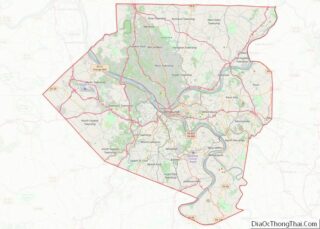
Bethel Park (officially the Municipality of Bethel Park) is a borough with home rule status in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, United States. It is a suburb within the Pittsburgh metropolitan area, located approximately 7 miles (11 km) southwest of Pittsburgh. The population was 33,577 as of the 2020 census.
| Name: | Bethel Park municipality |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 37 |
| LSAD Description: | municipality (suffix) |
| State: | Pennsylvania |
| County: | Allegheny County |
| Incorporated: | 1949 (borough) |
| Elevation: | 1,197 ft (365 m) |
| Total Area: | 11.70 sq mi (30.31 km²) |
| Land Area: | 11.70 sq mi (30.31 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km²) |
| Total Population: | 33,577 |
| Population Density: | 2,869.34/sq mi (1,107.85/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 15102, 15234, 15236, 15241 |
| Area code: | 412 |
| FIPS code: | 4206064 |
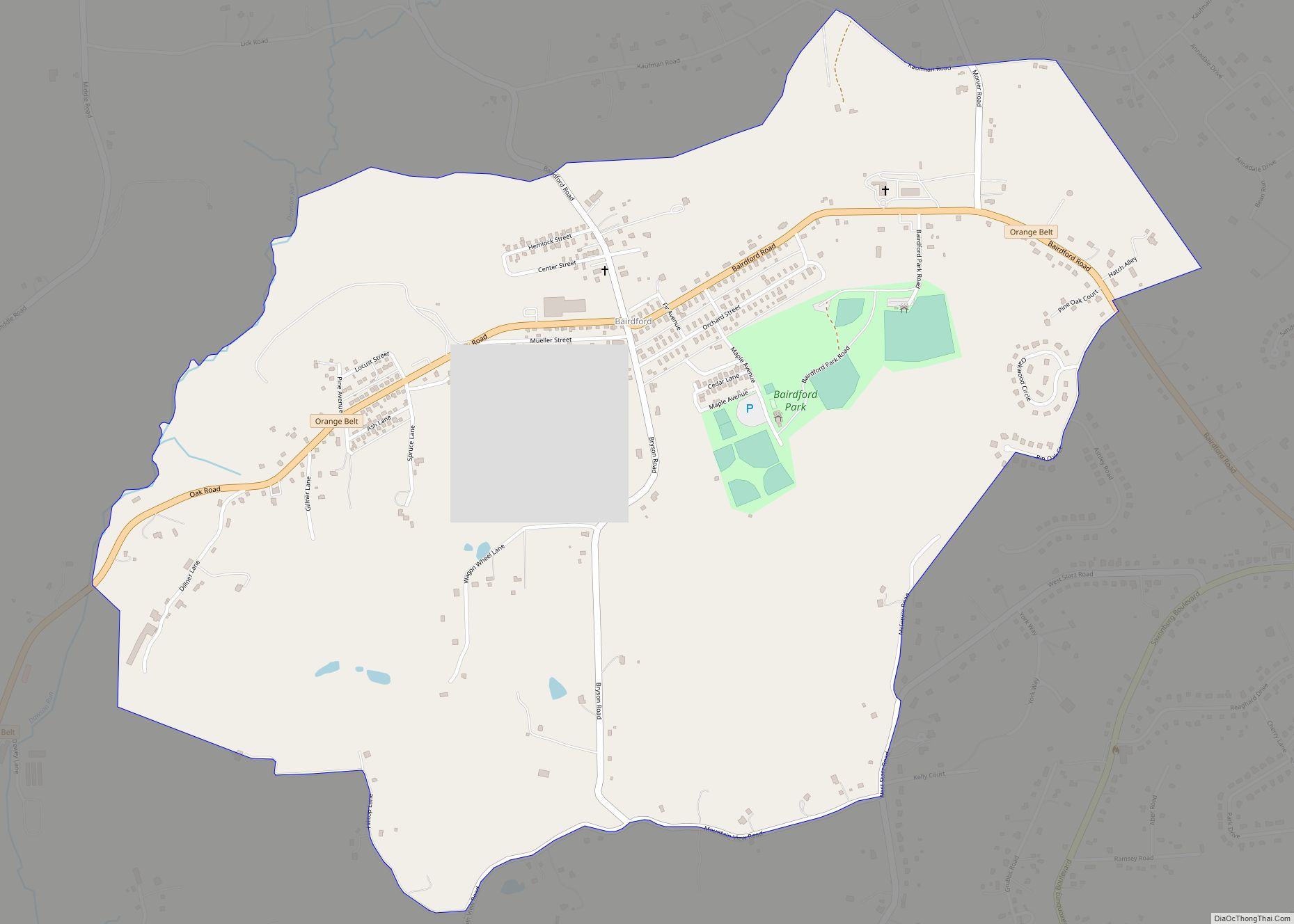
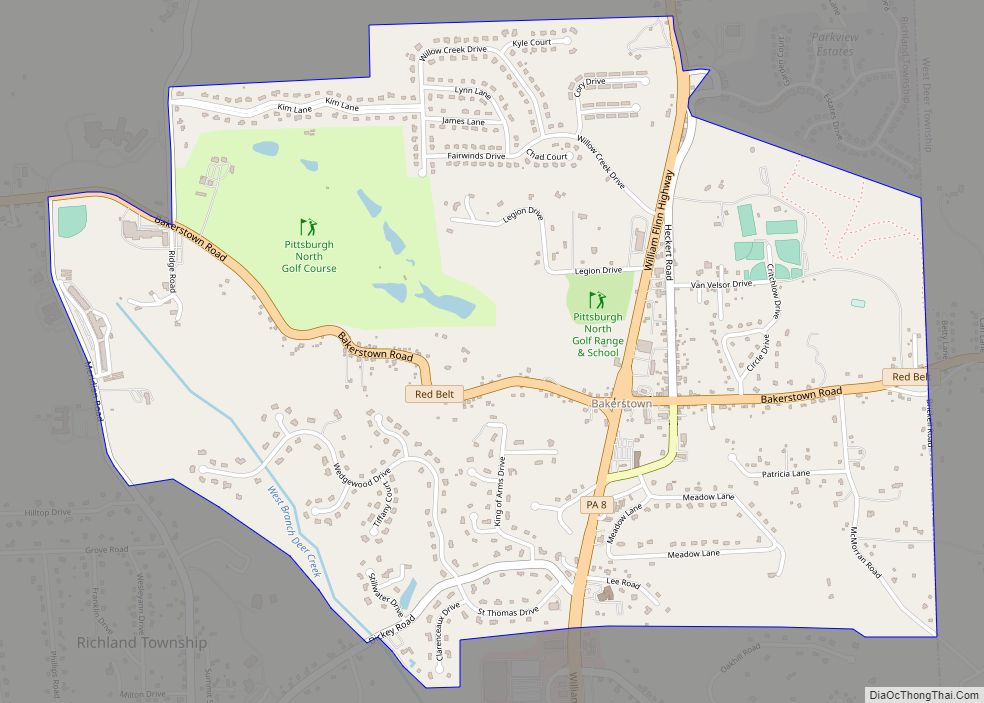
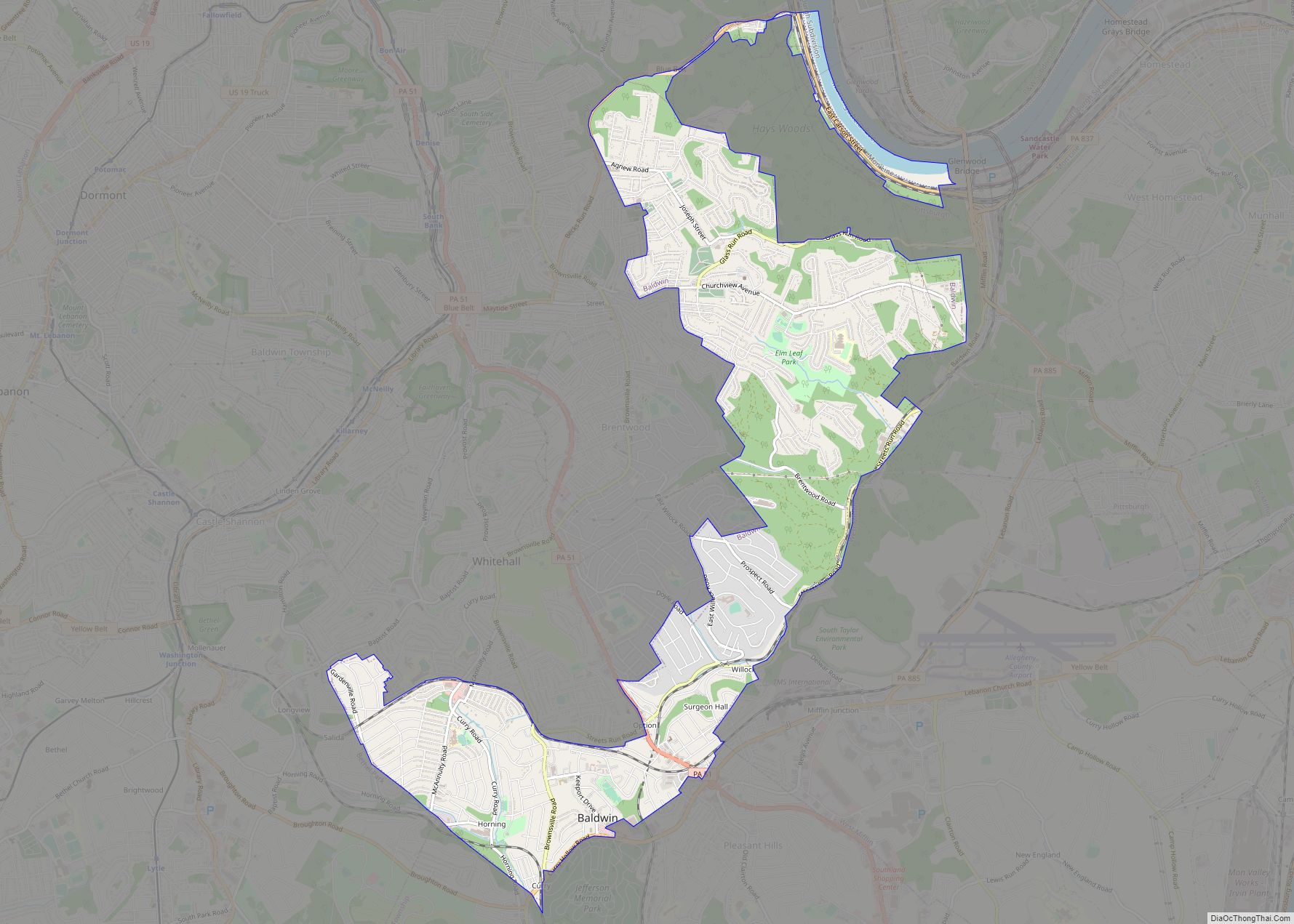
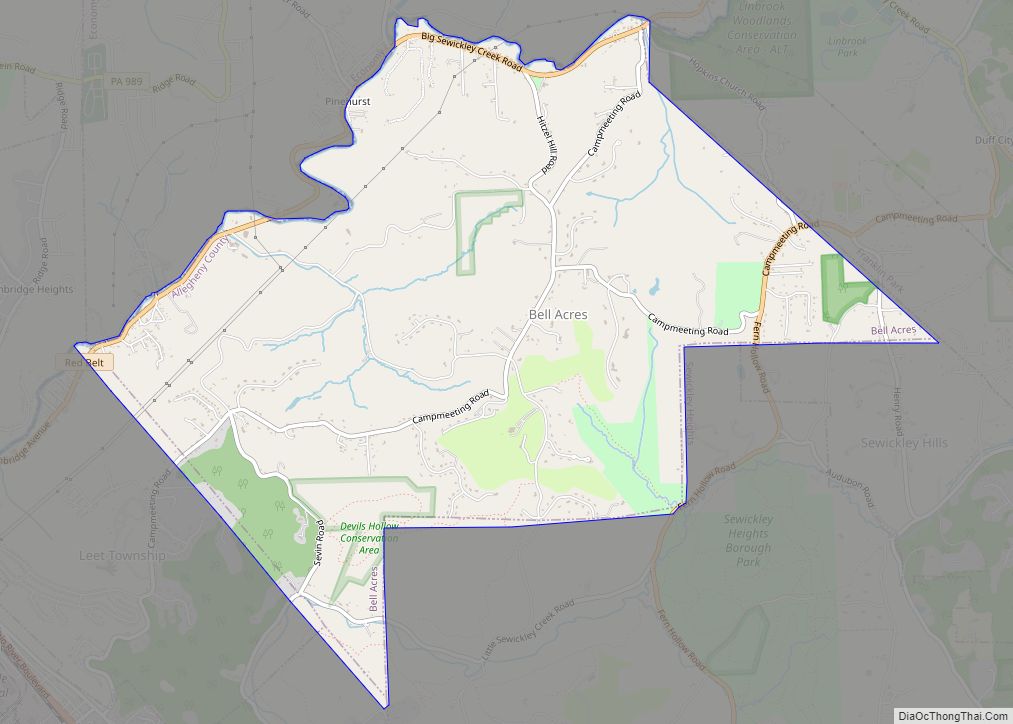
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Bethel Park location map. Where is Bethel Park municipality?
History
The area that is now Bethel Park was originally settled around 1800 and was established as Bethel Township in 1886. It was named after Bethel Presbyterian Church, which in turn was named after the ancient Israelite sanctuary of Bethel. Bethel Park was incorporated as a borough on March 17, 1949, and became a home rule municipality in 1978.
The first armored car robbery in the U.S. occurred on March 11, 1927, when a Brinks truck, heading towards the Coverdale Mine about a mile away was attacked. Paul Jaworski and Flatheads gang destroyed the road with dynamite to steal a mining payroll.
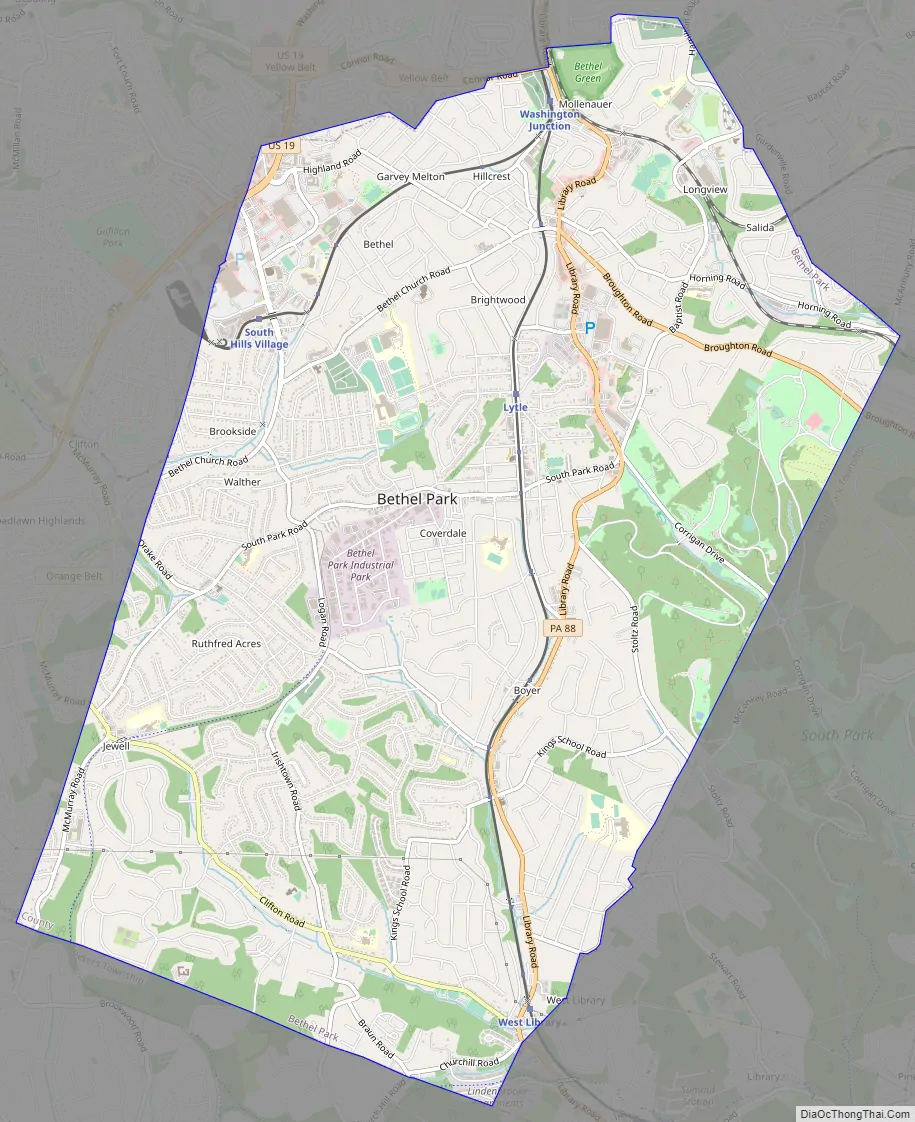
Bethel Park Road Map
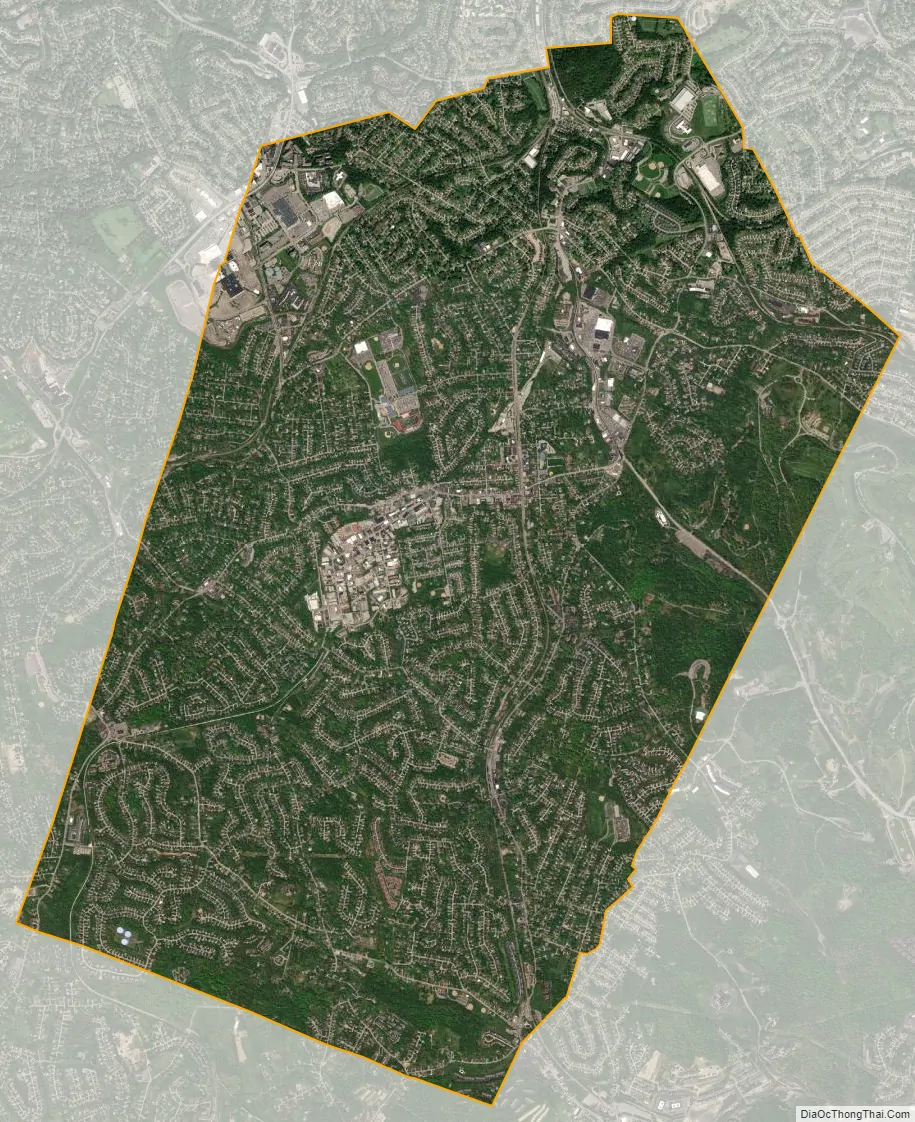
Bethel Park city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the borough had a total area of 11.7 square miles (30 km), all land. Its average elevation is 1,197 feet (365 m) above sea level. Bethel Park lies at the margin between the Pittsburgh Low Plateau and Waynesburg Hills Sections of the Allegheny Plateau physiographic province. The area is characterized as a maturely dissected region where the ephemeral minor tributaries converge into the tributaries of principal streams.
The highest point in Bethel Park is Rocky Ridge, in the southwestern portion of the borough, 1,370 feet (420 m), and the lowest point is at the intersection of the Piney Fork and Alsip Run creeks, 980 feet (300 m), in the southeast corner.
Surrounding towns
Bethel Park has seven borders, including Castle Shannon to the north, Whitehall to the north-northeast, Baldwin to the northeast, South Park to the east and southeast, Peters Township in Washington County to the south, Upper St. Clair to the west, and Mt. Lebanon to the north-northwest.
Geology
The exposed rocks in Bethel Park are mostly composed of sandstone, limestone, shale, and a few coal layers (Redstone, Waynesburg, Washington, etc.). The ages of the exposed rocks bracket the late Pennsylvanian epoch (Gzhelian age; approximately 303 million years ago) near the lowest elevations, and Early Permian period (Asselian age; approximately 297 million years ago) near the highest parts of the southern part of Bethel Park (e.g. Rocky Ridge). These sedimentary rocks were deposited as the sea level rose and fell along an ancient coastline (with the region alternating between delta, shallow lake, and shallow sea), and finally being uplifted with the formation of the Appalachian Mountains.
Bethel Park is underlain by the Pennsylvania-age Monongahela Formation. The Monongahela Formation consists of the Uniontown member and the underlying Pittsburgh member, and the base is the Pittsburgh coal seam. Much of southern Allegheny County is undermined, and the PADEP indicates that all of Bethel Park was undermined.
A portion of the area is underlain by the Pittsburgh Terminal No. 8 Mine (Cortis and others, 1975), which was commonly known as the “H” Mine and the Coverdale Mine. The mine opened around 1920. The historic operations of the Coverdale Mine are apparent on a Bridgeville 7.5-minute topographic map. A “Mine Dump” is shown adjacent to the Montour Railroad tracks and South Park Road. Coal was mined through vertical shafts accessing inclined slopes following the dip of the Pittsburgh coal seam. Mine voids in the inclined slope resulted from the practice of room and pillar mining during the early 20th century. The Coverdale Mine is closed and largely unflooded.
See also
Map of Pennsylvania State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Allegheny
- Armstrong
- Beaver
- Bedford
- Berks
- Blair
- Bradford
- Bucks
- Butler
- Cambria
- Cameron
- Carbon
- Centre
- Chester
- Clarion
- Clearfield
- Clinton
- Columbia
- Crawford
- Cumberland
- Dauphin
- Delaware
- Elk
- Erie
- Fayette
- Forest
- Franklin
- Fulton
- Greene
- Huntingdon
- Indiana
- Jefferson
- Juniata
- Lackawanna
- Lancaster
- Lawrence
- Lebanon
- Lehigh
- Luzerne
- Lycoming
- Mc Kean
- Mercer
- Mifflin
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Montour
- Northampton
- Northumberland
- Perry
- Philadelphia
- Pike
- Potter
- Schuylkill
- Snyder
- Somerset
- Sullivan
- Susquehanna
- Tioga
- Union
- Venango
- Warren
- Washington
- Wayne
- Westmoreland
- Wyoming
- York
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming