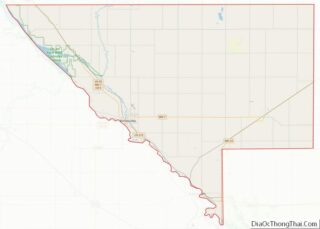
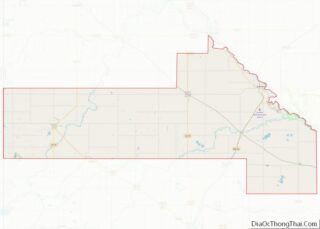
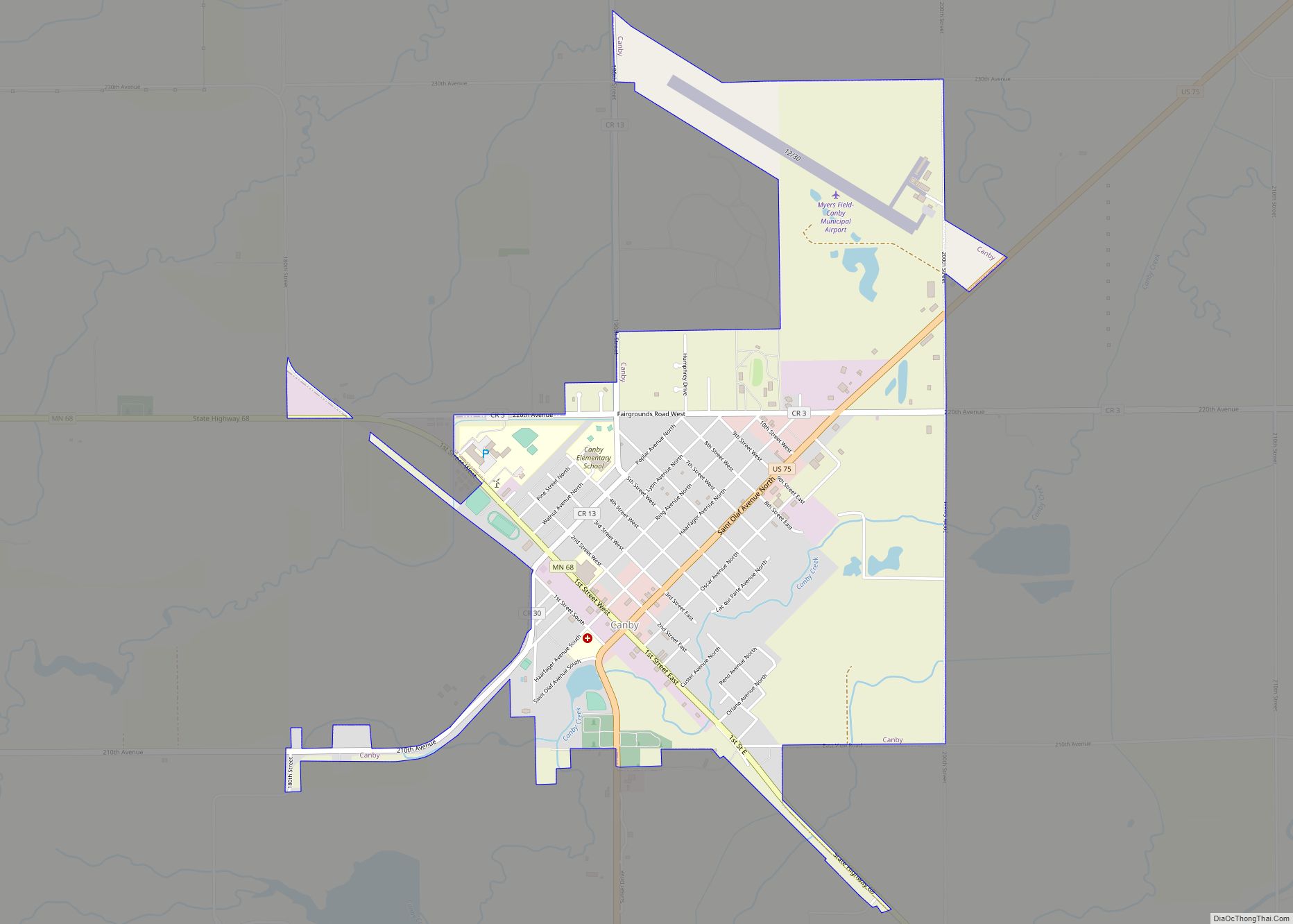
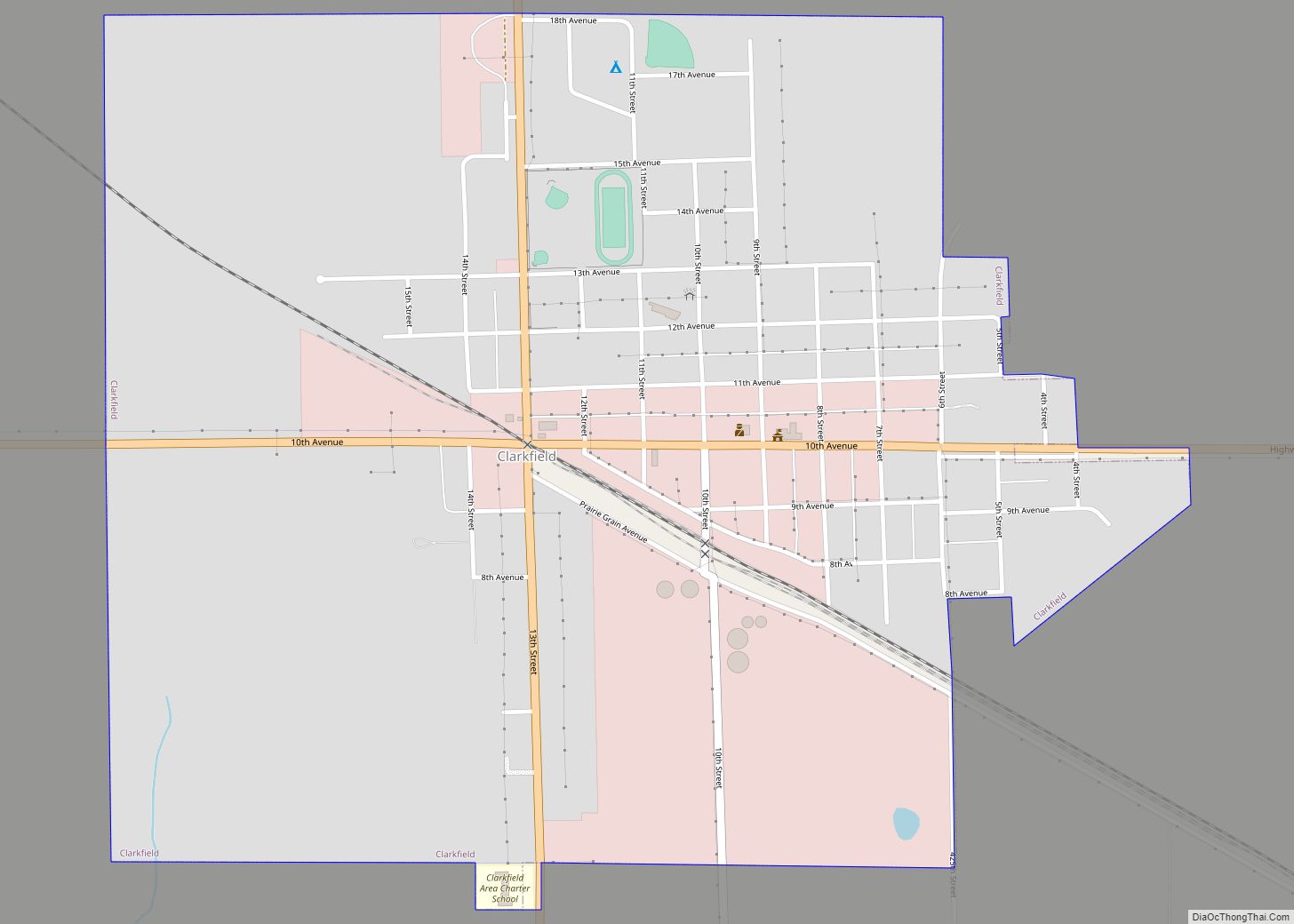
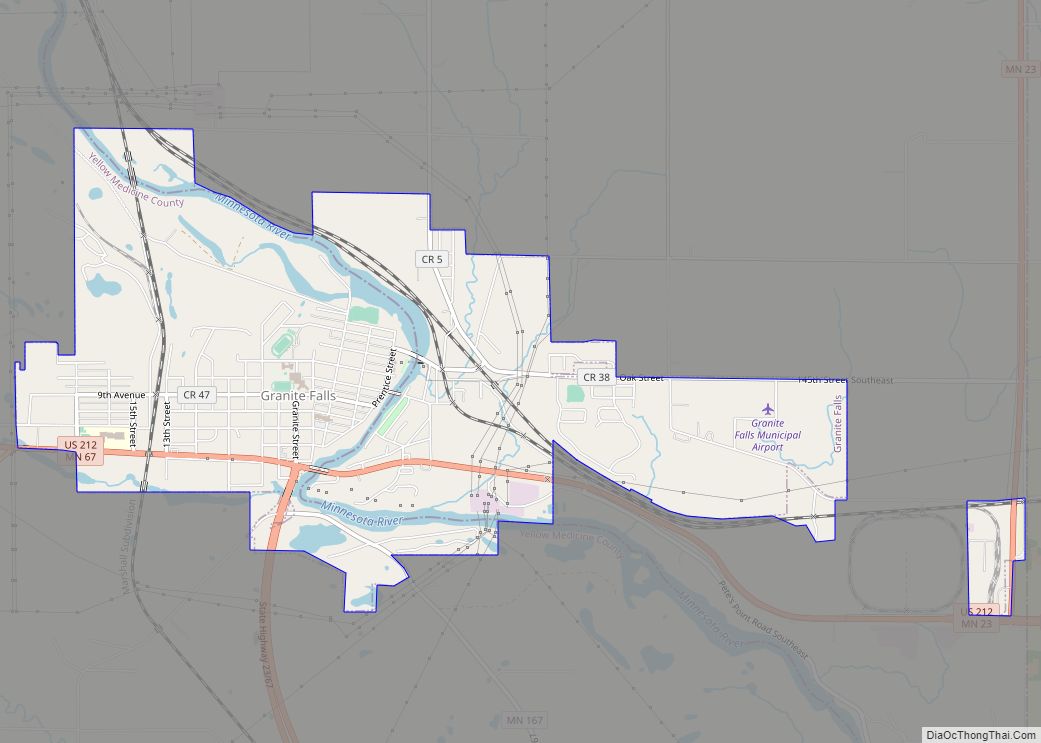
Granite Falls is a city located mostly in Yellow Medicine County, Minnesota, of which it is the county seat with a small portion in Chippewa County, Minnesota. The population was 2,737 at the 2020 census. The Andrew John Volstead House, a National Historic Landmark, is located in Granite Falls.
| Name: | Granite Falls city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Minnesota |
| County: | Chippewa County, Yellow Medicine County |
| Elevation: | 915 ft (279 m) |
| Total Area: | 3.73 sq mi (9.66 km²) |
| Land Area: | 3.49 sq mi (9.05 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.24 sq mi (0.61 km²) |
| Total Population: | 2,737 |
| Population Density: | 783.34/sq mi (302.48/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 56241 |
| Area code: | 320 |
| FIPS code: | 2725280 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0644347 |
| Website: | granitefalls.com |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Granite Falls location map. Where is Granite Falls city?
History
Shortly after the two eastern Dacotah reservations lost their lands north of the Minnesota river in 1858 a settlement developed at Granite Falls. According to the obituary of the Chippewa war Chief Mou-zoo-mau-nee, the people of Granite Falls asked the Chippewa for protection. The Chippewa sent 150 warriors.
In 1870 a post office began operating at Granite Falls. The town was platted in 1872 and named for deposits of granite rock in the area. In 1874 the county seat was moved to Granite Falls and a small one courtroom courthouse was erected. In 1876 the Norwegian Evangelical Lutheran Congregation was formed and a church was built. Granite Falls was incorporated as a city in 1879 with East Granite Falls joining in 1889. The existing county courthouse was erected in 1880. In 1888 the Chicago, Milwaukee and St. Paul Railroad built the town train station that still stands. The rail line remains active as a short line operated by the Twin Cities and Western Railroad (TC&W).
A grain elevator was built along the rail lines that today exists as the Farmers Co-Op elevator. In 2005 Granite Falls Energy LLC began producing Corn ethanol and extract Corn oil at their newly constructed plant.
2000 tornado
On July 25, 2000, the city of Granite Falls and Yellow Medicine County were hit by a powerful tornado. The tornado first touched down in rural parts of the county west-northwest of Granite Falls, hitting the city at 6:10 pm. After tearing through the residential sections of town, the tornado lifted at approximately 6:25PM after being on the ground for over nine miles. One person was killed, more than a dozen were injured, and the town and surrounding area suffered millions of dollars in property damage. Most of the damage in Granite Falls was rated F2 and F3, but the extent of the damage at the corner of 9th Avenue and 14th Street caused the National Weather Service to classify it as an F4 tornado.
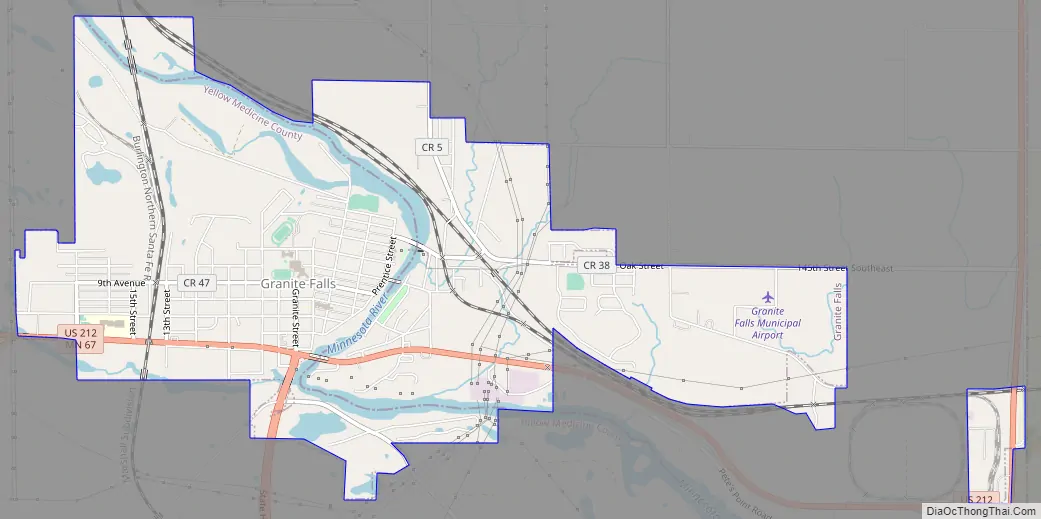
Granite Falls Road Map
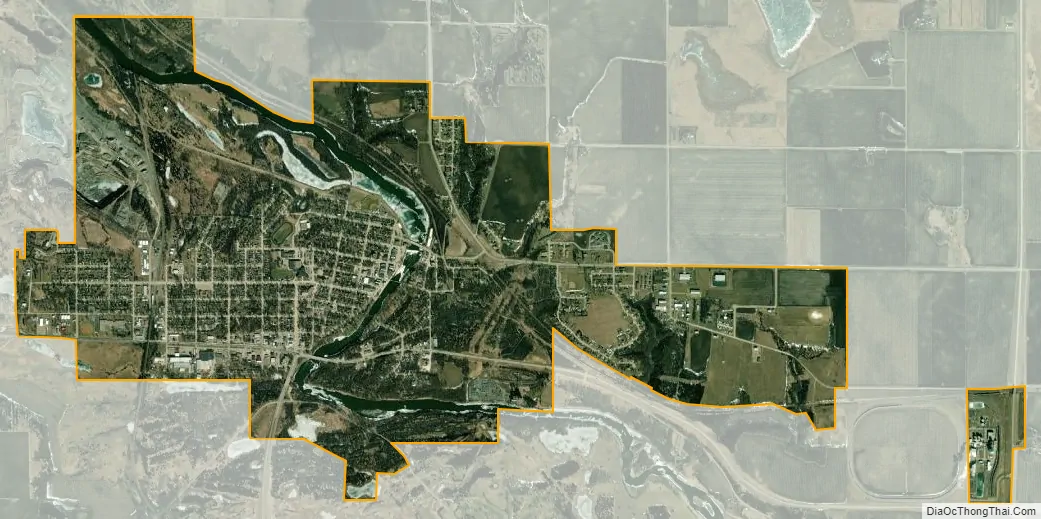
Granite Falls city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 3.82 square miles (9.89 km), of which 3.59 square miles (9.30 km) is land and 0.23 square miles (0.60 km) is water.
U.S. Highway 212 and Minnesota State Highways 23 and 67 are three of the main routes in the city.
Climate
Granite Falls, along with the rest of Minnesota, has a humid continental climate with significant differences between seasons. With a July mean temperature of 22.2 °C (72.0 °F) Granite Falls just falls into the hot-summer zone of the Köppen classification of the humid continental climate regime. Winters are cold and dry influenced by arctic air masses affecting it through its continental position, while summers are influenced by humid subtropical air masses bringing hot temperatures and significant rainfall. Transitional periods are very short, since only April and October are between 0 °C (32 °F) and 10 °C (50 °F) in daily mean temperatures, with May–September being clearly above and November–March averaging below freezing. The middle three months in each of those cycles are also clearly warmer and colder, respectively, than the months at the beginning or at the end of transitional periods. That is in turn a typical feature of continental climates.
See also
Map of Minnesota State and its subdivision:- Aitkin
- Anoka
- Becker
- Beltrami
- Benton
- Big Stone
- Blue Earth
- Brown
- Carlton
- Carver
- Cass
- Chippewa
- Chisago
- Clay
- Clearwater
- Cook
- Cottonwood
- Crow Wing
- Dakota
- Dodge
- Douglas
- Faribault
- Fillmore
- Freeborn
- Goodhue
- Grant
- Hennepin
- Houston
- Hubbard
- Isanti
- Itasca
- Jackson
- Kanabec
- Kandiyohi
- Kittson
- Koochiching
- Lac qui Parle
- Lake
- Lake of the Woods
- Lake Superior
- Le Sueur
- Lincoln
- Lyon
- Mahnomen
- Marshall
- Martin
- McLeod
- Meeker
- Mille Lacs
- Morrison
- Mower
- Murray
- Nicollet
- Nobles
- Norman
- Olmsted
- Otter Tail
- Pennington
- Pine
- Pipestone
- Polk
- Pope
- Ramsey
- Red Lake
- Redwood
- Renville
- Rice
- Rock
- Roseau
- Saint Louis
- Scott
- Sherburne
- Sibley
- Stearns
- Steele
- Stevens
- Swift
- Todd
- Traverse
- Wabasha
- Wadena
- Waseca
- Washington
- Watonwan
- Wilkin
- Winona
- Wright
- Yellow Medicine
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming