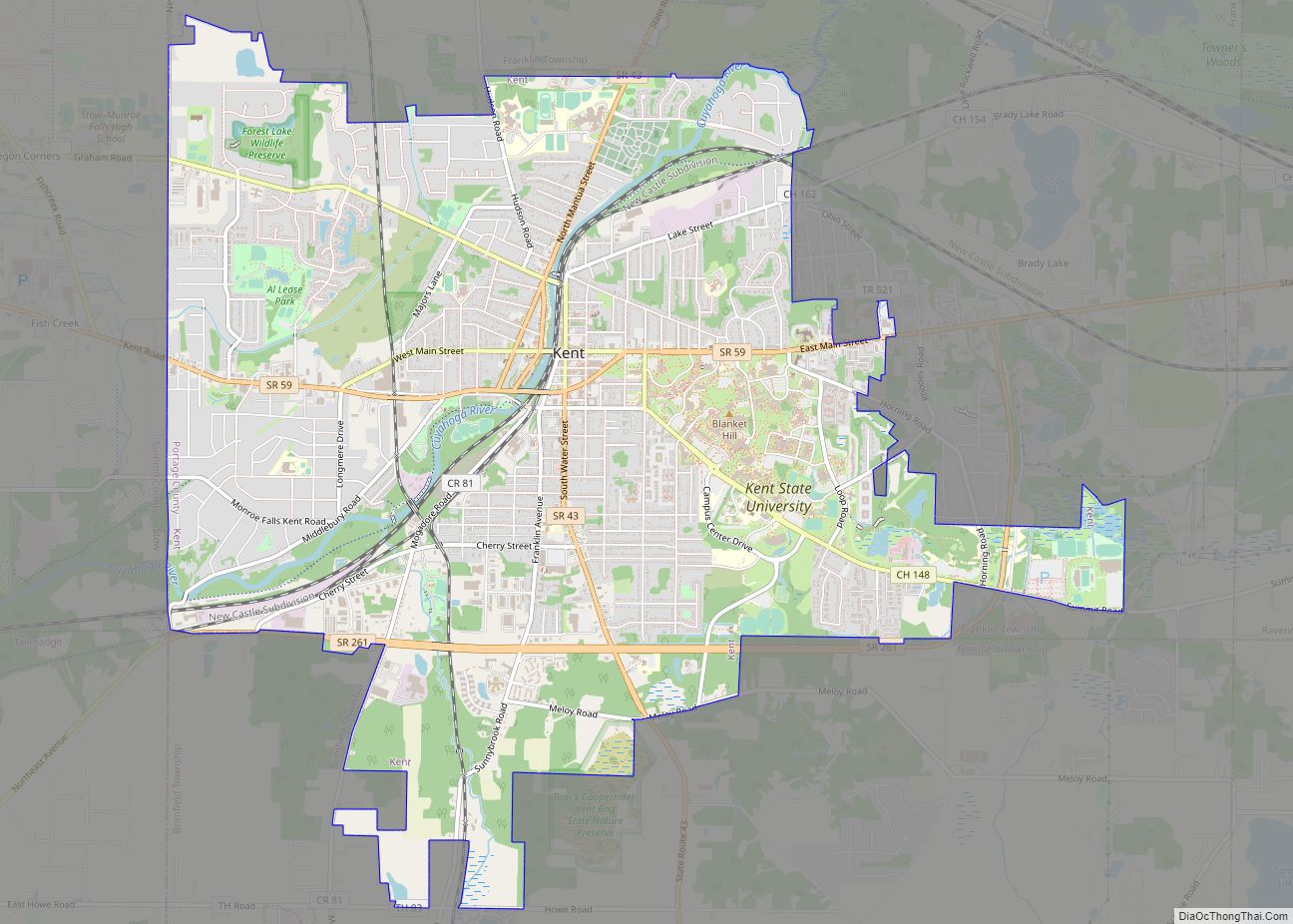
Kent is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the largest city in Portage County. It is located along the Cuyahoga River in Northeast Ohio on the western edge of the county. The population was 28,215 at the 2020 Census. The city is counted as part of the Akron metropolitan area and the larger Cleveland–Akron–Canton combined statistical area.
Part of the Connecticut Western Reserve, Kent was settled in 1805 and was known for many years as Franklin Mills. Settlers were attracted to the area due to its location along the Cuyahoga River as a place for water-powered mills. Later development came in the 1830s and 1840s as a result of the settlement’s position along the route of the Pennsylvania and Ohio Canal. Leading up to the American Civil War, Franklin Mills was noted for its activity in the Underground Railroad. With the decline of the canal and the emergence of the railroad, the town became the home of the Atlantic and Great Western Railroad maintenance shops through the influence of Marvin Kent. In 1864 the town was renamed Kent in honor of and in gratitude for Marvin Kent’s efforts. It was incorporated as a village in 1867 and became a city after the 1920 Census. Today Kent is a college town best known as the home of the main campus of Kent State University, founded in 1910, and as the site of the 1970 Kent State shootings.
Historically a manufacturing center, education is the city’s largest economic sector with Kent State University being the city’s, and one of the region’s, largest employers. The Kent City School District and the Kent Free Library provide additional education opportunities and resources. Many of Kent’s demographic elements are influenced by the presence of the university, particularly the median age, median income, and those living below the poverty level. The city is governed by a council-manager system with a city manager, a nine-member city council, and a mayor. Kent has nearly 20 parks and preserves and hosts a number of annual festivals including ones related to Earth Day, folk music, and the U.S. Independence Day. In addition to the Kent State athletic teams, the city also hosts a number of amateur and local sporting events at various times during the year. Kent is part of the Cleveland–Akron media market and is the city of license for three local radio stations and three television stations and includes the regional affiliates for National Public Radio (NPR) and the Public Broadcasting Service (PBS). Local transportation infrastructure includes a public bus service and hike-and-bike trails. As the home of the Davey Tree Expert Company, Kent is known as “The Tree City” while residents are referred to as “Kentites”. The city has produced a number of notable individuals, particularly in politics, athletics, and the entertainment industry.
| Name: | Kent city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Ohio |
| County: | Portage County |
| Founded: | November 1805 |
| Incorporated: | 1867 |
| Elevation: | 1,056 ft (322 m) |
| Total Area: | 9.33 sq mi (24.17 km²) |
| Land Area: | 9.22 sq mi (23.89 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.11 sq mi (0.28 km²) |
| Total Population: | 28,215 |
| Population Density: | 3,059.53/sq mi (1,181.23/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 44240, 44242, 44243 |
| Area code: | 330, 234 |
| FIPS code: | 3939872 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 2395512 |
| Website: | kentohio.org |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Kent location map. Where is Kent city?
History
The region was originally inhabited by various tribes of American Indians, including the early Mound Builders. Around 1780, Captain Samuel Brady achieved notoriety for his activities in the area, including his famous leap of 21 feet (6 m) over the Cuyahoga River to avoid capture by an unknown band of American Indians. The site, known as Brady’s Leap, is now a city park. Settlement by Europeans began in the late 1790s and early 19th century. As part of the Connecticut Western Reserve, the area was divided into survey townships in 1798 and almost all of what is now Kent was originally part of Town 3 Range 9, which would eventually be known as Franklin Township. Aaron Olmsted, a wealthy Connecticut merchant, had purchased the 16,000-acre (6,500 ha) township and named it for his son Aaron Franklin Olmsted.
Franklin Township was surveyed in 1803 and settled in November 1805 when John Haymaker and his family moved west from Warren to the banks of the Cuyahoga River. They were joined by John’s brother George and their father Jacob Haymaker and their families early the next year, and built a gristmill in 1807. Initial growth in the area was slow, but eventually two small villages would develop due to the potential for power generated by the Cuyahoga River that could be used in gristmills and manufacturing. The first village, known as Franklin Mills, or locally as the “Lower Village”, developed mostly around the original Haymaker property. In 1818, Joshua Woodard arrived in the area and began constructing buildings just north of the village forming the “Upper Village” that would come to be known briefly as Carthage.
In the 1820s, Franklin Mills was included in the route of the Pennsylvania and Ohio Canal (P & O Canal). When construction began on the canal in the mid-1830s, land speculation was rampant in many areas of northeast Ohio along the canal, including Franklin Mills. As a result, an industrial and business region was established along the east side of the river in what is now downtown Kent. Factories and mills were either planned or constructed along the Cuyahoga River, some of which either were never built or ultimately failed, due mostly to effects of the Panic of 1837. A lock and attached arch dam, however, was completed in 1836. The canal officially opened in 1840, but would only operate into the 1860s. By the 1870s the canal was completely shut down.
In the era leading up to the American Civil War, Franklin Mills was an active stop on the Underground Railroad, giving fugitive slaves shelter on their escape to Canada. There were three notable stops in Franklin Mills, one of which still stands as of 2010. During this period, from 1835 to 1839, noted American abolitionist John Brown moved to the village, operating a tannery along the Cuyahoga River with Zenas Kent.
In 1863 the Atlantic and Great Western Railroad was constructed through Franklin Mills, due largely to the efforts of local businessman Marvin Kent, son of Zenas Kent. Marvin Kent had started his own railroad company, the Franklin and Warren Railroad, in 1851 after Franklin Mills, already home to several Kent family ventures and properties, was bypassed by the Cleveland and Pittsburgh Railroad that same year. Kent was also successful in getting the village named as the location of the railroad’s maintenance yards and shops in 1864. The geographic location along the railroad and being home to the shops reinvented and revitalized the village as an important stop on the east–west line between St. Louis and New York City. The shops would open in 1865 and the railroad would play an important part of Kent’s industry and development through the early 20th century before the shops were completely shut down in 1930. To honor Marvin Kent, the village was renamed Kent in 1864, although this change was not official until the village was incorporated on May 6, 1867.
John Davey came to Kent in 1881 as head grounds keeper at Standing Rock Cemetery, and planted several trees, landscaped the cemetery, and performed experiments on trees. In 1901, he published his theories on tree surgery with his book The Tree Doctor, and later established the Davey Tree Expert Company in 1909. The efforts of Davey and the presence of Davey Tree led to the establishment of “The Tree City” as a nickname for Kent, which is reflected in the city’s seal. The company continues to be headquartered in Kent and serves as the city’s largest private employer.
After a fire destroyed the Seneca Chain Company in 1909, one of the city’s main industries at the time, city leaders created the Kent Board of Trade in 1910, a forerunner to the Chamber of Commerce. The new Board was successful later that year in having Kent selected out of twenty northeastern Ohio cities as the site of a new teacher training college, which became known as the “Kent State Normal School”. The site for the school was on 53 acres (21 ha) of land donated by William S. Kent, son of Marvin Kent, on what was then the eastern edge of town. By 1929 the school was renamed Kent State College after the establishment of a college of liberal arts and degrees in the arts and sciences and in 1935 was renamed Kent State University after it was given authorization to grant advanced graduate degrees. The bill giving Kent State university status was signed into law by Ohio governor and Kent native Martin L. Davey, son of tree surgeon John Davey. During the 1950s and 1960s the growth of Kent State University combined with the effects of suburbanization resulted in significant population growth for the city, rising from just over 12,000 residents at the 1950 census to over 28,000 by 1970. Black squirrels were brought to the campus from Canada in 1961 by Kent State University head groundskeeper Larry Woodell. The squirrels have become an icon for both KSU and the city and are often used as unofficial mascots and symbols.
In early May 1970, protests began on the campus of Kent State University over the United States’ invasion of Cambodia in the Vietnam War. These protests and demonstrations, which included rioting in downtown Kent on May 2, culminated in the Kent State shootings on May 4, 1970, where four students were killed and nine were wounded by the Ohio Army National Guard. Several memorials have been placed at the site over the years and commemorations have been held annually since 1971. In 2010 the entire site was listed on the National Register of Historic Places. Also during the late 1960s and into the 1970s, construction of Haymaker Parkway, completed in 1975, brought changes to the city’s layout while eliminating ongoing problems with traffic congestion and blocked rail crossings.
Kent received national attention in 1995 when the city’s water was named “Best Tasting Municipality Water” at the Berkeley Springs International Water Tasting. The water and mayor Kathleen Chandler were featured on the March 3 episode of The Tonight Show with Jay Leno. Since then, Kent has placed in the top five a total of six times with the most recent being a fifth-place finish in 2011. In 2003, the 1836 arch dam was bypassed to meet water quality standards set by the Ohio Environmental Protection Agency. To preserve the historic dam, a small park was built behind the dam and the river was rerouted through the old canal lock. During warm-weather months, water is pumped over the dam. The park, known as Heritage Park, was formally dedicated in May 2005.
From 1881 to 2016, downtown Kent was home to a flour mill, housed in a complex originally built from 1880 to 1881 by the Williams brothers and later acquired by the Star of the West Milling Company. The mill closed in 2016 after Star of the West consolidated operations to Willard, Ohio, and the complex was sold to a local developer in 2019. On the morning of December 2, 2022, part of the complex caught fire. In addition to the Kent Fire Department, 11 additional area fire departments and multiple other agencies responded. The fire destroyed part of the original 1881 mill building and the grain elevator, built in 1890, and damaged other parts of the complex. The adjacent taller white silos, built in 1936, were not damaged.
Redevelopment
Beginning in 2008, several redevelopment projects in the downtown area, some of which had been discussed for decades, were put into motion and resulted in nearly $110 million in total investment from public and private sources. The first of these was the Phoenix Project, a development privately financed by Kent resident Ron Burbick that renovated and expanded a section of commercial space along East Main Street. Included in the project was construction of a pedestrian alleyway lined with small shops, eventually known as Acorn Alley, which opened in 2009. A second phase of Acorn Alley opened in late 2011. Other aspects of the redevelopment, which include a 360-space parking deck and bus transfer station, a hotel and conference center, and three separate mixed-use buildings, began to take shape in 2010 following the demolition of several buildings in a four block area. New offices for Ametek and the Davey Tree Expert Company opened in late 2012 along with several new small businesses on the first floors of each building. The hotel, operated by Kent State University, opened in June 2013 and the new parking garage, operated by the Portage Area Regional Transportation Authority (PARTA) opened April 30, 2013, as the Kent Central Gateway. In addition to parking, the facility functions as PARTA’s main bus transfer station and has storefronts on the ground level facing East Erie Street. Included in the redevelopment was the purchase and renovation of the old Kent hotel, which first opened in 1920. After being mostly vacant since 1979 and completely vacant since 2000, it re-opened on April 1, 2013, as the new home to the Kent location of Buffalo Wild Wings and also houses offices, a wine and jazz bar, and apartments. A five-story mixed-use building called The Landmark was completed in 2014 and construction started in November 2015 on an additional five-story mixed-use building featuring microapartments, scheduled to be completed in 2016. The developments attracted the attention of The Plain Dealer and The New York Times and earned the city and university the 2013 Larry Abernathy Award from the International Town–Gown Association in recognition of the positive town–gown cooperation and collaboration.
Additional development has been ongoing on the campus of Kent State University and the largely residential neighborhood located between downtown Kent and the western edge of campus. The university began buying properties in that neighborhood in 2007 and by December 2012 had acquired 43. Construction of the University Esplanade extension, designed to link campus with downtown, started in August 2012 after several of the buildings in the area, most of which had been rental homes, were demolished or moved. The Esplanade extension continued a segment of the Portage Hike and Bike Trail that extends to Dix Stadium and was completed in October 2013. Kent State constructed a $48 million, 110,091 square feet (10,227.8 m) facility for the College of Architecture and Environmental Design along the Esplanade extension and also relocated the former home of May Prentice, the first female faculty member at Kent State, to the extension as the home for the Wick Poetry Center. Construction on the architecture building started in October 2014 and was completed in August 2016. In total, there are plans totaling approximately $150 million for several other facilities and upgrades across campus, including a new building for the College of Applied Engineering, Sustainability and Technology and a renovation and reorganization of the facilities for the School of Art. The city and county have also seen developments in the same area. A new county municipal courthouse on East Main Street was completed in April 2014, and in 2015, Kent City Council approved the sale of the city hall complex to a private developer for construction of a five-story apartment building on the site, which opened in August 2016.
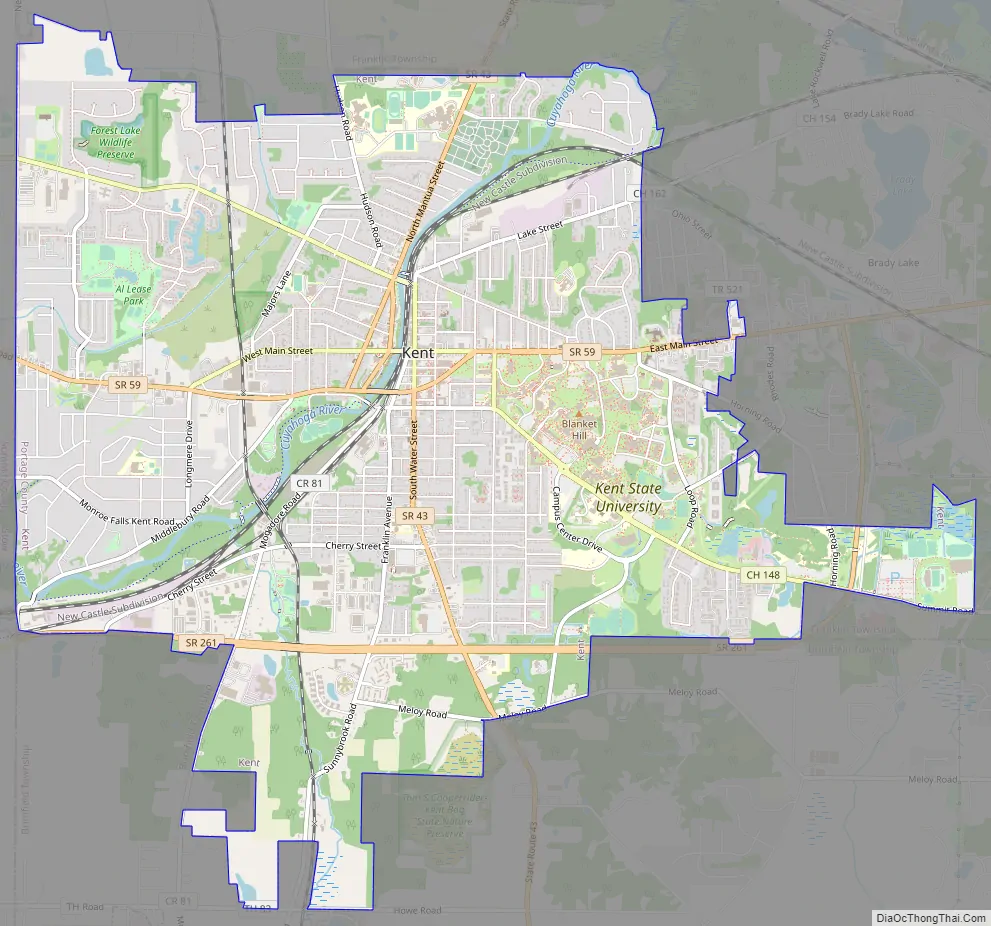
Kent Road Map
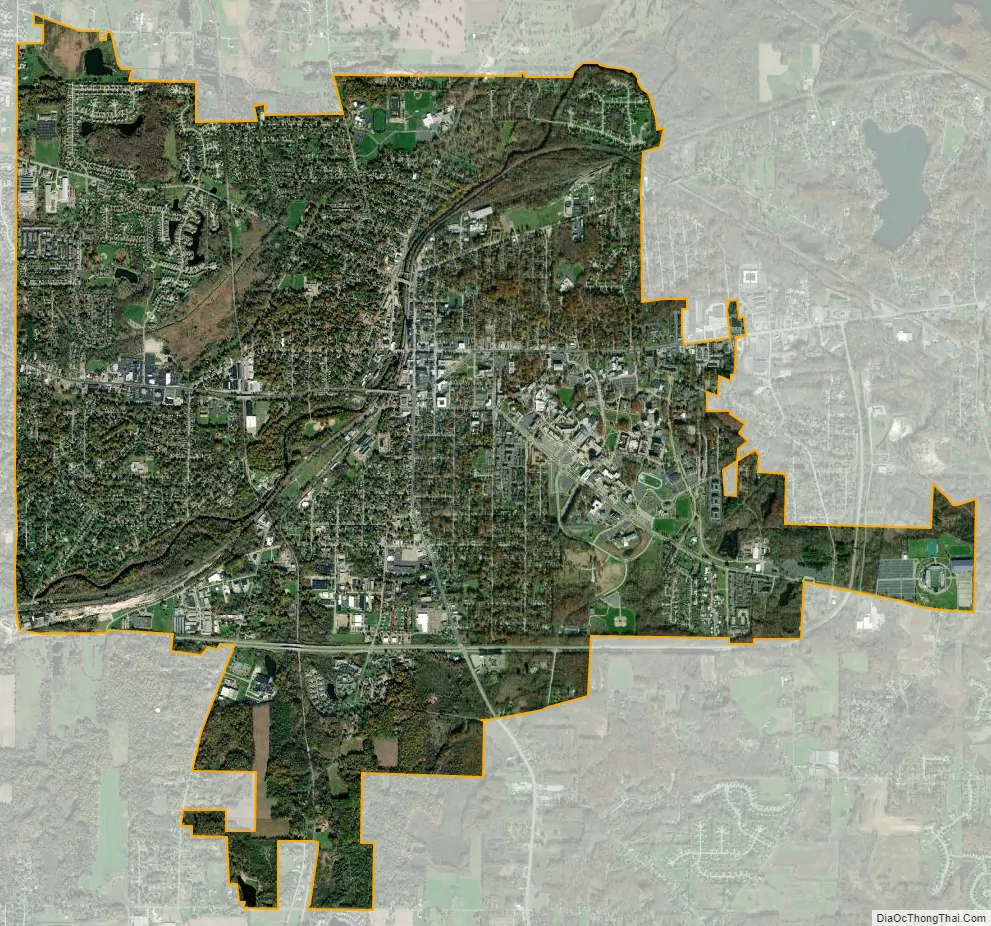
Kent city Satellite Map
Geography
Kent is located in west-central Portage County in Northeast Ohio approximately 10 miles (20 km) northeast of Akron and 30 miles (50 km) southeast of Cleveland. It is bordered by Franklin Township on the north and east, the unincorporated community of Brady Lake on the east, Brimfield Township on the south, and Stow on the west. Other nearby communities include Ravenna to the east and Sugar Bush Knolls and Streetsboro to the north. It is included in the Akron Metropolitan Statistical Area and the larger Cleveland–Akron–Canton Combined Statistical Area.
Located on the western end of the Glaciated Allegheny Plateau, the topography of Kent includes rolling hills and varied terrain. The Cuyahoga River passes through the city, cutting a gorge with a drop of nearly 40 feet (10 m) adjacent to the downtown area. The United States Geological Survey lists the city’s elevation at 1,056 feet (322 m) above sea level at a point near Kent’s geographic center. Elevations vary slightly within the city limits with several buildings on the Kent State University campus at altitudes in excess of 1,160 feet (350 m) and points as high as 1,200 feet (370 m). According to the United States Census Bureau, as of 2010 the city has a total area of 9.28 square miles (24.04 km), of which 9.17 square miles (23.75 km) is land and 0.11 square miles (0.28 km) is water.
Climate
Kent’s climate is classified as a humid continental climate in the Dfa Köppen climate classification meaning it typically has very warm, humid summers and cold, snowy winters with moderate and variable spring and autumn seasons. The record high temperature is 103 °F (39 °C), set on July 7, 1988, with the record low of −22 °F (−30 °C) recorded January 17, 1982. During the spring and summer months, thunderstorms are fairly common and the area is susceptible to tornadoes, though the last recorded tornado in Kent occurred in 1973. Effects from tropical systems can also be felt, usually taking the form of increased humidity, rain, and wind, such as with the remnants of Hurricane Ike in September 2008. During the winter months, snowfall is common and can occur in large quantities with considerable cloud cover. Kent is not considered part of the Lake Erie snowbelt, though lake-effect snow does occur at times. The city is in what is referred to as the “secondary snowbelt”, meaning it will receive heavier snowfall totals from lake-effect snow when certain wind directions are more prevalent, but typically sees far less snowfall than areas to the north closer to Lake Erie. While temperatures below the freezing point are typical in the winter months, thaw periods where temperatures exceed 50 °F (10 °C) and even 60 °F (16 °C) are not uncommon in January and February.
See also
Map of Ohio State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Allen
- Ashland
- Ashtabula
- Athens
- Auglaize
- Belmont
- Brown
- Butler
- Carroll
- Champaign
- Clark
- Clermont
- Clinton
- Columbiana
- Coshocton
- Crawford
- Cuyahoga
- Darke
- Defiance
- Delaware
- Erie
- Fairfield
- Fayette
- Franklin
- Fulton
- Gallia
- Geauga
- Greene
- Guernsey
- Hamilton
- Hancock
- Hardin
- Harrison
- Henry
- Highland
- Hocking
- Holmes
- Huron
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Knox
- Lake
- Lake Erie
- Lawrence
- Licking
- Logan
- Lorain
- Lucas
- Madison
- Mahoning
- Marion
- Medina
- Meigs
- Mercer
- Miami
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Morgan
- Morrow
- Muskingum
- Noble
- Ottawa
- Paulding
- Perry
- Pickaway
- Pike
- Portage
- Preble
- Putnam
- Richland
- Ross
- Sandusky
- Scioto
- Seneca
- Shelby
- Stark
- Summit
- Trumbull
- Tuscarawas
- Union
- Van Wert
- Vinton
- Warren
- Washington
- Wayne
- Williams
- Wood
- Wyandot
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming