Hesperia is a city in San Bernardino County, California, United States. It is located 35 miles (56 km) north of downtown San Bernardino in Victor Valley and surrounded by the Mojave Desert. Because of its relatively high elevation and the unique and moderate weather patterns of the region, Hesperia is part of what is locally called the High Desert. The name “Hesperia” means “western land”. The 2019 census report estimates that the city has a population of 95,750.
| Name: | Hesperia city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | California |
| County: | San Bernardino County |
| Incorporated: | July 1, 1988 |
| Elevation: | 3,186 ft (971 m) |
| Total Area: | 72.78 sq mi (188.50 km²) |
| Land Area: | 72.69 sq mi (188.26 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.10 sq mi (0.25 km²) 0.15% |
| Total Population: | 90,173 |
| Population Density: | 1,317.31/sq mi (508.62/km²) |
| FIPS code: | 0633434 |
| Website: | cityofhesperia.us |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Hesperia location map. Where is Hesperia city?
History
The first inhabitants of the area were the Desert Serrano (Vanyume). The village of Wá’peat, among several other villages that were located along the Mojave River, were within the vicinity of what is now Hesperia. These villages were occupied into the early 1800s and had deep ties with one another. An acorn-gathering festival was held at Wá’peat that involved villagers from across the Mojave River area.
Hesperia began as a Spanish land grant: Rancho San Felipe, Las Flores y el Paso del Cajon, founded in 1781. The land was sparsely inhabited desert during Spanish-Mexican rule in the 19th century. The U.S. annexed the region along with Southern California after the Mexican-American War in 1848.
In 1869, Max Stobel purchased 35,000 acres (14,000 ha) from the United States Government Land Office for $40,000. While several attempts were made to subdivide and encourage colonization, the land was primarily used for agricultural purposes, with raisin grapes the primary product.
The town site was laid out in 1891 by railroad company land developers of the Santa Fe Railroad, which was completed that year. Hesperia was named for Hesperus, the Greek god of the West. The railroad land developers published pamphlets distributed across the country with boosterism of Hesperia, California, as a potential metropolis, to become “the Omaha of the West” or projections to have over 100,000 people by 1900, but only 1,000 moved in.
Hesperia grew relatively slowly until the completion of US Routes 66, 91, and 395 in the 1940s, followed by Interstate 15 in the late 1960s. About 30 square miles (78 km) of land were laid out for possible residential development.
In the early 1950s, land developer M. Penn Phillips and his silent financial partner, boxer Jack Dempsey, financed the building of roads and land subdivisions, promoting lots sales on television. They built the Hesperia Inn and golf course, which attracted a variety of Hollywood celebrities. The Hesperia Inn also housed the Jack Dempsey Museum.
The main wave of newcomers, though, arrived at Hesperia in the 1980s. Suburban growth transformed the small town of 5,000 people in 1970 to a moderate-sized city with a population over 60,000 by 2000, and an estimated population over 95,000 as of July 1, 2018.
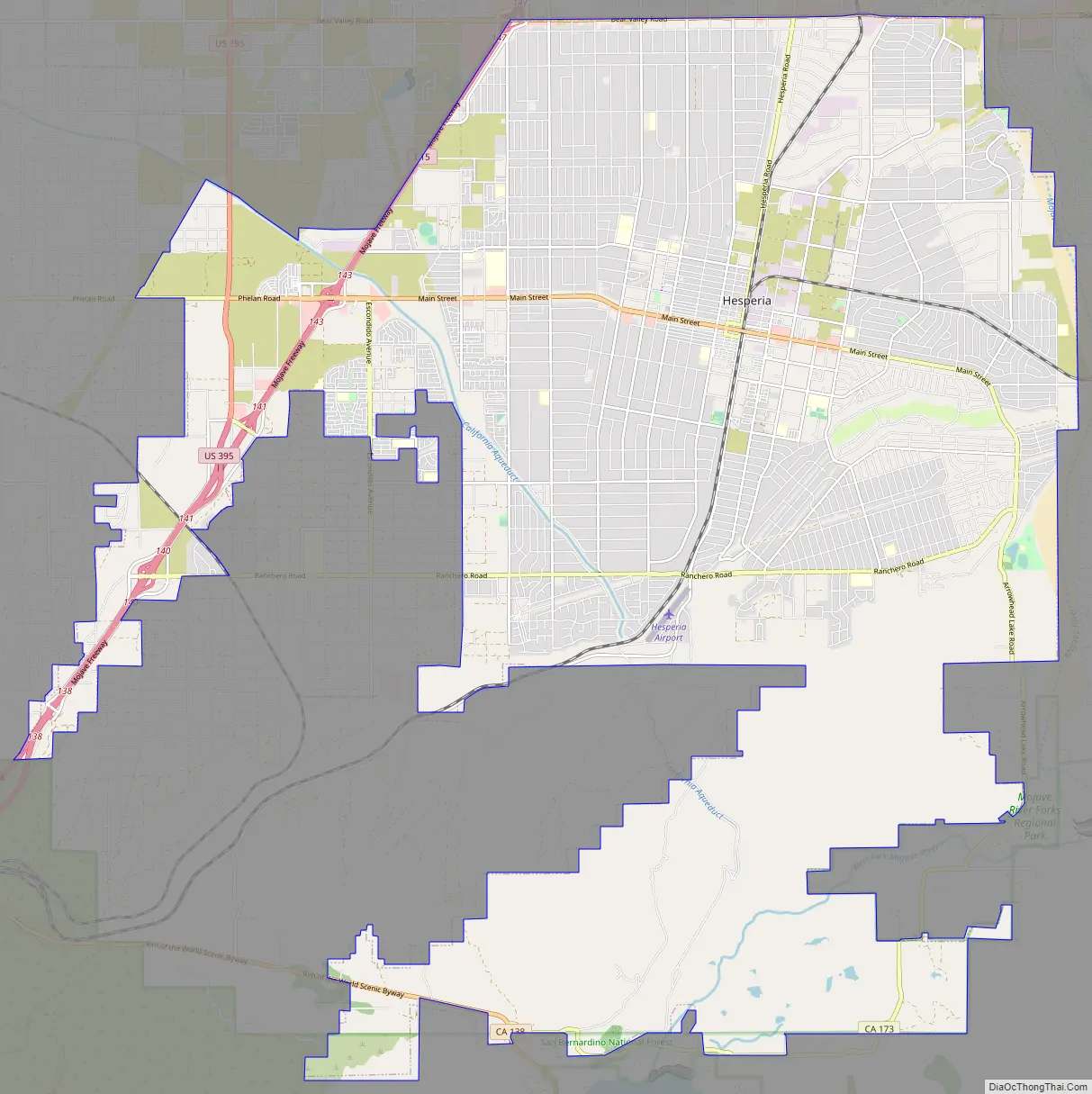
Hesperia Road Map
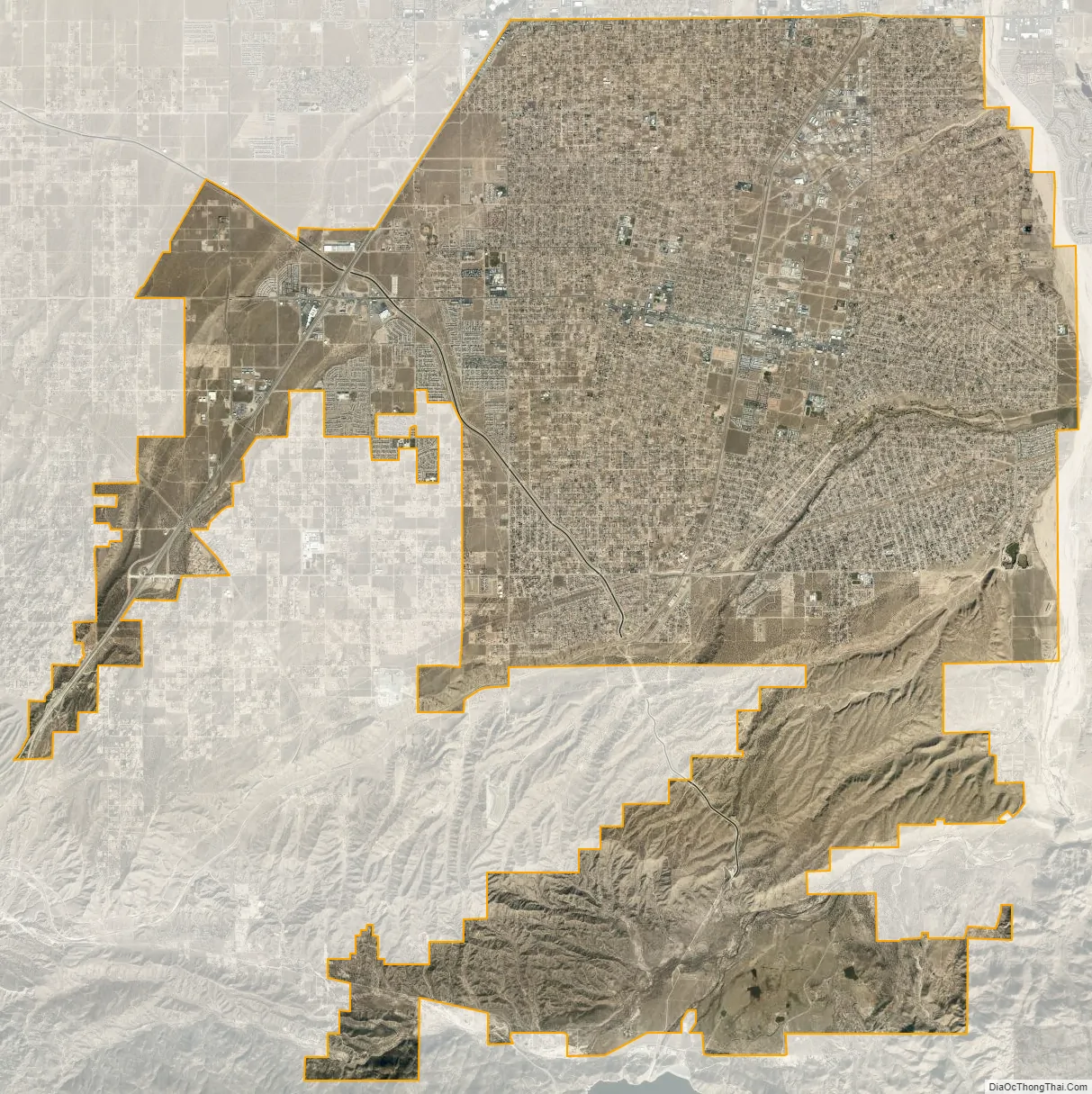
Hesperia city Satellite Map
Geography
Hesperia is a city in the Mojave Desert, and the California Aqueduct traverses the area. Much of the native flora of Hesperia is classified as California desert vegetation, dominated by junipers, joshua trees, and sagebrush. The elevation rises from 3,200 feet (980 m) in the north to about 4,000 feet (1,200 m) above sea level to the south.
The San Andreas Fault, a major tectonic plate boundary of the Pacific and North American plates a few miles south of Hesperia in the Cajon Pass, has occasional seismic activity.
Hesperia is located at 3,186 feet (971 m) above sea level and is a neighbor of Victorville, Oak Hills, and Apple Valley. The Mojave River flows northerly through the east side of the city, while the California Aqueduct splits the city from north to south en route to Silverwood Lake.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 73.2 square miles (190 km), with 73.1 square miles (189 km) of land and 0.1 square miles (0.26 km) (0.15%) covered by water.
On the southern edge of Hesperia, where the city meets the desert by the airport to the east, is a somewhat pronounced mesa.
Climate
According to the Köppen climate classification, Hesperia has a cold desert climate, BWk on climate maps.
Winter days are cool with high temperatures averaging around 60 °F (16 °C), but temperatures get cold overnight, as the average low temperatures for December and January are around freezing. It is also the area’s wet season. The rain shadow caused by the mountain ranges to the south and west shields Hesperia from the majority of winter rainfall, but heavy rain is not uncommon. Winter snowfall is sporadic – the average yearly snowfall amount is 4.4 inches.
Summer days are very hot, with high temperatures typically nearing 100 °F (38 °C). This excessive heat is typical of the Mojave Desert as a whole. The large diurnal temperature variation, though, provides substantial relief overnight. In the later part of the season, sporadic summer thunderstorms associated with the North American monsoon can bring power outages and local flash floods.
See also
Map of California State and its subdivision:- Alameda
- Alpine
- Amador
- Butte
- Calaveras
- Colusa
- Contra Costa
- Del Norte
- El Dorado
- Fresno
- Glenn
- Humboldt
- Imperial
- Inyo
- Kern
- Kings
- Lake
- Lassen
- Los Angeles
- Madera
- Marin
- Mariposa
- Mendocino
- Merced
- Modoc
- Mono
- Monterey
- Napa
- Nevada
- Orange
- Placer
- Plumas
- Riverside
- Sacramento
- San Benito
- San Bernardino
- San Diego
- San Francisco
- San Joaquin
- San Luis Obispo
- San Mateo
- Santa Barbara
- Santa Clara
- Santa Cruz
- Shasta
- Sierra
- Siskiyou
- Solano
- Sonoma
- Stanislaus
- Sutter
- Tehama
- Trinity
- Tulare
- Tuolumne
- Ventura
- Yolo
- Yuba
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming