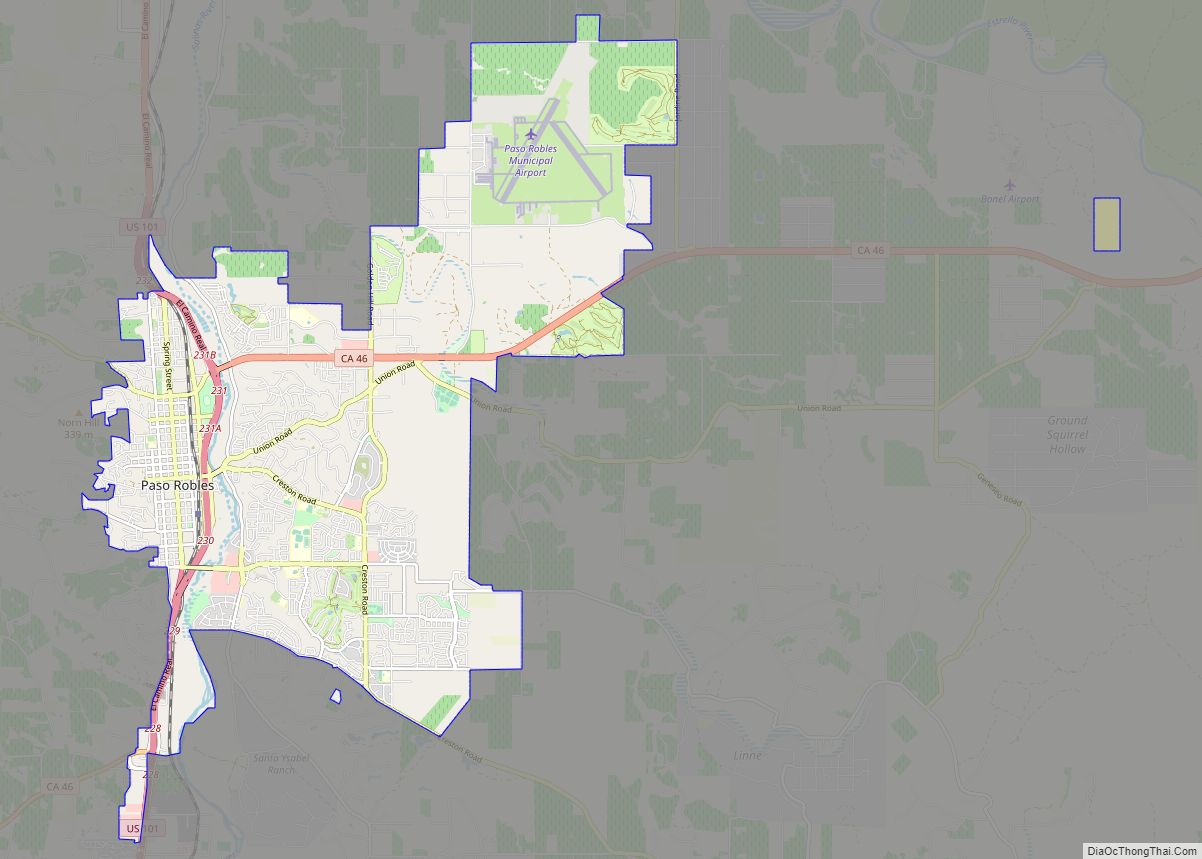
Paso Robles (/ˌpæsə ˈroʊbəlz/ PASS-oh ROH-buhlz), officially El Paso de Robles (Spanish for “The Pass of Oaks”), is a city in San Luis Obispo County, California, United States. Located on the Salinas River approximately 30 miles (48 km) north of San Luis Obispo, the city is known for its hot springs, its abundance of wineries, its production of olive oil, almond orchards, and for playing host to the California Mid-State Fair.
| Name: | City of El Paso de Robles (Paso Robles) |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | California |
| County: | San Luis Obispo County |
| Incorporated: | March 11, 1889 |
| Elevation: | 732 ft (223 m) |
| Total Area: | 19.66 sq mi (50.92 km²) |
| Land Area: | 19.65 sq mi (50.89 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.01 sq mi (0.03 km²) 1.57% |
| Total Population: | 29,793 |
| Population Density: | 1,636.37/sq mi (631.81/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 93446, 93447 |
| Area code: | 805/820 |
| FIPS code: | 0622300 |
| Website: | prcity.com |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
El Paso De Robles location map. Where is City of El Paso de Robles (Paso Robles)?
History
This area of the Central Coast, known as the City of El Paso De Robles, Paso Robles, or simply “Paso”, is known for its thermal springs. Native Americans known as the Salinan lived in the area thousands of years before the mission era. They knew this area as the “Springs” or the “Hot Springs.” A tribal site on present-day Paso Robles was named elewexe, Obispeño for “Swordfish”.
Paso Robles is located on the Rancho Paso de Robles Mexican land grant that was purchased by James and Daniel Blackburn in 1857. Their partner was Drury James of Kentucky, a veteran of the Mexican War and uncle of the outlaw Jesse James. The land was a rest-stop for travelers of the Camino Real trail, and was known for its mineral hot springs. Franciscan priests from neighboring Mission San Miguel constructed the first mineral baths in the area. During this period, Paso Robles began to attract the settlers who established cattle ranches, apple and almond orchards, dairy farms, and vineyards.
In 1864, the first El Paso de Robles Hotel was constructed and featured a hot mineral springs bath house. Three locations (Paso Robles Inn, River Oaks Hot Springs, and Franklin Hot Springs) have offered the mineral bath hot spring experience which brought people like Ignacy Jan Paderewski to Paso Robles.
James and Daniel Blackburn donated two blocks to the city for a public park to be used for the pleasure of its citizens and visitors. Two exceptions were made to requirement that it be used for a public park: allowing the building of the Carnegie Library, and the conversion of the library to a museum. The grounds were laid out by a Mr. Redington and a planting day was held when each citizen set out his own donation. Originally, the whole park was hedged in by a fence of cactus, and in 1890 a bandstand was built with money raised by private theatricals.
In 1886, after the coming of the Southern Pacific Railroad, work began on laying out a town site, with the resort as the nucleus. Two weeks after the first train arrived on October 31, 1886, a three-day celebration was held including a special train from San Francisco bringing prospective buyers, who toured the area and enjoyed the daily barbecues. On November 17, the “Grand Auction” was held, resulting in the sale of 228 lots.
The local agent for the SPR when it arrived in Paso Robles was R. M. “Dick” Shackelford, a Kentucky native who had come to California in 1853 to dig for gold. Shackelford had a varied career, going from gold mining to hauling freight by ox team, to lumbering, which took him to Nevada, where he served one term as a delegate in the state’s first legislature for Washoe County. By 1886 Shackelford had returned to California and was living in Paso Robles, where he began buying up extensive property, building warehouses and starting lumber yards along the railroad’s route. Shackelford also established the Southern Pacific Milling Company, which had a virtual monopoly on local milling until local farmers, in an effort to break Shackelford’s stranglehold, themselves organized their own milling cooperative, the Farmers’ Alliance Flour Mill.
In 1889, the same year that Paso Robles incorporated as a city, construction began on a new hotel. The hotel required over one million bricks and cost $160,000. The El Paso de Robles Hotel opened for business in 1891. The hotel was three stories tall and built of solid masonry, set off by sandstone arches. This ensured the hotel was completely fireproof. The hotel also featured a seven-acre (28,000 m) garden and nine-hole golf course. Inside there was a library, a beauty salon, a barber shop, and various billiard and lounging rooms. The new hotel also offered an improved hot springs plunge bath as well as 32 individual bath rooms. The 20 by 40-foot (12 m) plunge bath was considered one of the finest and most complete of its time in the United States.
On January 17, 1914, one of the world’s most well-known concert pianists and composers came to the hotel: Ignace Paderewski. After three weeks of treatments at the hotel’s mineral hot springs for his arthritis, he resumed his concert tour. He later returned to live at the hotel and bought two ranches west of Paso Robles.
During the next 30 years, the hotel was visited by other notables: Boxing champion Jack Dempsey, President Theodore Roosevelt, Adela Rogers St. Johns, Phoebe Apperson Hearst (the mother of William Randolph Hearst), actors Douglas Fairbanks, Boris Karloff, Bob Hope, and Clark Gable all stayed at the El Paso de Robles Hotel. And when Major League baseball teams used Paso Robles as a spring training home, the Pittsburgh Pirates and Chicago White Sox stayed at the hotel and soaked in the mineral hot springs to soothe tired muscles.
For a time, Paso Robles was known as the “Almond City” because the local almond growers created the largest concentration of almond orchards in the world. The ranchers in the outlying areas were very important to the Paso Robles area. On these ranches were cattle and horses, grain crops (primarily wheat and barley), garden produce and fruit and nut orchards. Many of these ranch lands and orchards have become vineyards for the many wineries which currently draw tourists to the area.
To show their appreciation to the ranchers, in October 1931 the business people established Pioneer Day, which is still an annual celebration. Pioneer Day is celebrated on the second Saturday in October.
- Vintage wagon
- View from the Paso Robles Inn
In December 1940, a fire completely destroyed the El Paso de Robles Hotel. Guests staying the night escaped unharmed. The night clerk who discovered the fire suffered a fatal heart attack immediately after sounding the alarm. Within months after the blaze, plans for a new hotel to be built on the site were drawn up. The design was an entirely new concept: A garden inn-hotel, designed to accommodate motor vehicle travelers. By February 1942 construction was complete and the Paso Robles Inn opened for business.
In 1955, scores of national media came to Paso Robles after pop culture icon and actor James Dean was pronounced dead in town following his tragic car accident just east of the city. A roadside memorial in his honor stands in nearby Cholame, for fans to pay tribute to the star.
Through the 1960s and 1970s, the City of Paso Robles experienced significant growth. The area’s wine industry flourished, the California Mid-State Fair expanded into a regional attraction, and local lakes, such as Lake Nacimiento, became family vacation destinations.
The waters
As far back as 1795, Paso Robles has been spoken of and written about as “California’s oldest watering place”—the place to go for springs and mud baths. In 1864, a correspondent to the San Francisco Bulletin wrote that there was every prospect of the Paso Robles hot springs becoming the watering place of the state. By 1868 people were coming from as far away as Oregon, Nevada, Idaho, and even Alabama. Besides the well-known mud baths, there were the Iron Spring and the Sand Spring, which bubbles through the sand and was said to produce delightful sensations.
In 1882, Drury James and the Blackburn brothers issued a pamphlet advertising “El Paso de Robles Hot and Cold Sulphur Springs and the Only Natural Mud Baths in the World”. By then there were first-class accommodations: a reading room, barber shop, and telegraph office; a general store, a top-of-the-line livery stable, and comfortably furnished cottages for families that preferred privacy to quarters in the hotel. Visitors could stay in touch with the rest of the world, as there were two daily mails, a Western Union telegraph office, and a Wells Fargo agency with special rates for guests. As the springs became more and more a destination of the well-to-do as a place to go to socialize, the original purpose of the springs—to heal—became peripheral.
The bathhouse was erected over the sulphur spring in 1888, with a plunge and thirty-seven bath rooms. In the following year, work began on the large Hot Springs Hotel (today the Paso Robles Inn), which was completed in 1900 and burned down 40 years later. Since the privileges of using the baths were restricted to guests of the hotel and many sufferers of the ailments the baths cured could not pay the rates of the fashionable hotel, a few businessmen in Paso Robles made arrangements with Felix Liss for the right to bore for sulphur water on a lot which Liss owned. A sulphur well was reached, a bath house built and baths offered at an affordable rate of 25 cents. The establishment was later offered to the city and is currently the site of the Municipal Pool.
Wine
Paso Robles’ growth industry—wine—has a long history with the area. Wine grapes were introduced to the Paso Robles soil in 1797 by the Spanish conquistadors and Franciscan missionaries. Spanish explorer Francisco Cortez envisioned an abundant wine-producing operation and encouraged settlers from Mexico and other parts of California to cultivate the land. The first vineyardists in the area were the Padres of the Mission San Miguel, and their old fermentation vats and grapevine artwork can still be seen at the Mission, north of the city of Paso Robles.
Commercial winemaking was introduced to the Paso Robles region in 1882 when Andrew York, a settler from Indiana, began planting vineyards and established the Ascension Winery at what became York Mountain Winery and is now Epoch Winery. When York purchased the land, it was primarily apple orchards, with a small plot of wine grape vines. York found that the climate and soil were more suitable for vineyards and he expanded the vineyards. Within a few years, he found that the vines were yielding more than he could market, prompting him to build a small, stone winery.
Following Andrew York’s early success in the wine business, Gerd and Ilsabe Klintworth planted a vineyard in the Geneseo/Linne area in approximately 1886. They were licensed to sell jugs of Zinfandel, Port, and Muscatel, as well as some of the area’s first white wine made from Burger grapes. The Casteel Vineyards in the Willow Creek area were planted just prior to 1908. Casteel wines were stored and aged in a cave cellar. Cuttings from the old vines provided the start for other vineyards, still producing in the area today.
As the popularity of wines began to grow, so did the Paso Robles wine region. Lorenzo and Rena Nerelli purchased their vineyard at the foot of York Mountain in 1917. Their Templeton Winery was the area’s first to be bonded following the repeal of Prohibition.
The early 1920s saw a flurry of winemaking activity when several families immigrated to the area to establish family vineyards and wineries. Sylvester and Caterina Dusi purchased a vineyard in 1924. The old head-pruned Zinfandel vines are now owned and cultivated by their son, Benito. The Martinelli, Busi, Vosti, Steinbeck and Bianchi Winery vineyards were also established around this time.
The Paso Robles wine region gained more notoriety when Ignace Paderewski, the famous Polish statesman and concert pianist, visited Paso Robles, became enchanted with the area, and purchased 2,000 acres (8.1 km). In the early 1920s, he planted Petite Sirah and Zinfandel on his Rancho San Ignacio vineyard in the Adelaide area. Following Prohibition, Paderewski’s wine was made at York Mountain Winery. The wines produced from grapes grown on Rancho San Ignacio went on to become award-winners. Paso Robles’ reputation as a premier wine region became firmly established as a result of this and later successes, and through to the late 1960s and early 1970s, a new generation of vineyard pioneers came forth and flourished in the Paso Robles area.
San Simeon earthquake
At 11:15 am PST on December 22, 2003, the San Simeon earthquake struck about 25 miles (40 km) northwest of Paso Robles. The earthquake registered 6.6 on the moment magnitude scale and had a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). Two deaths occurred when the roof slid off the clock tower building, a popular landmark in downtown Paso Robles. The dormant underground springs that had once been used for the spa were brought back to life, causing flooding and a large sinkhole in the parking lot of the city hall and library. Due to lengthy environmental and engineering considerations, it took until December 2010 for the sinkhole to be filled and the parking lot resurfaced. Paso Robles has dedicated a new clock tower in memory of the two women who died.
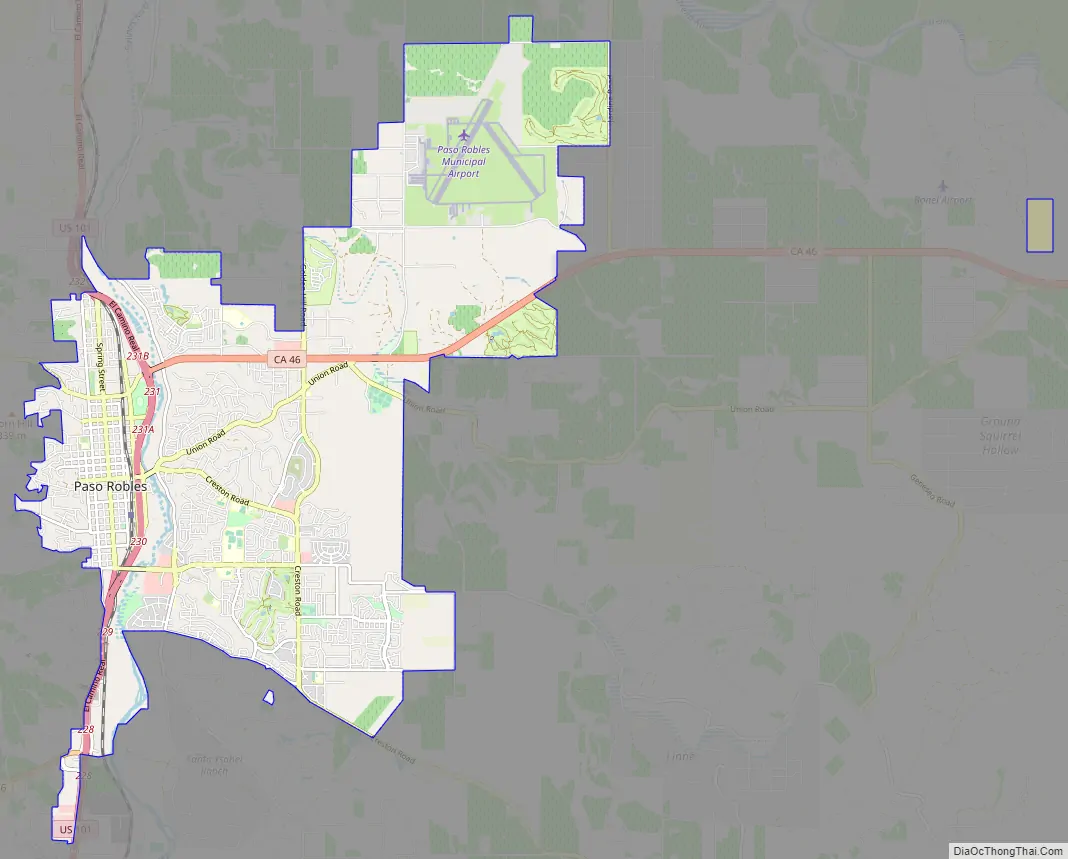
El Paso De Robles Road Map
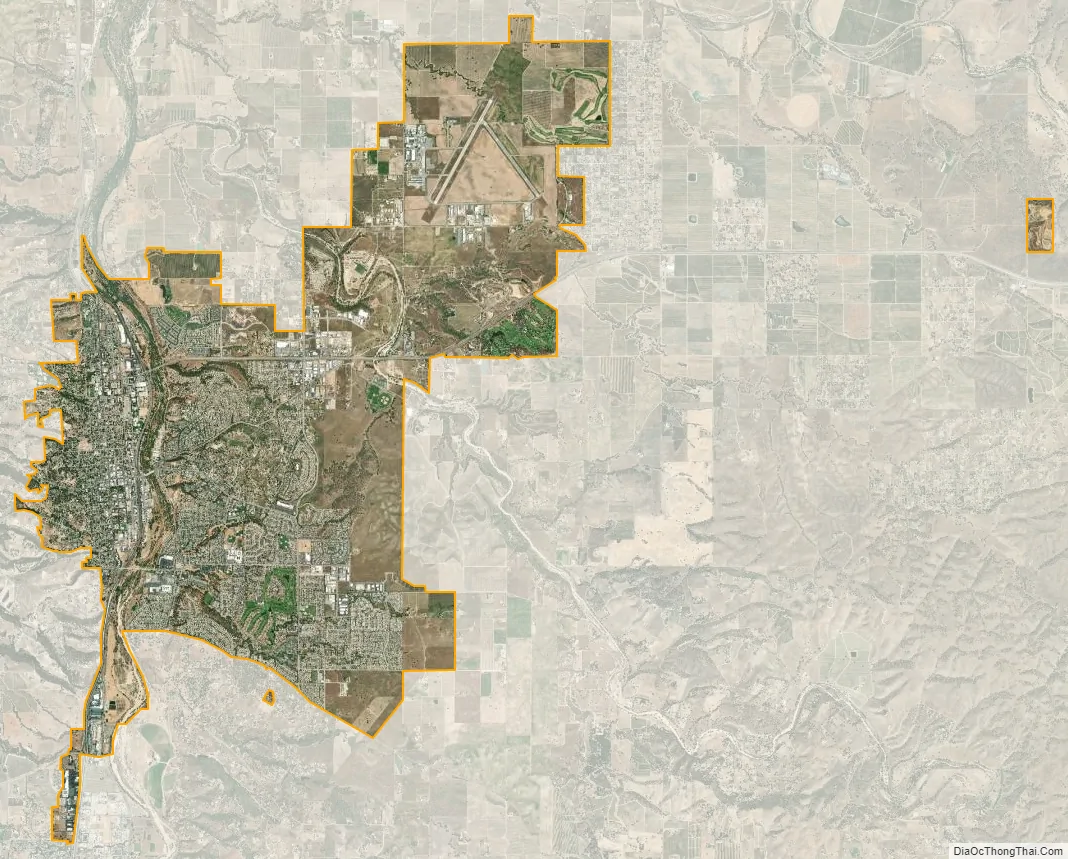
El Paso De Robles city Satellite Map
Geography
Paso Robles is approximately halfway between the cities of Los Angeles and San Francisco.
The topography of the area consists of gentle rolling hills on the eastern half of the city, and foothill peaks which rise in elevation to the Santa Lucia Coastal Range on the west, which are all blanketed in the Californian chaparral environment, which is mainly dry grassland and oak woodland. Paso Robles sits on the eastern foothills of the Santa Lucia Coastal Mountain Range, which lies directly to the West of the city, and runs in a north–south direction, starting at Monterey, then runs down south to its terminus, in the San Luis Obispo area. The city is located at the southern end of the fertile Salinas River Valley, which is centered in between the Temblor Range (including the San Andreas Fault), which lie about 28 miles (45 km) to the East, and the Santa Lucia Coastal Range, which lie directly west, rising up from the city’s western border. Paso Robles sits at the border where northern San Luis Obispo County and southern Monterey County meet, and is situated roughly 24 miles (39 km), or 20 minutes, inland from the Pacific Ocean.
Climate
The Paso Robles area has a hot-summer Mediterranean climate (Csa) typical of coastal Southern California. The climate is defined by long, hot, dry summers and brief, cool, rainy winters. Paso Robles enjoys long-lasting, mild autumns and occasional early springs, giving the region a unique climate suitable for growing a variety of crops (ranging from primarily grapes, to olives, to almonds and other tree nuts). The city receives an average annual rainfall of about 14.71 inches (374 mm) per year, and most of this precipitation falls during winter and early spring. Paso Robles often receives less than 10 inches (250 mm) of rain per year and typically, no rain falls from May through September. Summers in Paso Robles tend to be very hot, with daily temperatures frequently exceeding 100 °F (38 °C) from late June to as late as mid September, and occasionally exceeding 110 °F (43 °C). Paso Robles’ summers feature an unusually large daytime-nighttime temperature swing, where there may be a profound temperature difference, as much as 50 °F (28 °C), between the daytime highs and the overnight lows. This large diurnal swing permits the planting of certain grape varieties that would otherwise not be suited to the region. Winters are often very cool and moist, with daytime temperatures reaching into the low 50s°F (10 °C). Mornings and nights differ from the daytime average, as they tend to be quite cold (especially in December and January), where lows reach as low as 22 °F (−6 °C). Due to the somewhat close proximity to the Pacific Ocean, the marine layer occasionally makes it over the coast range and into Paso Robles, creating fog. Unlike typical California coastal marine fog, this fog is not long lasting, and typically burns off before 10am.
The all-time record high temperature at the National Weather Service cooperative city office was 117 °F (47 °C) on August 13, 1933. It also reached the same temperature a few more times, most recently on September 6, 2020. The record low temperature was 0 °F (−18 °C) on January 6, 1913, making Paso Robles the lowest elevation in California to reach that low temperature. There are an average of 81.0 days with high temperatures of 90 °F (32 °C) or higher and an average of 64.0 days with low temperatures of 32 °F (0 °C) or lower. The 30-year average (1971–2000) annual precipitation is 15.17 inches (385 mm), falling on an average of 47 days. The wettest year was 1941 with 29.19 inches (741 mm) of precipitation and the dryest year was 1947 with 4.24 inches (108 mm). The most precipitation in one month was 14.76 inches (375 mm) in January 1916. The most precipitation in 24 hours was 5.25 inches (133 mm) on December 6, 1966. Although snow is rare in Paso Robles, 4.0 inches fell on April 5, 1929, and on December 15, 1988. As well as February 24, 2023
At the Paso Robles Municipal Airport, the record high temperature was 115 °F on June 15, 1961, and July 20, 1960. The record low temperature was 8 °F (−13 °C) on December 22, 1990. There are an average of 86.7 days with highs of 90 °F (32 °C) or higher and an average of 53.6 days with lows of 32 °F (0 °C) or lower. The 30-year average (1971–2000) annual precipitation was 12.57 inches (319 mm), falling on an average of 42 days. The wettest year was 1995 with 25.56 inches (649 mm) and the driest year was 2007 with 4.20 inches (107 mm). The most precipitation in one month was 12.19 inches (310 mm) in January 1969. The most precipitation in 24 hours was 5.47 inches (139 mm) on March 10, 1995. The record snowfall was 4.0 inches (100 mm) on December 15, 1988.
See also
Map of California State and its subdivision:- Alameda
- Alpine
- Amador
- Butte
- Calaveras
- Colusa
- Contra Costa
- Del Norte
- El Dorado
- Fresno
- Glenn
- Humboldt
- Imperial
- Inyo
- Kern
- Kings
- Lake
- Lassen
- Los Angeles
- Madera
- Marin
- Mariposa
- Mendocino
- Merced
- Modoc
- Mono
- Monterey
- Napa
- Nevada
- Orange
- Placer
- Plumas
- Riverside
- Sacramento
- San Benito
- San Bernardino
- San Diego
- San Francisco
- San Joaquin
- San Luis Obispo
- San Mateo
- Santa Barbara
- Santa Clara
- Santa Cruz
- Shasta
- Sierra
- Siskiyou
- Solano
- Sonoma
- Stanislaus
- Sutter
- Tehama
- Trinity
- Tulare
- Tuolumne
- Ventura
- Yolo
- Yuba
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming