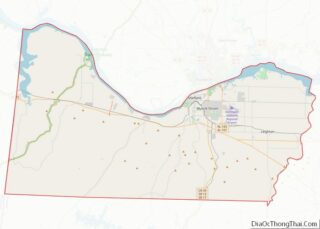
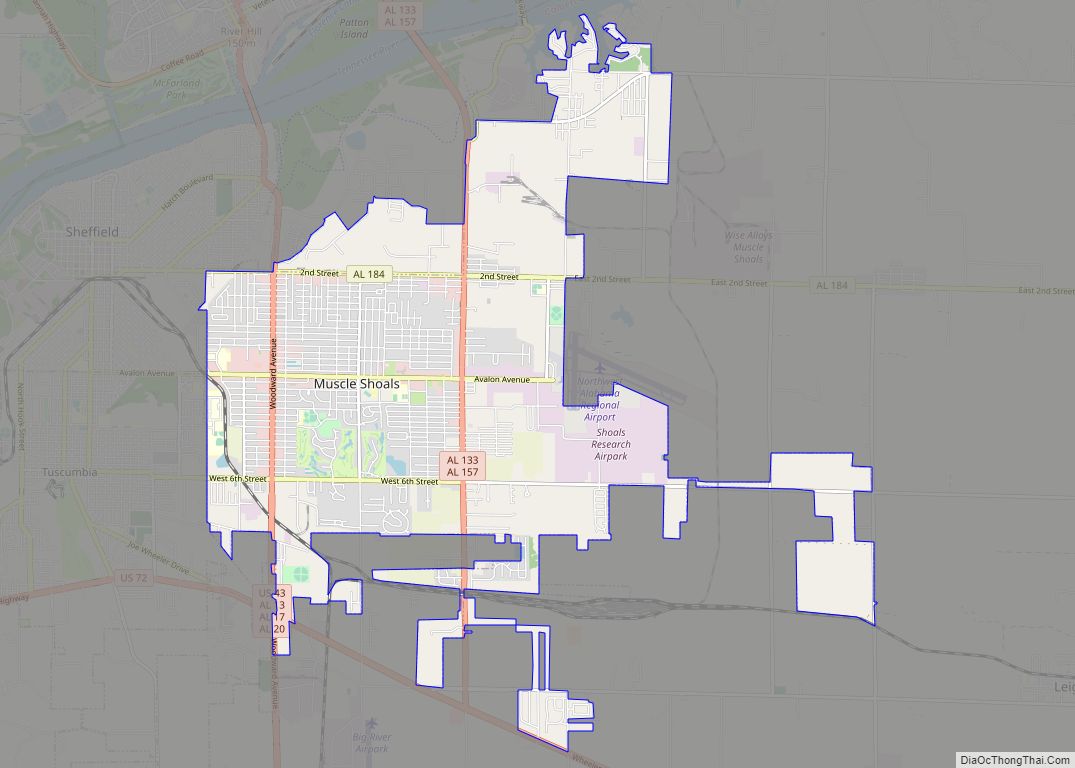
Muscle Shoals is the largest city in Colbert County, Alabama. It is located on the left bank of the Tennessee River in the northern part of the state and, as of the 2010 census, its population was 13,146. The estimated population in 2019 was 14,575.
Both the city and the Florence-Muscle Shoals Metropolitan Area (including four cities in Colbert and Lauderdale counties) are commonly called “the Shoals”. Northwest Alabama Regional Airport serves the Shoals region, located in the northwest section of the state.
Due to its strategic location along the Tennessee River, Muscle Shoals had long been territory of Native American tribes. In the late 18th and early 19th centuries, as Europeans entered the area in greater number, it became a center of historic land disputes. The new state of Georgia had ambitions to anchor its western claims (to the Mississippi River) by encouraging European-American development here, but that project did not succeed.
Under President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s administration during the Great Depression, the Tennessee Valley Authority was established to create infrastructure and jobs, resulting in electrification of a large rural area along the river. The Ford Motor Company did build and operate a plant for many years in the Listerhill community, three miles east of Muscle Shoals; it closed in 1982 as part of industrial restructuring when jobs moved out of the country.
Since the 1960s, the city has been known for music. Local studios and artists developed the “Muscle Shoals Sound”, including FAME Studios in the late 1950s and Muscle Shoals Sound Studio in 1969.
| Name: | Muscle Shoals city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Alabama |
| County: | Colbert County |
| Incorporated: | April 24, 1923 |
| Elevation: | 525 ft (160 m) |
| Land Area: | 16.80 sq mi (43.52 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.02 sq mi (0.05 km²) |
| Population Density: | 968.58/sq mi (373.96/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 35660(obsolete), 35661, 35662 |
| FIPS code: | 0153016 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 2404345 |
| Website: | www.cityofmuscleshoals.com |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Muscle Shoals location map. Where is Muscle Shoals city?
History
Like other areas along waterways, this was important to indigenous peoples for thousands of years. The area of Muscle Shoals was a part of the historic Cherokee hunting grounds dating to at least the early eighteenth century, if not earlier. Many Cherokee fought against the rebels during the late American Revolutionary War, hoping to expel them from their territories.
After the Revolution, Cherokee attitudes toward the new U.S. republic were divided, as settlers increasingly encroached on their territory. An anti-American faction, dubbed the Chickamauga, separated from more conciliatory Cherokees, and moved into present-day south-central and southeastern Tennessee. Most of this band settled along the Chickamauga Creek, from which their name was derived. They claimed Muscle Shoals as part of their domain. When Anglo-Americans attempted to settle the region in the 1780s and 1790s, the Chickamaugas bitterly resisted them.
The Upper Creek, residing in what is now north and central Alabama, also resented any European or Euro-American presence in the region. A major incident occurred in 1790, when U.S. President George Washington sent an expedition under Major John Doughty in an attempt to establish a fort and trading post at Muscle Shoals. This expedition was nearly annihilated by a Chickamauga and Creek party sent to destroy it, and the administration abandoned the project. Meanwhile, Francisco Luis Hector de Carondelet, governor of the Spanish Louisiana, was in conversations with the Indian confederation to stablish a fort in 1792.
Anglo-American settlers in Tennessee continued to agitate for control of this region. The site was particularly desirable, as it controlled access to fine cotton-producing land immediately to its south. In 1797, John Sevier, the first governor of Tennessee, complained to Andrew Jackson that “The prevention of a settlement at or near the Muscle Shoals is a manifest injury done the whole western country.” At Sevier’s behest, Jackson attempted to persuade Congress and President John Adams to fund a new expedition to take control of the site, but to no avail.
U.S. officials finally took control of the region in the wake of the U.S. invasion of Creek country during the War of 1812. Jackson and General John Coffee obtained cession of the land from both the Cherokee and Creek (who had continued to dispute possession) by treaty, without permission from the federal government. Secretary of War William H. Crawford refused to recognize the cession, and reconfirmed Cherokee ownership, leading to personal enmity between him and Jackson. The political struggle over the lands was eventually won by Jackson and his backers, who gained passage in Congress of the Indian Removal Act in 1830. When Jackson, as president, implemented the policy of Indian Removal, Muscle Shoals was used as a site from which to exile the Upper Creek to Indian Territory (now Oklahoma).
During World War I President Wilson authorized a dam on the Tennessee River just downstream of Muscle Shoals to help power nitrate plants for munitions. The first plant started producing nitrates two weeks after the armistice, but the dam was not completed until 1924.
Meanwhile, in 1922 Henry Ford tried to buy the nitrate works and the unfinished dam. The Michigan car manufacturer and industrialist proposed leasing the uncompleted hydro-electric dam at Muscle Shoals on the Tennessee River in Alabama. The US War Department had begun the project during World War I, and engineers estimated a cost of $40 million to complete. At this time, public projects were financed either through raising taxes—which, Congress was unwilling to do at the time- or by issuing bonds. For the Muscle Shoals project, the proposal was for 30-year bonds at 4% interest.
Ford and his friend and fellow inventor Thomas Edison balked at the idea that the US government should have to pay $48 million in interest on top of the $40 million they would have to pay back—all for a project that would benefit the public (the argument being that the hydro-electric dam and accompanying fertilizer plants would create jobs and revitalize the area). Responding to the bond issue, Edison remarked: “Any time we wish to add to the national wealth, we are compelled to add to the national debt.” Edison and Ford hoped that a new monetary system could be created where dollar bills were issued directly to workers and manufacturer, with the money being backed by the goods they produced rather than the gold and silver held in bank vaults. Congress eventually rejected Ford’s idea.
The project of area development based on hydroelectric power languished until the Great Depression. President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s administration created the Tennessee Valley Authority in 1933 to construct needed infrastructure and install an electrical system in the rural area, using newly generated electricity from the dam complex.
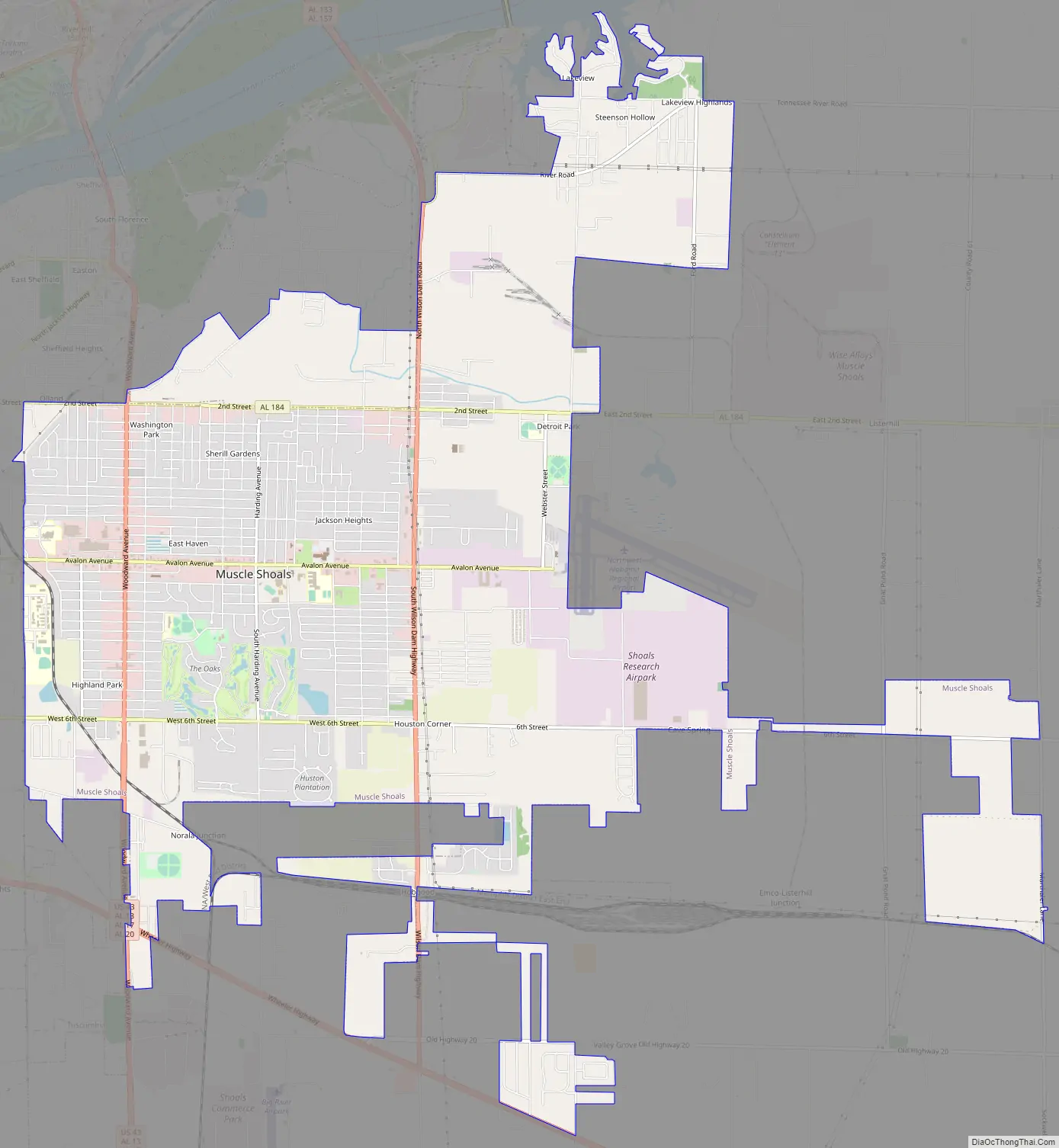
Muscle Shoals Road Map
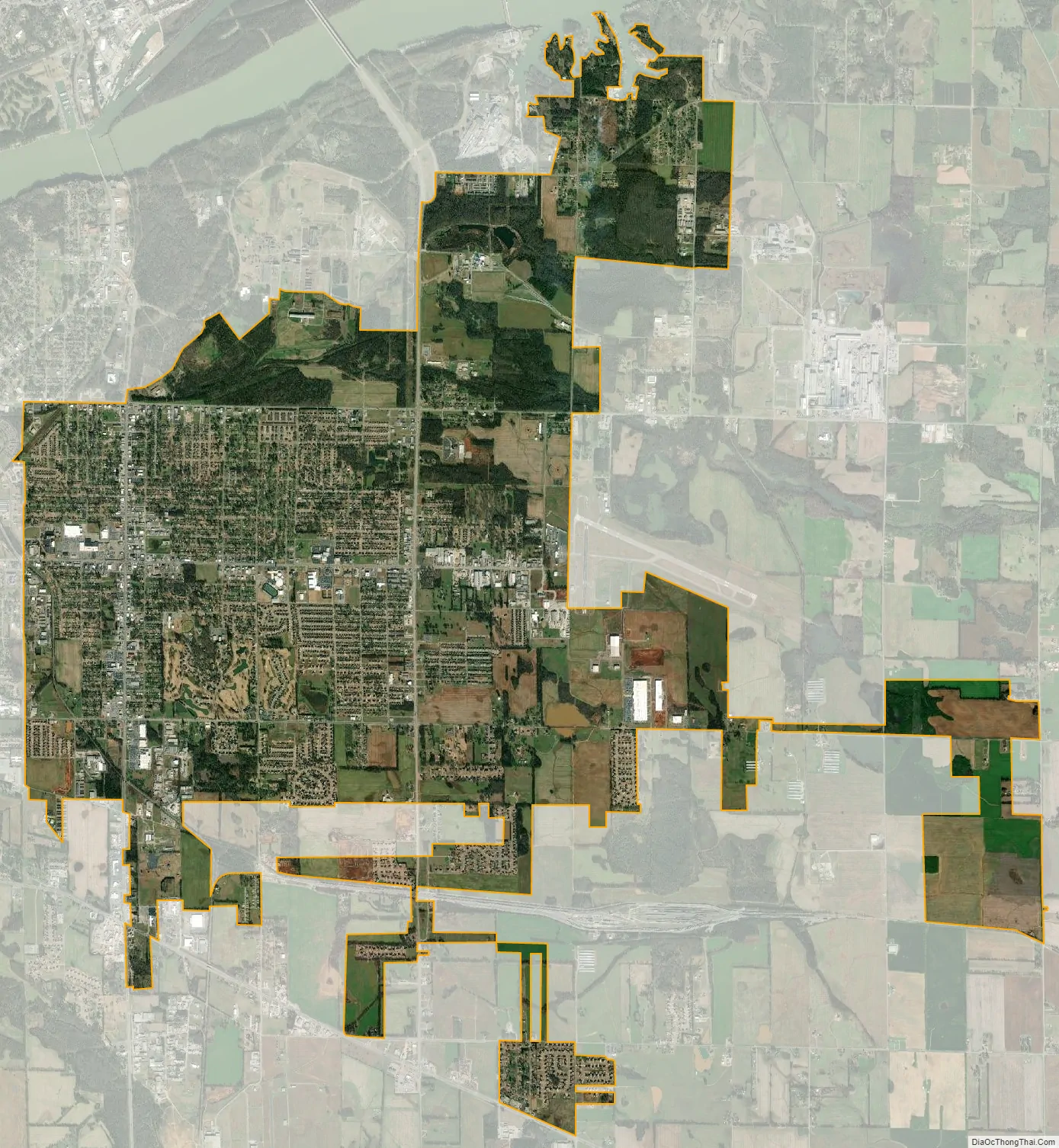
Muscle Shoals city Satellite Map
Geography
Muscle Shoals is located on the south bank of the Tennessee River at 34°45′03″N 87°39′01″W / 34.750788°N 87.650278°W / 34.750788; -87.650278.
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 15.6 square miles (40.3 km), of which 0.02 square miles (0.05 km), or 0.13%, is water. The local hardiness zone is 7b. Interactive Map | USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map Archived July 4, 2019, at the Wayback Machine
Climate
See also
Map of Alabama State and its subdivision:- Autauga
- Baldwin
- Barbour
- Bibb
- Blount
- Bullock
- Butler
- Calhoun
- Chambers
- Cherokee
- Chilton
- Choctaw
- Clarke
- Clay
- Cleburne
- Coffee
- Colbert
- Conecuh
- Coosa
- Covington
- Crenshaw
- Cullman
- Dale
- Dallas
- De Kalb
- Elmore
- Escambia
- Etowah
- Fayette
- Franklin
- Geneva
- Greene
- Hale
- Henry
- Houston
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Lamar
- Lauderdale
- Lawrence
- Lee
- Limestone
- Lowndes
- Macon
- Madison
- Marengo
- Marion
- Marshall
- Mobile
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Morgan
- Perry
- Pickens
- Pike
- Randolph
- Russell
- Saint Clair
- Shelby
- Sumter
- Talladega
- Tallapoosa
- Tuscaloosa
- Walker
- Washington
- Wilcox
- Winston
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming