Estes Park /ˈɛstɪs/ is a statutory town in Larimer County, Colorado, United States. The town population was 5,904 at the 2020 United States Census. Estes Park is a part of the Fort Collins, CO Metropolitan Statistical Area and the Front Range Urban Corridor. A popular summer resort and the location of the headquarters for Rocky Mountain National Park, Estes Park lies along the Big Thompson River. Landmarks include The Stanley Hotel and The Baldpate Inn. The town overlooks Lake Estes and Olympus Dam.
| Name: | Estes Park town |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 43 |
| LSAD Description: | town (suffix) |
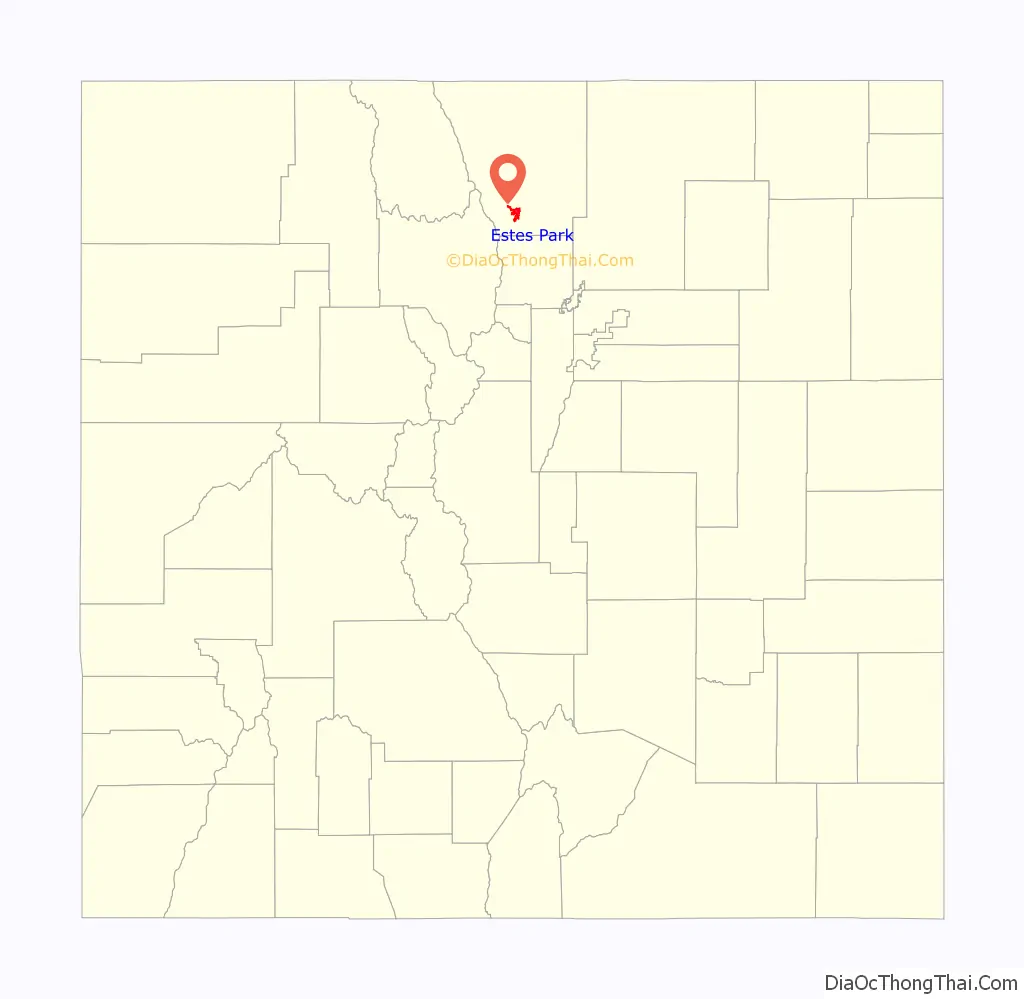
| State: | Colorado |
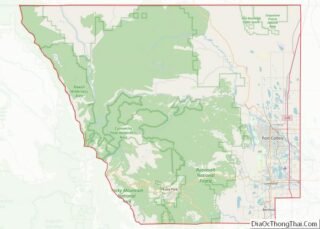
| County: | Larimer County |
| Incorporated: | April 17, 1917 |
| Elevation: | 7,522 ft (2,293 m) |
| Total Area: | 6.897 sq mi (17.862 km²) |
| Land Area: | 6.822 sq mi (17.668 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.075 sq mi (0.194 km²) |
| Total Population: | 5,904 |
| Population Density: | 865/sq mi (334/km²) |
| Area code: | 970 |
| FIPS code: | 0825115 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0204674 |
| Website: | estespark.colorado.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Estes Park location map. Where is Estes Park town?
History
Early history
Before Europeans came to the Estes Park valley, the Arapaho Indians lived there in the summertime and called the valley “the Circle.” When three elderly Arapahoes visited Estes Park in 1914, they pointed out sites they remembered from their younger days. A photograph at the Estes Park Museum identified the touring party as Shep Husted, guide; Gun Griswold, a 73-year-old judge; Sherman Sage, a 63-year-old chief of police; Tom Crispin, 38-year-old reservation resident and interpreter; Oliver W. Toll, recorder; and David Robert Hawkins, a Princeton student.
In the 1850s, the Arapaho had spent summers camped around Mary’s Lake, where their rock fireplaces, tipi sites, and dance rings were still visible. They also recalled building eagle traps atop Longs Peak to get the war feathers coveted by all tribes. They remembered their routes to and from the valley in detail, naming trails and landmarks. They pointed out the site of their buffalo trap, and described the use of dogs to pack meat out of the valley. Their recollections included a battle with Apaches in the 1850s, and fights with Utes who came to the area to hunt bighorn sheep, so all three of those tribes used the valley’s resources.
Whites probably came into the Estes Park valley before the 1850s as trappers, but did not stay long. The town is named after Missouri native Joel Estes, who founded the community in 1859. Estes moved his family there in 1863. One of Estes’ early visitors was William Byers, a newspaper editor who wrote of his attempted ascent of Longs Peak in 1864, publicizing the area as a pristine wilderness.
Griff Evans and his family came to Estes Park in 1867 to act as caretakers for the former Estes ranch. Recognizing the potential for tourism, he began building cabins to accommodate travelers. Soon it was known as the first dude ranch in Estes Park, with guides for hunting, fishing, and mountaineering.
The 4th Earl of Dunraven and Mount-Earl, a young Anglo-Irish peer, arrived in late December 1872 under the guidance of Texas Jack Omohundro, subsequently made numerous visits, and decided to take over the valley for his own private hunting preserve. Lord Dunraven’s ‘land grab’ didn’t work, but he controlled 6,000 acres before he changed tactics and opened the area’s first resort, the Estes Park Hotel, which was destroyed by fire in 1911.
In 1873, Englishwoman Isabella Bird, the daughter of an Anglican minister, came to the United States. Landing at San Francisco, she came overland to Colorado, where she borrowed a horse and set out to explore the Rocky Mountains with a guide, the notorious James Nugent, aka ‘Rocky Mountain Jim’. She wrote A Lady’s Life in the Rocky Mountains, a memoir of their travels, including the breathtaking ascent of Longs Peak, where she was literally hauled up the steep pitches “like a bale of goods.”
On June 19, 1874, Rocky Mountain Jim and neighbor Griff Evans (see above) had an argument. Having had bitter history with each other, Nugent and Evans hated each other and were deep personal rivals when it came to tour guiding tourists. The argument escalated until Evans blasted Jim in the head with his rifle shotgun. Evans then traveled to Fort Collins to file an assault charge against Nugent, but he was arrested and tried for first degree murder when Jim Nugent died on September 9, 1874, of the bullet wound. Evans was put on trial, but the case was soon dismissed due to the lack of witnesses to the shooting. On August 9, 1875, the Loveland court-house acquitted Evans of any charges in the case.
William Henry Jackson photographed Estes Park in 1873.
Alex and Clara (Heeney) MacGregor arrived soon after and homesteaded at the foot of Lumpy Ridge. The MacGregor Ranch has been preserved as a historic site. In 1874, MacGregor incorporated a company to build a new toll road from Lyons, Colorado, to Estes Park. The road became what is today U.S. Highway 36. Before that time, however, the “road” was only a trail fit for pack horses. The improved road brought more visitors into Estes Park; some of them became full-time residents and built new hotels to accommodate the growing number of travelers.
In 1884, Enos Mills (1870-1922) left Kansas and came to Estes Park, where his relative Elkanah Lamb lived. That move proved significant for Estes Park because Mills became a naturalist and conservationist who devoted his life after 1909 to preserving nearly a thousand square miles of Colorado as Rocky Mountain National Park. He succeeded and the park was dedicated in 1915.
Enos Mills’ younger brother Joe Mills (1880-1935) came to Estes Park in 1889. He wrote a series of articles about his youthful experiences for Boys Life which were later published as a book. After some years as a college athletics coach, he and his wife returned to Estes Park and built a hotel called The Crags on the north side of Prospect Mountain, overlooking the village. They ran that business in the summer while he continued his coaching career in winters at University of Colorado in Boulder.
Many early visitors came to Estes Park in search of better health. The Rocky Mountain West especially attracted those with pulmonary diseases, and in Estes Park some resorts catered to them, providing staff physicians for their care.
Recent history
In 1903, a new road was opened from Loveland through the Big Thompson River canyon to Estes Park, increasing access to the valley. In 1907, three Loveland men established the first auto stage line from Loveland to Estes Park with three five-passenger touring Stanley Steamers. The following year, Mr. Stanley built nine-passenger steam busses and opened a bus line between Lyons and Estes Park.
By 1912, Estes Park had its own seasonal newspaper, the Estes Park Trail, which provided advertising for the local hotels and other businesses. It was a year-round weekly by 1921. In 1949, Olympus Dam was finished, creating Lake Estes, giving the town its main source of drinking water.
Today, Estes Park’s outskirts include The Stanley Hotel, built in 1909. An example of Edwardian opulence, the building had Stephen King as a guest, inspiring him to change the locale for his novel The Shining from an amusement park to the Stanley’s fictional stand-in, the Overlook Hotel. Olympus Dam, on the outskirts of the town, is the dam that creates Lake Estes, a lake which is the site for boating and swimming in Estes Park. There are some hotels on the shore, including the Estes Park Resort.
Land was still being homesteaded in the area in 1914, when Katherine Garetson (1877-1963) filed on land near the base of Longs Peak. She built a cabin and started a business known as the Big Owl Tea Place. She proved up on her homestead claim in 1915, and left a memoir of her years there.
In 1916 the Estes Valley Library was founded by the Estes Park Women’s Club. It originally formed part of the old schoolhouse and contained only 262 printed works.
Estes Park was also the site of the organization of the Credit Union National Association, an important milestone in the history of American credit unions.
Trail Ridge Road, the highest continuous highway in the United States, runs from Estes Park westward through Rocky Mountain National Park, reaching Grand Lake over the continental divide.
The town suffered severe damage in July 1982 from flooding caused by the failure of Lawn Lake Dam. The flood’s alluvial fan can still be seen on Fall River Road. The downtown area was extensively renovated after the flood, and a river walk was added between the main street, Elkhorn Avenue, and the Big Thompson River.
Historic ski areas
Estes Park was home to a number of now defunct ski areas:
- Davis Hill
- Hidden Valley
- Leydman Hill Jump
- Old Man Mountain
Estes Park vicinity was also the home of other resorts and tourist attractions.
Major flooding events
The town flooded in 1982 and suffered extensive damage due to the failure, “after years of disrepair and neglect”, of an earthen dam several miles upstream.
Both U.S. Highway 36 and U.S. Highway 34, the major routes into town, were severely damaged. Hundreds of Estes Park residents were also isolated by the destruction of sections of Fish Creek Road and all nine crossings across Fish Creek. Damaged sewer lines dumped raw sewage down the creek and into the Big Thompson River.
Estes Park Road Map
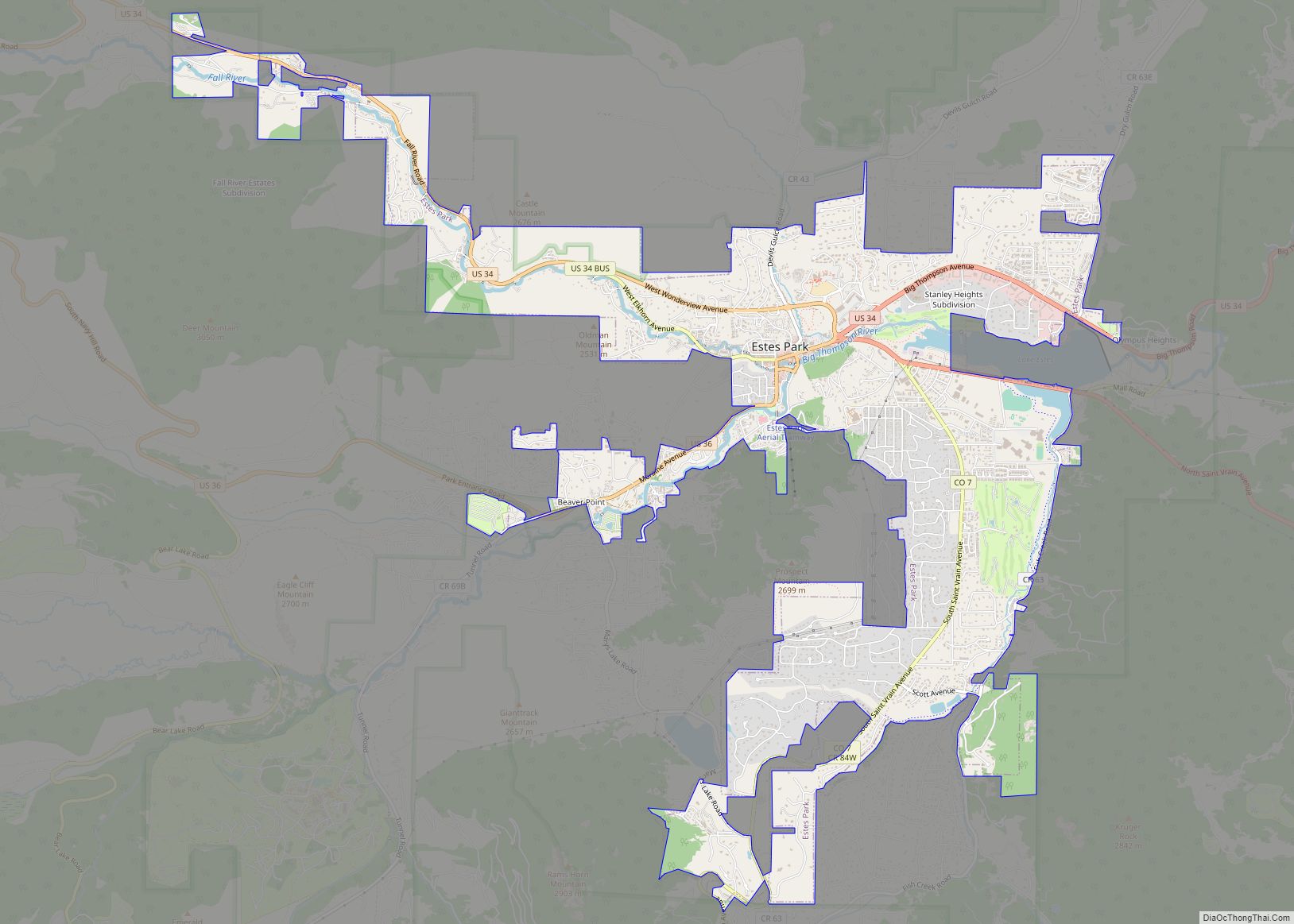
Estes Park city Satellite Map
Geography
Estes Park sits at an elevation of 7,522 feet (2,293 m) on the front range of the Rocky Mountains at the eastern entrance of the Rocky Mountain National Park. Its location is 40°22′22″N 105°31′09″W / 40.372856°N 105.519136°W / 40.372856; -105.519136. Its north, south and east extremities border the Roosevelt National Forest. Lumpy Ridge lies immediately north of Estes Park.
At the 2020 United States Census, the town had a total area of 4,414 acres (17.862 km) including 48 acres (0.194 km) of water.
Climate
Estes Park has a humid continental climate (Koppen: Dfb). Summers days are typically warm, sometimes hot, while winter days are usually cold, with lows dropping into the teens and sometimes the single digits.
See also
Map of Colorado State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Alamosa
- Arapahoe
- Archuleta
- Baca
- Bent
- Boulder
- Broomfield
- Chaffee
- Cheyenne
- Clear Creek
- Conejos
- Costilla
- Crowley
- Custer
- Delta
- Denver
- Dolores
- Douglas
- Eagle
- El Paso
- Elbert
- Fremont
- Garfield
- Gilpin
- Grand
- Gunnison
- Hinsdale
- Huerfano
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Kiowa
- Kit Carson
- La Plata
- Lake
- Larimer
- Las Animas
- Lincoln
- Logan
- Mesa
- Mineral
- Moffat
- Montezuma
- Montrose
- Morgan
- Otero
- Ouray
- Park
- Phillips
- Pitkin
- Prowers
- Pueblo
- Rio Blanco
- Rio Grande
- Routt
- Saguache
- San Juan
- San Miguel
- Sedgwick
- Summit
- Teller
- Washington
- Weld
- Yuma
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming