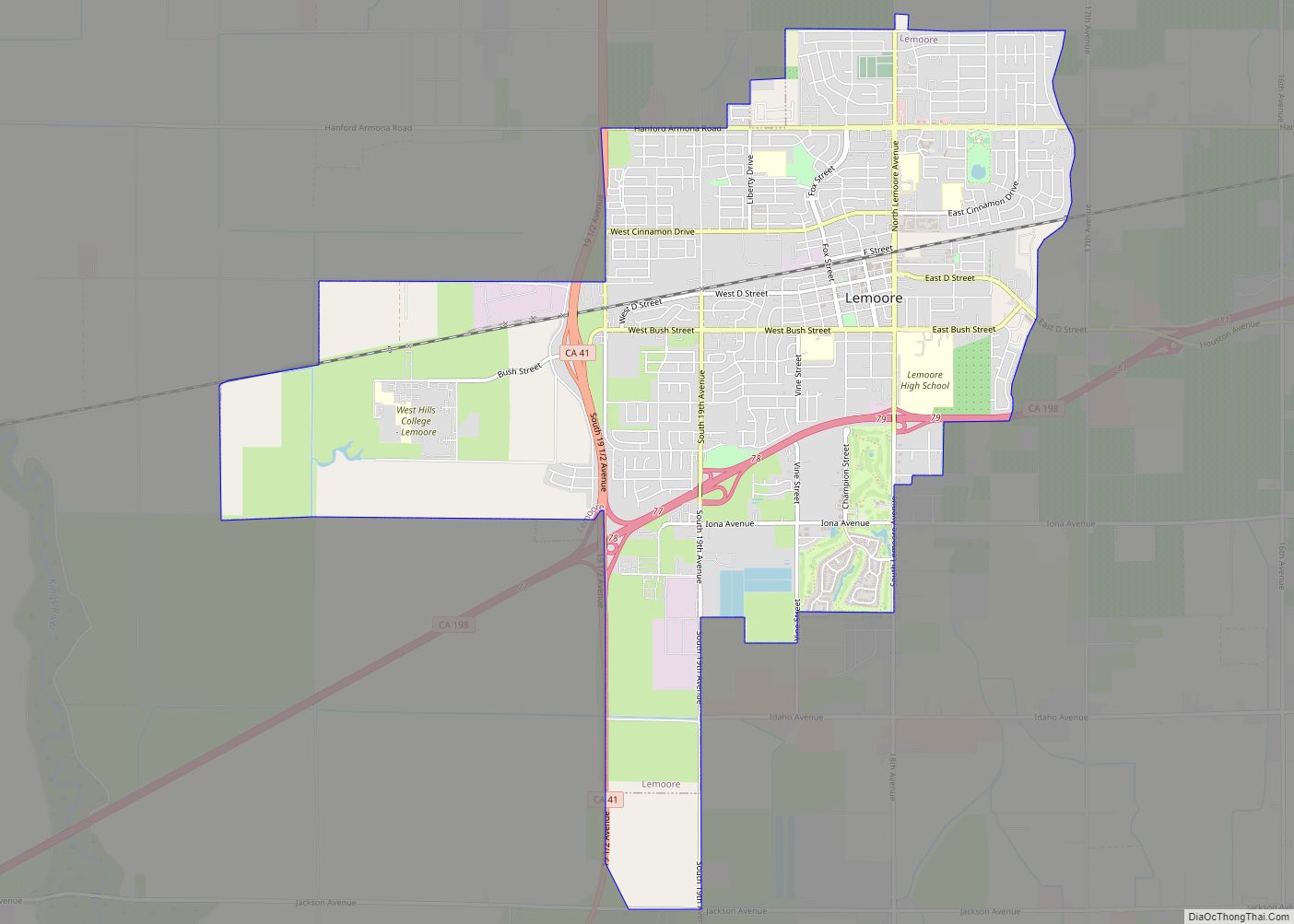
Lemoore (formerly, La Tache and Lee Moore’s) is a city in Kings County, California, United States. Lemoore is located 7.5 miles (12 km) west-southwest of Hanford, at an elevation of 230 feet (70 m). It is part of the Hanford-Corcoran Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA Code 25260). The population was 24,531 at the 2010 Census. The California Department of Finance estimated that Lemoore’s population was 26,725 on July 1, 2019.
Lemoore is home to Naval Air Station Lemoore, a master jet base housing F-18 and F-35 squadrons assigned to the Pacific fleet.
| Name: | Lemoore city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | California |
| County: | Kings County |
| Incorporated: | July 4, 1900 |
| Elevation: | 230 ft (70 m) |
| Total Area: | 8.81 sq mi (22.83 km²) |
| Land Area: | 8.81 sq mi (22.83 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km²) 0% |
| Total Population: | 24,531 |
| Population Density: | 3,032.11/sq mi (1,170.67/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 93245, 93246 |
| Area code: | 559 |
| FIPS code: | 0641152 |
| Website: | www.lemoore.com |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Lemoore location map. Where is Lemoore city?
History
Dr. Lovern Lee Moore first made his home in what was western Tulare County, California—now the City of Lemoore—in April, 1871. It was on the northern shoreline (just above the high-water mark) of Tulare Lake, then potentially the largest freshwater body of water in the US, outside of the Great Lakes. The American pioneers from eastern states saw this as a stretch of vast virgin land on which sheep, horses and wild animals had grazed but had never been cultivated.
By the time Dr. Moore arrived, scores of individual farms dotted the landscape, but as Tulare Lake retreated, more became continually available. The soil was rich and productive as it had been brought down and deposited for centuries from the high Sierras by the Kings River and the Los Gatos Creek alluvial fan from the Coast Range. Wells were easy to dig, as the water level was unusually high. So water was plentiful for irrigation from shallow wells farm families installed. Raising of sheep and grains were principal concerns of farmers in the area.
However, the pioneers were somewhat isolated, since they had to drive by horse as far as 6 miles (9.7 km) northeast to Grangeville settlement, to get mail or newspapers. It was even farther to Kingston for other supplies. Hanford was not founded until later in 1877. Even the area was called by various names, believed to be of Indian origin, such as Latache, Tailholt, or just, in English, the Lake District.
Dr. Lee Moore proved to be a man of vision. He decided to knit together the scores of surrounding farm families, to secure a post office, and some local center for conducting business which could be hastened by direct means of communicating with the outside world. He must also have had the hope of attracting the railroad, which was then being planned but was not built until six years later.
The first steps he took to organize a community began in early 1872, when he surveyed a 10-acre (40,000 m) subdivision in what is now the land immediately west of the present Lemoore High School. In August 1872 he had established the first real estate development in this district and had laid out and named the streets after other pioneer families. In the summer of 1872 land auctions were held and lots went to the highest bidder. Prices ranged from $75 to $150 per lot. One business lot was sold for $600, rated as a very high price, considering the value of the dollar in 1872. Dr. Moore’s home was believed to be situated where the grammar school playground on Bush Street is now located.
The year 1872 was a busy one for the inhabitants. In addition to sales at the subdivision and putting in of streets, new buildings for homes and businesses began to arise. This was the start of a real community, but it still lacked a school, a definitely accepted name, and a post office.
All these developed in the next eventful year of 1873. Dr. Moore had presented a signed petition to the U.S. Post Office Department in distant Washington for a post office in the new town in 1872, but his petition was not granted until 1873.
At that time it was common custom to name communities after their founders or some prominent person of the day. The naming of Hanford and Porterville are examples of this common practice.
The Lemoore post office first opened in 1875.
For some reason the U.S. Post Office objected to the name “Latache,” so, by about the 1920s it combined the founder’s name by omitting one letter “e”,from Lee and called the new post office Lemoore after Lee Moore. In that way the new community received its new name.
In the same year, 1873, a Mr. Armstrong donated 2 acres (8,100 m) of land for the first school building in Lemoore. It was a frame structure 18 feet (5.5 m) by 30 feet (9.1 m), completed and dedicated at a country dance held in December 1873.
The railroad came to what is now Kings County in 1877. At that date Grangeville was the largest community in the entire area. After some dispute with its residents, rail officials decided to by-pass that settlement and went through Hanford. Lemoore, by that time had shown healthy growth. It could have been through the foresight of Dr. Moore in setting a head-start in ’72 which attracted the rail route to his budding community. The line was put through Lemoore in 1877 parallel to Front Street, now called E Street.
This re-directed the business growth of the town toward the railroad station from where Dr. Moore first encouraged residence and business activity. It eventually made E (Front Street) and D Streets the main business avenues of the community.
After 25 years of service to the Lemoore area, Dr. Lee Moore died on September 11, 1898. The number of new residents he had helped bring into the world numbered in the thousands.
In 1883 the town then had a flouring mill of 200 barrels daily capacity. It was an important shipping point for wheat and wool, and not long afterwards became a center for fruit, but in its early period many fires retarded its growth.
Many of the early settlers of the Lemoore District were cultured people, and Lemoore attained a reputation for literary and musical accomplishments unmatched by many pioneer towns. There was an early literary society that had a long and noteworthy existence.
In 1893 Tulare County, by act of the State Legislature, was split into two areas. Western Tulare County became what is now Kings County. In creating the new County of Kings there was keen competition between Hanford and Lemoore as to which would become the county seat. By that time Hanford’s population had exceeded Lemoore’s and the addition of the Santa Fe Railroad’s main line through Hanford gave it the advantage of two rail lines instead of one. The result was the construction of the County Courthouse in that city.
Lemoore became an incorporated city on 4 July 1900, which opened a new era for the community, with government by an elected City Council. Lemoore residents have always taken a keen interest in local political activities.
Bob E. Baldock designed and opened for play in 1928 a 9-hole golf course. The City of Lemoore had it remodeled in 1991, by Bill Phillips to add to the community an exciting 18-hole golf course.
Military
In 1941, the Lemoore Army Air Field opened as an Army Air Forces training field. The Federal Government acquired 1,466 acres (593 ha) for the Lemoore Basic Flying School in 1941–42. Approximately 488 acres (197 ha) were acquired by grant deed from individual land owners, 963 acres (390 ha) were leased from the City of Lemoore and 14 acres (5.7 ha) were acquired by transfer from the National Housing Agency. In 1961, The Army Air Field was converted into what is now Naval Air Station Lemoore, a Naval Aviation base 7 miles west of Lemoore. Since 1961, The base has grown to become the largest Master Jet Base in the Navy. NAS Lemoore hosts five carrier air wings, mostly made up of F-18s and F-35 jets.
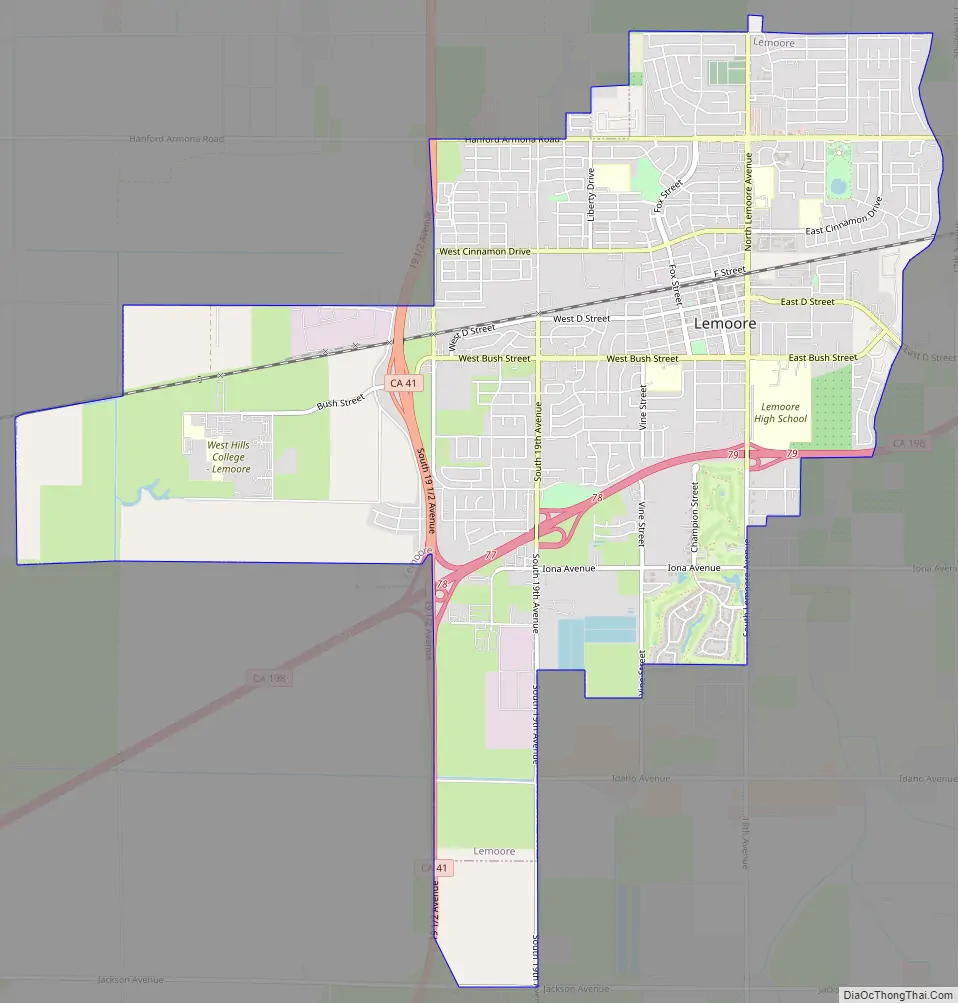
Lemoore Road Map
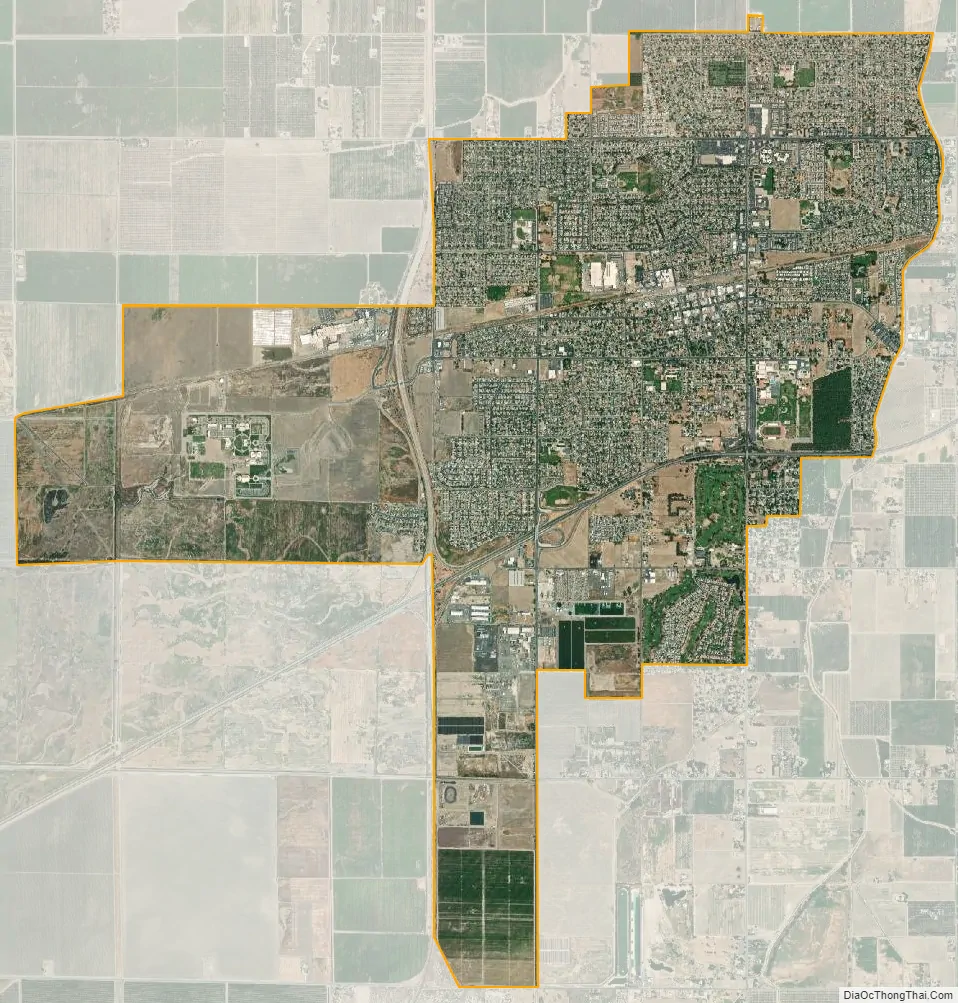
Lemoore city Satellite Map
Geography
The maps published by Thos. H. Thompson in 1892, shows three high water levels of the giant Tulare Lake in different years. The highest lake level, the one Thompson labeled “original lake line” skirts or touches the 1892 town of Lemoore’s south-west corner at the current intersection of State Route 41 and State Route 198. On Thompson’s map, Lemoore is on the east bank, and about five miles away Lemoore Naval Air Station would have been on the west bank of the pointy northern tip of Tulare Lake at its maximum size. At the extreme northern point of Tulare Lake was its natural, occasional “flood year” spillway northbound into Bogg Slough, Fresno Slough, and the San Joaquin River’s watershed, onward to the sea at San Francisco Bay. The present (2014) remaining marshy remnants of Bogg Slough, with its unfarmed oxbow structures may be the last of their kind to avoid the plow in the Kings-San Joaquin river system. This “summit,” or spillway is located just a few miles north-west of Lemoore, off Grangeville Blvd at elevation 210 feet (64 m). The spillway was wide, shallow and confusing, choked with tall tule rushes, and without observable landmarks. Only one commercial boat is known to have sailed from Tulare Lake to the San Francisco delta. Tulare Lake had huge economic importance in the region, both for the very large population of Indians, and the white pioneers. The lake supported a large commercial fishery feeding San Francisco, and a steam powered ferry servicing several towns and settlements. The receding lake continually opened up new agricultural lands for settlement. Because of its source streams being diverted, the last time the lake overflowed was 1878, and today it no longer exists.
Because the natural summit or border between the Kings River basin and the San Joaquin River’s watershed, and the Kings River itself nearly intersect near Lemoore, a number of huge water works that control regional water flow are also located nearby. For example, in flood years the Kings River is diverted west into the so-called “North Fork Kings River,” to Crescent Weir and related major levees eastward to the north-flowing Fresno Slough and to the sea, preventing a resurgence (“flooding”) of Tulare Lake to the south. This “switch point” is located just north of Lemoore right off of Highway 41 and Elgin Ave at the New Island Weirs. In many cases the prehistoric Kings River bed has been obliterated and new channels have been constructed. However, as of 2014, in satellite images (such as Google maps, etc.) the remains of many of the old channels can still be detected.
Other towns built just above the Tulare Lake high-water shoreline include Kettleman City and Alpaugh (once also called Hog Island, Root Island, and Atwell’s Island). Satellite maps indicate that highways, railroads, and property lines are aligned with the historic lake shores. Also, many of the farms can be seen to be much larger within its various historic shore lines than in the surrounding areas.
Climate
According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Lemoore has a semi-arid climate, abbreviated “BSk” on climate maps.
See also
Map of California State and its subdivision:- Alameda
- Alpine
- Amador
- Butte
- Calaveras
- Colusa
- Contra Costa
- Del Norte
- El Dorado
- Fresno
- Glenn
- Humboldt
- Imperial
- Inyo
- Kern
- Kings
- Lake
- Lassen
- Los Angeles
- Madera
- Marin
- Mariposa
- Mendocino
- Merced
- Modoc
- Mono
- Monterey
- Napa
- Nevada
- Orange
- Placer
- Plumas
- Riverside
- Sacramento
- San Benito
- San Bernardino
- San Diego
- San Francisco
- San Joaquin
- San Luis Obispo
- San Mateo
- Santa Barbara
- Santa Clara
- Santa Cruz
- Shasta
- Sierra
- Siskiyou
- Solano
- Sonoma
- Stanislaus
- Sutter
- Tehama
- Trinity
- Tulare
- Tuolumne
- Ventura
- Yolo
- Yuba
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming