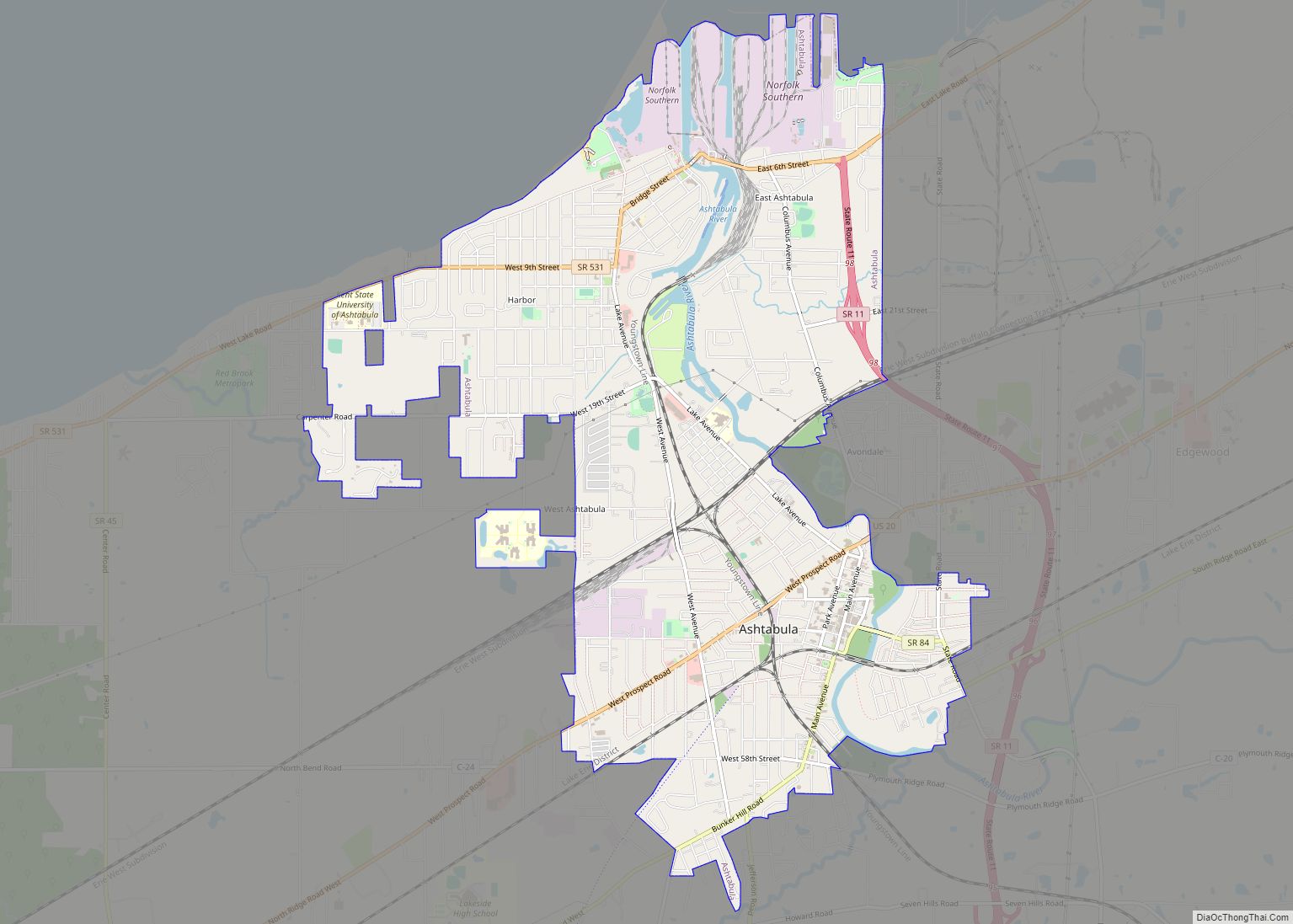
Ashtabula (/ˌæʃtəˈbjuːlə/ ASH-tə-BYU-lə) is a city in Ashtabula County, Ohio, United States, and the center of the Ashtabula micropolitan area. It is located at the mouth of the Ashtabula River on Lake Erie, 53 miles (85 km) northeast of Cleveland. As of the 2020 census, the city had a total population of 17,975. Like many other cities in the Rust Belt, it has lost population due to a decline in industrial jobs since the 1960s.
The name Ashtabula is derived from ashtepihəle, which means ‘always enough fish to be shared around’ in the Lenape language. The city became an important destination on the Underground Railroad in the middle 19th century, as refugee slaves could take ships to Canada and freedom. Even in the free state of Ohio, they were at risk of being captured by slavecatchers. Beginning in the late 19th century, the city became a major coal port on Lake Erie at the mouth of the Ashtabula River northeast of Cleveland. Coal and iron were shipped here, the latter from the Mesabi Range in Minnesota. The city attracted immigrants from Finland, Sweden and Italy in the industrial period. Ashtabula hosts an annual Blessing of the Fleet Celebration, usually in late May or early June. As part of the celebration, a religious procession and prayer service is held at Ashtabula Harbor. The city was the site of the FinnFestUSA in 2007, a celebration of Finnish Americans.
| Name: | Ashtabula city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Ohio |
| County: | Ashtabula County |
| Elevation: | 673 ft (205 m) |
| Total Area: | 7.92 sq mi (20.53 km²) |
| Land Area: | 7.77 sq mi (20.11 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.16 sq mi (0.41 km²) |
| Total Population: | 17,975 |
| Population Density: | 2,314.58/sq mi (893.67/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 44004-44005 |
| Area code: | 440 |
| FIPS code: | 3902638 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1048468 |
| Website: | http://www.cityofashtabula.com/ |
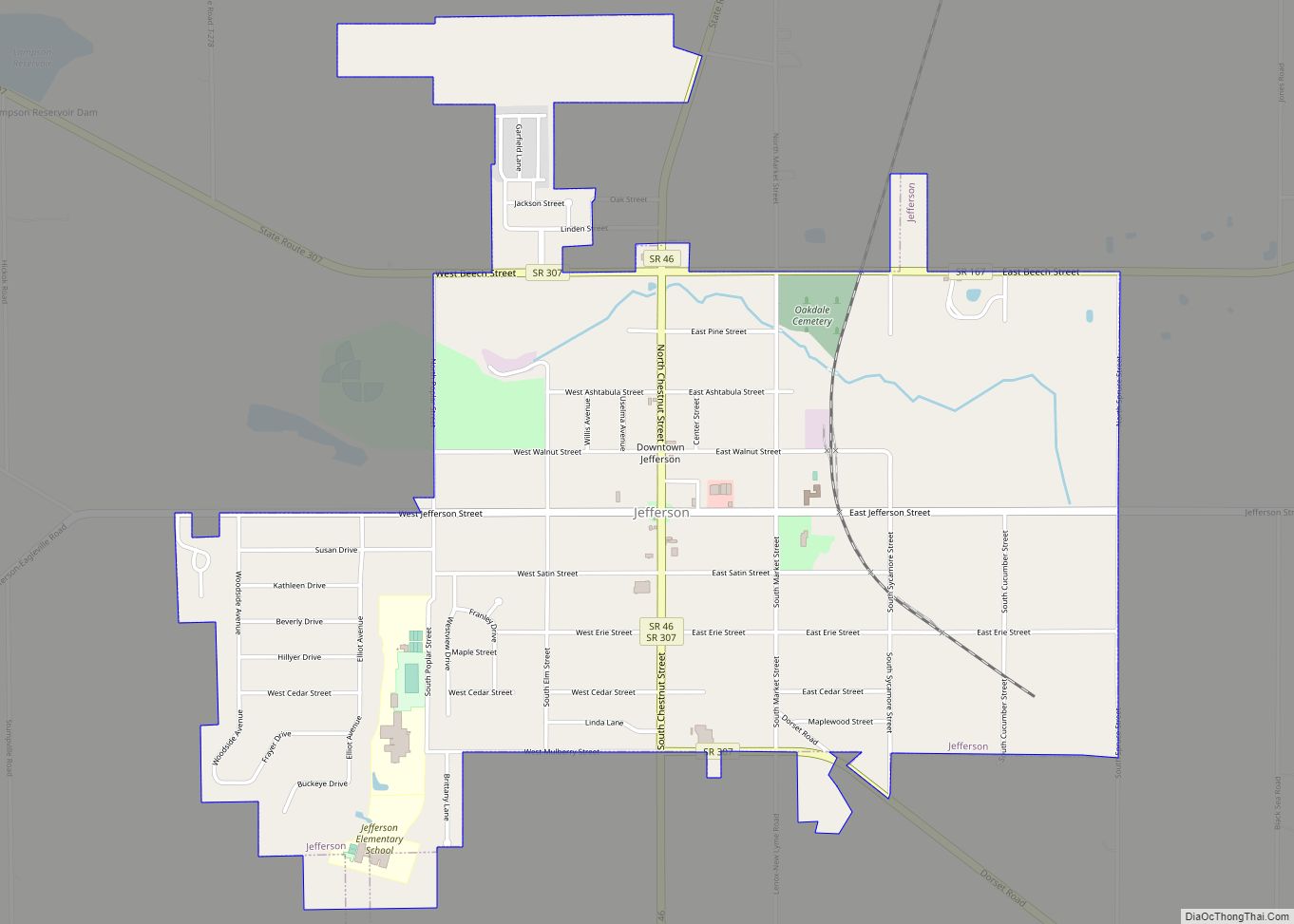
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
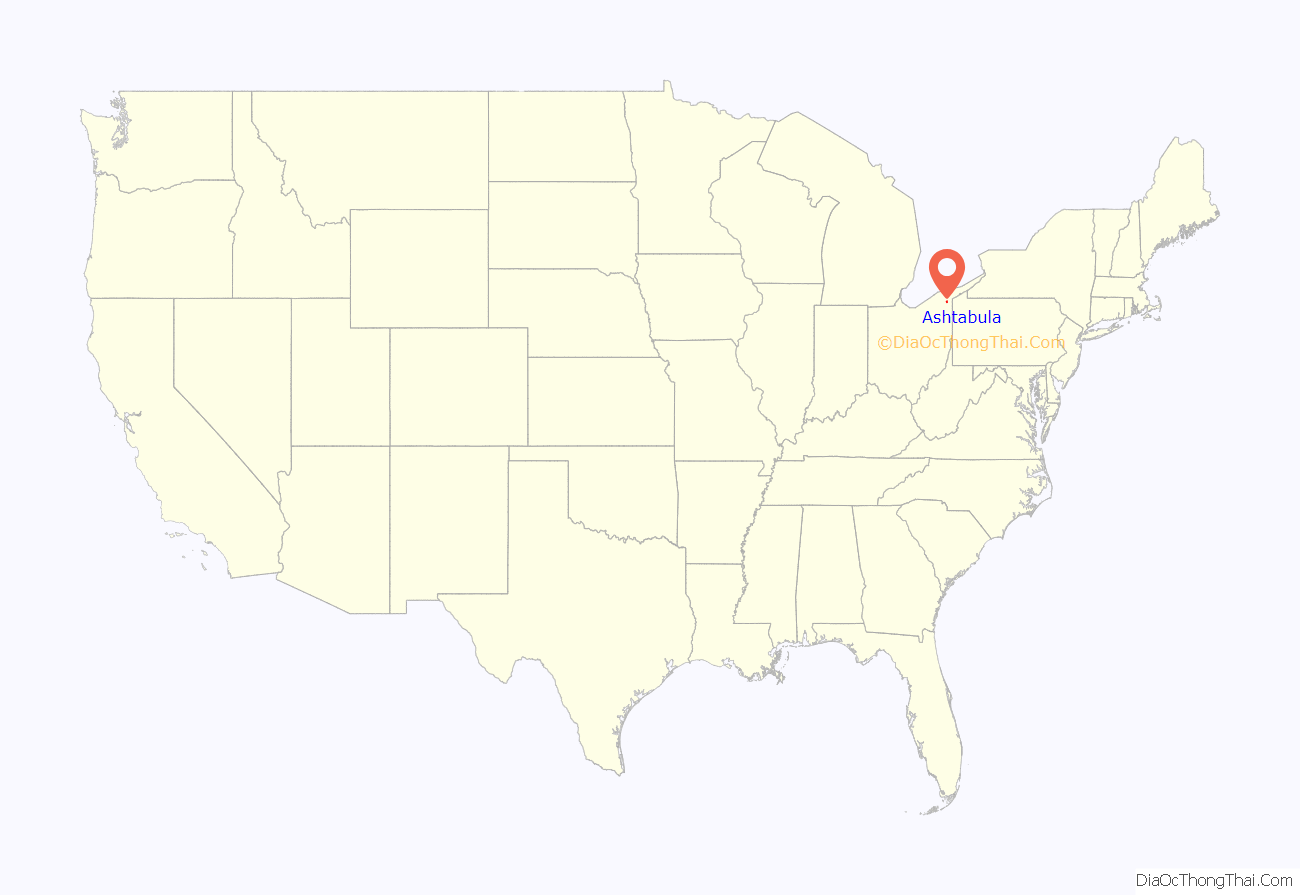
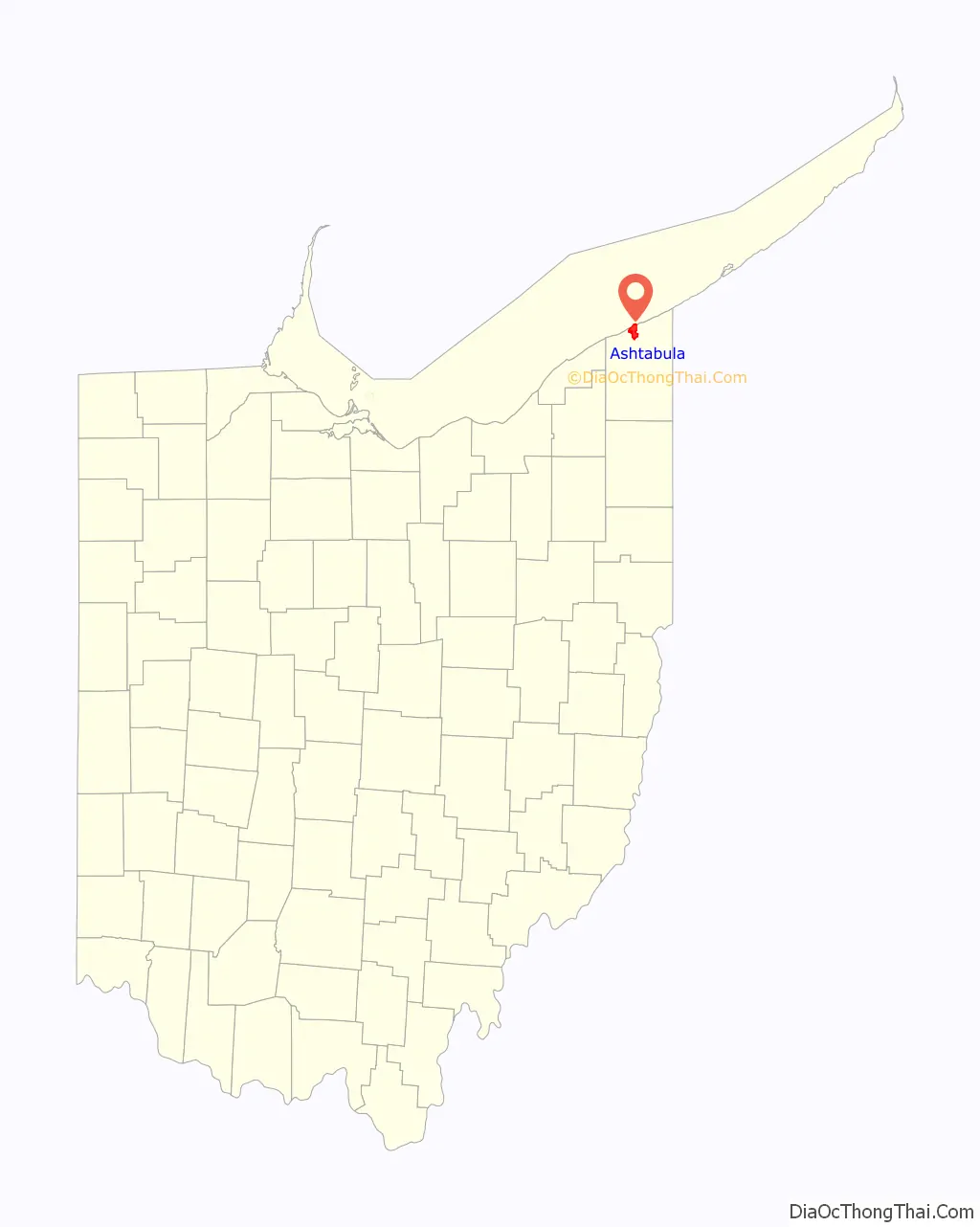
Ashtabula location map. Where is Ashtabula city?
History
This area had long been inhabited by indigenous peoples. After the American Revolutionary War, the United States mounted the Northwest Indian War to push Native American peoples out of what it then called the Northwest – the area of the Midwest south of the Great Lakes and west of the Appalachian Mountains. The success of this military effort resulted in more European Americans entering Ohio and nearby territories.
The site of Ashtabula was settled by such European Americans beginning in 1803. The city was incorporated in 1891. Located directly on Lake Erie and developed as a port for trade, the city contained several stops on the Underground Railroad. This informal, secret system was the means by which anti-slavery supporters helped escaped African-American slaves reach freedom in Canada in the years before the American Civil War. While Ohio was a free state, many refugee slaves still felt at risk of slavecatchers here, particularly after the Fugitive Slave Law of 1850 was passed. It required enforcement and cooperation by residents of free states to return escaped slaves and was biased toward slavecatchers, requiring little documentation of their claims. Among the Underground Railroad sites in Ashtabula is Hubbard House, one of the handful of former surviving termination points. Refugee slaves stayed in a basement of the house adjacent to the lake and then left on the next safe boat to Canada, gaining their freedom once they arrived in Ontario.
The city’s harbor has been important as a large ore and coal port since the end of the 19th century, and integral to the steel manufacturing that was developed around the Great Lakes. Lake steamers and barges, built at shipyards along the Great Lakes and setting new records for size and tonnage, delivered cargoes of iron ore from the Mesabi Range in Minnesota. This continues as a coal port; a long coal ramp is visible in the harbor. Ore shipments are unloaded from ‘lakers’ (Great Lakes freighters) and shipped to surviving steel mills in Pennsylvania. Industrial jobs have declined since the late 20th century with much steel manufacturing moved offshore.
An electric street railroad was built by Captain John N. Stuart in 1883. However, in July 1890, the city council dispossessed him of the street railroad and associated franchises via a disputable court decision. Shortly after, 600-700 men started to tear up and remove the tracks under the cover of darkness.
Many European immigrants, particularly from Finland, Sweden, and Italy, were attracted to the industrial jobs in Ashtabula in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, as they could learn and accomplish tasks without having a great command of English. Ethnic rivalries among these groups were once a major influence on politics and daily life in Ashtabula.
In 1915, Ashtabula became the first city in the United States to adopt a form of voting called proportional representation. This was an addition to the council-manager charter, originally passed in 1914, and served as a model for the National Municipal League. Twenty-four more cities would go on to use this single-transferable-vote (STV) system, with five in total in Ohio. Ethnic rivalries were one reason for the city’s switch, as STV enabled minorities to win political office. Another factor was disunity in the incumbent Republican Party. Voters repealed the system in 1929, using it for the last time in 1931. Despite two failed repeal campaigns in 1920 and 1926, political bosses and parties that lost power under STV eventually restored plurality voting, otherwise known as ‘winner take all.’
A substantial percentage of the current residents are descended from those early 20th-century immigrants. The population in the City of Ashtabula grew steadily until 1970 but has declined in recent years due to industrial restructuring and loss of jobs. Since the late 20th century, the city has become a destination for Hispanic or Latino immigrants, who by the 2010 census made up 9.3% of the population. (See ‘Demographics’ section below.)
Tragedies
Construction of railroads connected Ashtabula to a national network that contributed to its success as a port. On December 29, 1876, one of the nation’s most notorious rail accidents occurred, known as the Ashtabula River railroad disaster, Ashtabula Horror, or Ashtabula bridge disaster. As Lake Shore and Michigan Southern Railway Train No. 5, The Pacific Express, crossed the Ashtabula River bridge, the Howe truss structure collapsed, dropping the second locomotive and 11 passenger cars into the frozen creek 150 feet (46 m) below. A fire was started by the car stoves, and of the 159 people on board, 92 were killed and 64 were injured.
A rail ferry, also named Ashtabula, used to run from Ashtabula to Port Burwell, Ontario. The ferry was launched in 1906 and operated successfully for many decades. It collided with the steamer SS Ben Morell in September 1959, causing the ferry to sink.
On August 10, 1958, a natural gas leak was ignited by electrical equipment or lighting in Andover, Ohio a neighboring town. The resulting explosion destroyed a restaurant and five other buildings. 21 people were killed, and 15 injured.
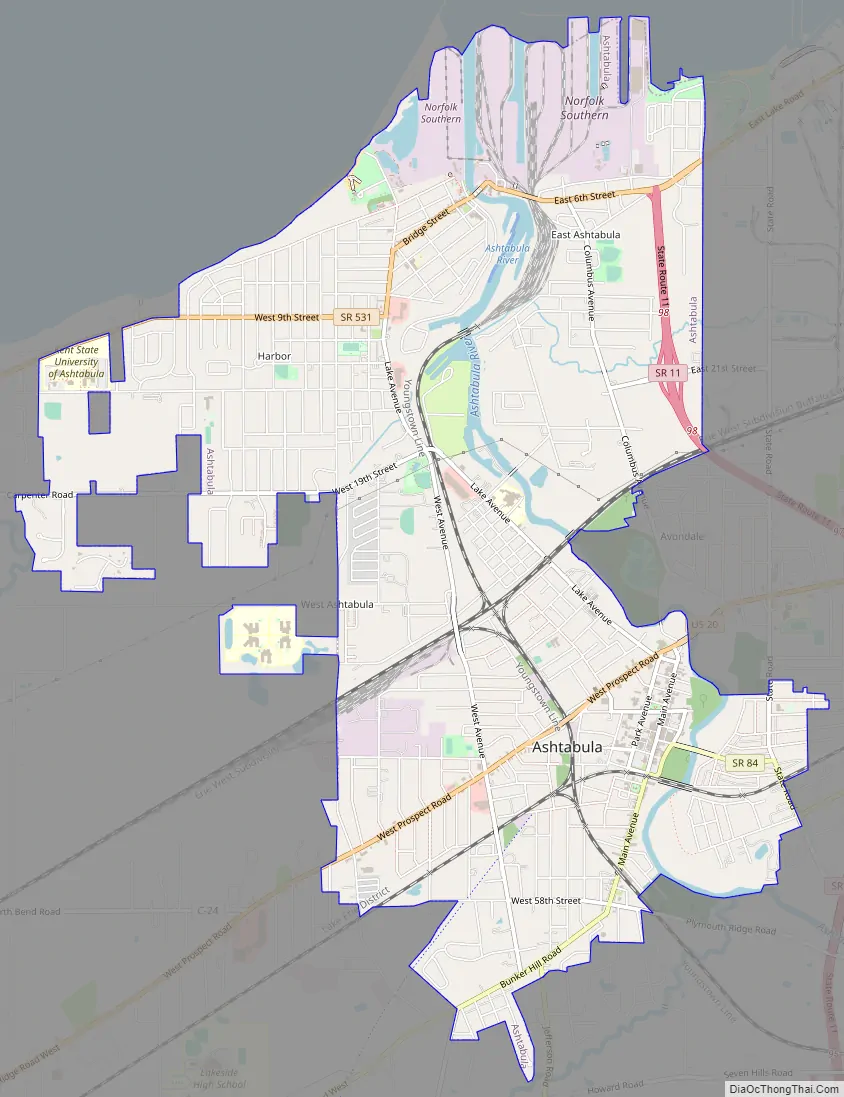
Ashtabula Road Map
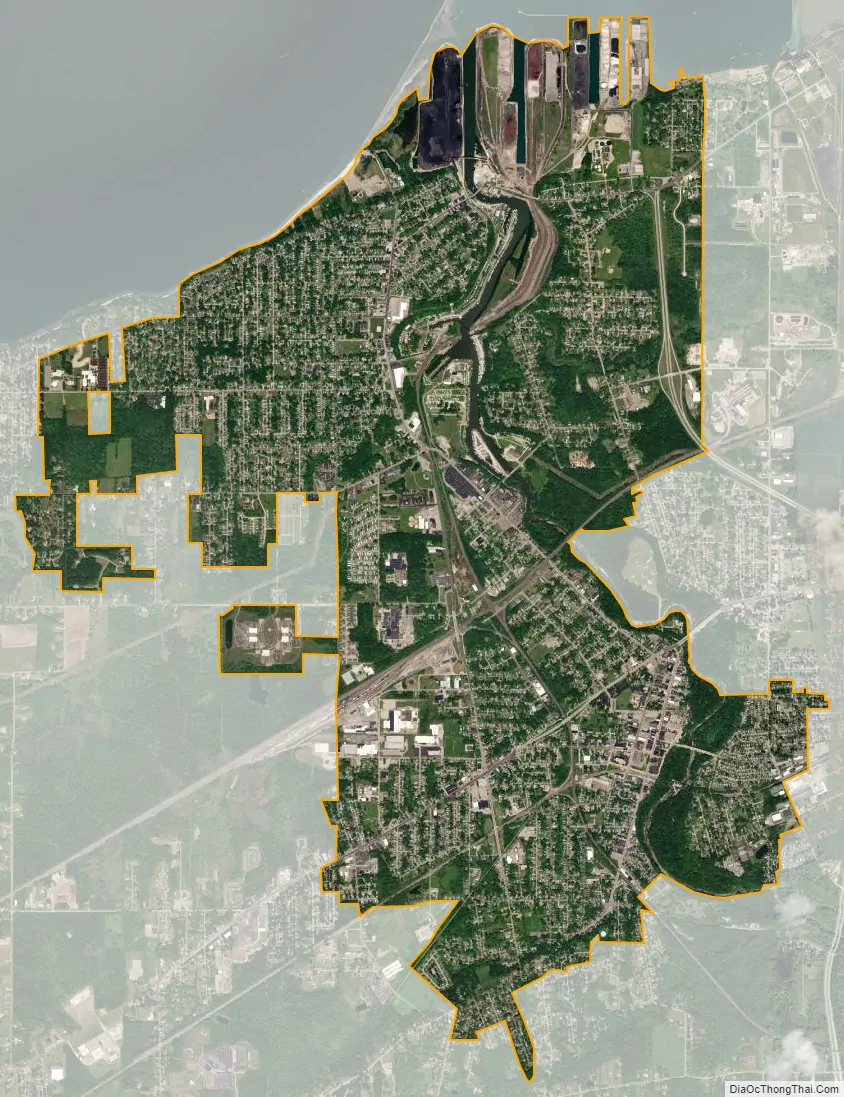
Ashtabula city Satellite Map
Geography
Ashtabula is located at 41°52′38″N 80°47′49″W / 41.87722°N 80.79694°W / 41.87722; -80.79694 (41.877138, −80.796976).
According to the 2010 census, the city has a total area of 7.91 square miles (20.5 km), of which 7.74 square miles (20.0 km) (or 97.85%) is land and 0.17 square miles (0.44 km) (or 2.15%) is water.
Ashtabula is bordered by Lake Erie to the north and has a prominent harbor where the Ashtabula River flows into the lake. The Ashtabula Harbor was a primary coal harbor and still serves to ship. It has two public beaches: Walnut Beach, near the harbor, and Lake Shore Park, originally a Public Works Administration project during the Great Depression, on the opposite side of the harbor.
Part of the city lies in Ashtabula Township, and part lies in Saybrook Township.
The Ashtabula area receives a considerable amount of snow throughout the winter, with the average snowfall being 68 inches (173 cm). Much of the snow comes from lake-effect snow bands from the Great Lakes.
See also
Map of Ohio State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Allen
- Ashland
- Ashtabula
- Athens
- Auglaize
- Belmont
- Brown
- Butler
- Carroll
- Champaign
- Clark
- Clermont
- Clinton
- Columbiana
- Coshocton
- Crawford
- Cuyahoga
- Darke
- Defiance
- Delaware
- Erie
- Fairfield
- Fayette
- Franklin
- Fulton
- Gallia
- Geauga
- Greene
- Guernsey
- Hamilton
- Hancock
- Hardin
- Harrison
- Henry
- Highland
- Hocking
- Holmes
- Huron
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Knox
- Lake
- Lake Erie
- Lawrence
- Licking
- Logan
- Lorain
- Lucas
- Madison
- Mahoning
- Marion
- Medina
- Meigs
- Mercer
- Miami
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Morgan
- Morrow
- Muskingum
- Noble
- Ottawa
- Paulding
- Perry
- Pickaway
- Pike
- Portage
- Preble
- Putnam
- Richland
- Ross
- Sandusky
- Scioto
- Seneca
- Shelby
- Stark
- Summit
- Trumbull
- Tuscarawas
- Union
- Van Wert
- Vinton
- Warren
- Washington
- Wayne
- Williams
- Wood
- Wyandot
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming