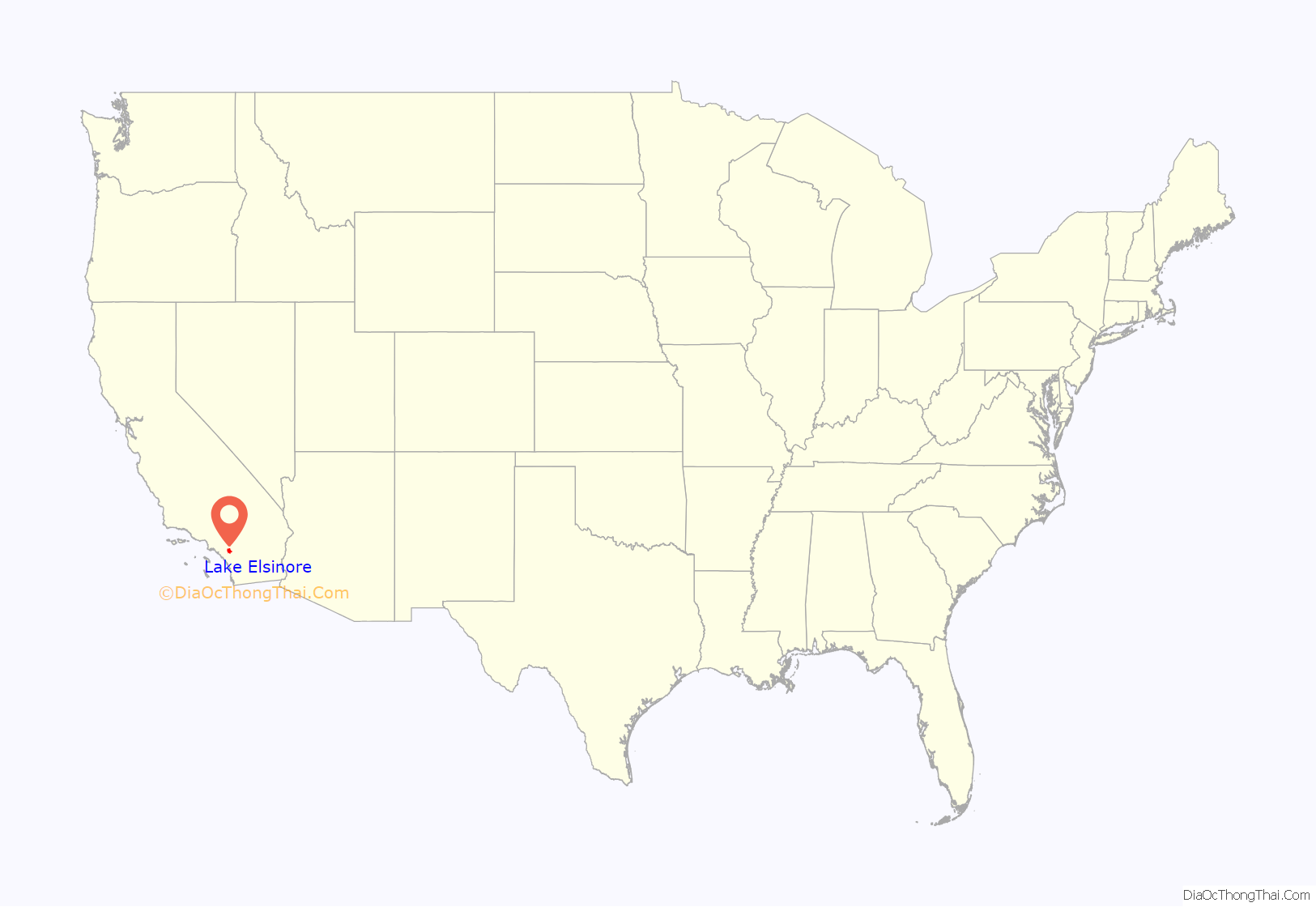
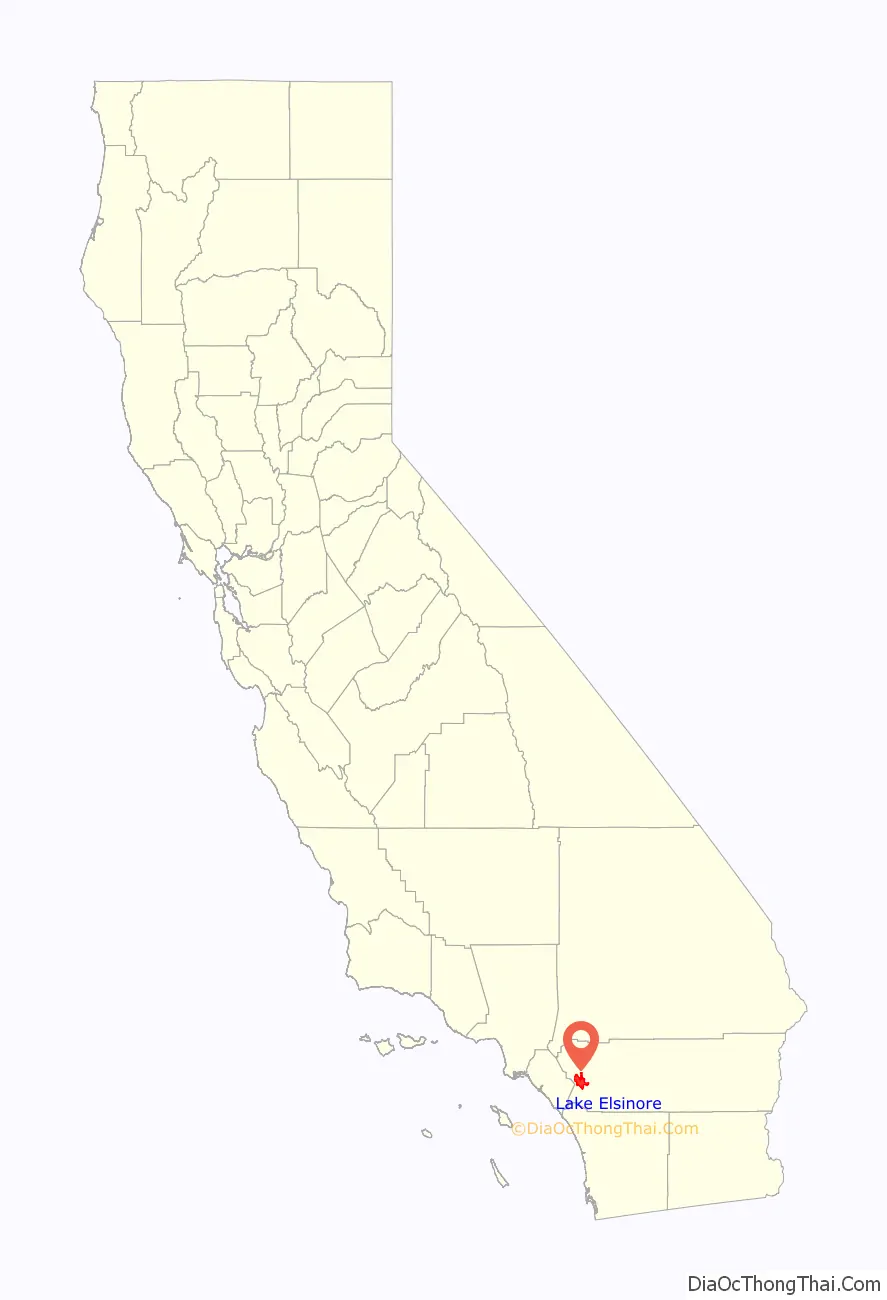
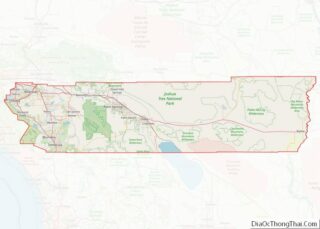
Lake Elsinore is a city in western Riverside County, California, United States. Established as a city in 1888, it is on the shore of Lake Elsinore, a natural freshwater lake about 3,000 acres (1,200 ha) in size. The city has grown from a small resort town in the late 19th and early 20th centuries to a suburban city with over 70,000 residents.
| Name: | Lake Elsinore city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | California |
| County: | Riverside County |
| Incorporated: | April 9, 1888 |
| Elevation: | 1,296 ft (395 m) |
| Total Area: | 43.51 sq mi (112.70 km²) |
| Land Area: | 38.24 sq mi (99.03 km²) |
| Water Area: | 5.28 sq mi (13.67 km²) 13.14% |
| Total Population: | 70,265 |
| Population Density: | 1,837.47/sq mi (709.45/km²) |
| Area code: | 951 |
| FIPS code: | 0639486 |
| Website: | www.lake-elsinore.org |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Lake Elsinore location map. Where is Lake Elsinore city?
History
Native Americans have long lived in the Elsinore Valley. The Luiseño people were the earliest known inhabitants. Their pictographs can be found on rocks on the Santa Ana Mountains and in Temescal Valley, and artifacts have been found all around Lake Elsinore and in the local canyons and hills.
Overlooked by the expedition of Juan Bautista de Anza, the largest natural lake in Southern California was first seen by the Spanish Franciscan padre Juan Santiago, exploring eastward from the Mission San Juan Capistrano in 1797. In 1810, the water level of the Laguna Grande was first described by a traveler as being little more than a swamp about a mile long. Later in the early 19th century, the lake grew larger, providing a spot to camp and water their animals for Mexican rancheros, American trappers, the expedition of John C. Frémont, and the immigrants during the California Gold Rush as they traveled along the southern shore of the lake on what later became the Southern Emigrant Trail and the route of the Butterfield Overland Mail.
On January 7, 1844, Julian Manriquez acquired the land grant to Rancho La Laguna, a tract of almost 20,000 acres (8,100 ha) which included the lake and an adobe being built near the lake on its south shore at its western corner that was described by Benjamin Ignatius Hayes, who stayed there overnight January 27, 1850.
In 1851, Abel Stearns acquired the rancho and sold it in 1858 to Augustin Machado. Augustin Machado built a seven-room adobe ranch house and an outbuilding on the southwest side of the lake. Soon after, Rancho La Laguna became a regular stop on the Butterfield Overland Mail route between Temecula 20 mi (32 km) to the southeast and the Temescal station 10 mi (16 km) to the northwest. The old Manriquez adobe was used as the station house. Over the years, a framed addition and a second story were added, and it was used as a post office for the small settlement of Willard from 1898 until September 30, 1902. The building stood until it was razed in 1964, at what is now 32912 Macy Street. Today, three palm trees still grow in front of the site along Macy Street in front of the property.
As a result of the Great Flood of 1862, the level of the lake was very high, so the Union Army created a post at the lake to graze and water their horses. In the great 1862–65 drought, most of the cattle in Southern California died and the lake level fell, especially during 1866 and 1867, when practically no rain fell. However, the lake was full again in 1872, when it overflowed down its outlet through Temescal Canyon.
While most of the old Californio families lost their ranchos during the great drought, the La Laguna Rancho remained in the hands of the Machado family until 1873, when most of it was sold to Englishman Charles A. Sumner. Juan Machado retained 500 acres (200 ha) on the northwest corner of the lake, where his adobe still stands near the lake at 15410 Grand Avenue.
After 1872, the lake again evaporated to a very low level, but the great rains in the winter of 1883–84 filled it to overflowing in three weeks. Descriptions of the lake at this time say that large willow trees surrounding the former low-water shore line stood 20 ft (6.1 m) or more below the high-water level and were of such size that they must have been 30 or more years old. This indicated the high water of the 1860s and 1870s must have been of a very short duration.
On October 5, 1883, Franklin H. Heald and his partners Donald Graham and William Collier bought the remaining rancho, intending to start a new town. In 1884, the California Southern Railroad built a line from Colton through the Cañon de Rio San Jacinto (now Railroad Canyon) to link with San Diego, and a rail station La Laguna appeared near the corner of what is now Mission Trail and Diamond Drive. On April 9, 1888, Elsinore became the 73rd city to be incorporated in California, just 38 years after California became a state. Originally, Elsinore was in San Diego County, but the city became part of Riverside County upon its creation in 1893. It was named Elsinore after the Danish city in Shakespeare’s “Hamlet”, which is now its sister city (Helsingør). Another source maintains Elsinore is a corruption of “el señor”, Spanish for “the gentleman”, because the city site had been owned by a don.
The rainfall until 1893 was greater than normal, and the lake remained high and overflowed naturally on three or four occasions during that time. The lake water was purchased by the Temescal Water Company for the irrigation of land in Corona. Its outlet channel was deepened, permitting gravity flow down the natural channel of Temescal Canyon to Corona for a year or more after the water level sank below the natural elevation of its outlet. As the lake surface continued to recede, a pumping plant was installed and pumping was continued a few seasons, but the concentration of salts in the lake, due to the evaporation and lack of rainfall, soon made the water unfit for irrigation and the project was abandoned by the company.
From the beginning, the mineral springs near the lake attracted visitors seeking therapeutic treatments. In 1887, the Crescent Bath House, now known as “The Chimes”, was built; it still stands in historic downtown and is a registered national historic site. By 1888, the economy was supported by coal and clay mining at what became the town of Terra Cotta, gold mining in the Pinacate Mining District, ranching, and the agriculture of fruit and nuts. After 1893, the lake’s water level sank almost continuously for nearly 10 years, with a slight rise every winter. Heavier precipitation, beginning in 1903, gradually filled the lake to about half the depth above its minimum level since 1883. Then, in January 1916, a flood rapidly raised the level to overflowing.
Lake Elsinore was a popular destination in the first half of the 1900s for celebrities to escape the urban Hollywood scene. Many of their homes still stand on the hills surrounding the lake, including Aimee’s Castle, a unique Moorish-style house built by Aimee Semple McPherson. Also, actor Bela Lugosi, known for his lead role in Universal Pictures’ film, Dracula, built a home that still exists in the city’s Country Club Heights district.
The Riverside Daily Press published this description in December 1919:
The lake also hosted teams for Olympic training and high-speed boat racing in the 1920s. The lake went dry in the mid-1930s, but refilled by 1938.
During World War II, the lake was used to test seaplanes, and a Douglas Aircraft plant making wing assemblies for Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress bombers was located in the city. The lake ran dry during most of the 1950s and was refilled in the early 1960s.
Despite its relatively small African American population, it has the distinction of electing the first black city councilman in California, Thomas R. Yarborough, in 1948. Yarborough went on to become one of three African American mayors elected in California in 1966.
In 1972, citizens of the city voted to rename it Lake Elsinore. More than a week of heavy rains in 1980 flooded the lake, destroying surrounding homes and businesses. Since then, a multimillion-dollar project has been put into place to maintain the water supply at a consistent level, allowing for homes to be built close to the lake. Overflow water in the Lake spills out via Alberhill Creek, a tributary of Temescal Creek. In 2007, an aeration system was added to help with the lake’s ecosystem.
Rapid population growth in the mid-2000s altered the appearance and image of Lake Elsinore from a small lakeside town of 3,800 people in 1976 to a bedroom community of upper middle-class professionals. The city was ranked as the 12th fastest growing city in California between 2000 and 2008. Now, over 70,000 residents as of the 2020 census live there, and formerly open hillsides have been converted into housing tracts.
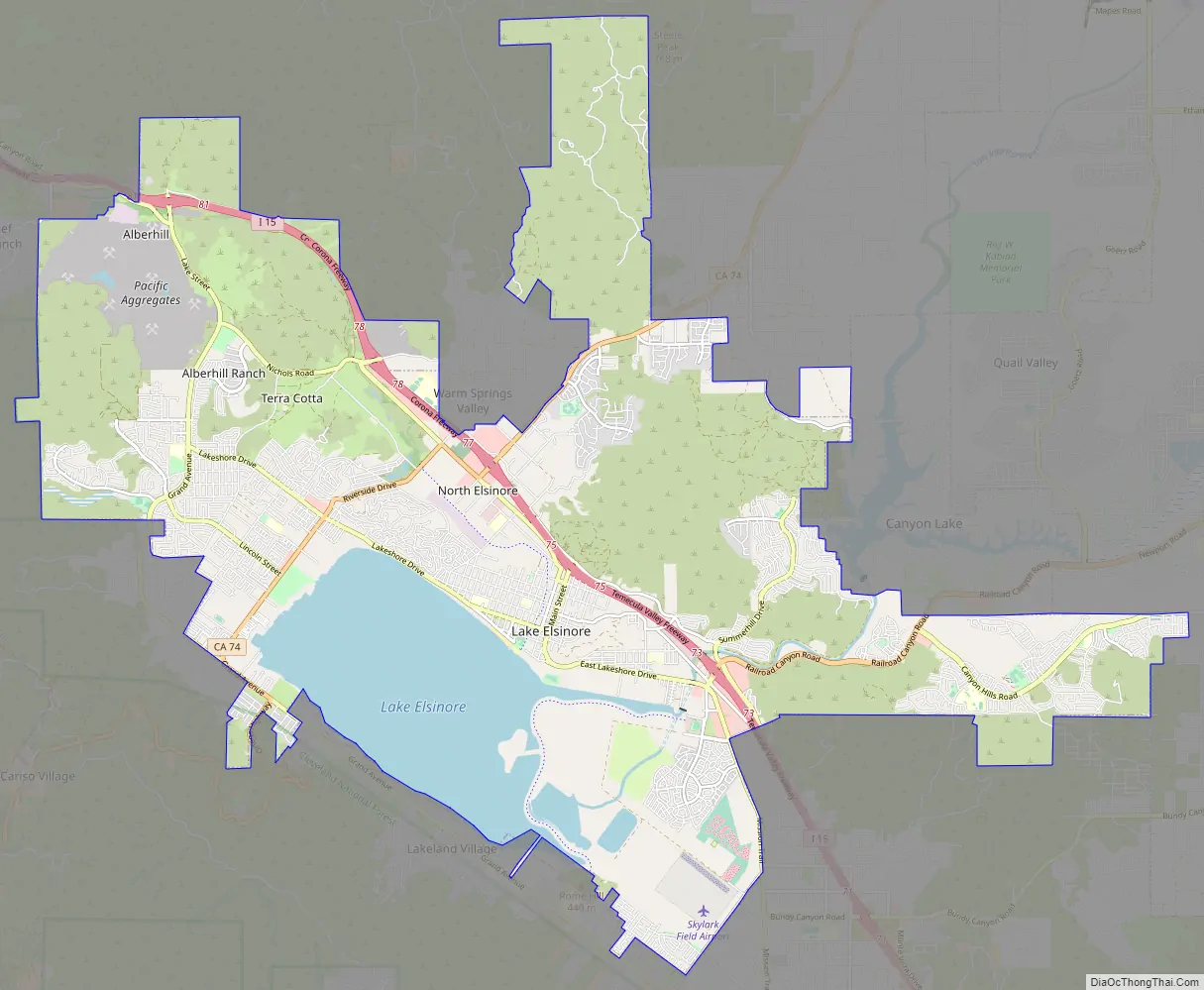
Lake Elsinore Road Map
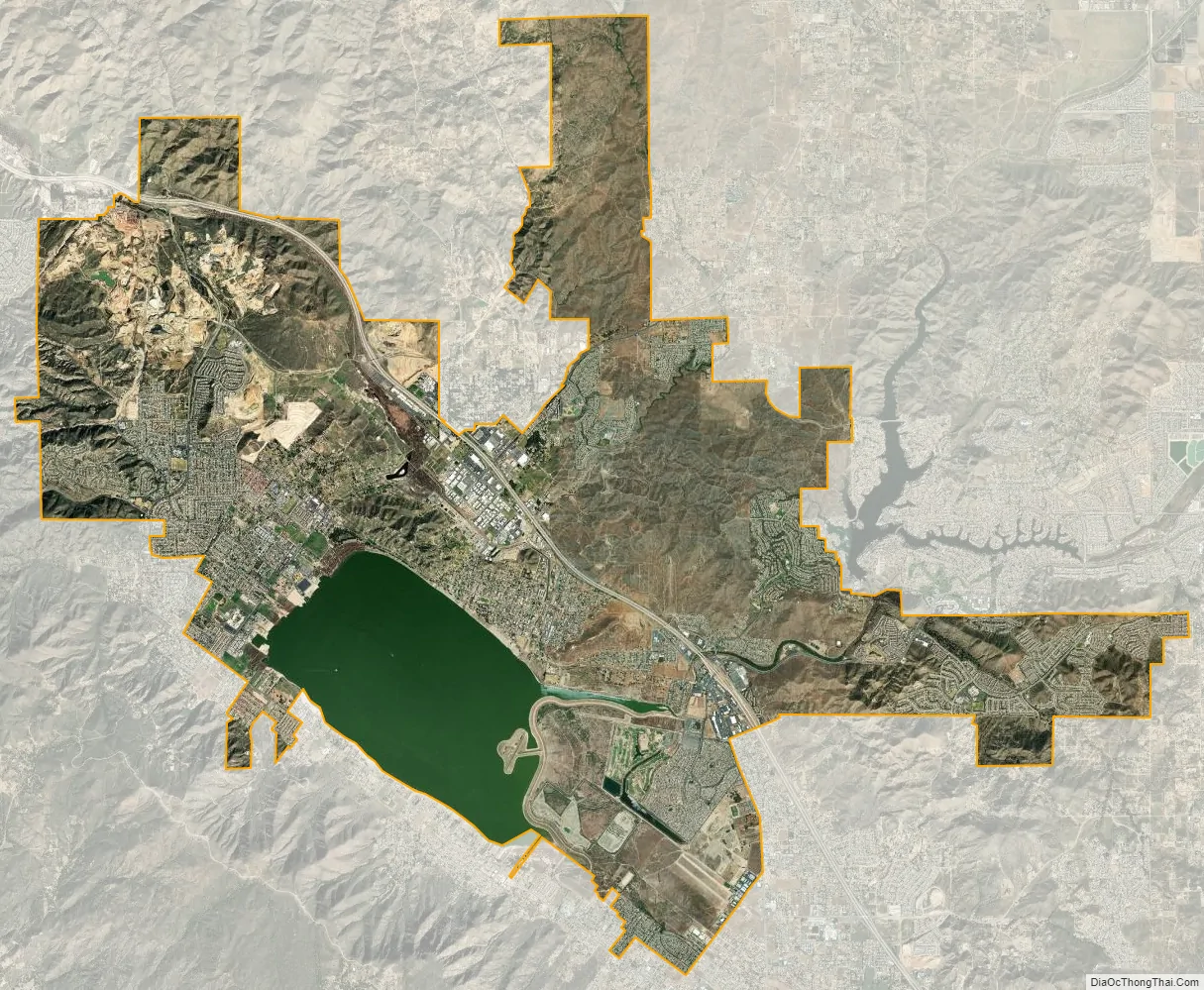
Lake Elsinore city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 41.7 sq mi (108.0 km) of which 36.2 sq mi (93.8 km) of it is land and 5.5 sq mi (14.2 km), or 13.14%, is covered by water.
Lake Elsinore, originally Laguna Grande, is the largest natural freshwater lake in Southern California and is situated at the lowest point within the 750-square-mile (1,900 km) San Jacinto River watershed at the terminus of the San Jacinto River, where its headwaters are found on the western slopes of San Jacinto Peak with its North Fork, and Lake Hemet with its South Fork. Lake levels are healthy at 1,244 feet (379 m) above sea level with a volume of 30,000 acre⋅ft (37 Gl) that often fluctuate, although much has been done recently to prevent the lake from drying up, flooding, or becoming stagnant. At 1,255 feet (383 m), the lake would spill into the outflow channel on its northeastern shore, known properly as Temescal Wash, flowing northwest along I-15, which feeds Temescal Creek, which dumps into the Santa Ana River just northwest of the City of Corona. It then flows to Orange County, out to the Pacific Ocean just south of Huntington State Beach.
Lake Elsinore is bordered by the Elsinore Mountains to the west, which are a part of the larger Santa Ana Mountain Range, and receive a few inches of snowfall a few days each year. Included in the Santa Ana Mountains is the Cleveland National Forest and the community of El Cariso. Lake Elsinore is northwest of Wildomar and the northern portion is part of the Temescal Canyon. To the east of the lake are the much older and more eroded slopes of the Temescal Mountains.
Districts
Lake Elsinore is a city which encompasses a large geographical area. To better distinguish the wide range of neighborhoods, the city is organized into 11 districts. Each district beholds its own unique geography, culture, age, and history which together make Lake Elsinore a very diverse and culturally rich city. They are the Alberhill, Ballpark, Business, Country Club Heights, East Lake, Historic, Lake Edge, Lake Elsinore Hills, Lake View, North Peak, and Riverview Districts.
The Alberhill District is characterized by rolling terrain, vacant land, and the newly constructed Alberhill Ranch neighborhood. Much of the topography in the central areas, east and west of Lake Street, has been substantially altered as a result of the Alberhill District’s long history of extractive/mining activities. Mining operations in the Alberhill District began at Terra Cotta roughly the same time the region’s first railroad, the California Southern Railroad, was completed in the 1880s. A spur of the railroad originally built to Terra Cotta was extended into the central portion of the Alberhill District. The Atchison, Topeka, and Santa Fe Railroad built a line up from Corona through Alberhill to Elsinore after the line through Railroad Canyon was washed out in the 1920s. These events helped shape the growth of the District. Mining operations for coal and especially clay have continued to exist since the late 19th century, and occupy a significant portion of the Alberhill District. Through the years, Pacific Clay Products Company has purchased the local mines and has become the sole operating clay mine in the region.
The Ballpark District takes its name from the Lake Elsinore Diamond Stadium, a first-class minor league baseball stadium constructed in 1994. It is home to the Lake Elsinore Storm professional baseball team, an affiliate of the San Diego Padres. The area was once the site of the first train depot in Lake Elsinore, but no train tracks or structures from that era remain.
The developed area within the Business District, in Warm Springs Valley, is relatively new and has the strongest concentration of industrial and commercial uses within the city. In addition, it hosts several big-box retailers, the Lake Elsinore Outlets, the lake’s outlet channel, Temescal Creek, and marshlands. It is bordered by Country Club Heights to the west and Interstate 15 to the east, with a small portion extending to the east side of I-15. Sections of the Atchison, Topeka, & Santa Fe Railroads that passed through the Business District during the 1800s have been removed. In addition, a historic ranching and homesteading site with previous ranching and homesteading activities is located nearby the route where the railroad once existed.
The Country Club Heights District is distinctly marked by the steep hillsides of the Clevelin Hills, views of the lake and the City, and is a key part of Lake Elsinore’s history. The issues mentioned above have presented development constraints for Country Club Heights since its historic beginnings dating back to 1912. The area was the target of an elaborate land scheme promoted in Los Angeles. The Mutual Benefit and Loan Society of Los Angeles acquired two pieces of dry, “hill-land” within a few miles north of “town-land” that the Press claimed was not worth ten cents an acre. The Mutual Benefit and Loan Society offered to give a 25-by-100-foot (7.6 m × 30.5 m) lot to anyone who asked; however, the person receiving the lot had to pay ten dollars for a membership in the Club, and one dollar per month dues for five years. In 1924, the Clevelin Realty Corporation, headed by Abe Corlin (President) and Henry Schultz (Treasurer-Secretary), began selling additional lots in Country Club Heights and launched a real estate sales promotion in the area. The Clevelin Hills took their name from this company.
Noteworthy sites in the Country Club Heights District include: the Schultz Mansion (now Bredlau Castle) and the Corlin Mansion, both built by the Corporation on the Clevelin Hills in 1926 for Henry Schultz and Abe Corlin, respectively, who had originated the Clevelin Realty development. The Bredlau castle is over 9,000 sq ft (840 m), and includes a hidden room with a sliding bookcase door that was used during Prohibition. These stately homes overlooking the lake were the site for many social gatherings. The winding roads of Country Club Heights are adorned with historic Marbelite lampposts, designed by Henry Barkschat. In 2007, the City of Lake Elsinore restored the historic lampposts along Lakeshore Drive.
In October 1928, Aimee Semple McPherson, a renowned evangelist, commissioned Architect Edwin Dickman to design for her a palatial home in Country Club Heights, which has since won fame as “Aimee’s Castle”. This is said to be a house born of Hollywood, inspired by Moorish architectural design. This home served as the evangelist’s part-time home until 1939, when it passed to new ownership. After changing hands many times, in 2005, International Church of the Foursquare Gospel, the modern incarnation of McPherson’s Foursquare Gospel, purchased and restored the property after years of neglect.
The Clevelin Country Club (later known as the Lake Elsinore Country Club, The Spa Club and the Casino Del Elsinore) was built to be the main attraction of the Country Club Heights subdivision. Prominent members of the club included Mrs. Wallace Reid, Marie Prevost, Reginald Denny, Jack Dempsey, Bert Lytell, Damon Runyon and Joe Stecher, for whom the streets are so named This Spanish-Mediterranean Moorish accented architectural masterpiece had over 20,000 square feet of floor space and included a ballroom, banquet hall, sleeping quarters, and a tunnel system to hidden rooms. The Country Club closed during the depression, but reopened in 1951. It has closed again before 1981, at which point restoration work was being undertaken, but by 1990 the property was vacant and derelict. The Country Club succumbed to arson in 2001.
The East Lake District is partially developed and contains the newly constructed Summerly neighborhood. It is a generally flat area that does not contain any registered historic structures. However, portions of the East Lake District were used during prehistoric times by Native American Indians as flaking and grinding stations. In addition, a historic ranching and homesteading site is located just outside the East Lake District along the border with Lakeland Village to the southwest. More recently, the East Lake District has also been home to popular motocross, skydiving, glider plane, and hang gliding activities. Throughout the city’s history, Lake Elsinore has alternated between severe floods and droughts. Most of the East Lake District lies within a 100-year floodplain adjacent to and southeast of the lake. As a result, the district has been significantly affected during wet seasons and high water levels in the lake. Major floods occurred in 1884 and in 1916. In 1969, 7 in (180 mm) of rain fell in 11 days and severely flooded the lake’s shores. The East Lake District’s proximity to the lake and flood storage is a key consideration in all planned development and several projects have been implemented to prevent the lake from flooding again.
The Historic District has been the focal point of the city since its incorporation in 1888.
In 1925, W.R. Covington and Associates of Santa Monica purchased 650 ft (200 m) of lake frontage and three blocks of slightly improved land across Poe Street from Warm Springs Park. A clubhouse, swimming pool, and other facilities projected to cost $200,000 (or $3.1 million today) were built on this property. No records have been found to provide the date when a fire destroyed the clubhouse, but remnants of the burned structure and surrounding trees examined in 1942 indicate the fire must have occurred soon after the building was constructed. The Covington resort was built in the Town of Elsinore.
Today, several unregistered historic buildings exist, including the Crescent Bath House, also known as “The Chimes”; The Chamber of Commerce (Santa Fe Train Station); The Cultural Center (The Methodist Church); Armory Hall; The Ambassador Hotel (Elsinore Consolidated Bank); Jean Hayman House; and Elsinore City Park The neighborhoods in this area are the oldest in the city, and its commercial strip along Main Street is considered to be downtown.
The Lake Edge District area has had a long and eventful history, with the lake as a focal point for the Native Americans, Europeans, Mexicans, early founders of the City, and the multitude of visitors and locals who continue to come to its shores for entertainment and recreation. Many developments occurred along or within proximity of the lake’s edge during the second half of the 19th and the first half of the 20th centuries.
The Lake Edge District encompasses the ruins of the city’s oldest standing structure, the Machado Adobe House, Rancho La Laguna This site was the location of the Laguna Grande Butterfield Stage Station. This structure succumbed to arson in 2017.
A structure of historical interest is Meyer & Holler designed Southern California Athletic and Country Club, former Elsinore Naval Military Academy building, located along Grand Avenue near the intersection of Ortega Highway.
A newly constructed campground, marina, and boat launch is located on the northwest side of the lake.
The Lake Elsinore Hills District encompasses a large and varied terrain including broad plains, rolling hills, steep slopes, sensitive habitats, and watercourses, with elevations ranging from 1,300 to 2,170 feet (400 to 660 m) above the sea level. Many areas of the Lake Elsinore Hills District are not readily accessible or able to be developed, so have remained vacant. Two large bodies of water located within close proximity of the Lake Elsinore Hills District are the City’s lake to the southwest and Canyon Lake to the east, which is located within the city of Canyon Lake. Some of the higher elevations offer panoramic views of the City’s lake and the Santa Ana Mountains. The neighborhoods in this district include Tuscany Hills, Canyon Hills, and Rosetta Canyon.
The northwestern areas of the Lake View District offer beautiful views of the lake and the neighboring mountains, and are characterized by high elevations, steep slopes, and a series of canyons. The remaining areas of the Lake View District are relatively flat in the lower elevations. Historically, the northern portion of the Lake View District has remained mostly undeveloped, with the exception of the La Laguna Estates neighborhood above McVicker Canyon Park. Similar to the areas further north, the Atchison, Topeka, and Santa Fe Railroad and abundant mining opportunities extant in the late 19th century brought both residents and visitors to the area. Historic ranching and homesteading, including Torn Ranch, were generally located to the northwest of Machado Street, which was an important roadway lined with beautiful deodar trees. Most of the lower-lying areas of the Lake View District to the north have been recently developed and primarily include single-family homes. Other neighborhoods in this area include Northshore and Lake Terrace, which were both formerly orange groves. Another area in this district at the intersection of Riverside and Lakeshore Drives has long been to referred to as “Four Corners” by local residents.
The Riverview District is a combination of steep terrain and flat areas nestled between a knoll with steep slopes, a major watercourse, and the lake. Higher elevations and steep slopes are located in the northwest areas of the Riverview District, which function as a physical border with most of the adjacent Historic District. The San Jacinto River floodway, located within the Riverview District along the eastern and southern areas, is the city’s major watercourse. The river flows southwest from Canyon Lake through the Lake Elsinore Hills District and the Riverview District, then ultimately empties into the lake.
Climate
Lake Elsinore has a mild semi-arid climate (Köppen climate classification BSk/BSh), with hot, almost rainless summers and mild, wetter winters. While too dry for this classification, its thermal regime and precipitation distribution resembles that of a hot-summer Mediterranean climate (Köppen Csa), which is present in many surrounding areas. On average, the hottest month is July, and the coolest month is December. The highest recorded temperature was 118 °F (47.8 °C), first recorded on August 12, 1933, and the lowest recorded temperature was 10 °F (−12.2 °C) on December 30, 1974. The maximum average precipitation occurs in February, and the minimum average precipitation in June, although less than half of all Junes, Julies, Augusts, and Septembers record any precipitation whatsoever. The greatest amount of precipitation ever received in one day was 5.28 inches (134 mm), on February 15, 1927.
See also
Map of California State and its subdivision:- Alameda
- Alpine
- Amador
- Butte
- Calaveras
- Colusa
- Contra Costa
- Del Norte
- El Dorado
- Fresno
- Glenn
- Humboldt
- Imperial
- Inyo
- Kern
- Kings
- Lake
- Lassen
- Los Angeles
- Madera
- Marin
- Mariposa
- Mendocino
- Merced
- Modoc
- Mono
- Monterey
- Napa
- Nevada
- Orange
- Placer
- Plumas
- Riverside
- Sacramento
- San Benito
- San Bernardino
- San Diego
- San Francisco
- San Joaquin
- San Luis Obispo
- San Mateo
- Santa Barbara
- Santa Clara
- Santa Cruz
- Shasta
- Sierra
- Siskiyou
- Solano
- Sonoma
- Stanislaus
- Sutter
- Tehama
- Trinity
- Tulare
- Tuolumne
- Ventura
- Yolo
- Yuba
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming