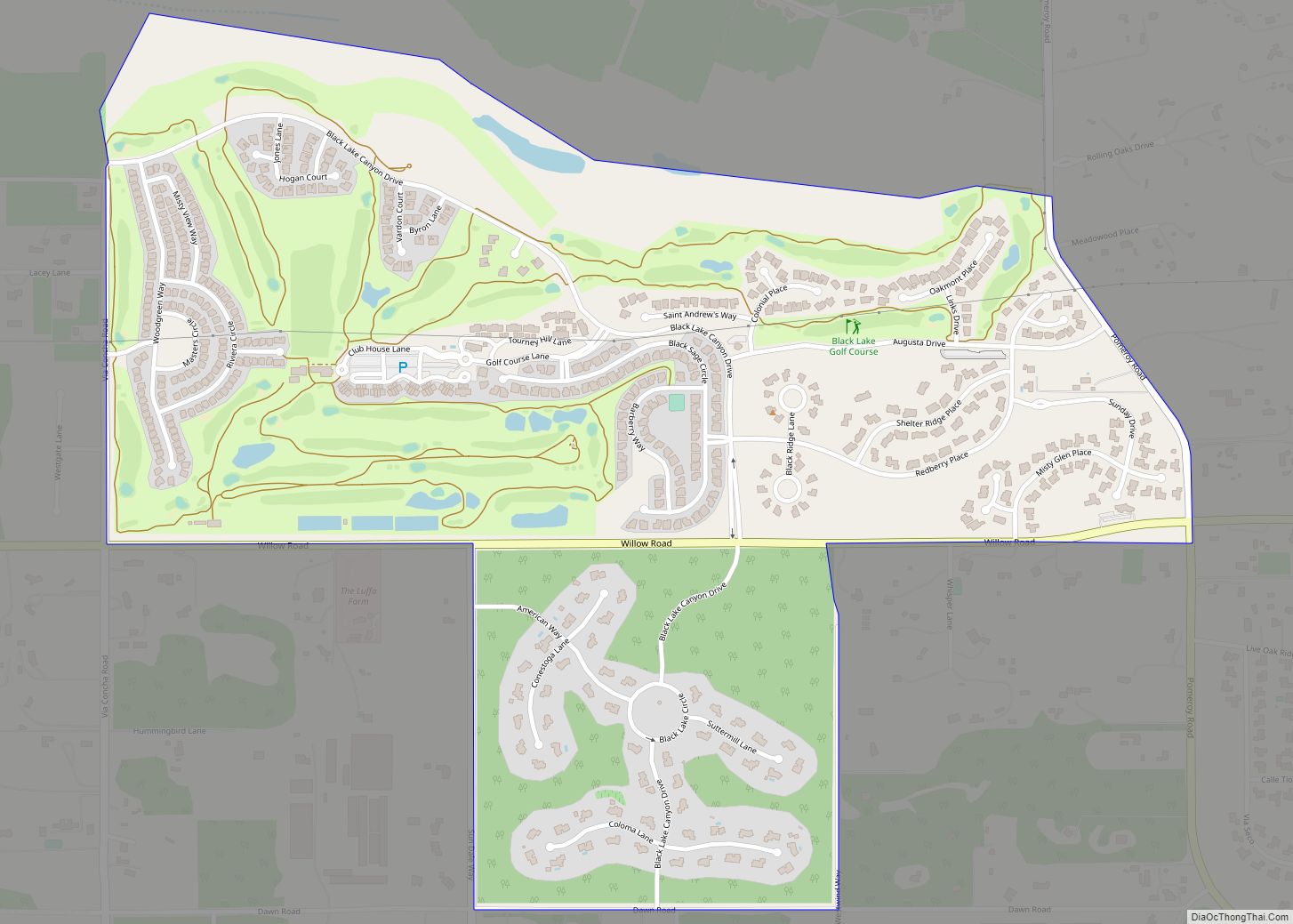
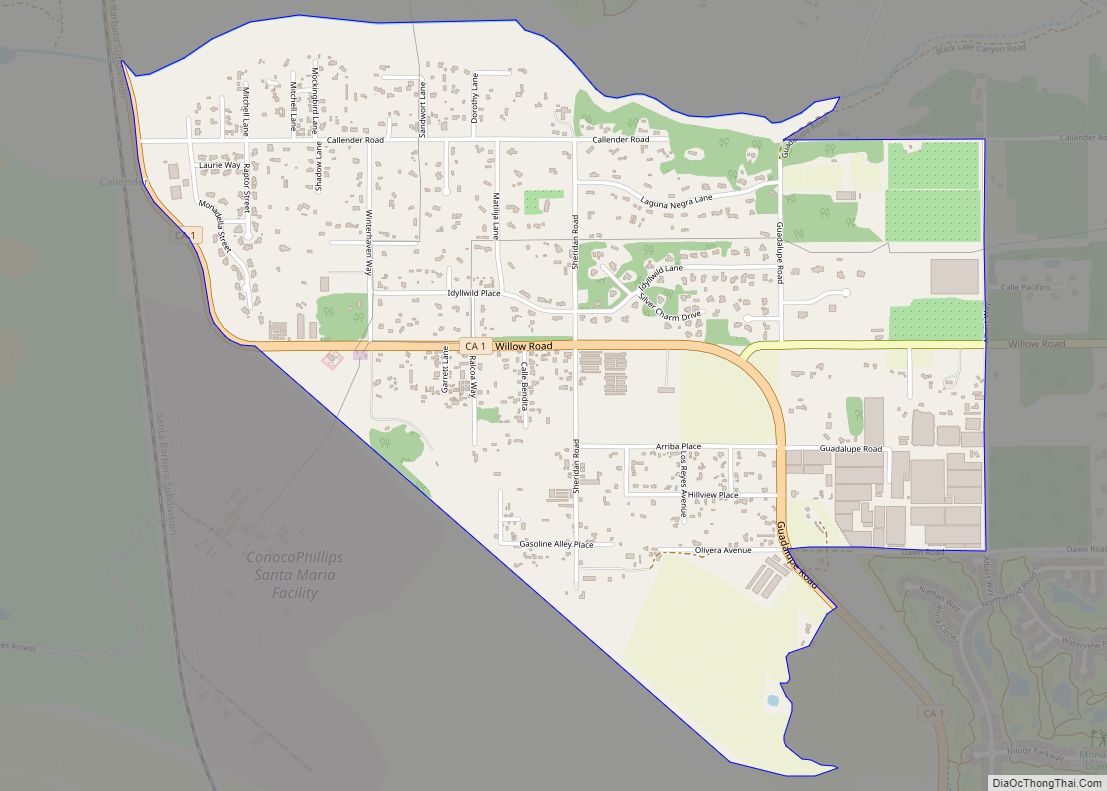
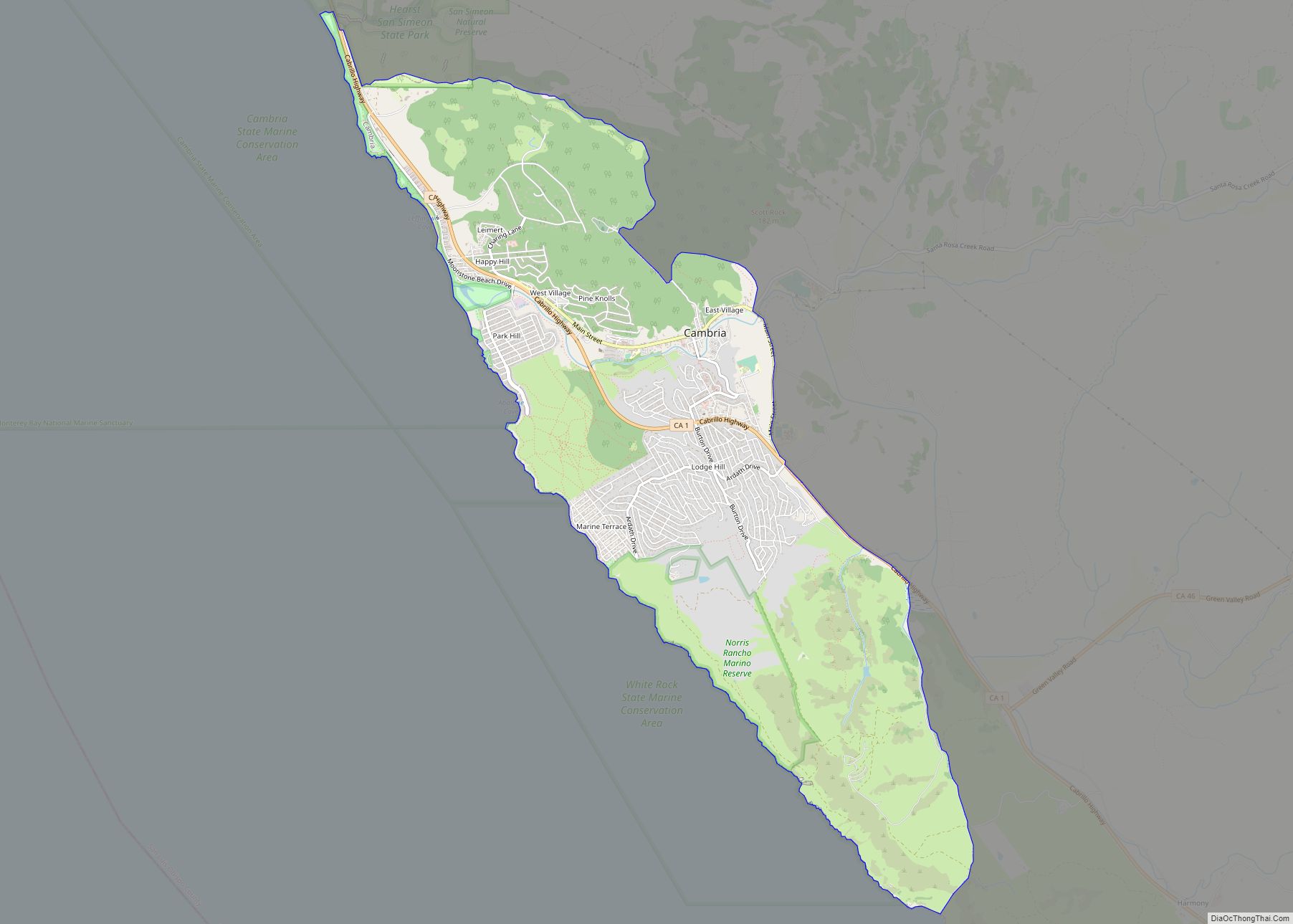
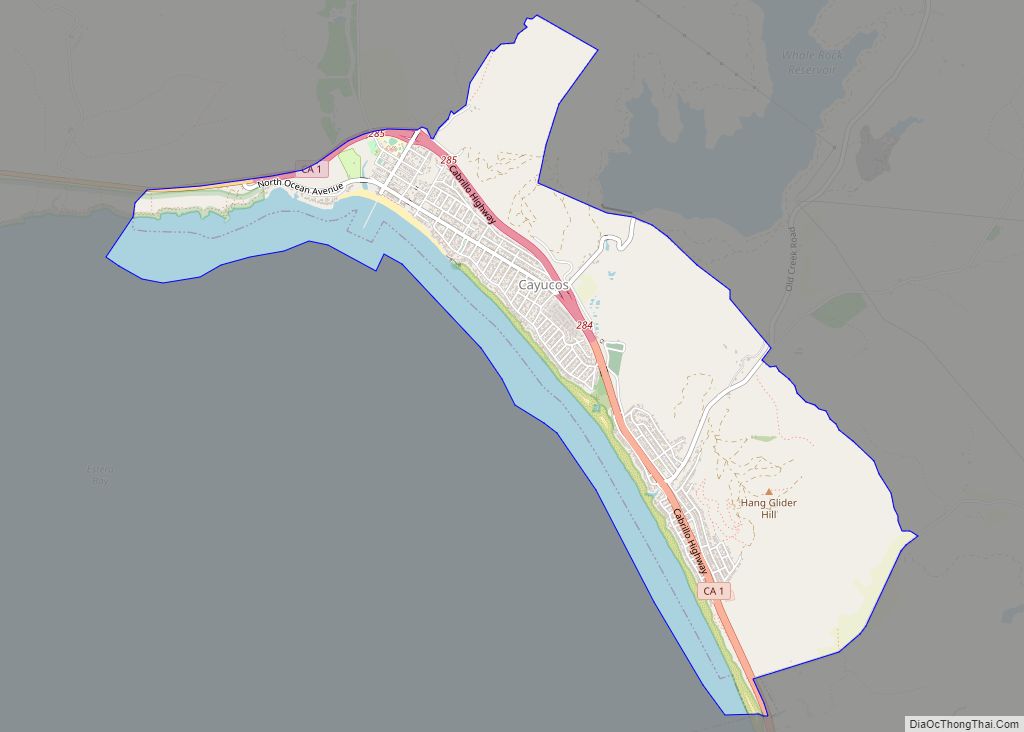
San Luis Obispo (Spanish for ‘St. Louis the Bishop’; /sæn ˌluːɪs əˈbɪspoʊ/; Spanish: [san ˈlwis oˈβispo]; Chumash: tiłhini) is a city and county seat of San Luis Obispo County, in the U.S. state of California. Located on the Central Coast of California, San Luis Obispo is roughly halfway between the San Francisco Bay Area in the north and Greater Los Angeles in the south. The population was 47,063 at the 2020 census.
San Luis Obispo was founded by the Spanish in 1772, when Saint Junípero Serra established Mission San Luis Obispo de Tolosa. The town grew steadily through the Mexican period before a rapid expansion of San Luis Obispo following the American Conquest of California. San Luis Obispo is a popular tourist destination, known for its historic architecture, vineyards, and hospitality, as well as for being home to California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo.
| Name: | San Luis Obispo city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | California |
| County: | San Luis Obispo County |
| Founded: | September 1, 1772 |
| Incorporated: | February 16, 1856 |
| Elevation: | 233 ft (71 m) |
| Total Area: | 13.25 sq mi (34.32 km²) |
| Land Area: | 13.11 sq mi (33.94 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.15 sq mi (0.38 km²) 1.13% |
| Total Population: | 47,063 |
| Population Density: | 3,589/sq mi (1,386/km²) |
| Area code: | 805 |
| FIPS code: | 0668154 |
| Website: | slocity.org |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
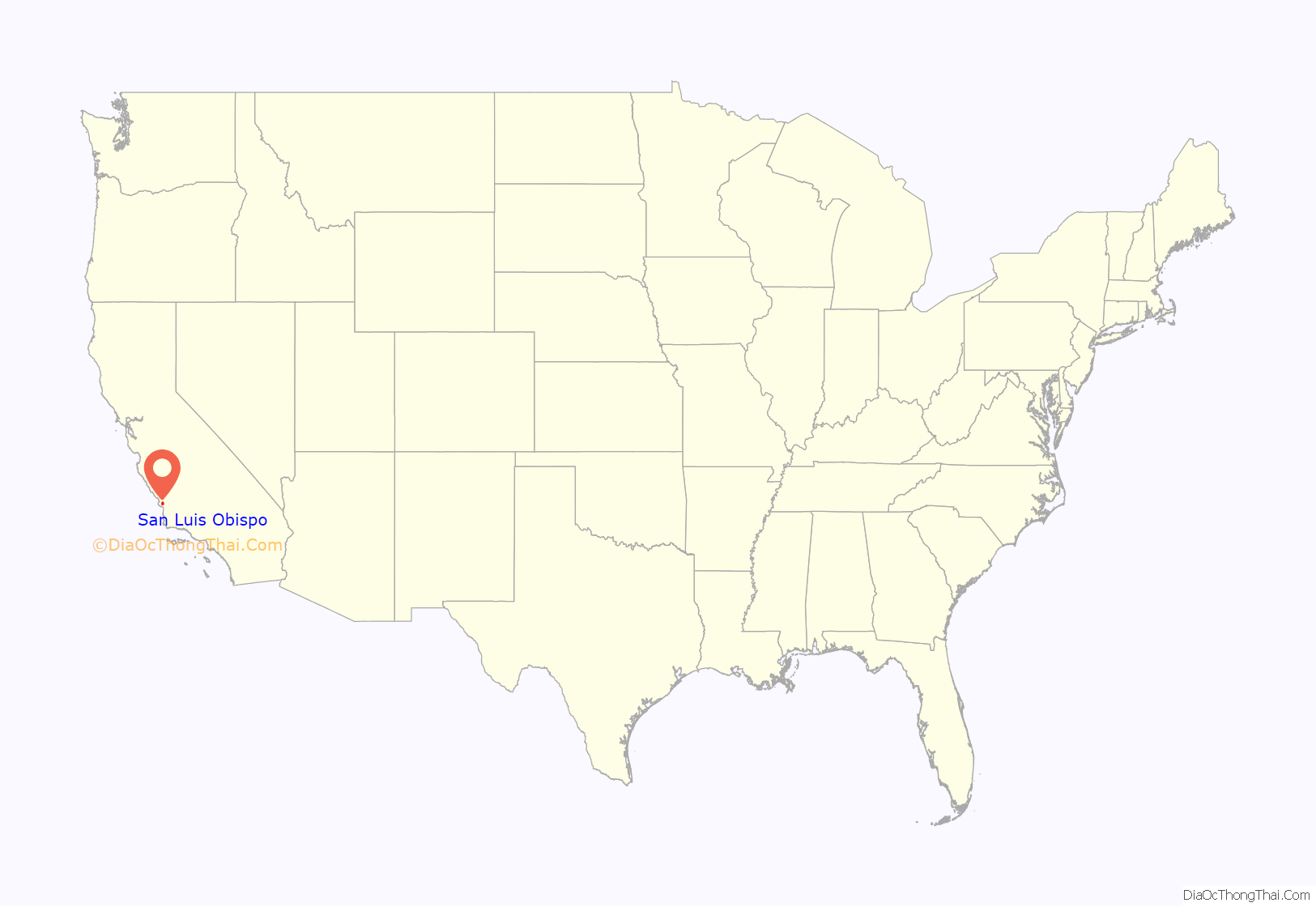
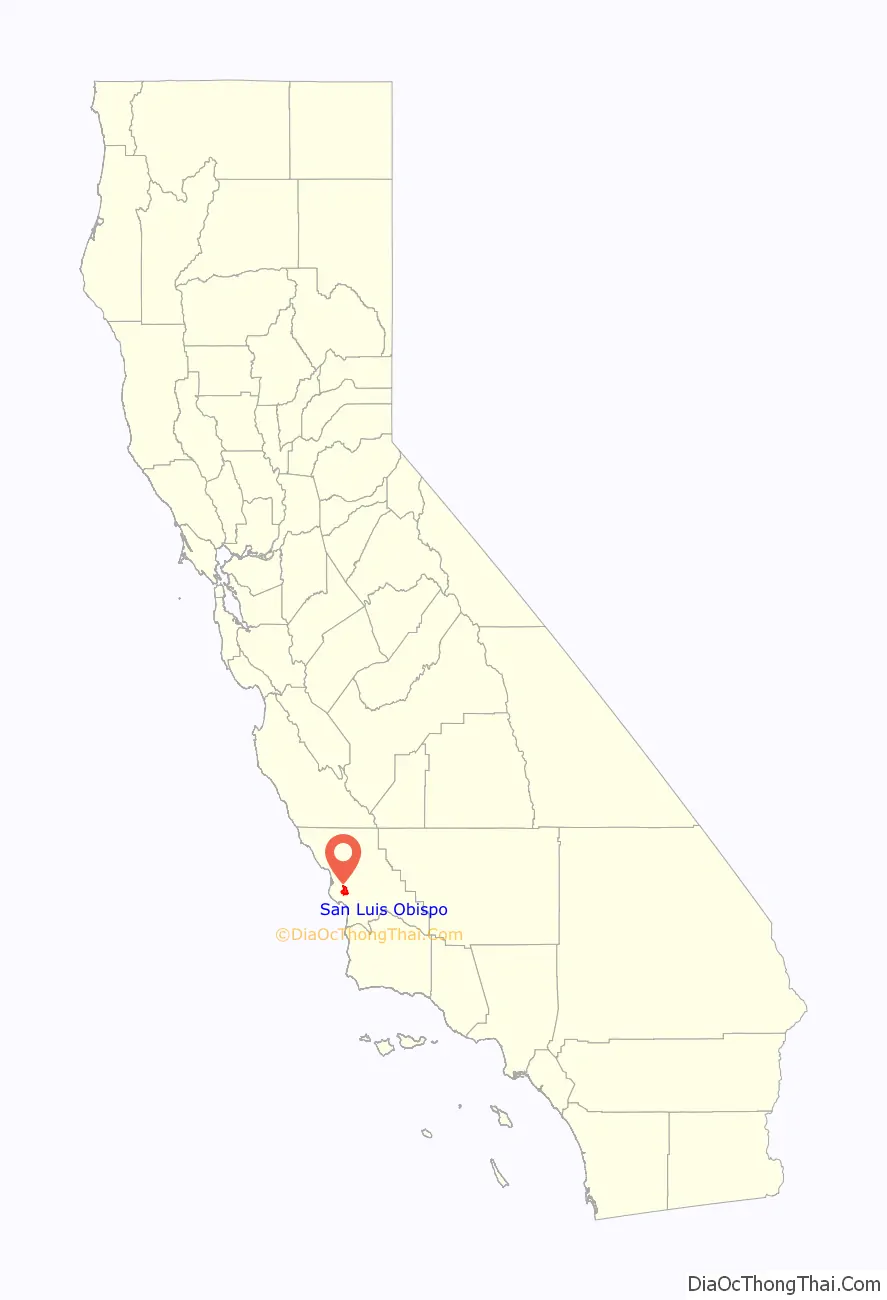
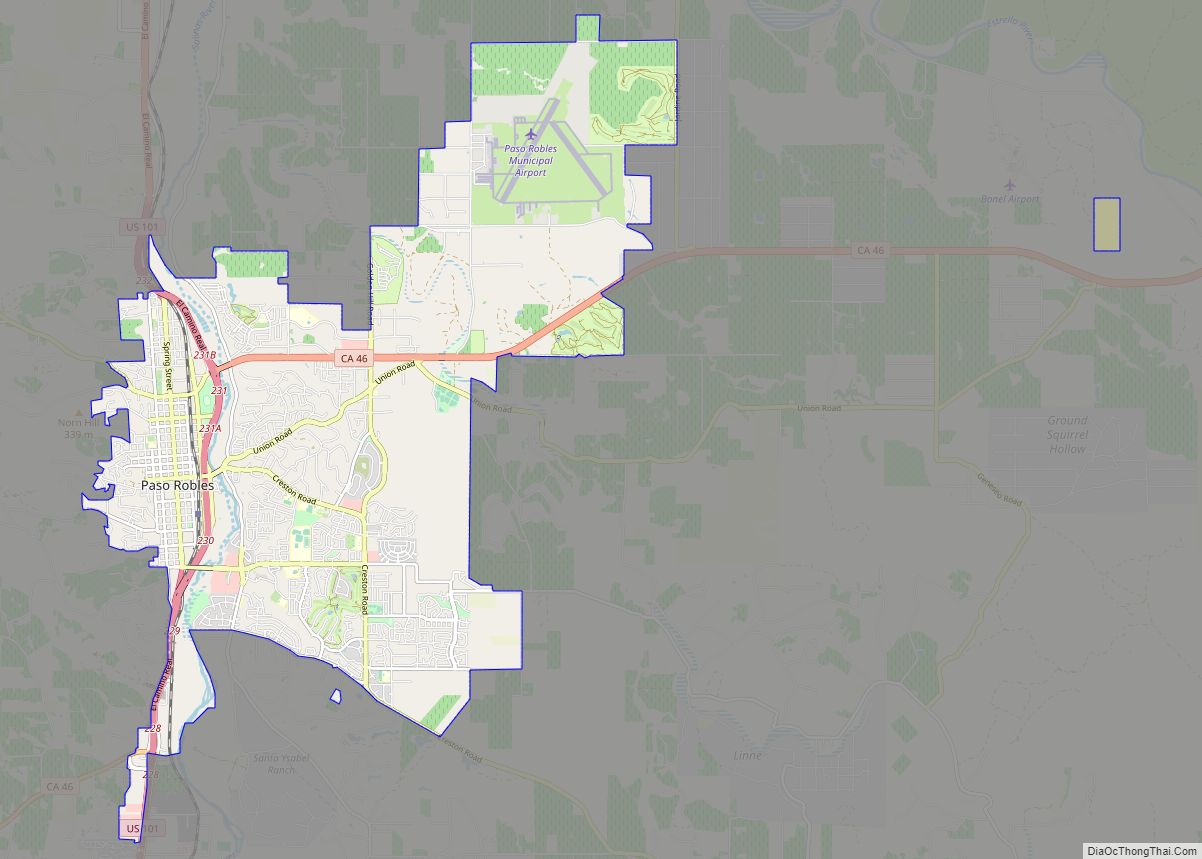
San Luis Obispo location map. Where is San Luis Obispo city?
History
The earliest human inhabitants of the local area were the Chumash people. One of the earliest villages lies south of San Luis Obispo and reflects the landscape of the early Holocene when estuaries came farther inland. The Chumash people used marine resources of the inlets and bays along the Central Coast and inhabited a network of villages, including sites at Los Osos and Morro Creek. The tribal site on present-day San Luis Obispo was named tiłhini (Obispeño for ‘Place of the full moon’).
Spanish period
During the Spanish Empire expansion throughout the world, specifically in 1769, Franciscan Junípero Serra received orders from Spain to bring the Catholic faith to the natives of Alta California; the idea was to unify the empire under the same religion and language. Mission San Diego was the first Spanish mission founded in Alta California that same year.
On September 7, 1769, an expedition led by Gaspar de Portolá entered the San Luis Obispo area from coastal areas around today’s Pismo Beach. One of the expedition’s three diarists, padre Juan Crespí, recorded the name given to this area by the soldiers as Cañada de Los Osos (“cañada” translates as “valley” or “canyon”). The party traveled north along San Luis Obispo Creek, turned west through Los Osos Valley, and reached Morro Bay on September 9.
In 1770, Portola established the Presidio of Monterey and Junípero Serra founded the second mission, San Carlos Borromeo, in Monterey. The mission was moved to Carmel the following year.
In 1772, as the people of Presidio of Monterey and San Carlos Borromeo faced starvation, owing to a lack of supplies, Commander Pedro Fages (a member of the Portolà expedition) led a hunting expedition to the Cañada de Los Osos to bring back food. Over twenty-five mule loads of dried bear meat and seed were sent north to relieve the missionaries, soldiers, and neophytes (baptized natives). It was after this that Junípero Serra decided that La Cañada de Los Osos would be an ideal place for the fifth mission.
The area had abundant supplies of food and water, the climate was also very mild, and the local Chumash were very friendly. With soldiers, muleteers, and pack animals carrying mission supplies, Junípero Serra set out from Carmel to reach the Valley of the Bears. On September 1, 1772, Junípero Serra celebrated the first Mass with a cross erected near San Luis Creek. The very next day, he departed for San Diego leaving Fr. José Cavaller, with the difficult task of building the mission. Fr. José Cavaller, five soldiers and two neophytes began building Mission San Luis Obispo de Tolosa (Spanish for ‘St. Louis Bishop of Toulouse’) which would later become the town of San Luis Obispo.
Mexican period
When the Mexican War of Independence from Spain broke out in 1810, all California missions had to become virtually self-sufficient, receiving few funds or supplies from Spanish sources. Beginning soon after Mexico won her independence from Spain in 1821, anti-Spanish feelings led to calls for expulsion of the Spanish Franciscans and secularization of the missions. Because the fledgling Mexican government had many more important problems to deal with than far-off California, actual secularization didn’t happen until the mid-1830s.
After 1834, the mission became an ordinary parish, and most of its huge land holdings were broken up into land grants called ranchos. The ranchos were given by Mexican land grant from 1837 to 1846, with the mission itself being granted in the final year. The central community, however, remained in the same location and formed the nucleus of today’s city of San Luis Obispo.
American period
Following the American Conquest of California, San Luis Obispo was the first town incorporated in the newly formed San Luis Obispo County. It remains the center of the county to the present. Early in the American period, the region was well known for lawlessness. It gained a reputation as “Barrio del Tigre” (or Tiger-Town) because of the endemic problem. Robberies and murders that left no witnesses were carried out on along the El Camino Real and elsewhere around San Luis Obispo for several years. Finally a gang of eight men committed a robbery with three murders and a kidnapping at the Rancho San Juan Capistrano del Camote in May 1858, that uncharacteristically left two witnesses alive. This brought about the formation of a vigilance committee in the County that killed one, the suspected leader of the gang Pio Linares, and lynched six others, a total of seven men suspected of such misdeeds (the most lethal in California history). Members of the committee remained influential members of the community for decades.
The ranchos remained focused on cattle after the conquest of California. With the discovery of gold, the county experienced a major economic surge with the rising price of beef, with the highest prices coming in 1851. The county remained focused on cattle until 1863, when a drought left most ranchos devastated. Residents quickly turned to other venues, leading to the breaking up of many of the ranchos and a major change in the economic climate of the town, which focused less on cattle ranching and more on dairies, agriculture, and mined goods from then onward.
San Luis Obispo once had a burgeoning Chinatown in the vicinity of Palm Street and Chorro Street. Laborers were brought from China by Ah Louis in order to construct the Pacific Coast Railway, roads connecting San Luis Obispo over the Cuesta Pass to Paso Robles and from Paso Robles to Cambria, and also the 1884 to 1894 tunneling through Cuesta Ridge for the Southern Pacific Railroad. The town’s Chinatown revolved around Ah Louis Store and other Palm Street businesses owned and run by Chinese business people. Today, Mee Heng Low chop suey shop is all that remains of the culture, although a slightly Chinatown-themed commercial development has been planned. A display of some of the unearthed relics from this period can be seen on the first floor of the Palm Street parking garage, which was built over the location where Chinatown once stood. The San Luis Obispo Historical Society (adjacent to the Mission) also contains rotating historical exhibits.
San Luis Obispo was also a popular stop en route to Los Angeles. U.S. Route 101 and California State Route 1 were constructed with the rise of car culture. Due to its popularity as a stop, it was the location of the first motel in the world, the Milestone Mo-Tel.
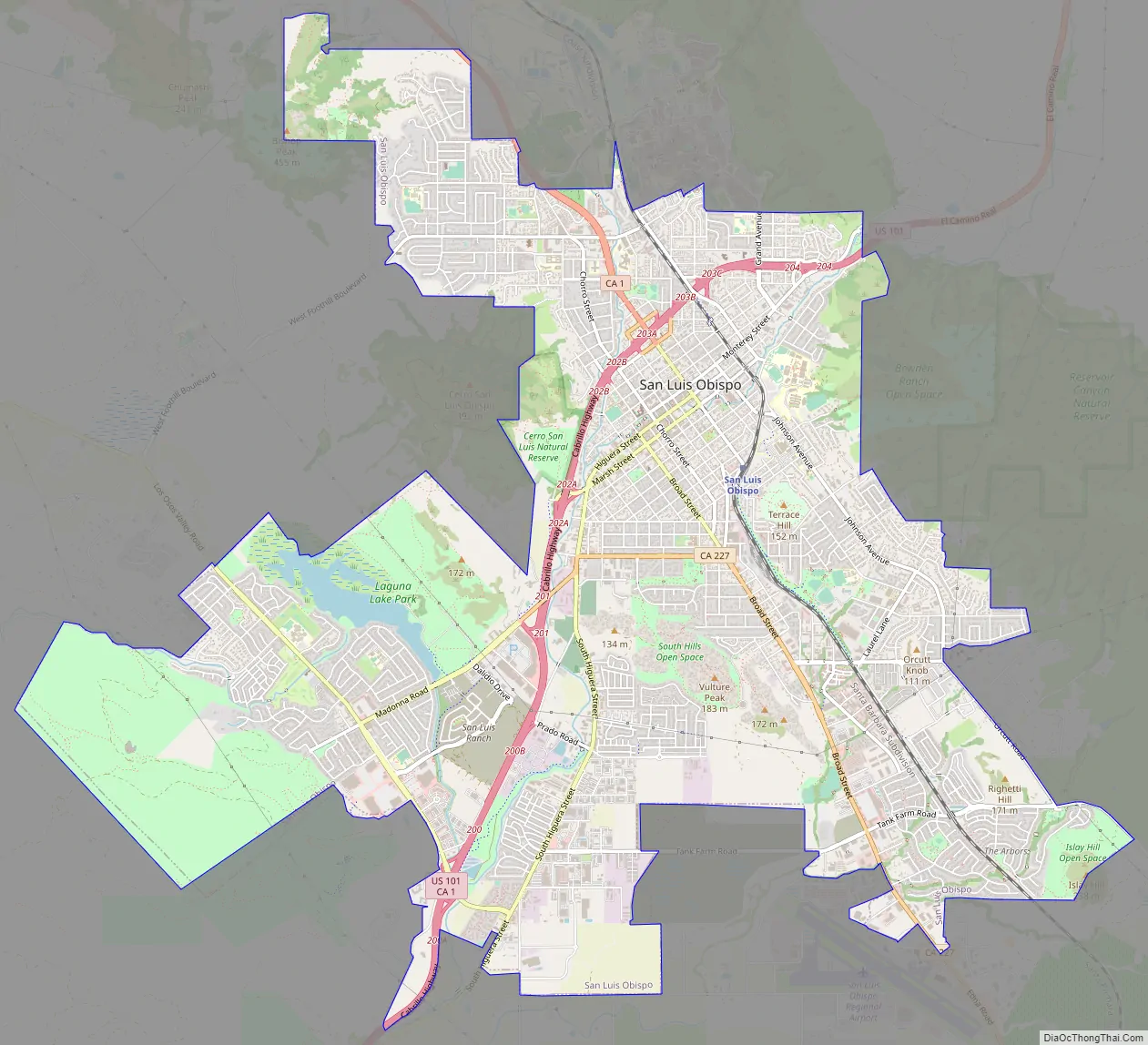
San Luis Obispo Road Map
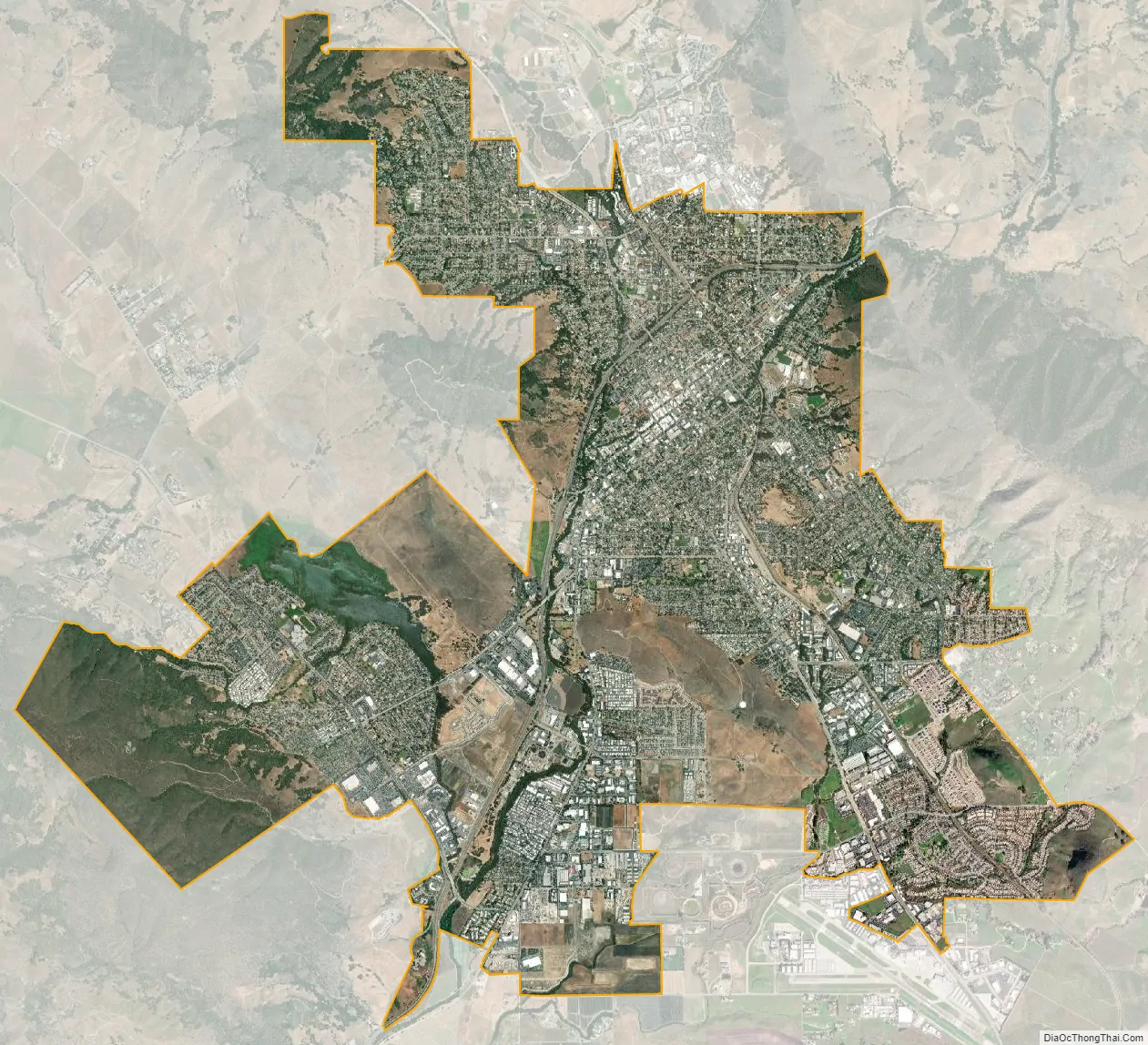
San Luis Obispo city Satellite Map
Geography
San Luis Obispo is located on U.S. Route 101, about 31 miles (50 km) north of Santa Maria.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 13.25 square miles (34.3 km), of which, 13.1 square miles (34 km) is land and 0.15 square miles (0.39 km) (1.13%) is water.
San Luis Obispo is on the West Coast of the United States and in the Central Coast of California. The Pacific Ocean is about 11 miles (18 km) west of San Luis Obispo. The Santa Lucia Mountains lie just east of San Luis Obispo. These mountains are the headwaters for San Luis Obispo Creek, whose watershed encompasses 84 square miles (220 km) surrounding the city and flows to the Pacific Ocean at Avila Beach.
San Luis Obispo is a seismically active area; there are a number of nearby faults including the San Andreas Fault. The Nine Sisters are a string of hills that partially run through San Luis Obispo. They are geologically noteworthy for being volcanic plugs. Six of the nine peaks are open to the public for recreation.
Climate
San Luis Obispo experiences a warm Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification Csb). On average it has 50 days with measurable rain per year, mostly during winter months. Summers are generally warm and sunny, often with morning fog from the Pacific coast. Winters are generally mild, though below freezing lows may be expected four nights per year. Measurable snowfall in San Luis Obispo has not officially been recorded since records began in 1870, although photos show about 0.3 inches (0.76 cm) fell in 1922 and snow flurries were reported in both 1988 and 2006. Temperatures do, however, vary widely at any time of the year, with 80 °F (27 °C) readings in January and February not uncommon. On January 15, 2021, the weather station at California Polytechnic University (San Luis Obispo) recorded a temperature of 93 degrees Fahrenheit, being the warmest “winter” temperature ever recorded in the city. Although heat extremes in the 110s have been recorded, the maritime moderation is generally strong due to the proximity to the cool ocean waters.
See also
Map of California State and its subdivision:- Alameda
- Alpine
- Amador
- Butte
- Calaveras
- Colusa
- Contra Costa
- Del Norte
- El Dorado
- Fresno
- Glenn
- Humboldt
- Imperial
- Inyo
- Kern
- Kings
- Lake
- Lassen
- Los Angeles
- Madera
- Marin
- Mariposa
- Mendocino
- Merced
- Modoc
- Mono
- Monterey
- Napa
- Nevada
- Orange
- Placer
- Plumas
- Riverside
- Sacramento
- San Benito
- San Bernardino
- San Diego
- San Francisco
- San Joaquin
- San Luis Obispo
- San Mateo
- Santa Barbara
- Santa Clara
- Santa Cruz
- Shasta
- Sierra
- Siskiyou
- Solano
- Sonoma
- Stanislaus
- Sutter
- Tehama
- Trinity
- Tulare
- Tuolumne
- Ventura
- Yolo
- Yuba
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming