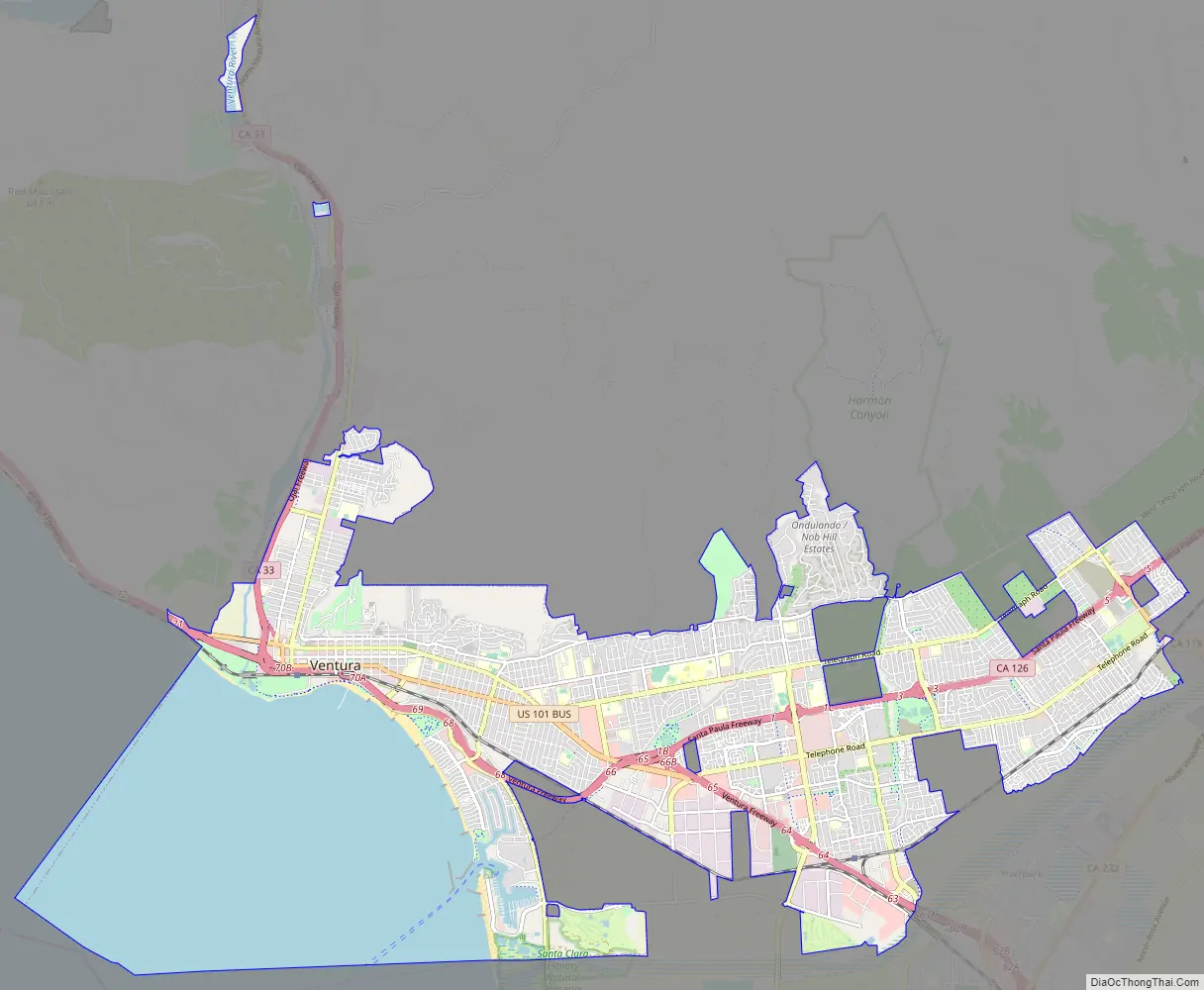
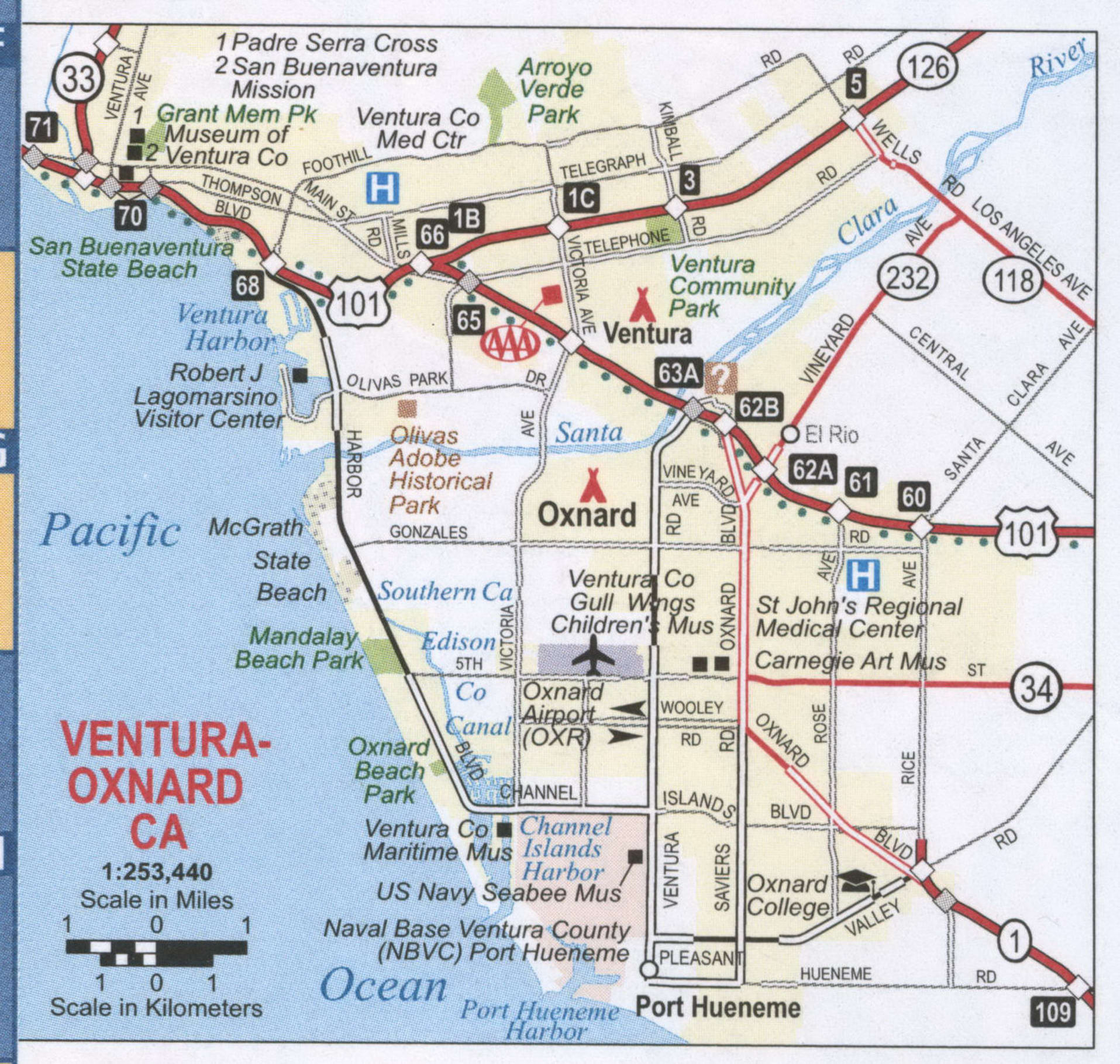
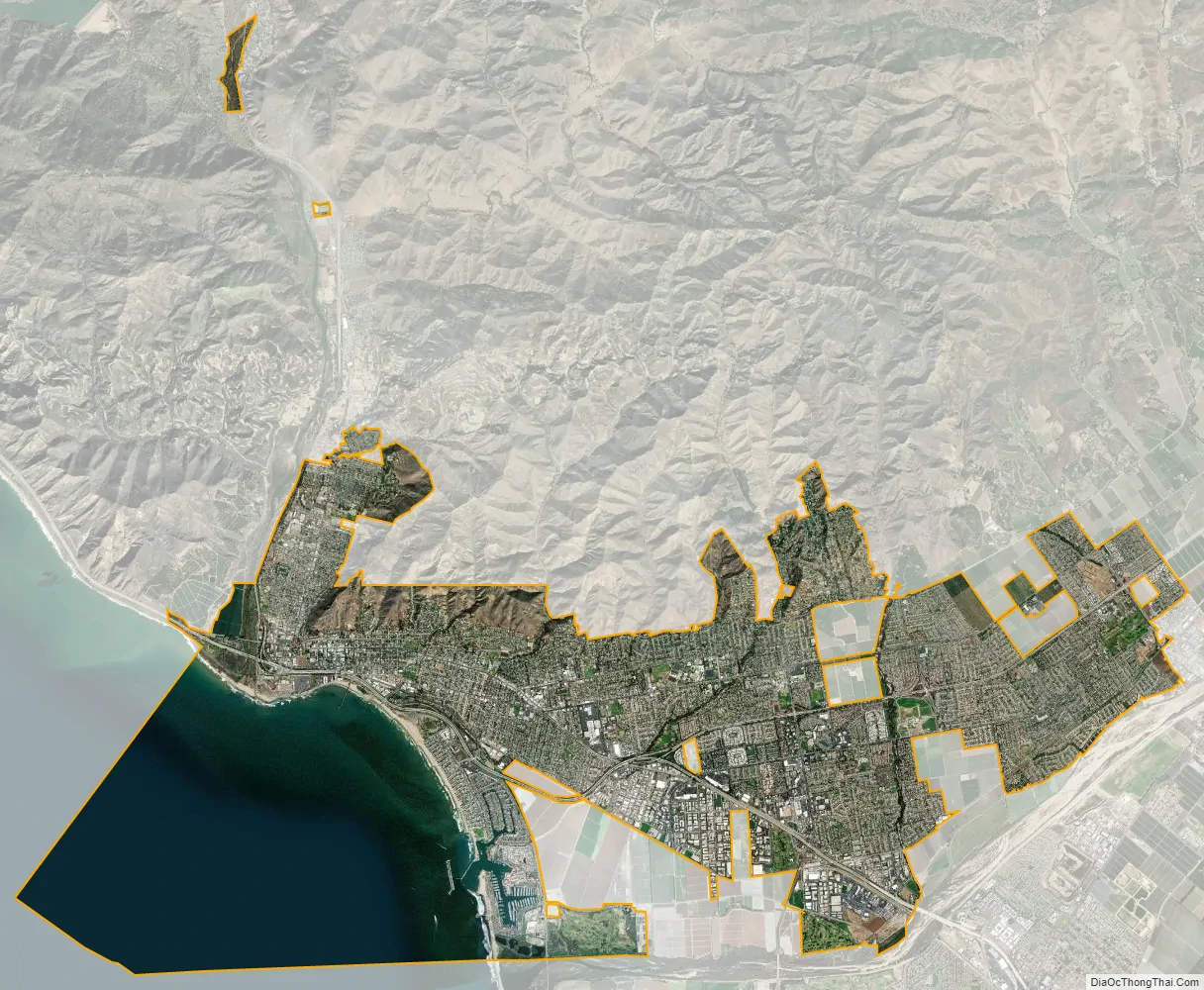
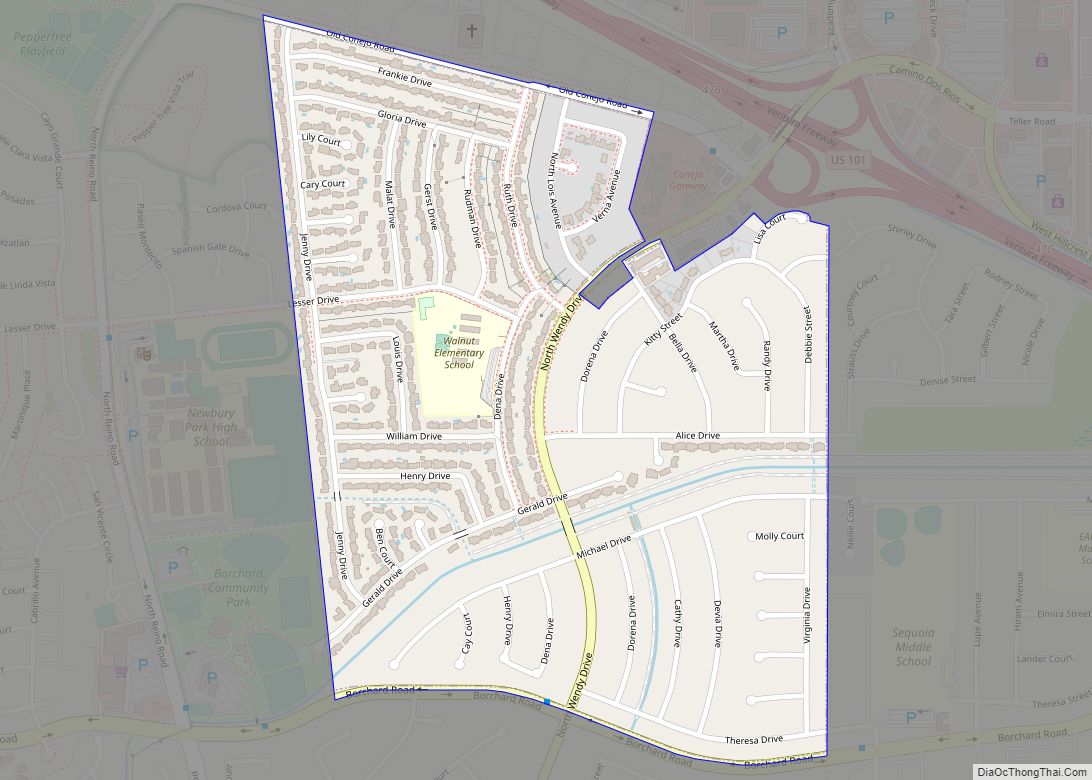
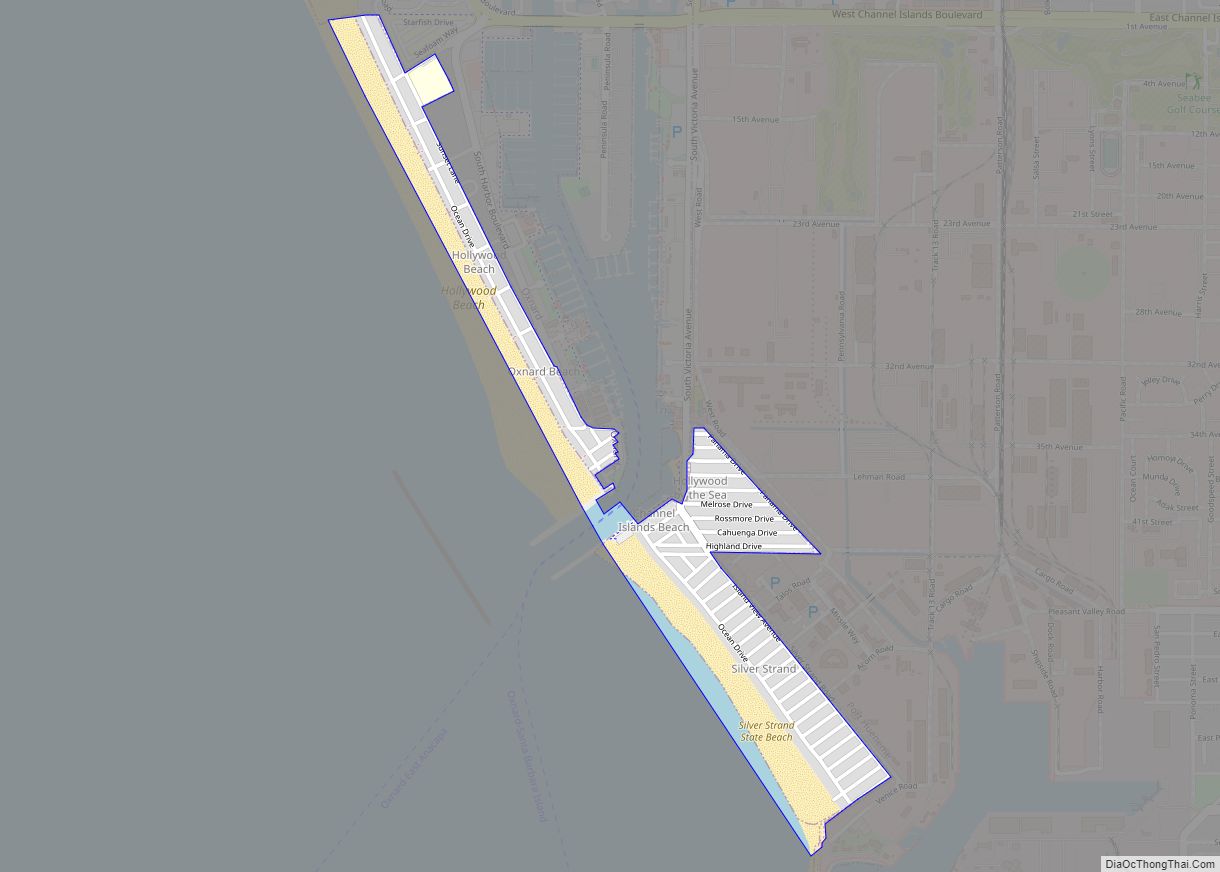
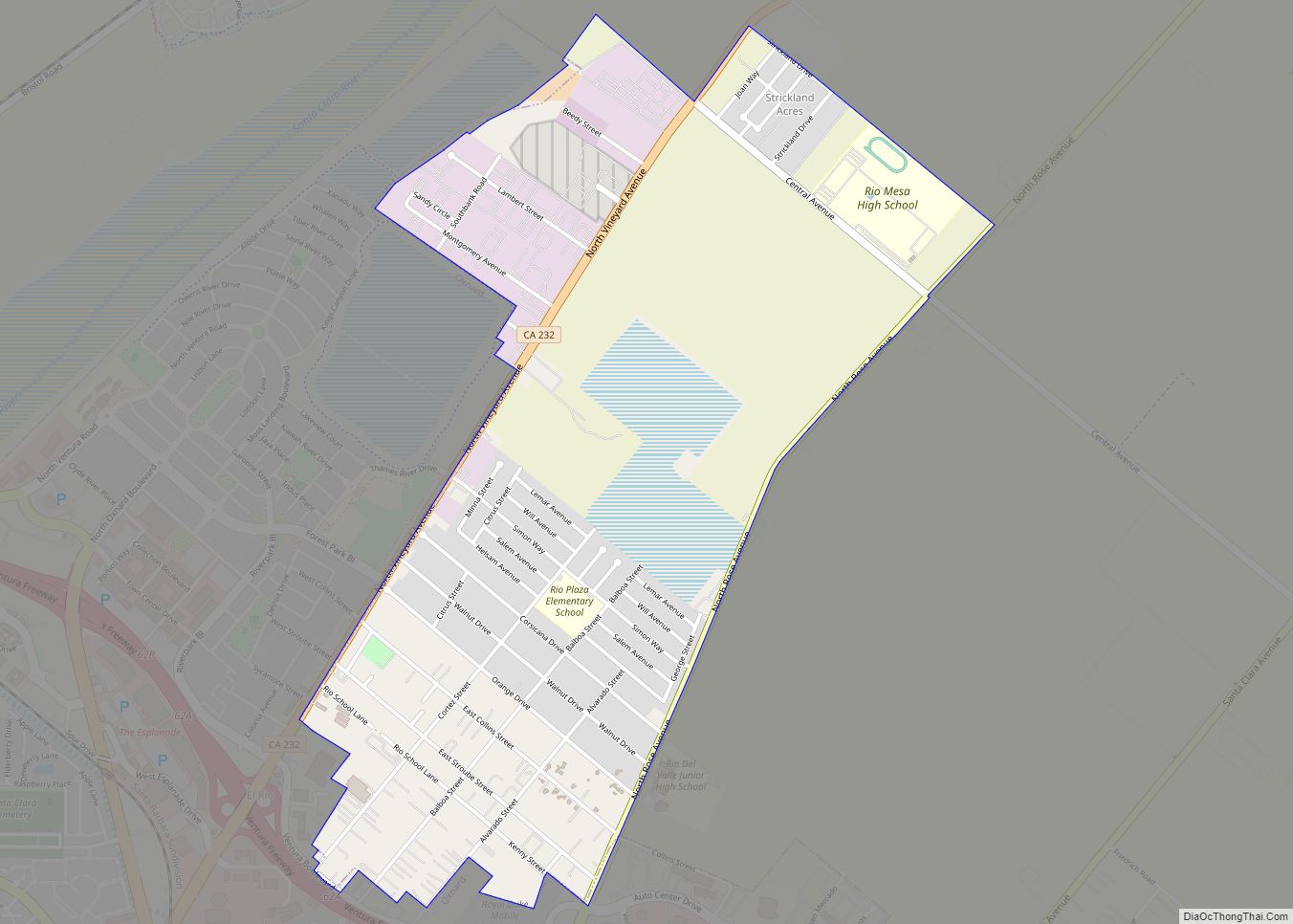
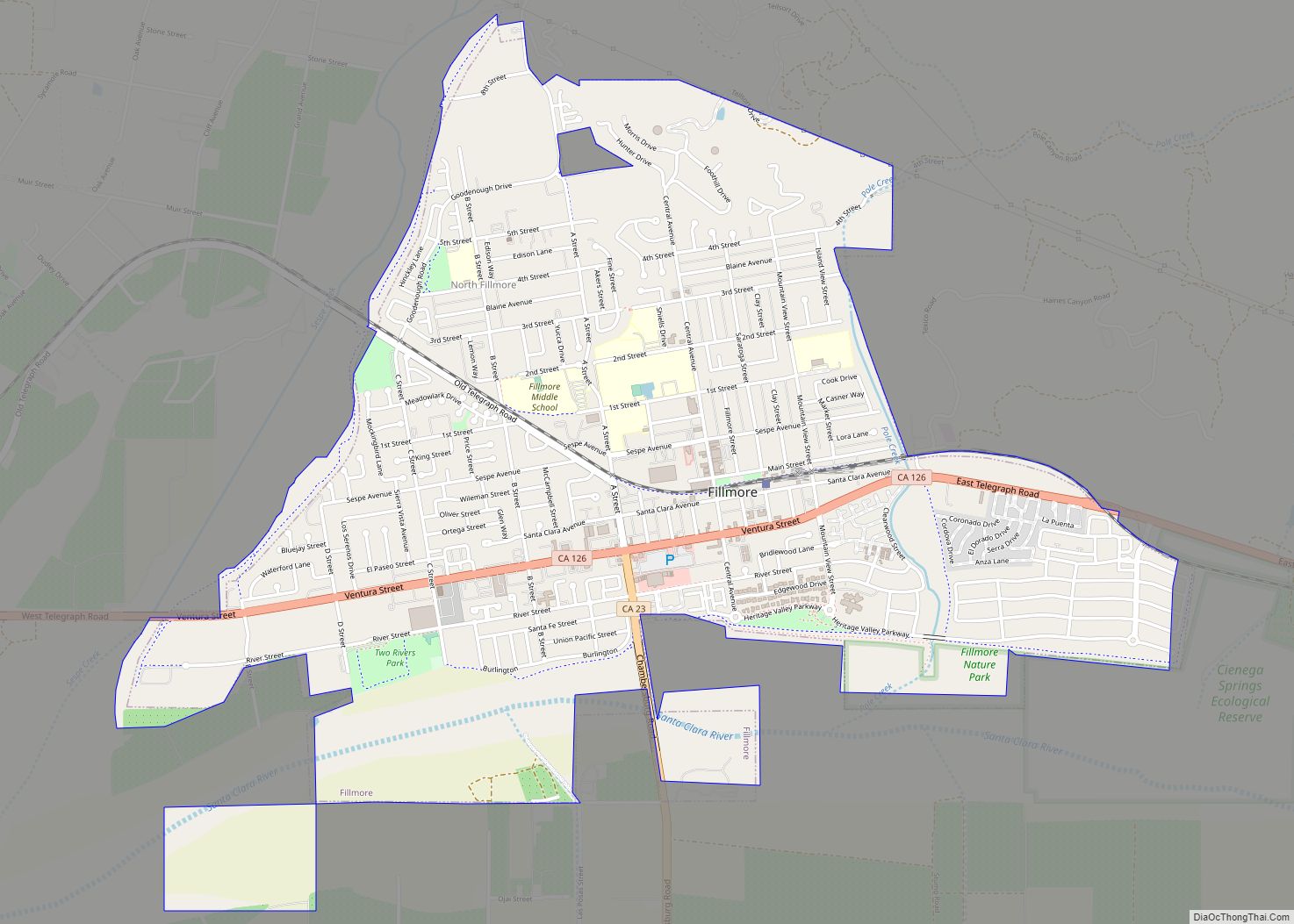
Ventura, officially named San Buenaventura (Spanish for “Saint Bonaventure”), is a city in and the county seat of Ventura County, California, United States. The population was 110,763 at the 2020 census. Ventura is a popular tourist destination, owing to its historic landmarks, beaches, and resorts.
Ventura has been inhabited by different peoples, including the Chumash Native Americans, for at least 10,000 years. With the arrival of Spanish missionaries in 1782, Mission San Buenaventura was established by Junípero Serra, giving the city its name. Following the Mexican secularization of the Californian missions, San Buenaventura was granted by Governor Pío Pico to Don José de Arnaz as Rancho Ex-Mission San Buenaventura and a small community arose. Following the American Conquest of California, San Buenaventura eventually incorporated as a city in 1866. The 1920s brought a major oil boom, which along with the post–World War II economic expansion, significantly developed and expanded Ventura.
| Name: | San Buenaventura (Ventura) city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | California |
| County: | Ventura County |
| Incorporated: | April 2, 1866 |
| Elevation: | 36 ft (11 m) |
| Total Area: | 32.29 sq mi (83.63 km²) |
| Land Area: | 21.89 sq mi (56.68 km²) |
| Water Area: | 10.41 sq mi (26.95 km²) 32.53% |
| Total Population: | 110,763 |
| Population Density: | 3,400/sq mi (1,300/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 93001–93007, 93009 |
| Area code: | 805 |
| FIPS code: | 0665042 |
| Website: | www.cityofventura.ca.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
History
Chumash
Archaeological discoveries in the area suggest that humans have populated the region for at least 10,000–12,000 years. Archaeological research demonstrates that the Chumash people have deep roots in central and southern coastal regions of California, and has revealed artifacts from their culture. Shisholop Village, designated Historic Point of Interest #18 by the city at the foot of nearby Figueroa Street, was the site of a Chumash village. They had keen oceanic navigational skills made use of the abundant local resources from sea and land. The Ventura Chumash were in contact with the Channel Islands Chumash; both mainland and island Chumash utilized large plank-sewn seagoing canoes, called Tomol, with the island people bringing shell bead money, island chert, and sea otter pelts to trade for mainland products like acorns and deer meat.
Spanish era
In 1769, the Spanish Portolà expedition, first recorded European visitors to inland areas of California, came down the Santa Clara River Valley from the previous night’s encampment near today’s Saticoy and camped near the outlet of the Ventura River on August 14. Fray Juan Crespi, a Franciscan missionary traveling with the expedition, noted that “we saw a regular town, the most populous and best laid-out of all that we had seen on the journey up to the present time.” Archaeological records found that the Chumash village they encountered was settled sometime around A.D. 1000. Junípero Serra, first leader of the Franciscans in California, founded Mission San Buenaventura in 1782 as his ninth and last mission established near the Chumash village as part of Spain’s colonization of Alta California. The mission was named for St. Bonaventure, a Thirteenth Century Franciscan saint and a Doctor of the Church. San Miguel Chapel was the first outpost and center of operations while the first Mission San Buenaventura was being constructed. The first mission burned in 1801 and a replacement building of brick and stone was completed in 1809. The bell tower and facade of the new mission was destroyed by an 1812 earthquake. The Mission was rebuilt and functions as a parish church.
Mexican era
The Mexican secularization act of 1833 was passed twelve years after Mexico won independence from Spain in 1821. Mission land was sold or given away in large grants called ranchos. Rancho Ex-Mission San Buenaventura was a 48,823-acre (197.58 km) grant that included downtown Ventura. The Battle of San Buenaventura was fought in 1838 between competing armies from northern and southern California. Governor Juan Bautista Alvarado granted Rancho San Miguel to Felipe Lorenzana and Raymundo Olivas, whose Olivas Adobe on the banks of the Santa Clara River was the most magnificent hacienda south of Monterey. Fernando Tico also received a Mexican land grant for Ojai and a parcel near the river in downtown Ventura.
American era
Following the American Conquest of California in the Mexican–American War, California became a U.S. territory in 1848 and a U.S. state in 1850. After the American Civil War, settlers came to the area, buying land from the Mexicans, or simply as squatters. Vast holdings were later acquired by Easterners, including railroad magnate Thomas A. Scott. He sent Thomas R. Bard to handle Scott’s property.
Ventura had a flourishing Chinese settlement in the early 1880s. The largest concentration of activity, known as China Alley, was just across Main Street from the Mission San Buenaventura.
Ventura Pier was built in 1872 at a cost of $45,000 and was the longest wooden pier in California. By 1917, it had been rebuilt to a length of 1,700 feet (520 m). Much of the pier was destroyed by a storm in 1995, but it was subsequently rebuilt.
In 1913, the Rincon Sea Level Road and the Ventura River Bridge opened.
The large Ventura Oil Field was first drilled in 1919 and at its peak produced 90,000 barrels per day (14,000 m/d). The development of the oil fields in the 1920s, along with the building of better roads to Los Angeles and the affordability of automobiles, enabled a major real estate boom. Contemporary downtown Ventura is defined by extant buildings from this period. Landmarks built during the oil boom include Ventura Theatre (1928), the First Baptist Church of Ventura (1926), the Ventura Hotel (1926), and the Mission Theatre (1928).
On March 12, 1928, the St. Francis Dam, 54 miles (87 km) inland, failed catastrophically, creating a flood that took over 600 lives as it flowed down the Santa Clara River to the ocean.
From the south, travel by auto was slow and hazardous, until the completion of a four-lane freeway (US Highway 101) over the Conejo Grade in 1959. This route, which was widened and improved by 1969, is known as the Ventura Freeway, which directly links Ventura with the rest of the Greater Los Angeles.
In 2017, the Thomas Fire started north of Ventura in Santa Paula and the Santa Ana Winds the fire spread into hillside neighborhoods of Ventura and into the area above downtown. Five hundred and four residences burned down in the city.
Geography
Ventura is located northwest of Los Angeles on the California coast. The western portion of the city stretches north along the Ventura River which is characterized by a narrow valley with steeply sloped areas along both sides. The steep slopes of the Ventura foothills abut the northern portion of the community. Much of the eastern portion is on a relatively flat alluvial coastal plain lying along the western edge of the Oxnard Plain. Several Barrancas extend from the foothills to the Santa Clara River which forms the city’s southerly boundary. The city extends up to the beginning of the Santa Clara River Valley at the historic community of Saticoy.
Ventura is within a seismically active region like much of California and is crossed by several potentially active fault systems. The Ventura Fault is capable of an 8.0 earthquake and a local tsunami up to 23 feet in height. According to the United States Census Bureau, Ventura has a total area of 32.1 square miles (83 km), of which 21.7 square miles (56 km) is land and 10.4 square miles (27 km), comprising 32.53%, is water.
Climate
Ventura has a Mediterranean climate, typical of most coastal California cities, with the sea breeze off the Pacific Ocean moderating temperatures. It is not uncommon for the city to be affected by Santa Ana winds off the Transverse Ranges on occasion, which increase temperatures dramatically.
See also
Map of California State and its subdivision:- Alameda
- Alpine
- Amador
- Butte
- Calaveras
- Colusa
- Contra Costa
- Del Norte
- El Dorado
- Fresno
- Glenn
- Humboldt
- Imperial
- Inyo
- Kern
- Kings
- Lake
- Lassen
- Los Angeles
- Madera
- Marin
- Mariposa
- Mendocino
- Merced
- Modoc
- Mono
- Monterey
- Napa
- Nevada
- Orange
- Placer
- Plumas
- Riverside
- Sacramento
- San Benito
- San Bernardino
- San Diego
- San Francisco
- San Joaquin
- San Luis Obispo
- San Mateo
- Santa Barbara
- Santa Clara
- Santa Cruz
- Shasta
- Sierra
- Siskiyou
- Solano
- Sonoma
- Stanislaus
- Sutter
- Tehama
- Trinity
- Tulare
- Tuolumne
- Ventura
- Yolo
- Yuba
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming