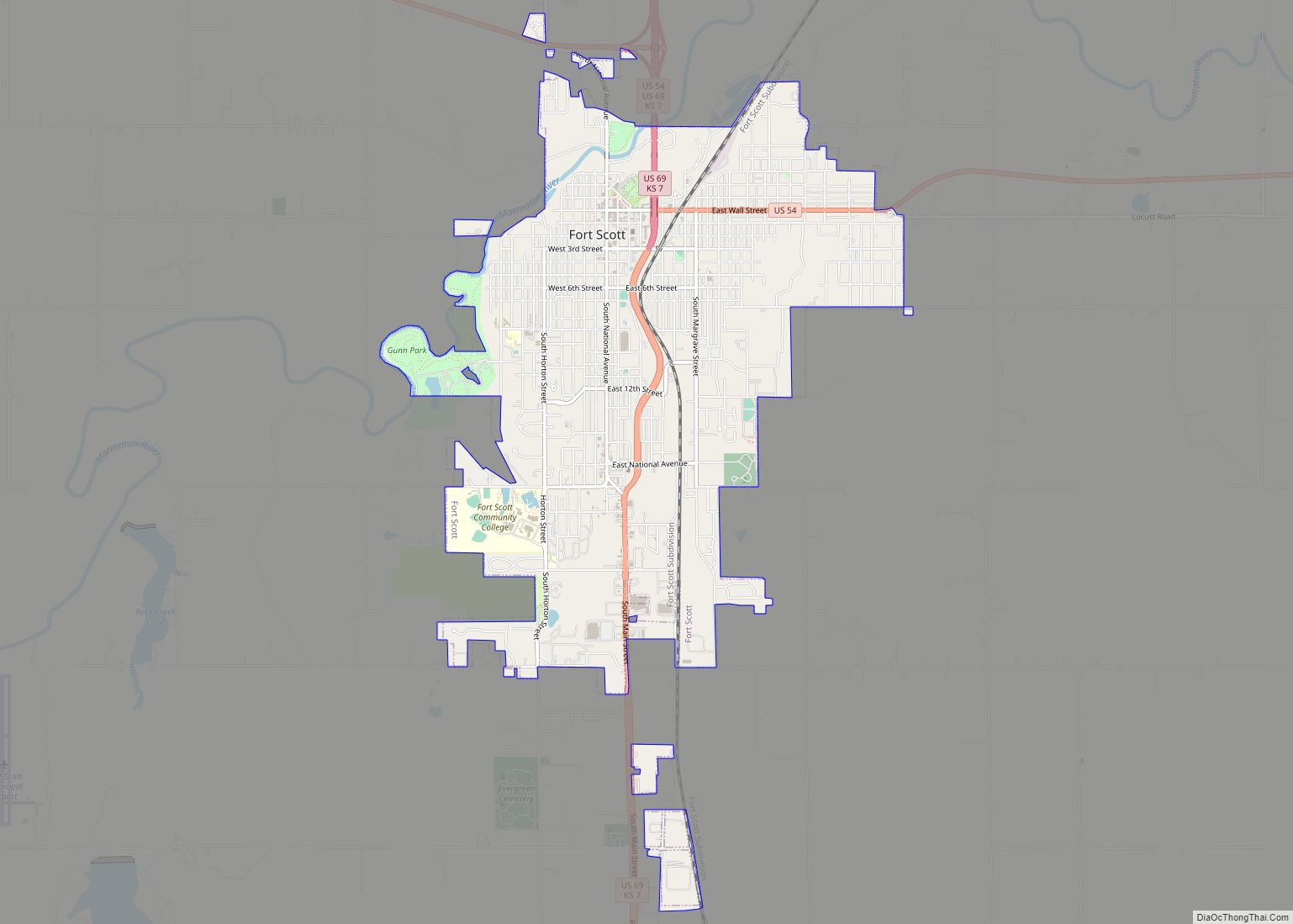
Fort Scott is a city in and the county seat of Bourbon County, Kansas, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 7,552. It is named for Gen. Winfield Scott. The city is located 88 miles (142 km) south of Kansas City on the Marmaton River. It is the home of the Fort Scott National Historic Site and the Fort Scott National Cemetery.
| Name: | Fort Scott city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Kansas |
| County: | Bourbon County |
| Founded: | 1850s |
| Incorporated: | 1860 |
| Elevation: | 846 ft (258 m) |
| Total Area: | 5.63 sq mi (14.58 km²) |
| Land Area: | 5.59 sq mi (14.47 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.04 sq mi (0.11 km²) |
| Total Population: | 7,552 |
| Population Density: | 1,300/sq mi (520/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 66701 |
| Area code: | 620 |
| FIPS code: | 2024000 |
| Website: | fscity.org |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
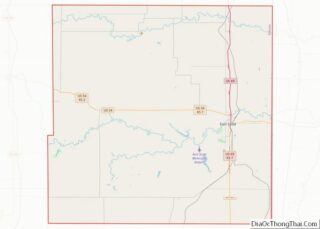
Fort Scott location map. Where is Fort Scott city?
History
Established and garrisoned by the U.S. Army from 1842–1853, soldiers at military Fort Scott assisted with the protection of the Permanent Indian Frontier. After the army abandoned the fort in 1853, the buildings were purchased by local settlers at a government auction in 1855. The community of Fort Scott was laid out in 1857, and was chartered as a city in 1860.
Between 1855 and 1861, the citizens of Fort Scott experienced the violent unrest that preceded the American Civil War on the Kansas and Missouri border. Eastern newspapers described this violence as “Bleeding Kansas”, a result of the national controversy concerning the extension of slavery into the new territories. On January 29, 1861, Kansas entered the union as a free state, but the turmoil of “Bleeding Kansas” continued throughout the Civil War.
During the Civil War, Fort Scott was a U.S Army district Headquarters, quartermaster supply depot, training center, and recruitment station. It was strategically vital to the defense of Kansas and the Midwest. A battle over the fort occurred in August 1861 just across the Missouri line in the Battle of Dry Wood Creek. The battle was a pro-South victory for Sterling Price and his Missouri State Guard. Price did not hold the fort and instead continued a northern push into Missouri in an attempt to recapture the state. James H. Lane (Senator) was to launch a Jayhawker offensive behind Price from Fort Scott that led to the Sacking of Osceola. The ill will of these actions was to be the basis for the 1976 Clint Eastwood film The Outlaw Josey Wales.
After the Civil War, Fort Scott was a premier city of the frontier, one of the largest cities in eastern Kansas. On three occasions, between 1870 and 1900, Fort Scott was in competition with Kansas City to become the largest railroad center west of the Mississippi. During the first half of the 20th century, Fort Scott became an agricultural and small industrial center which it continues to be today.
Downtown fire
On March 11, 2005, a fire destroyed several historic buildings in Fort Scott’s downtown. The Victorian-era buildings were among many that are a symbol of the town.
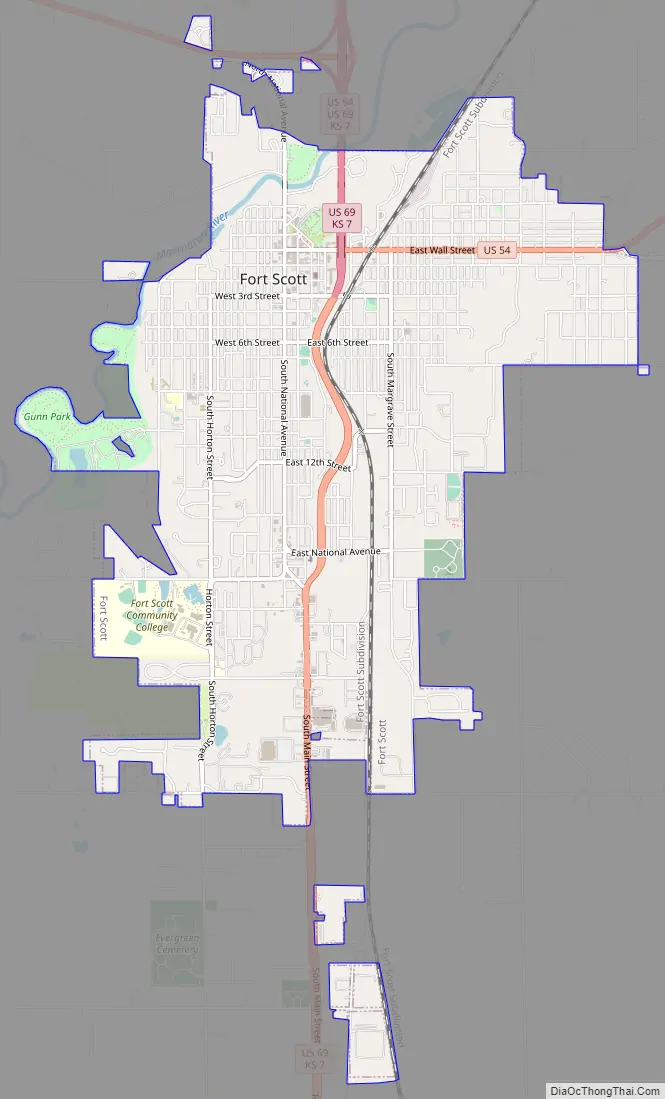
Fort Scott Road Map
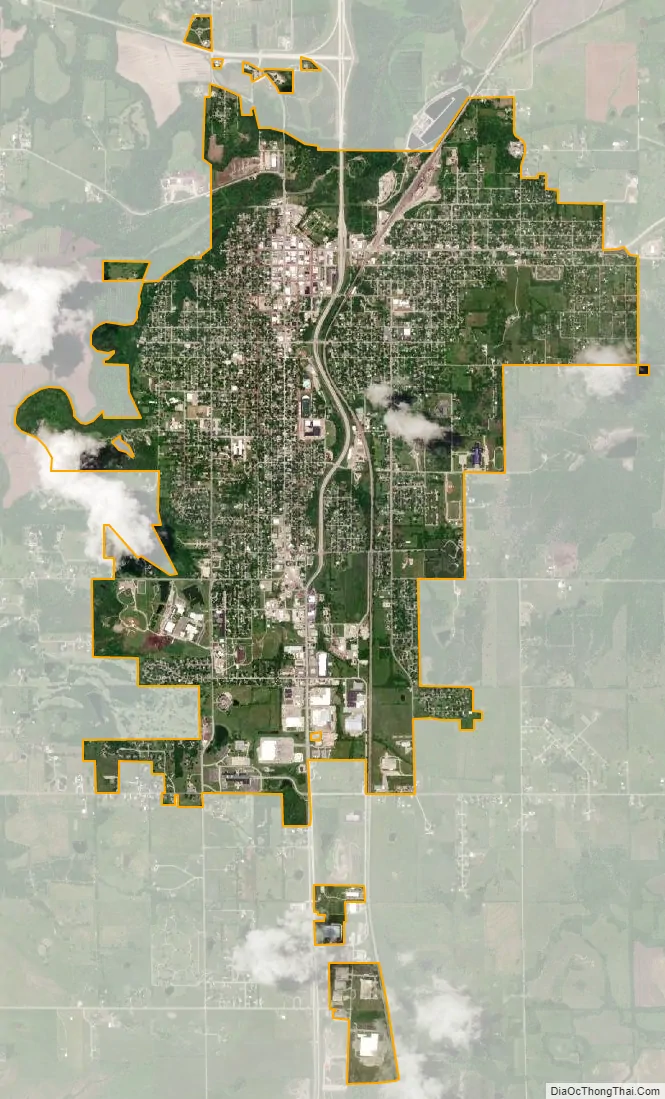
Fort Scott city Satellite Map
Geography
Fort Scott is located at 37°50′7″N 94°42′7″W / 37.83528°N 94.70194°W / 37.83528; -94.70194 (37.835180, −94.702015) at an elevation of 846 feet (258 m). It lies on the Osage Plains on the south side of the Marmaton River. Located at the intersection of U.S. Routes 54 and 69 in southeast Kansas, Fort Scott is approximately 54 miles (87 km) north of Joplin, Missouri, 92 miles (148 km) south of Kansas City, and 143 miles (230 km) east of Wichita.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 5.59 square miles (14.48 km), of which 5.55 square miles (14.37 km) is land and 0.04 square miles (0.10 km) is water.
Climate
Fort Scott has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cfa) with hot, humid summers and cool winters. The average temperature in Fort Scott is 57 °F or 13.9 °C with temperatures exceeding 90 °F or 32.2 °C on an average of 52.6 afternoons a year and dropping below 32 °F or 0 °C during an average of 100.6 mornings per year. On average, Fort Scott experiences 83.3 days of precipitation a year. Annual snowfall averages 8.4 inches or 0.21 metres. Precipitation averages 44.49 inches or 1,130 millimetres per year. On average, January is the coolest month, July the hottest and June the wettest. The hottest temperature recorded in Fort Scott was 120 °F (48.9 °C); recorded twice on July 13, 1954 and July 14, 1954. The coldest temperature recorded was −24 °F (−31.1 °C) on February 13, 1905.
See also
Map of Kansas State and its subdivision:- Allen
- Anderson
- Atchison
- Barber
- Barton
- Bourbon
- Brown
- Butler
- Chase
- Chautauqua
- Cherokee
- Cheyenne
- Clark
- Clay
- Cloud
- Coffey
- Comanche
- Cowley
- Crawford
- Decatur
- Dickinson
- Doniphan
- Douglas
- Edwards
- Elk
- Ellis
- Ellsworth
- Finney
- Ford
- Franklin
- Geary
- Gove
- Graham
- Grant
- Gray
- Greeley
- Greenwood
- Hamilton
- Harper
- Harvey
- Haskell
- Hodgeman
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Jewell
- Johnson
- Kearny
- Kingman
- Kiowa
- Labette
- Lane
- Leavenworth
- Lincoln
- Linn
- Logan
- Lyon
- Marion
- Marshall
- McPherson
- Meade
- Miami
- Mitchell
- Montgomery
- Morris
- Morton
- Nemaha
- Neosho
- Ness
- Norton
- Osage
- Osborne
- Ottawa
- Pawnee
- Phillips
- Pottawatomie
- Pratt
- Rawlins
- Reno
- Republic
- Rice
- Riley
- Rooks
- Rush
- Russell
- Saline
- Scott
- Sedgwick
- Seward
- Shawnee
- Sheridan
- Sherman
- Smith
- Stafford
- Stanton
- Stevens
- Sumner
- Thomas
- Trego
- Wabaunsee
- Wallace
- Washington
- Wichita
- Wilson
- Woodson
- Wyandotte
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming