Newark (/ˈnʊərk/ Noork) is a city in and the county seat of Licking County, Ohio, United States, located 40 miles (64 km) east of Columbus at the junction of the forks of the Licking River. The population was 49,934 at the 2020 census, making it the 18th-largest city in Ohio. It is part of the Columbus metropolitan area.
It is the site of much of the Newark Earthworks, a major ancient complex built by the Hopewell culture. The Great Circle portion and additional burial mounds are located in the neighboring city of Heath, Ohio. This complex has been designated as a National Historic Landmark and is operated as a state park by the Ohio History Connection.
| Name: | Newark city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Ohio |
| County: | Licking County |
| Elevation: | 833 ft (254 m) |
| Total Area: | 21.37 sq mi (55.34 km²) |
| Land Area: | 20.89 sq mi (54.09 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.48 sq mi (1.25 km²) |
| Total Population: | 49,934 |
| Population Density: | 2,390.90/sq mi (923.12/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 43055, 43056, 43058, 43093 |
| Area code: | 740, 220 |
| FIPS code: | 3954040 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1065144 |
| Website: | http://www.newarkohio.net/ |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Newark location map. Where is Newark city?
History
Cultures of indigenous peoples lived along the river valleys for thousands of years before European contact. From more than two thousand years ago, 100 AD to 500 AD, people of the Hopewell culture transformed the area of Newark and Heath. They built many earthen mounds and enclosures, creating the single largest earthwork complex in the Ohio River Valley. The Newark Earthworks, designated a National Historic Landmark, have been preserved to document and interpret the area’s significant ancient history. The earthworks cover several square miles and about 206 acres. This is operated as a state park by the Ohio History Connection.
The Observatory Mound, Observatory Circle, and the interconnected Octagon earthworks span nearly 3,000 feet (910 m) in length. The Octagon alone is large enough to contain four Roman Coliseums. The Great Pyramid of Giza in Egypt would fit precisely within Observatory Circle. The even larger 1,180-foot (360 m)-diameter Newark Great Circle, located in Heath, is the largest circular earthwork in the Americas. The 8 feet (2.4 m)-high walls surround a 5 feet (1.5 m)-deep moat. At the entrance, the walls and moat are of greater and more impressive dimensions.
Contemporary archaeogeodesy and archaeoastronomy researchers have demonstrated that the Hopewell and other prehistoric cultures had advanced scientific understandings which they used to create their earthworks for astronomical observations, markings and celebrations. Researchers analyzed the placements, alignments, dimensions, and site-to-site interrelationships of the Hopewell earthworks to understand what had been done. Today, the Ohio Historical Society preserves the Great Circle Earthworks in a public park near downtown Newark, called Mound Builders Park (or the Newark Earthworks) located at 99 Cooper Ave, Newark, Ohio. The area of the Octagon Earthworks had been leased to a country club, but new arrangements in 1997 provide for more public access to it. Later American Indian tribes inhabiting the area at the time of European contact were distant descendants of the Hopewell peoples.
European-American settlement
After exploration by traders and trappers in earlier centuries, the first European-American settlers arrived in 1802, led by Gen. William C. Schenck. He named the new village after his New Jersey hometown.
Nineteenth-century investment in infrastructure resulted in growth in the town after it was linked to major transportation and trade networks. On July 4, 1825, Governors Clinton of New York and Morrow of Ohio dug the first shovelfuls of dirt for the Ohio and Erie Canal project, at the Licking Summit near Newark, Ohio. On April 11, 1855, Newark became a stop along the Pittsburgh, Cincinnati, Chicago and St. Louis Railroad that was built to connect Pittsburgh to Chicago and St. Louis. On April 16, 1857, the Central Ohio Railroad connected Newark west to Columbus, and later Newark maintained a station on the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad.
The Heisey Glass Company started in Newark in 1895. The factory operated there for 62 years, until the company’s demise in 1957 due to changing tastes. The National Heisey Glass Museum, operated by the Heisey Collectors of America, Inc., is located on Sixth Street in Newark.
In 1909, The Arcade was opened. Modeled after innovative European retail buildings, it became one of Newark’s first successful retail emporiums. Later versions of buildings that contained a variety of shops indoors became known as shopping malls. At 60,000 square feet (5,600 m), the Arcade is one-third the size of an average modern Wal-Mart.
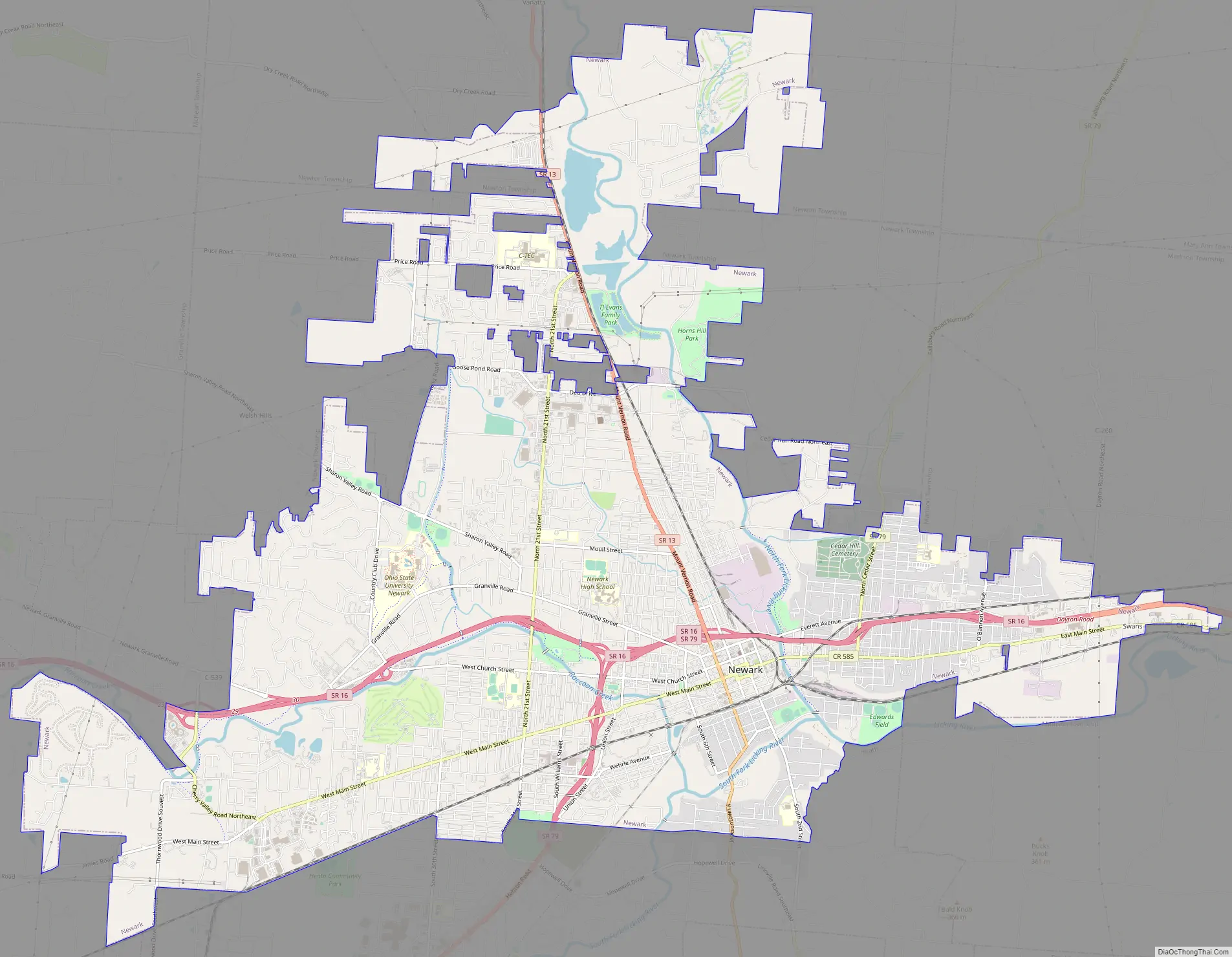
Newark Road Map
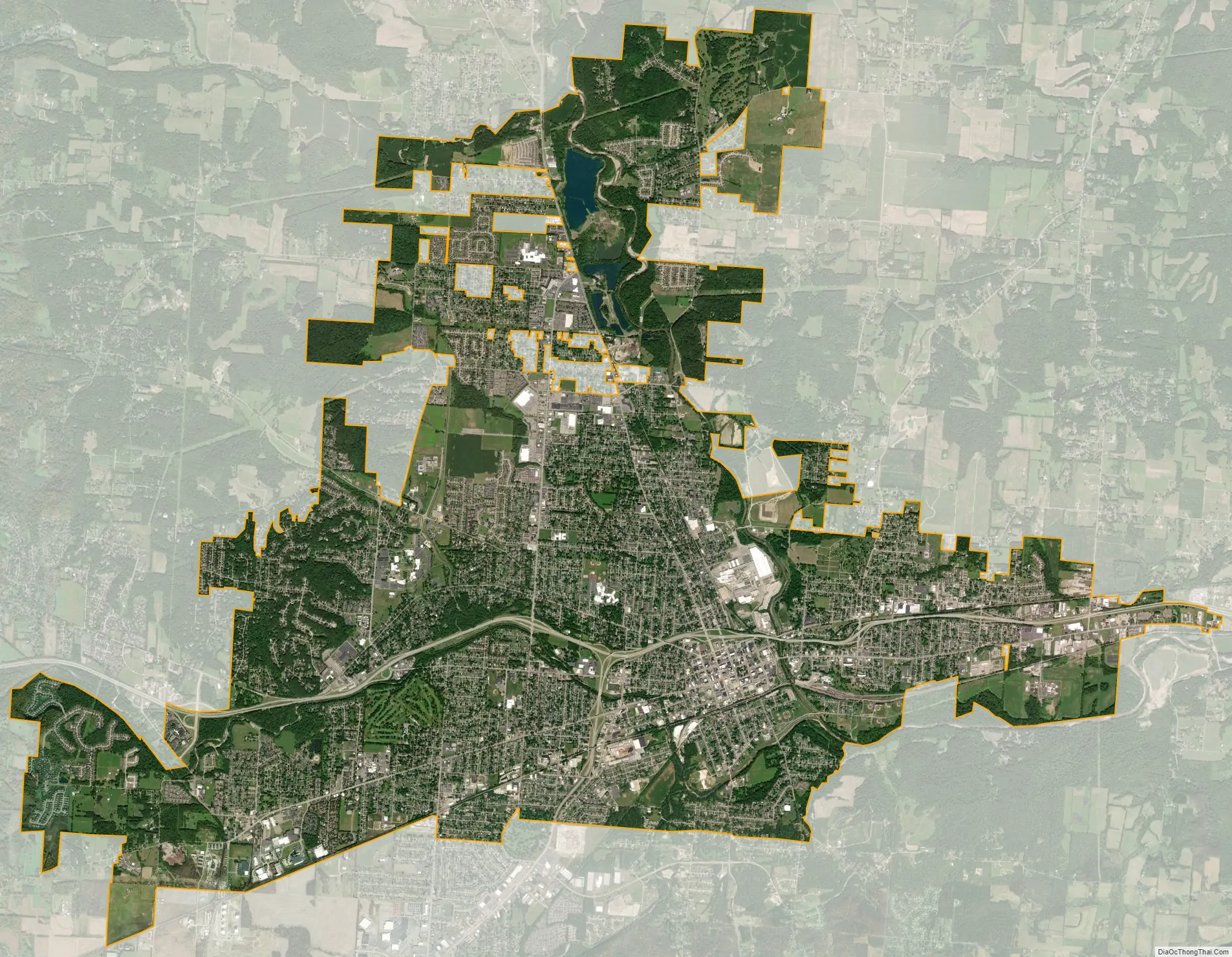
Newark city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 21.37 square miles (55.35 km), of which 20.88 square miles (54.08 km) is land and 0.49 square miles (1.27 km) is water. Newark is located at 40°3′47″N 82°25′0″W / 40.06306°N 82.41667°W / 40.06306; -82.41667 (40.063014, −82.416779).
Climate
See also
Map of Ohio State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Allen
- Ashland
- Ashtabula
- Athens
- Auglaize
- Belmont
- Brown
- Butler
- Carroll
- Champaign
- Clark
- Clermont
- Clinton
- Columbiana
- Coshocton
- Crawford
- Cuyahoga
- Darke
- Defiance
- Delaware
- Erie
- Fairfield
- Fayette
- Franklin
- Fulton
- Gallia
- Geauga
- Greene
- Guernsey
- Hamilton
- Hancock
- Hardin
- Harrison
- Henry
- Highland
- Hocking
- Holmes
- Huron
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Knox
- Lake
- Lake Erie
- Lawrence
- Licking
- Logan
- Lorain
- Lucas
- Madison
- Mahoning
- Marion
- Medina
- Meigs
- Mercer
- Miami
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Morgan
- Morrow
- Muskingum
- Noble
- Ottawa
- Paulding
- Perry
- Pickaway
- Pike
- Portage
- Preble
- Putnam
- Richland
- Ross
- Sandusky
- Scioto
- Seneca
- Shelby
- Stark
- Summit
- Trumbull
- Tuscarawas
- Union
- Van Wert
- Vinton
- Warren
- Washington
- Wayne
- Williams
- Wood
- Wyandot
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming