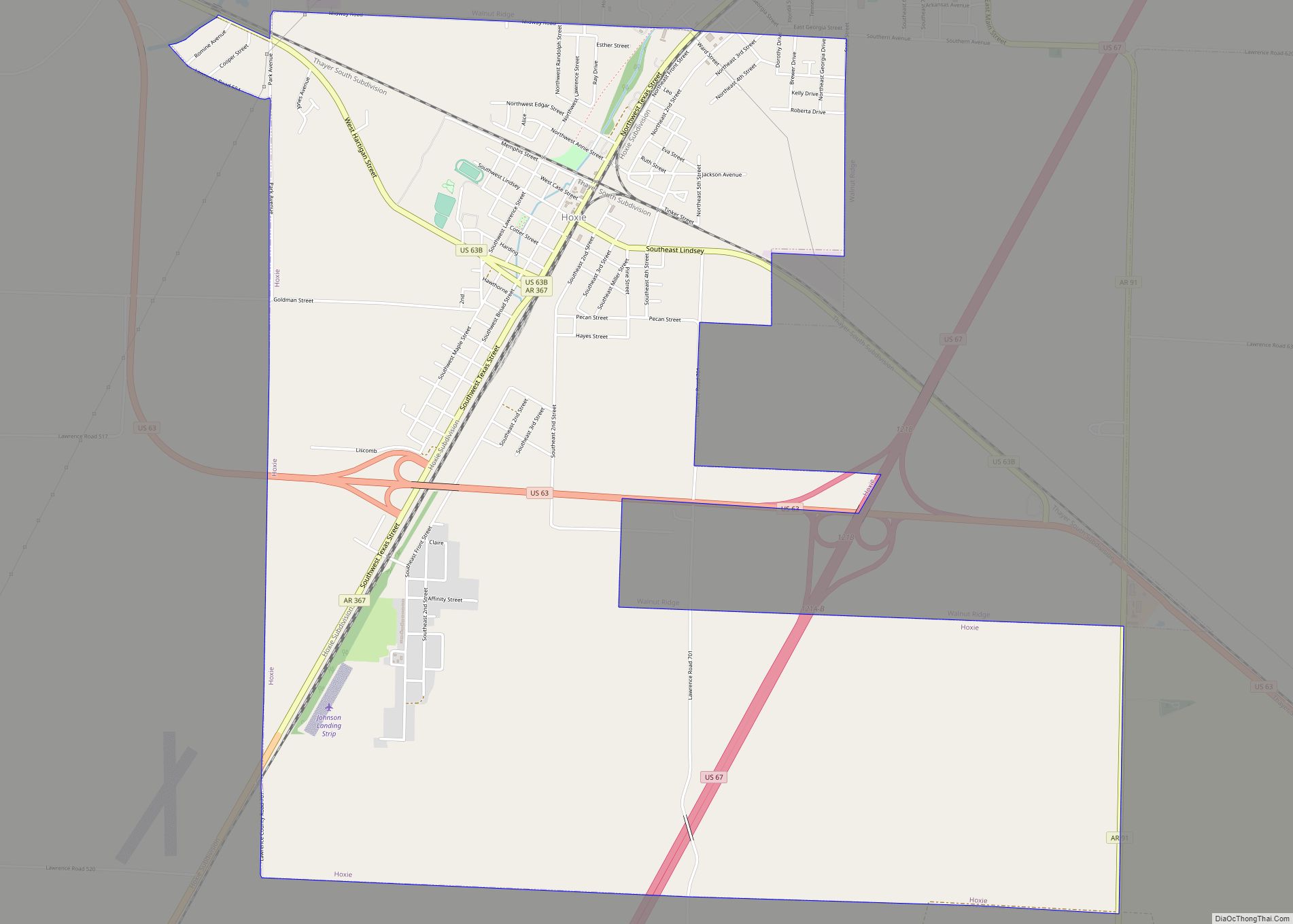
Hoxie is a city in Lawrence County, Arkansas, United States. It lies immediately south of Walnut Ridge. The population was 2,780 at the 2010 census.
| Name: | Hoxie city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Arkansas |
| County: | Lawrence County |
| Elevation: | 266 ft (81 m) |
| Total Area: | 6.67 sq mi (17.26 km²) |
| Land Area: | 6.67 sq mi (17.26 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km²) |
| Total Population: | 2,598 |
| Population Density: | 389.74/sq mi (150.48/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 72433 |
| Area code: | 870 |
| FIPS code: | 0533580 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0057952 |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
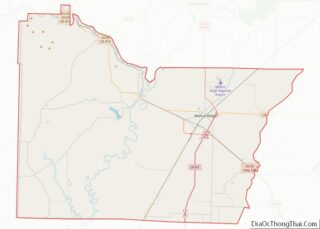
Hoxie location map. Where is Hoxie city?
History
The third Arkansas school to integrate
Prior to 1955, Hoxie maintained a dual system of education for younger students, one for white students and another one for black students. Rather than maintain two high schools, white high school students were educated locally, while black high school students were bused to a black school in Jonesboro. The negro school for grades 1-8 had only one teacher. On June 25, 1955, in response to the recent Brown v. Board of Education ruling, Hoxie’s superintendent, Kunkel Edward Vance, spearheaded plans to integrate the schools, and he received the unanimous support of Hoxie’s school board. On July 11, 1955, Hoxie schools recommenced and allowed African American students to attend. In order to do “what was morally right in the sight of God” and to “uphold the law of the land”, Vance insisted that all facilities, including restrooms and cafeterias, be integrated.
Although there were many nervous parents, the schools opening on July 11 went smoothly. The teachers and children got along fine, but unlike the two other school districts in Arkansas (Charleston and Fayetteville) that implemented partial integration, Hoxie attracted national attention. A team of photographers from Life Magazine was on hand to document the event. After the publication of the Life article, segregationists from outside the area converged on Hoxie in an unsuccessful attempt to reverse the school board decision. Handbills were printed making wild assertions including allegations of a plot between negroes, Communists, and Jews, and advocating for the death of “Race Mixers”. A group of local citizens, led by soybean farmer Herbert Brewer, confronted the school board in an unproductive meeting. After the meeting, Brewer organized a White Citizen’s Council, which called for students, both black and white to boycott the schools. Approximately one third of the white students refused to attend the schools beginning on August 4, 1955.
A lawyer, Amis Guthridge, the leader of White America, inc., attempted to draw more outside influence into the fray, inflaming passions with statements such as calling school integration a “plan that was founded in Moscow in 1924 to mongrelize the white race in America” and claimed that “white Methodist women” wanted integration so they could get negro men into their bedroom. Johnson, Guthridge and others fanned the flames, and were joined by Orval Faubus in trying to invoke fears of miscegenation in white husbands and parents. In one rally, a speaker shouted “they do not want equality, you know they don’t want equality”…”They want what you’ve got, they want your women!”
The Hoxie School Board filed suit against the segregationist leaders from Hoxie and elsewhere in the state and charged them with trespassing on school property, threatening picket lines, organizing boycotts, and intimidating school officials. In November 1955, United States District Judge for the Eastern District of Arkansas Thomas C. Trimble ruled that pro-segregationists had “planned and conspired” to prevent integration in Hoxie. In December 1955, he issued a permanent injunction and restraining order against the segregationists. Their appeal in the Eighth Circuit Court of Appeals was opposed by United States Attorney General Herbert Brownell and the U.S. Department of Justice. This marked the first intervention by the attorney general in support of any school district attempting to comply with the Brown decision. On October 25, 1956, the court ruled in favor of the Hoxie School Board.
U.S. Attorney Osro Cobb recalls that the situation at Hoxie
In 2003, David Appleby produced a documentary entitled Hoxie – The First Stand detailing the events of school integration in Hoxie. The film later received the Peabody Award and the Du Pont Award for Broadcast Journalism.
Train crash
On August 17, 2014, at 2:30 AM, two Union Pacific freight trains collided in Hoxie, killing two people and causing the evacuation of about 500 people within a 1.5 square mile radius. U.S. 67 was closed for approximately one week for cleanup and repair.
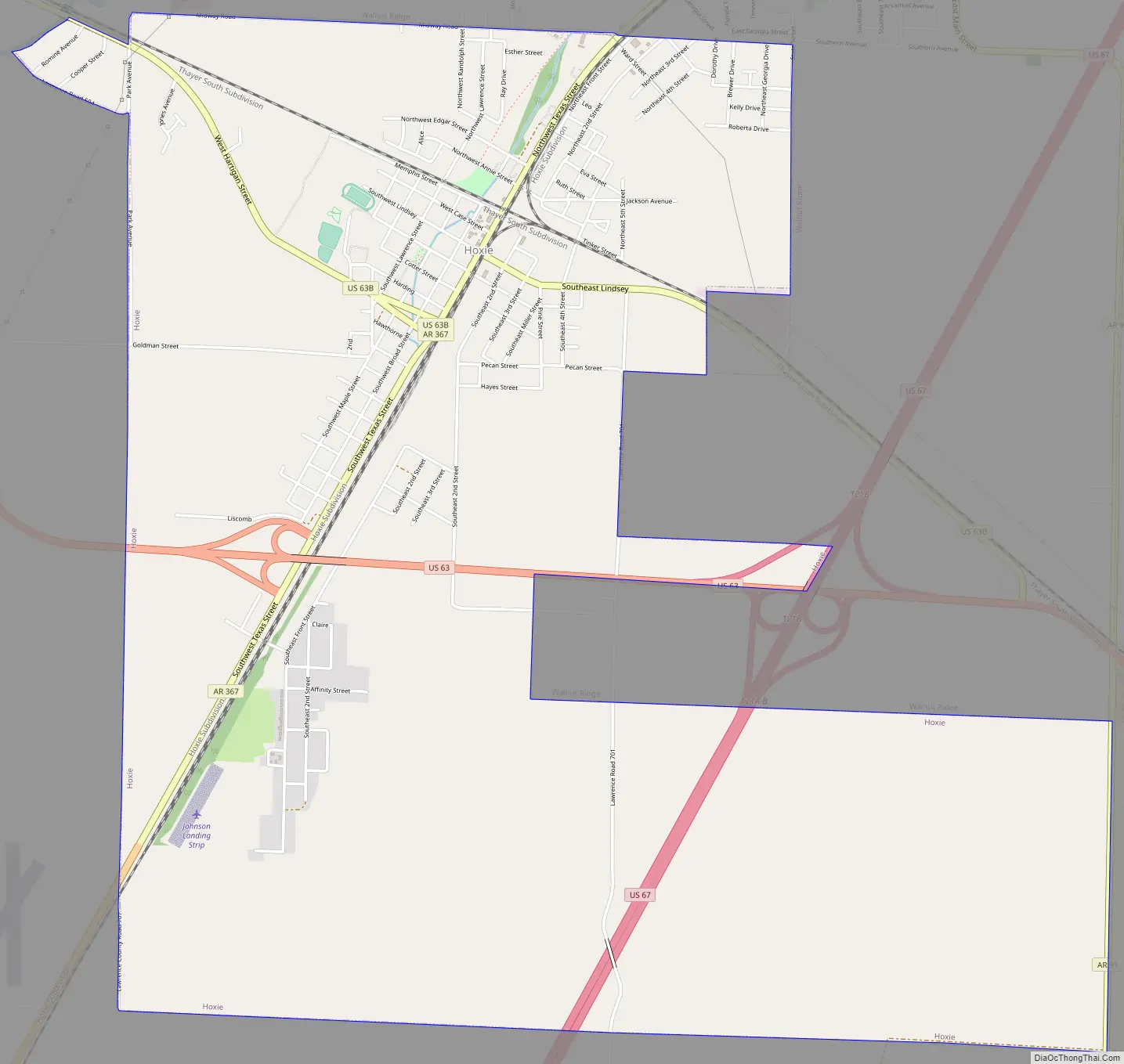
Hoxie Road Map
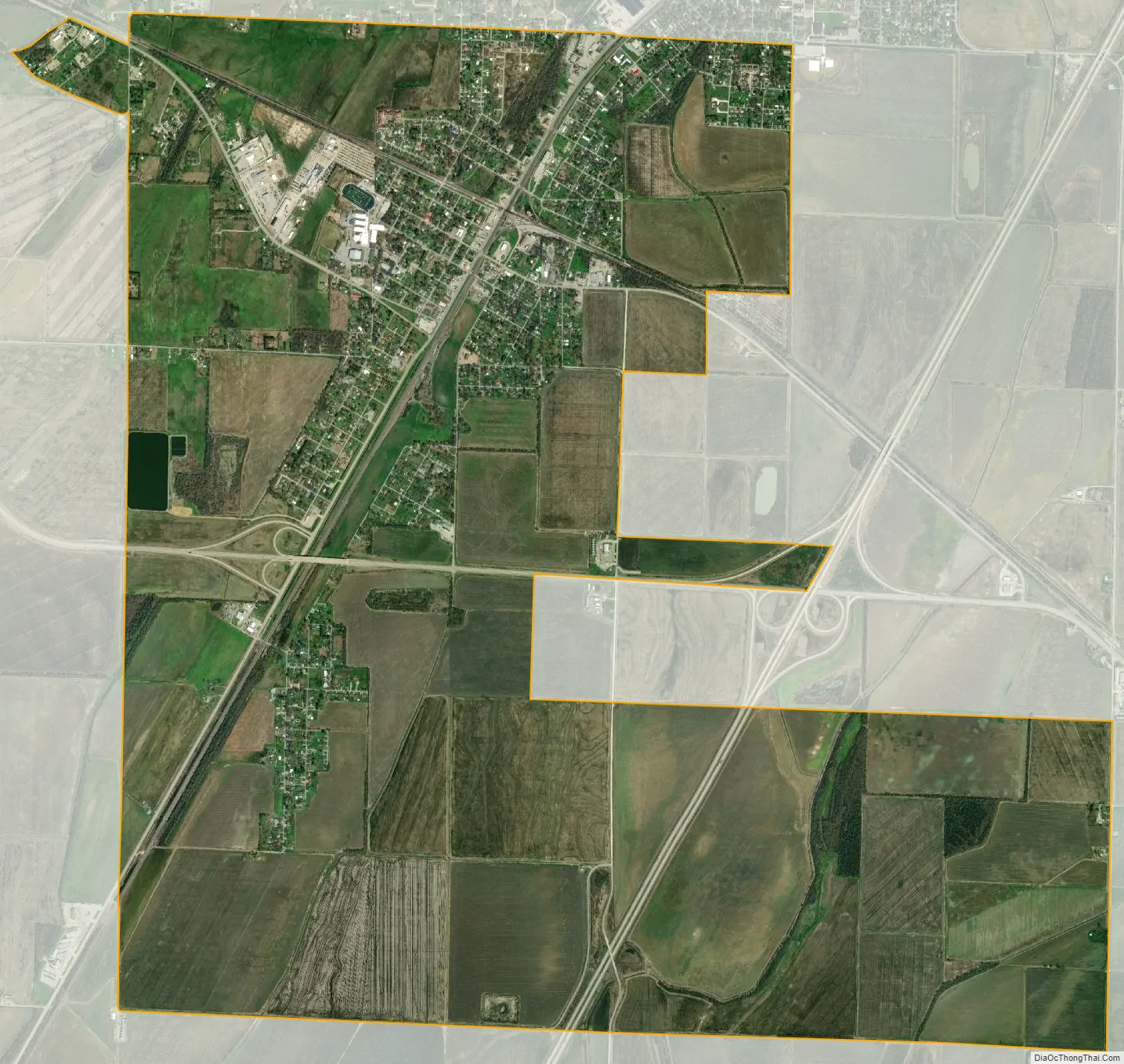
Hoxie city Satellite Map
Geography
Hoxie is located at 36°2′55″N 90°58′38″W / 36.04861°N 90.97722°W / 36.04861; -90.97722 (36.048616, -90.977296).
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 4.0 square miles (10 km), all land.
List of highways
- US 63
- U.S. 63 Business
- US 67
- U.S. 67 Business
U.S. Highways 63 and 67 intersect and cross each other in Hoxie. U.S. 63 enters Arkansas at the Missouri line at Thayer, Missouri, and Mammoth Spring, Arkansas, two contiguous cities. U.S. 63 then goes southeastward to connect with Interstate 55 near Turrell, in Crittenden County. It runs contiguous with I-55 and I-40 for a ways. Both those interstates cross the Mississippi River into Memphis, Tennessee. U.S. 63 is then contiguous with a number of other routes southward in Arkansas, leaving Arkansas for Louisiana at Junction City, in Union County. U.S. 67 is a southwest—northeast bisector of Arkansas.
Two railroads, the Burlington Northern-Santa Fe and the Union Pacific, have mainline tracks that cross each other at Hoxie—the BNSF in a generally northwest-southeast direction, and the UP in a generally north and south direction. This same situation also occurs in Jonesboro, in Craighead County.
See also
Map of Arkansas State and its subdivision:- Arkansas
- Ashley
- Baxter
- Benton
- Boone
- Bradley
- Calhoun
- Carroll
- Chicot
- Clark
- Clay
- Cleburne
- Cleveland
- Columbia
- Conway
- Craighead
- Crawford
- Crittenden
- Cross
- Dallas
- Desha
- Drew
- Faulkner
- Franklin
- Fulton
- Garland
- Grant
- Greene
- Hempstead
- Hot Spring
- Howard
- Independence
- Izard
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Johnson
- Lafayette
- Lawrence
- Lee
- Lincoln
- Little River
- Logan
- Lonoke
- Madison
- Marion
- Miller
- Mississippi
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Nevada
- Newton
- Ouachita
- Perry
- Phillips
- Pike
- Poinsett
- Polk
- Pope
- Prairie
- Pulaski
- Randolph
- Saint Francis
- Saline
- Scott
- Searcy
- Sebastian
- Sevier
- Sharp
- Stone
- Union
- Van Buren
- Washington
- White
- Woodruff
- Yell
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming