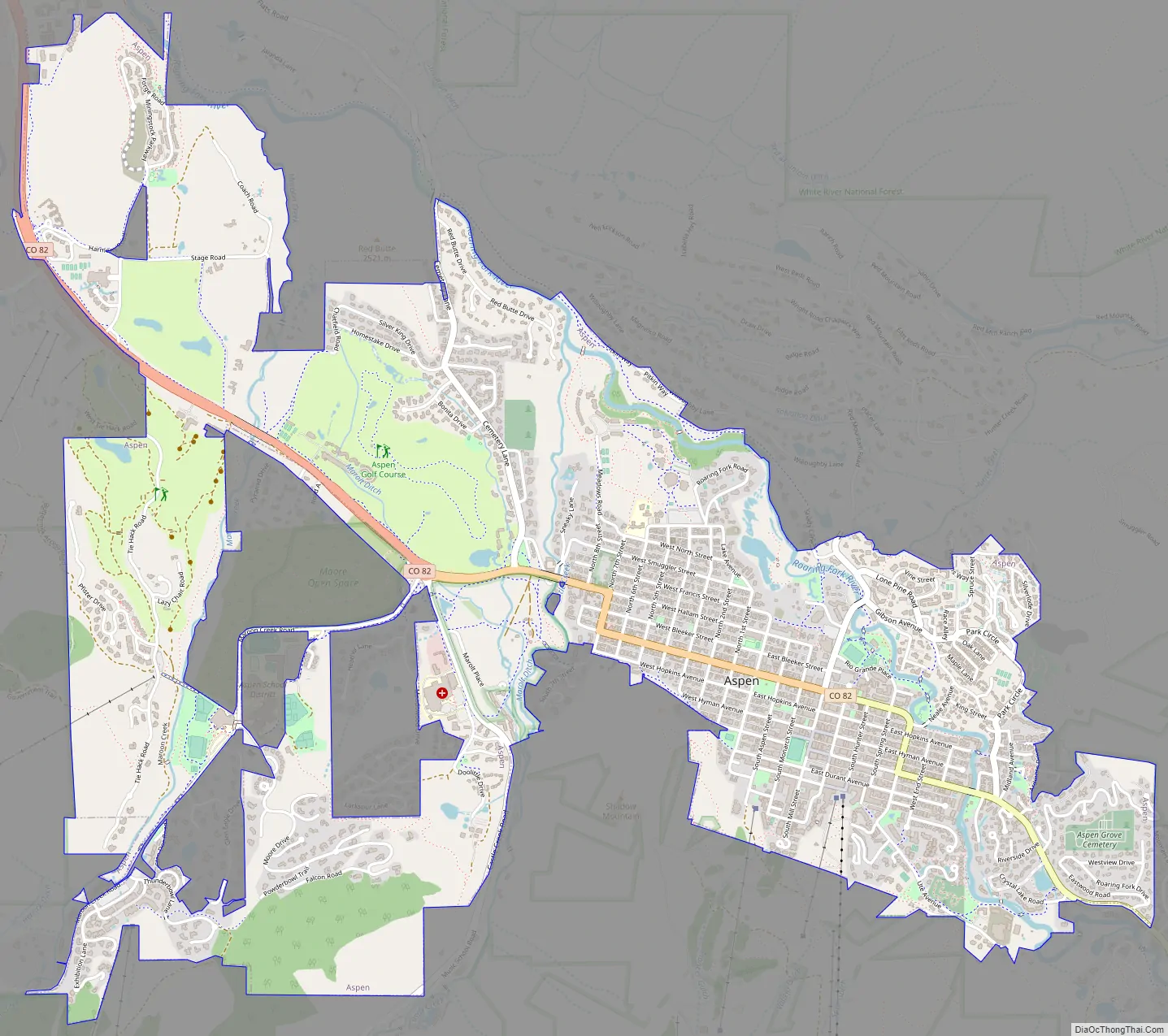
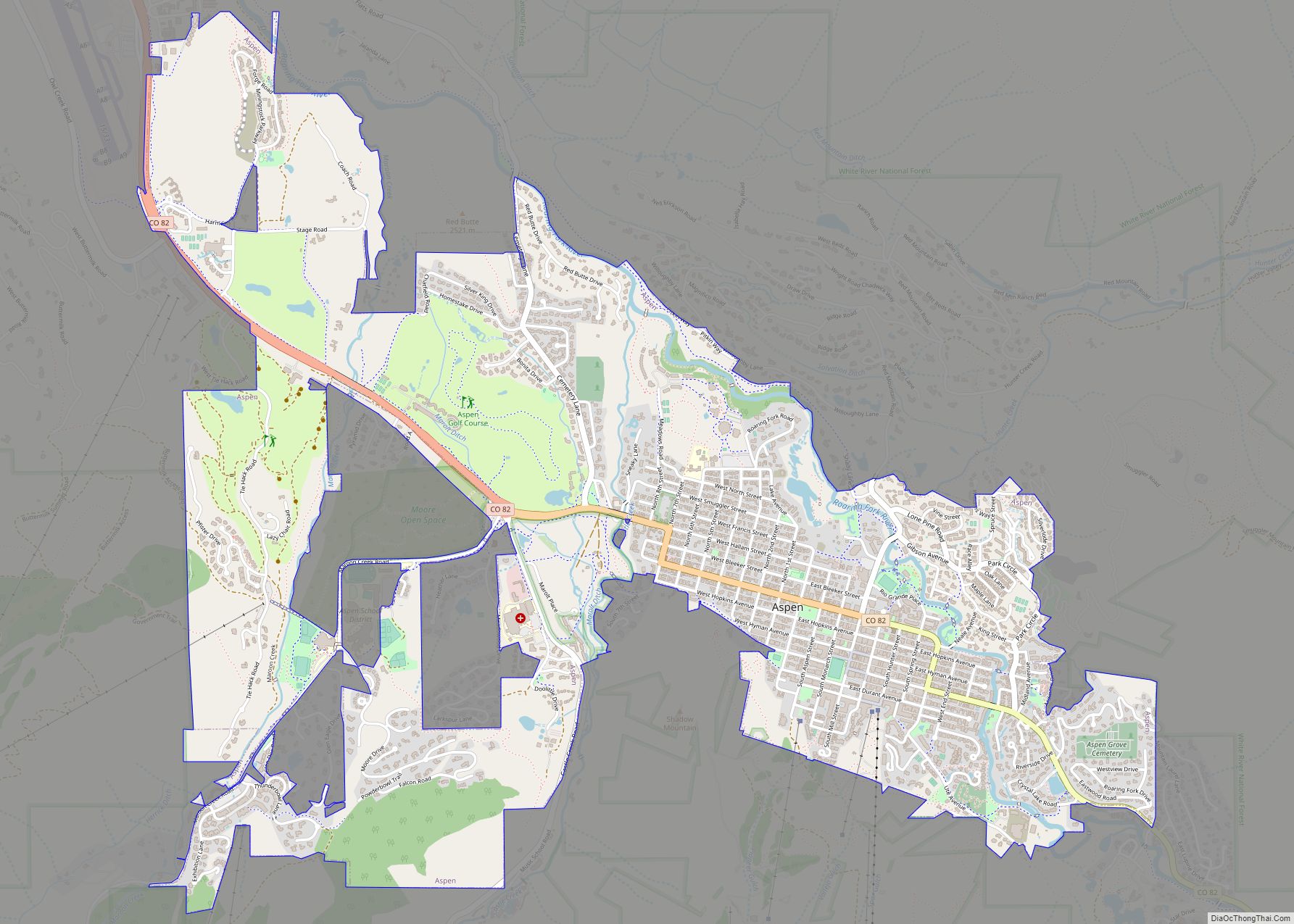
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Aspen location map. Where is Aspen city?
History
The city’s roots are traced to the winter of 1879, when a group of miners ignored pleas by Frederick Pitkin, Governor of Colorado, to return across the Continental Divide to avoid a Ute uprising. The Utes were fighting to maintain possession of their land and communities. Originally named Ute City, the small community was renamed Aspen in 1880, and, in its peak production years of 1891 and 1892, surpassed Leadville as the United States’ most productive silver-mining district. Production expanded due to the passage of the Sherman Silver Purchase Act of 1890, which doubled the government’s purchase of silver. In 1883, the Apostolic Vicarate of Colorado’s Bishop Machebeuf had the Reverend Edward Downey establish the first Catholic mission in Aspen.
By 1893, Aspen had banks, a hospital, a police department, two theaters, an opera house, and electric lights. Economic collapse came with the Panic of 1893, when President Cleveland called a special session of Congress and repealed the act. Within weeks, many of the Aspen mines were closed and thousands of miners were put out of work. It was proposed that silver be recognized as legal tender and the People’s Party (populists) adopted that as one of its main issues. Davis H. Waite, an Aspen newspaperman and agitator, was elected governor of Colorado on the Democratic ticket, but in time the movement failed.
Eventually, after wage cuts, mining revived somewhat, but production declined and by the 1930 census only 705 residents remained. Remaining, however, were stocks of old commercial buildings and residences, along with excellent snow. Aspen’s development as a ski resort began in the 1930s when investors conceived of a ski area, but the project was interrupted by World War II. Friedl Pfeifer, a member of the 10th Mountain Division who had trained in the area, returned to the area and linked up with industrialist Walter Paepcke and his wife Elizabeth. The Aspen Skiing Company was founded in 1946 and the city quickly became a well-known resort, hosting the FIS World Championships in 1950. Paepcke also played an important role in bringing the Goethe Bicentennial Convocation to Aspen in 1949, an event held in a newly designed tent by the architect Eero Saarinen. Aspen was then on the path to becoming an internationally known ski resort and cultural center, home of the Aspen Music Festival and School. The area would continue to grow with the development of three additional ski areas, Buttermilk (1958), Aspen Highlands (1958), and Snowmass (1967).
In the 1970s, Aspen became known as a playground for the rich and famous. Notable celebrities frequented the town and ski slopes, also John Denver was one of the more famous permanent residents. In 1978, Aspen was thoroughly photographed for the Aspen Movie Map project funded by the U.S. Department of Defense. The Movie Map is one of the earliest examples of virtual reality software.
In 1999, the city council passed a resolution to petition the US Congress and President Clinton to restrict US immigration. Aspen residents cited concerns about the environmental impacts of increased immigration on their community, including urban and suburban sprawl, pollution from the older automobiles typically driven by immigrants, and litter accumulating in the mountains attributable to the increasing population. The impetus for the resolution was the increasing number of trailer parks that housed the migrant workers employed locally in the service sector and ski industry. The parks were perceived to be degrading to the town’s image, property values, and environment. The move was led by Terry Paulson, an Aspen City Council member, and supported and guided by national groups such as the Carrying Capacity Network, and the Center for Immigration Studies. The resolution was discussed on the American Patrol Report website, contributing to a controversy over whether or not the resolution was racially motivated. Councilman Terry Paulson and some Aspen citizens insisted that it was motivated entirely by environmental concerns.
Aspen is notable as the smallest radio market tracked by Arbitron, ranked number 302.
Local media in Aspen include a public radio station, KJAX, a public television station, the Grassroots TV network; three commercial radio stations, KSNO, KTND, and KSPN; two daily newspapers, The Aspen Times and The Aspen Daily News; three local lifestyle magazines, Aspen Sojourner, Aspen Magazine and the biannual Aspen Peak; and a local, live, commercial lifestyle television channel, Aspen 82.
Aspen Road Map
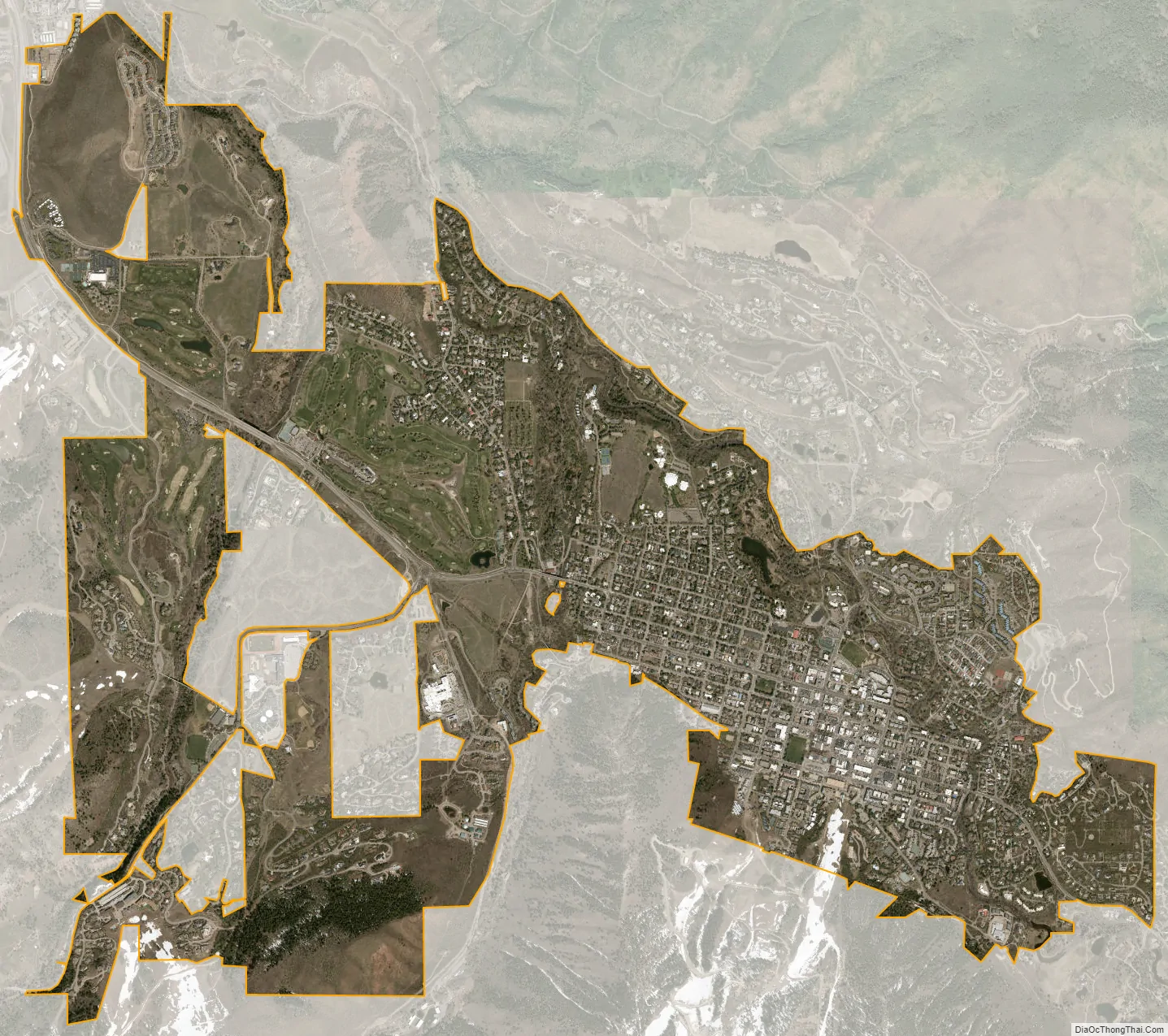
Aspen city Satellite Map
Geography
The city sits along the southeast (upper) end of the Roaring Fork Valley, along the Roaring Fork River, a tributary of the Colorado River about 40 miles (64 km) south of Glenwood Springs, Colorado. It is surrounded by mountain and wilderness areas on three sides: Red Mountain to the north, Smuggler Mountain to the east, and Aspen Mountain to the south.
Aspen is located at 39°11′32″N 106°49′28″W / 39.192297°N 106.824470°W / 39.192297; -106.824470, along State Highway 82.
At the 2020 United States Census, the city had a total area of 2,469 acres (9.992 km), all of it land.
Climate
Under the Köppen climate classification, Aspen has a humid continental climate (Köppen: Dfb) owing to its high elevation. There is a large diurnal temperature variation between daytime and nighttime temperatures, rendering summer days moderately warm and winter nights very cold for the latitude. Summer lows and winter highs are relatively moderate, with frosts being rare in summer and winter days often averaging above freezing.
See also
Map of Colorado State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Alamosa
- Arapahoe
- Archuleta
- Baca
- Bent
- Boulder
- Broomfield
- Chaffee
- Cheyenne
- Clear Creek
- Conejos
- Costilla
- Crowley
- Custer
- Delta
- Denver
- Dolores
- Douglas
- Eagle
- El Paso
- Elbert
- Fremont
- Garfield
- Gilpin
- Grand
- Gunnison
- Hinsdale
- Huerfano
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Kiowa
- Kit Carson
- La Plata
- Lake
- Larimer
- Las Animas
- Lincoln
- Logan
- Mesa
- Mineral
- Moffat
- Montezuma
- Montrose
- Morgan
- Otero
- Ouray
- Park
- Phillips
- Pitkin
- Prowers
- Pueblo
- Rio Blanco
- Rio Grande
- Routt
- Saguache
- San Juan
- San Miguel
- Sedgwick
- Summit
- Teller
- Washington
- Weld
- Yuma
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming