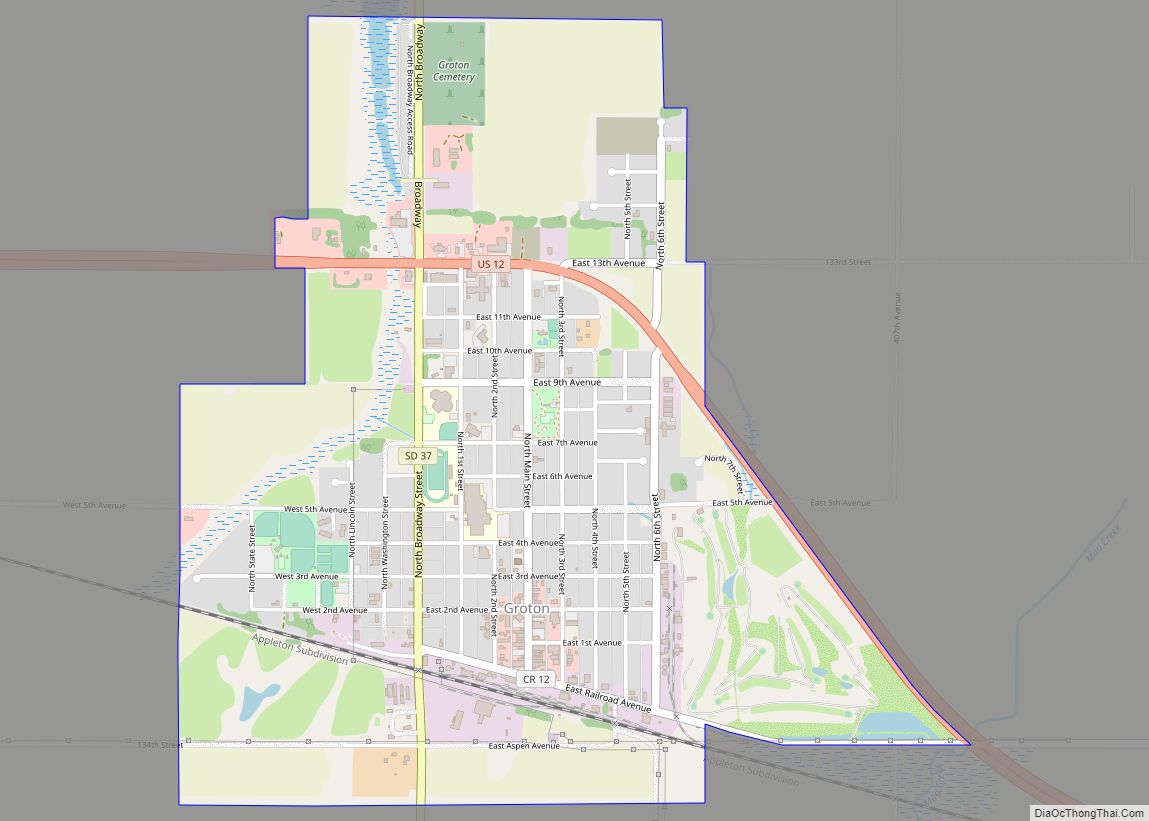
Aberdeen (Lakota: Ablíla) is a city in and the county seat of Brown County, South Dakota, United States, located approximately 125 miles (201 km) northeast of Pierre. The city population was 28,495 at the 2020 census, making it the third most populous city in the state after Sioux Falls and Rapid City. Aberdeen is the principal city of the Aberdeen Micropolitan Statistical Area, which includes all of Brown and Edmunds counties and has a population of 42,287 in 2020. Aberdeen is considered a college town, being the home of both Northern State University and Presentation College.
| Name: | Aberdeen city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | South Dakota |
| County: | Brown County |
| Elevation: | 1,302 ft (397 m) |
| Land Area: | 16.52 sq mi (42.78 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.08 sq mi (0.20 km²) |
| Population Density: | 1,725.19/sq mi (666.11/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 57401-57402 |
| Area code: | 605 |
| FIPS code: | 4600100 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1253581 |
| Website: | aberdeen.sd.us |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
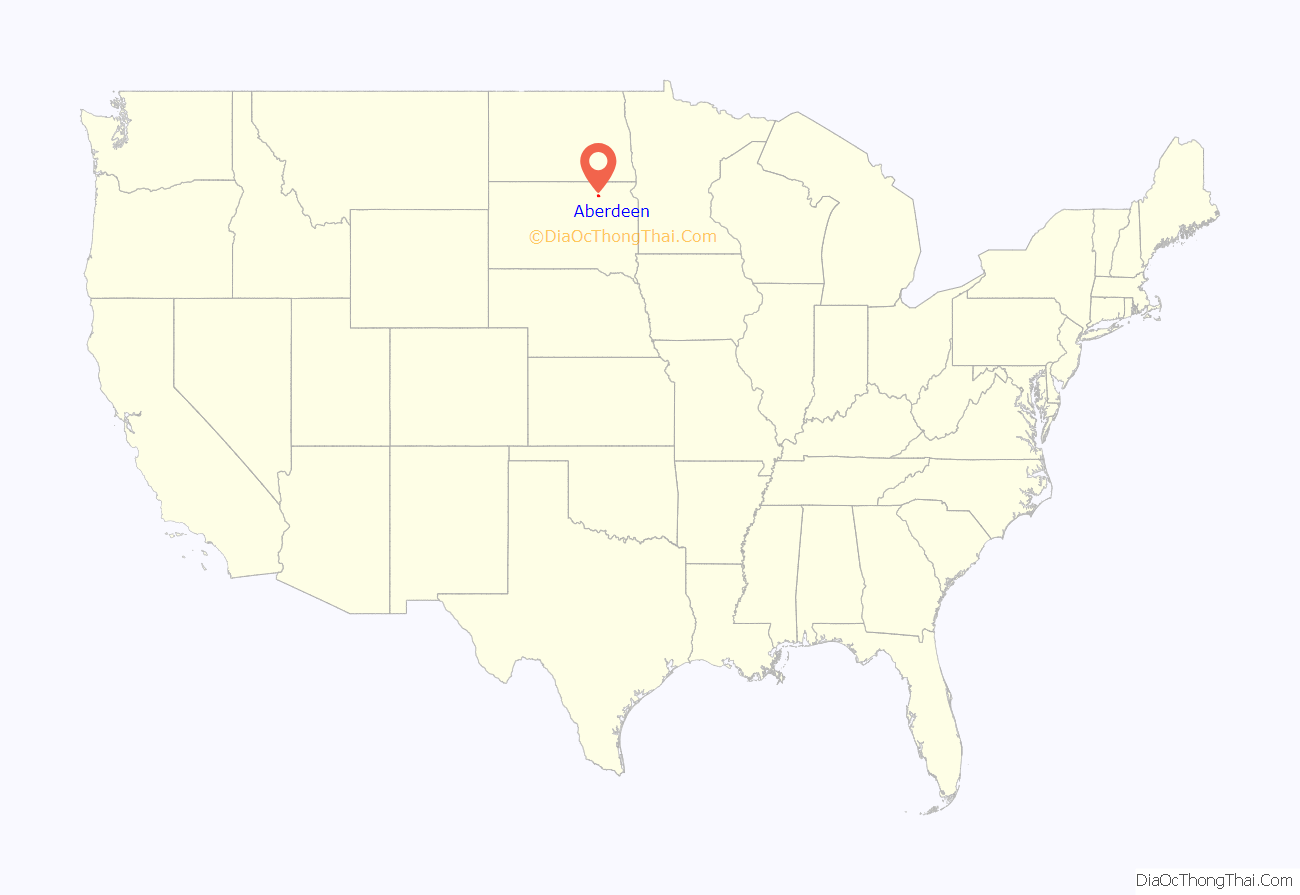
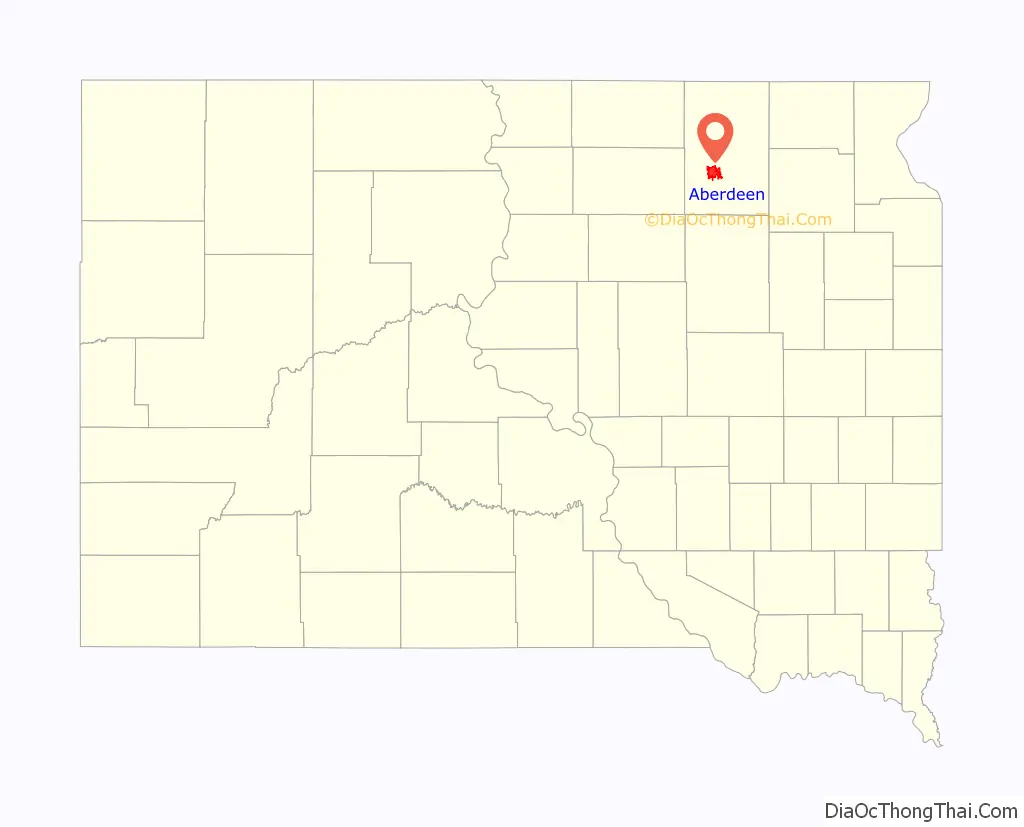
Aberdeen location map. Where is Aberdeen city?
History
Settlement
Before Aberdeen or Brown County was inhabited by European settlers, it was inhabited by the Sioux Indians from approximately 1700 to 1879. Europeans entered the region for business, founding fur trading posts during the 1820s; these trading posts operated until the mid-1830s. The first “settlers” of this region were the Arikara Indians, but they would later be joined by others.
The first group of Euro-American settlers to reach the area that is now Brown County was a party of four people, three horses, two mules, fifteen cattle, and two wagons. This group of settlers was later joined by another group the following spring, and, eventually, more settlers migrated toward this general area, currently known as Columbia, South Dakota. This town was established on June 15, 1879, was settled in 1880, and was incorporated in 1882.
Creation of the town
Aberdeen, like many towns of the Midwest, was built around the newly developing railroad systems. Aberdeen was first officially plotted as a town site on January 3, 1881, by Charles Prior, the superintendent of the Minneapolis office of the Chicago, Milwaukee, and St. Paul Railroad, or the Milwaukee Road for short, which was presided over by Alexander Mitchell, Charles Prior’s boss, who was responsible for the choice of town names. He was born in Aberdeen, Scotland, after which the town of Aberdeen was named. Aberdeen was officially founded on July 6, 1881, the date of the first arrival of a Milwaukee Railroad train. Aberdeen then operated under a city charter granted by the Territorial Legislature in March 1883.
As Aberdeen grew, many businesses and buildings were constructed along Aberdeen’s Main Street. However, this soon became a problem due to Aberdeen’s periodic flooding, which led to it being referred to as “The Town in the Frog Pond”. At first, this unique condition presented no problem to the newly constructed buildings because it had not rained very much but, when heavy rains fell, the Pond reappeared and flooded the basements of every building on Main Street, causing many business owners and home owners much turmoil. When this flooding happened, the city had one steam-powered pump that had to be used to dry out the entire area that had been flooded, which would take days, if not weeks – and more often than not, it would have rained again in this time period and caused even more flooding, even in the basements that had already been emptied of the water. When the water was gone from the basements, the city still had to deal with the mud that also resulted from the heavy rains.
The city decided in 1882 to build an artesian ditch to control the “Frog Pond” effects; the plan was later upgraded and developed into an artesian well in 1884 to combat the heavy rains and keep the basements from flooding. The artesian well was designed by the city engineers to prevent flooding and develop a water system. However, during the digging of the well, the water stream that was found underground was too powerful to be contained. The water came blasting out with violent force and had the entire Main Street submerged in up to four feet of water. The engineers realized the previous flaws of the artesian well plan and soon added a gate valve to the well to control the flow of water, giving Aberdeen its first working water supply.
Aberdeen had four different railroad companies with depots built in the newly developing town. With these four railroads intersecting here, Aberdeen soon became known as the “Hub City of the Dakotas”. When looking down on Aberdeen from above, the railroad tracks converging in Aberdeen resembled the spokes of a wheel converging at a hub, hence the name “Hub City of the Dakotas”. These four railroad companies are the reason why Aberdeen was able to grow and flourish as it did. The only railroad still running through Aberdeen is the BNSF Railway.
L. Frank Baum, who was later author of the book The Wizard of Oz and its many sequels, lived here with his wife and children for a few years in the early 1890s. He owned a store for over a year, which failed. He later published one of the city’s then nine newspapers. The city’s small amusement park has some features reflective of the Wizard of Oz series. After his sojourn in Aberdeen he moved to Chicago, Illinois in 1892.
1999 South Dakota Learjet crash
On October 25, 1999, a Learjet 35 carrying golfing star Payne Stewart and five others crashed in a field near Mina, 10 miles (16 km) west of Aberdeen. All on board died.
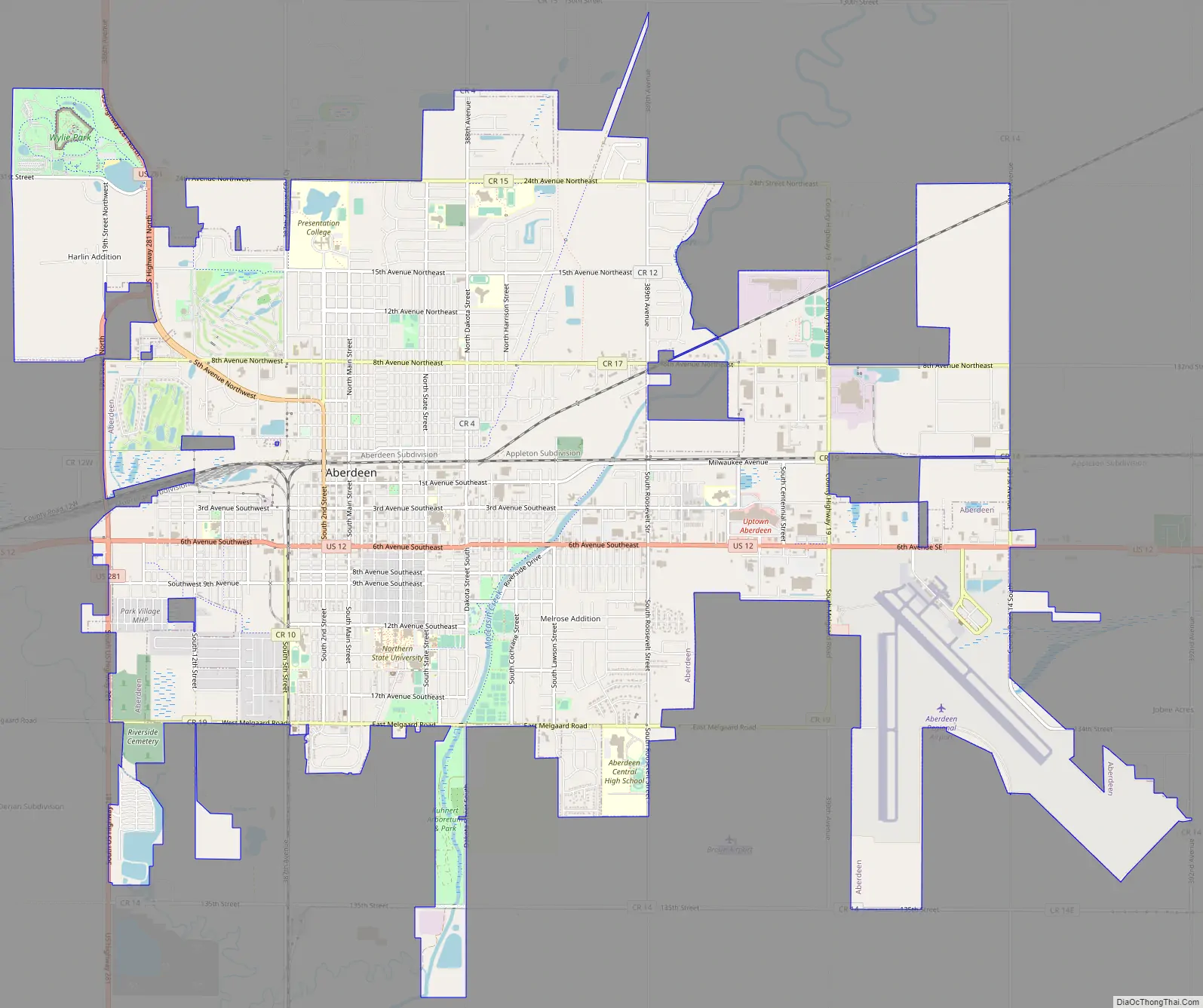
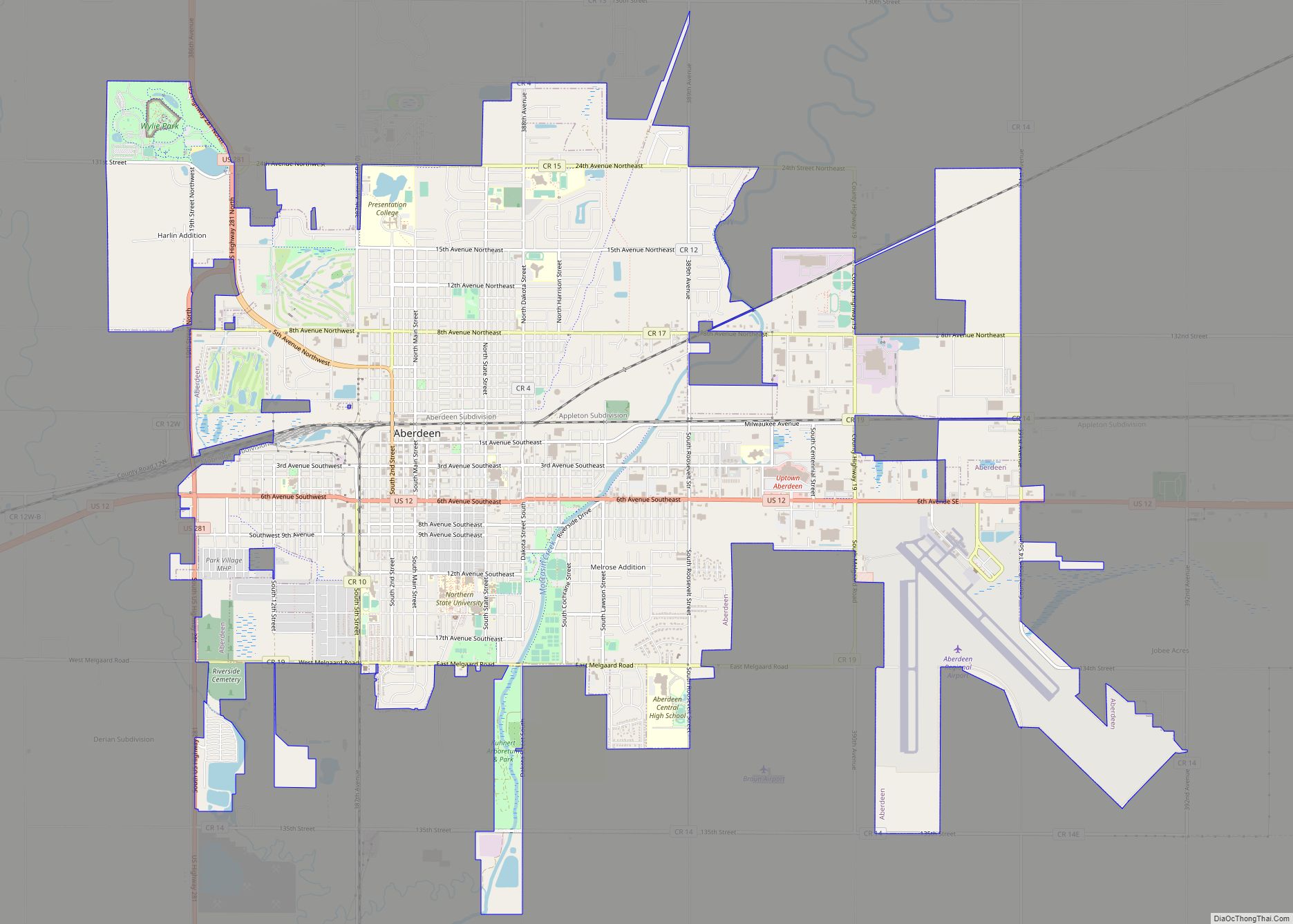
Aberdeen Road Map
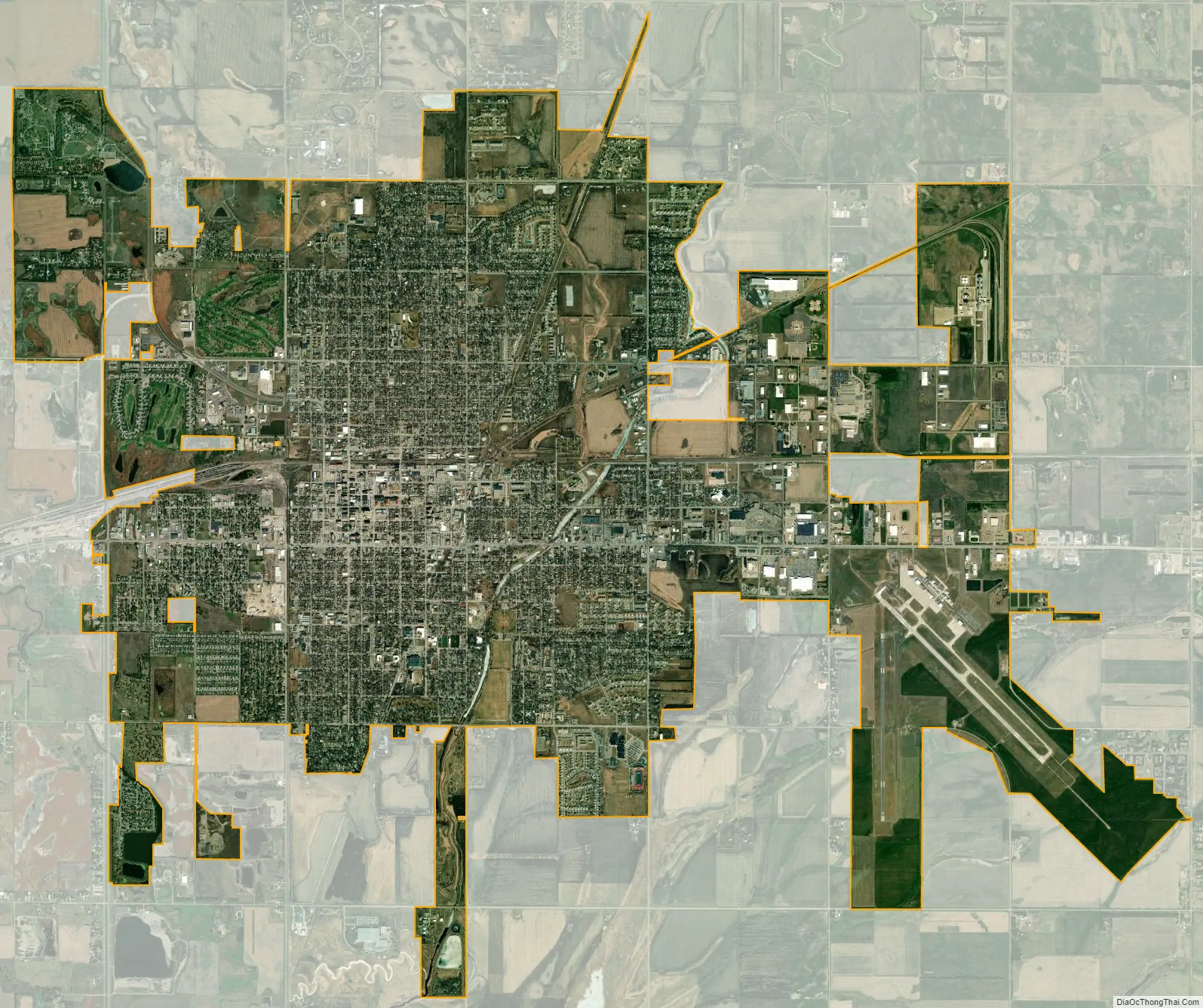
Aberdeen city Satellite Map
Geography
Aberdeen is located in northeastern South Dakota, in the James River valley, approximately 11 miles (18 km) west of the river. The James River enters northeastern South Dakota in Brown County, where it is dammed to form two reservoirs northeast of Aberdeen. The city is bisected by Moccasin Creek, a slow-moving waterway which flows south and then northeast to the James River.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 15.60 square miles (40.40 km), of which 15.50 square miles (40.14 km) is land and 0.10 square miles (0.26 km) is water.
Aberdeen has been assigned the ZIP code range 57401−57402.
Climate
Aberdeen experiences a humid continental climate (Köppen Dfa) influenced by its position far from moderating bodies of water. This brings four distinct seasons, a phenomenon that is characterized by hot, relatively humid summers and cold, dry winters, and it lies in USDA Hardiness Zone 4b. The monthly daily average temperature ranges from 12.8 °F (−10.7 °C) in January to 72.3 °F (22.4 °C) in July, while there are 16 days of 90 °F (32 °C)+ highs and 38 days with sub-0 °F (−18 °C) lows annually. Snowfall occurs mostly in light to moderate amounts during the winter, totaling 42 inches (107 cm). Precipitation, at 21.8 inches (554 mm) annually, is concentrated in the warmer months. Extreme temperatures have ranged from −46 °F (−43 °C) on January 12, 1912, and February 8, 1895, to 115 °F (46 °C) on July 6 and 15, 1936, although a −42 °F (−41 °C) reading occurred as recently as January 15, 2009.
The National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration maintains a National Weather Service office in Aberdeen. Their area of responsibility includes northern and eastern South Dakota and two counties in west-central Minnesota.
See also
Map of South Dakota State and its subdivision:- Aurora
- Beadle
- Bennett
- Bon Homme
- Brookings
- Brown
- Brule
- Buffalo
- Butte
- Campbell
- Charles Mix
- Clark
- Clay
- Codington
- Corson
- Custer
- Davison
- Day
- Deuel
- Dewey
- Douglas
- Edmunds
- Fall River
- Faulk
- Grant
- Gregory
- Haakon
- Hamlin
- Hand
- Hanson
- Harding
- Hughes
- Hutchinson
- Hyde
- Jackson
- Jerauld
- Jones
- Kingsbury
- Lake
- Lawrence
- Lincoln
- Lyman
- Marshall
- McCook
- McPherson
- Meade
- Mellette
- Miner
- Minnehaha
- Moody
- Pennington
- Perkins
- Potter
- Roberts
- Sanborn
- Shannon
- Spink
- Stanley
- Sully
- Todd
- Tripp
- Turner
- Union
- Walworth
- Yankton
- Ziebach
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming