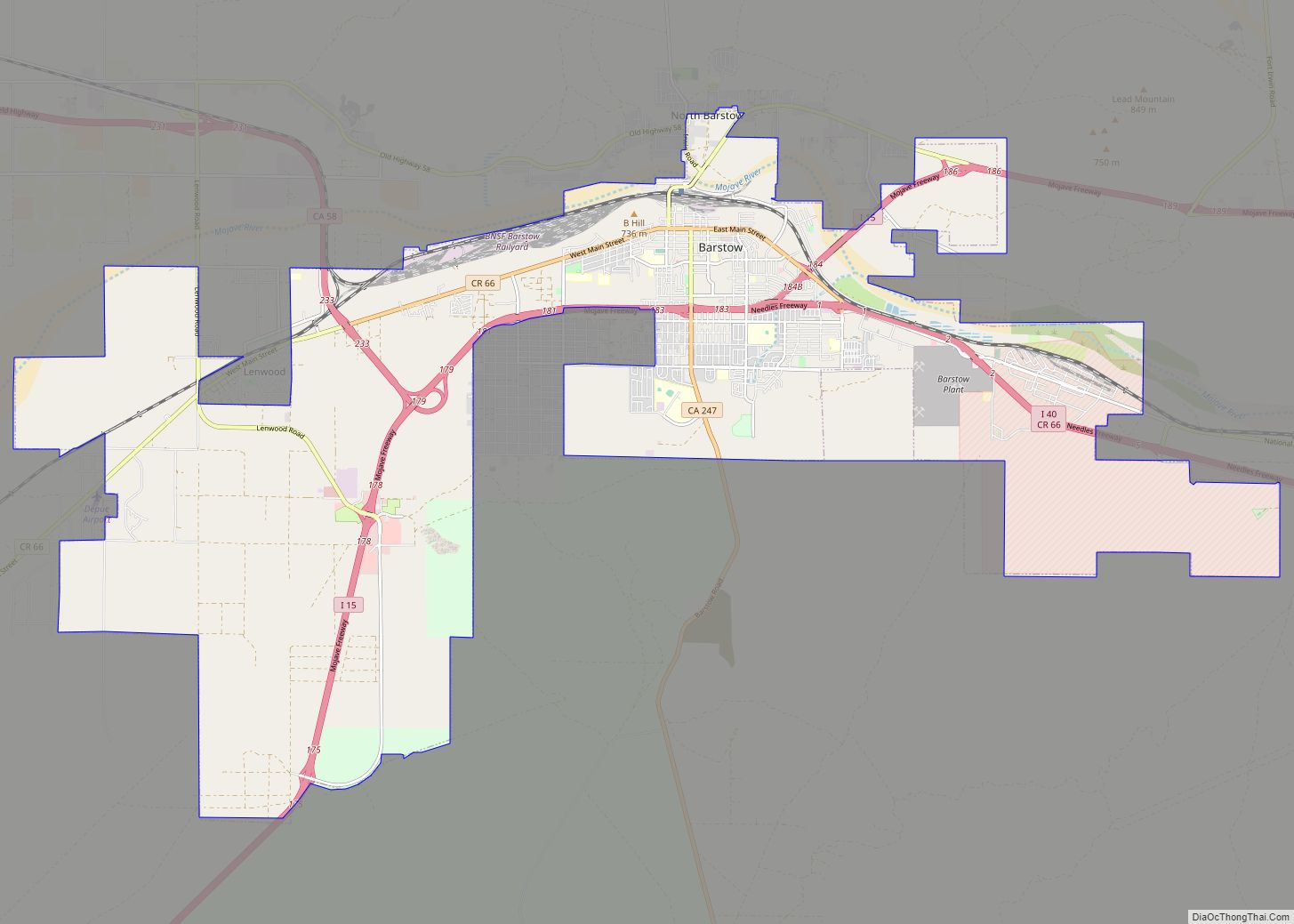
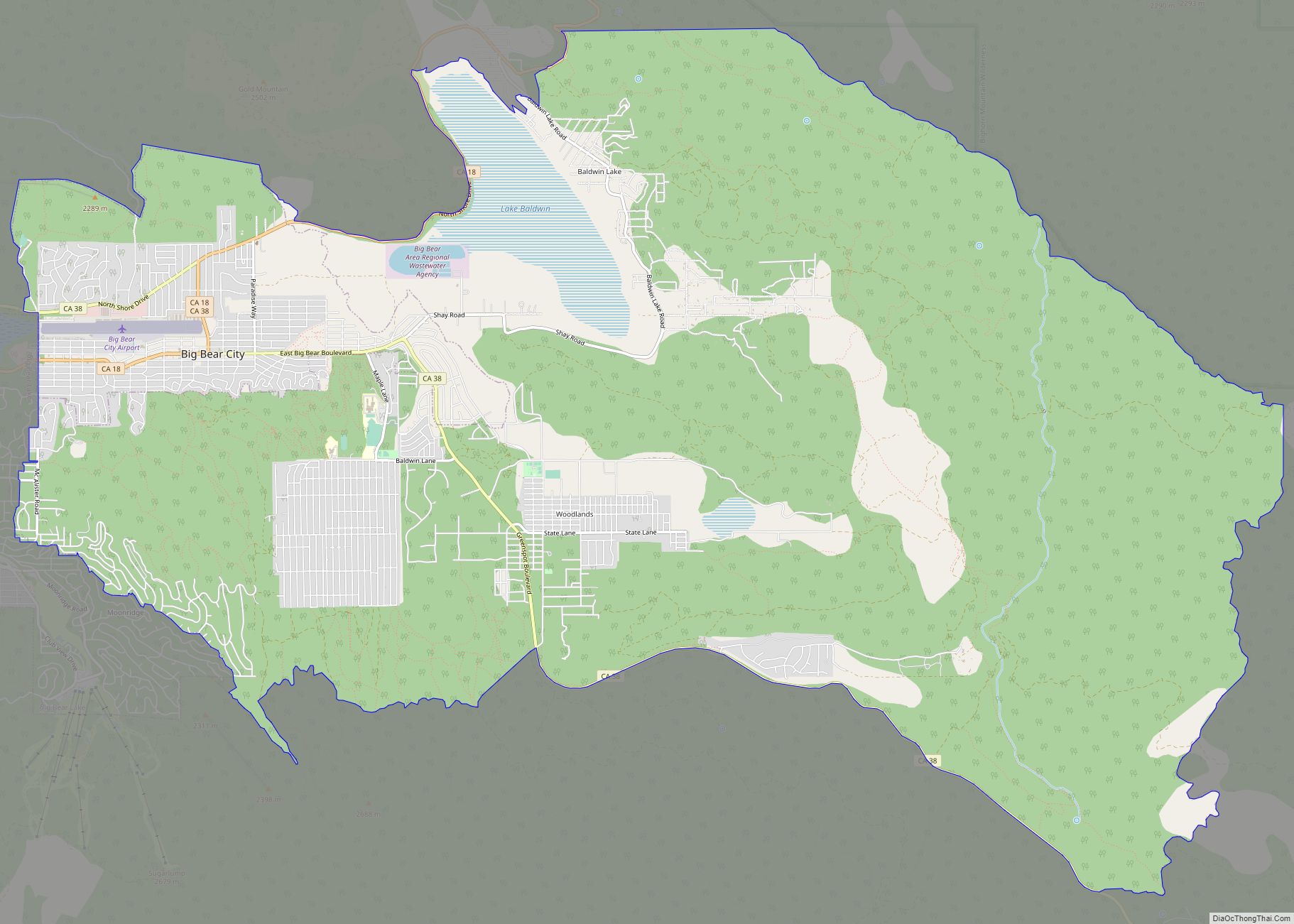
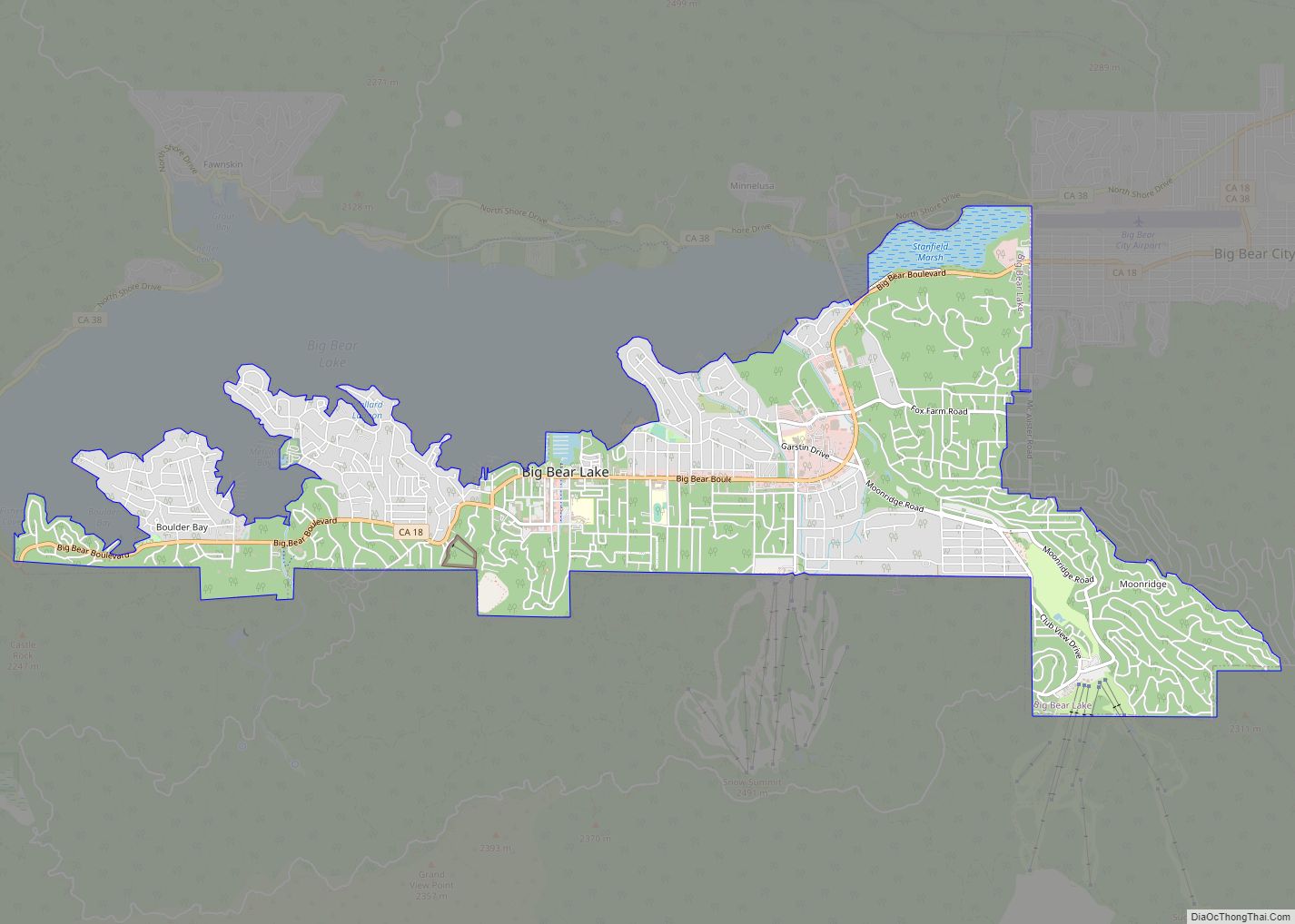
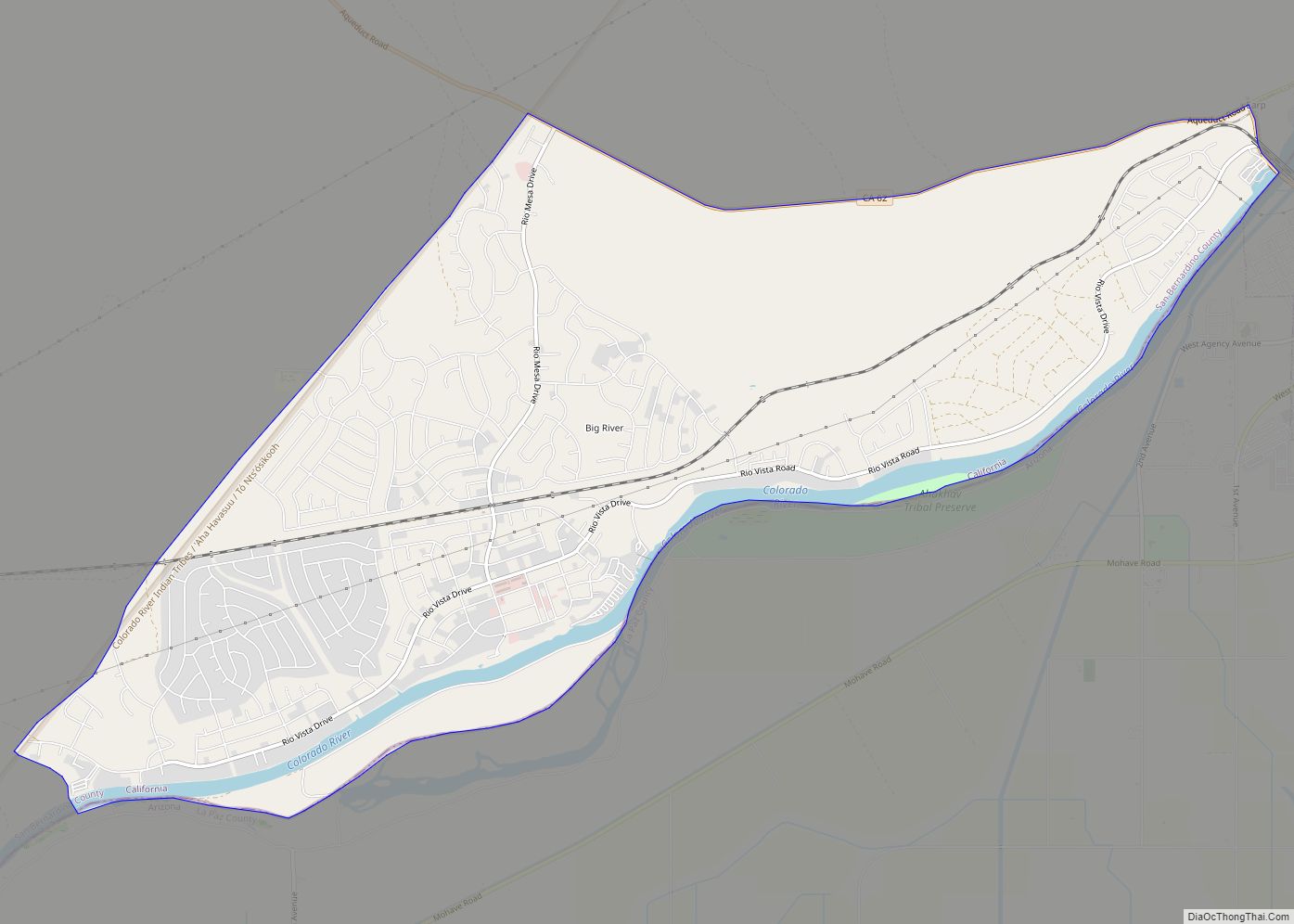
Chino (/ˈtʃiːnoʊ/ CHEE-noh; Spanish for “Curly”) is a city in the western end of San Bernardino County, California, United States, with Los Angeles County to its west and Orange County to its south in the Southern California region. Chino is adjacent to Chino Hills. Chino’s surroundings have long been a center of agriculture and dairy farming, providing milk products in Southern California and much of the southwestern United States. Chino’s agricultural history dates back to the Spanish land grant forming Rancho Santa Ana del Chino. The area specialized in fruit orchards, row crops, and dairy.
Chino is bounded by Chino Hills and Los Angeles County to the west, Pomona to the northwest, unincorporated San Bernardino County (near Montclair) to the north, Ontario to the northeast, Eastvale to the southeast in Riverside County and Orange County to the southwest. It is easily accessible via the Chino Valley (71) and Pomona (60) freeways. The population was 77,983 at the 2010 census.
Downtown Chino is home to satellite branches of the San Bernardino County Library and Chaffey Community College, the Chino Community Theatre, the Chino Boxing Club and a weekly Farmer’s Market. In 2008, the city of Chino was awarded the prestigious “100 Best Communities for Youth” award for the second time in three years. Chino hosted shooting events for the 1984 Summer Olympics at the Prado Olympic Shooting Park in the Prado Regional Park.
| Name: | Chino city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | California |
| County: | San Bernardino County |
| Incorporated: | February 28, 1910 |
| Elevation: | 728 ft (222 m) |
| Total Area: | 29.70 sq mi (76.93 km²) |
| Land Area: | 29.61 sq mi (76.68 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.10 sq mi (0.25 km²) 0.04% |
| Total Population: | 91,403 |
| Population Density: | 3,087.42/sq mi (1,192.05/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 91708, 91710 |
| Area code: | 909 |
| FIPS code: | 0613210 |
| Website: | www.cityofchino.org |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Chino location map. Where is Chino city?
History
The Tongva had a settlement called Wapijangna in the Santa Ana River watershed. Some residents of Wapijanga were baptized at Mission San Gabriel, which was established in 1771. The Spanish crown claimed the land until Mexican independence was finalized and possession fell to the Mexican government.
Some twenty years later, Mexican governor of Alta California Juan Bautista Alvarado granted Rancho Santa Ana del Chino to Antonio Maria Lugo of the prominent Lugo family. Two years later, his successor, Governor Micheltorena, granted an additional three leagues to Lugo’s son-in-law Isaac Williams, who took charge of the rancho. Williams kept large quantities of horses and cattle, which attracted the envy of raiding Native Americans as well as unscrupulous whites. One of the latter was James Beckwourth, who, in 1840, posed as an otter hunter and stayed at Rancho Chino to determine the location of the area’s animals, which he then reported to Walkara, the Ute mastermind of the raids.
Early in the Mexican–American War, the Battle of Chino took place at Williams’ rancho. The battle ended prior to the arrival of the Mormon Battalion, dispatched on behalf of the United States, who instead labored in the rancho’s agricultural harvest and constructed a grist mill.
During the California Gold Rush, the rancho was a popular stopover for travelers, and in the mining fury, coal was discovered there. In 1850, California was admitted to the union, and the process of separating privately held lands from the public domain began. The Williams claim to the Chino Rancho was patented in 1869.
Richard Gird was the next owner of the Rancho. Beginning in 1887, his land was subdivided and laid out. It became the “Town of Chino,” and incorporated into a city in 1910. Sugar beets, corn, and alfalfa were raised there.
The Chino Valley, located at the foot of an alluvial plain with fertile topsoil reaching depths of 4 feet (1.2 m), was an agricultural mecca from the 1890s up through the mid-20th century. Sugar beets were a significant part of the economy in the early 1900s, followed by sweet corn (marketed as “Chino corn” throughout the Pacific coast area), peaches, walnuts, tomatoes, and strawberries. The city’s official logo/crest features an overflowing cornucopia.
The dairy industry flourished from the 1950s through the 1980s, with dairy-friendly zoning in the southwest corner of San Bernardino County encouraging many ethnic Dutch families to locate there and become the cornerstone of the industry. Chino’s large, highly efficient dairies made it the largest milk-producing community in the nation’s largest milk-producing state.
Because of its pastoral setting and rural flavor, Chino was a popular site for Hollywood crews to shoot “Midwestern” settings. 1960s movies included Bus Riley’s Back in Town starring Ann-Margret and Michael Parks; The Stripper, with Joanne Woodward; and the mid-1960s TV series Twelve O’Clock High, refashioning Chino’s rural airport into a British airfield with quonset huts among farm fields.
In the 1970s, Chino developed into a small suburban city, forming the western anchor of the Inland Empire region, and now the city’s development has gradually taken on a more middle-class character. There are still many industrial areas as well as farm animals such as goats and chickens. According to the 2004 FBI UCR, the city had about 3.6 violent crimes per 1,000 population, which is typical for an American suburb, and its property crime below average.
On July 11, 2017, in a special election, Chino voters voted against Measure H, which would have allowed 30 acres (12 ha) of rural land located near Ontario to be used to build a total of 180 new homes by home builder D.R. Horton. The measure faced considerable opposition from city residents, despite support from the Chino Chamber of Commerce and school district.
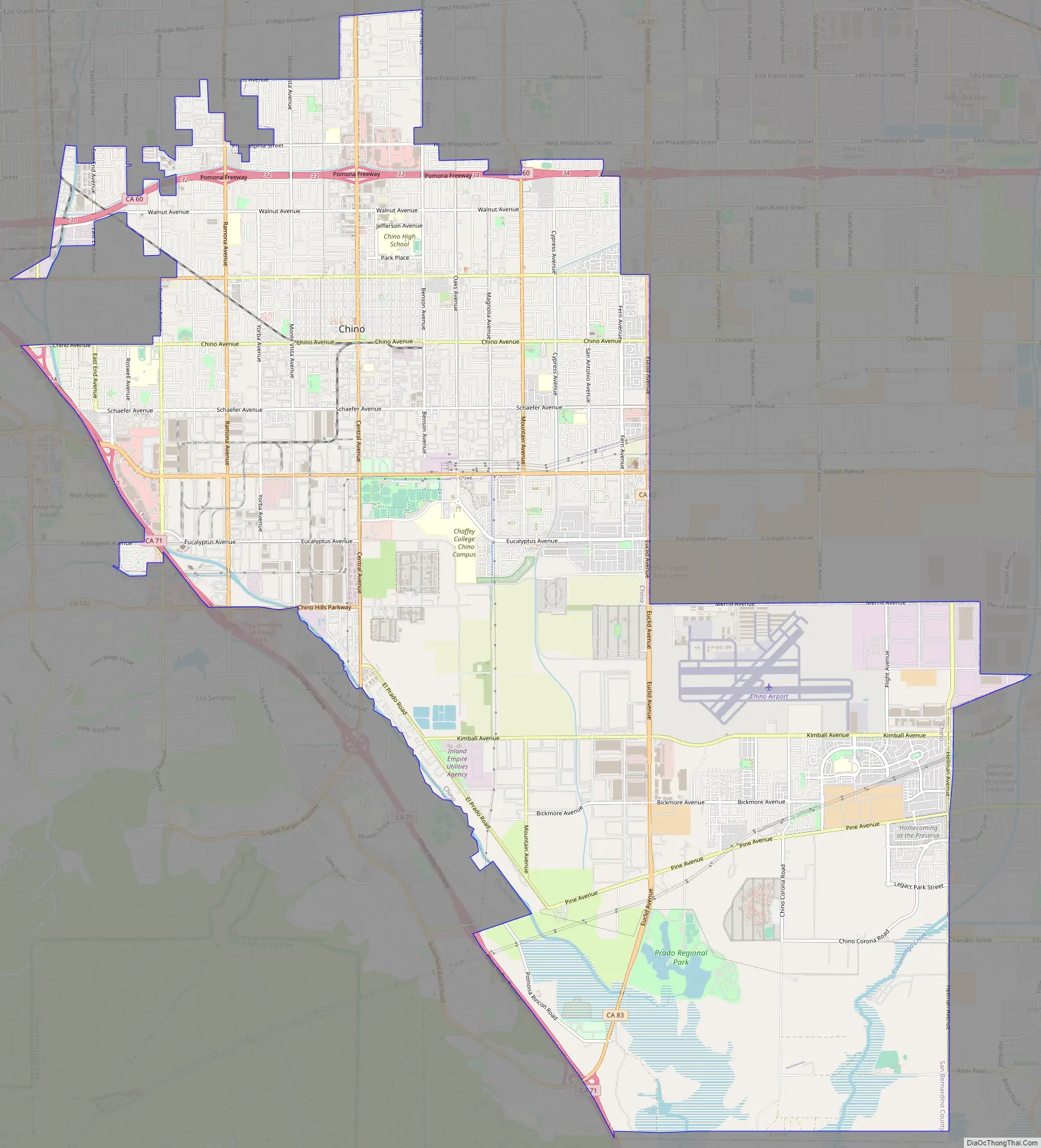
Chino Road Map
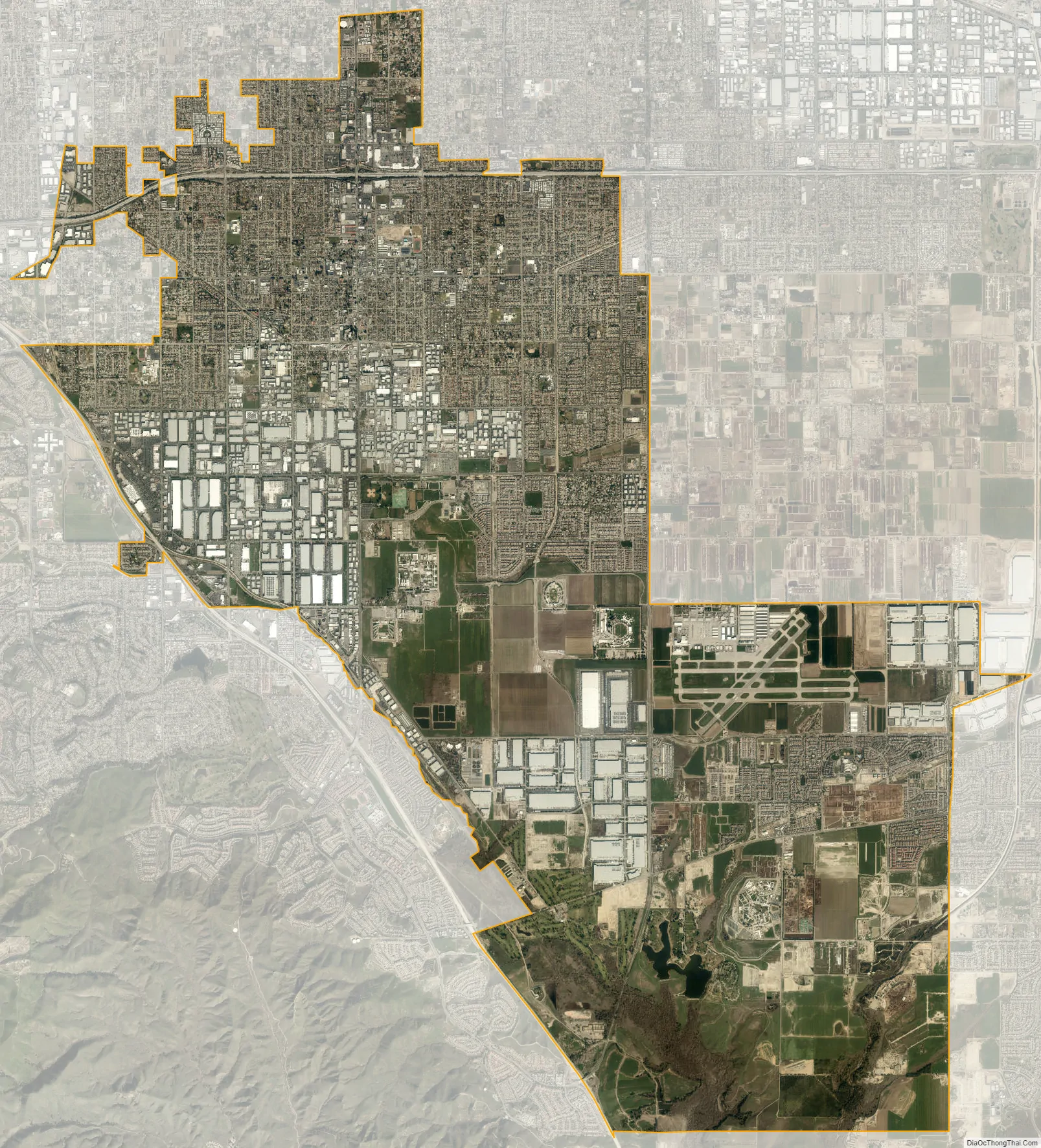
Chino city Satellite Map
Geography
Chino is located at 34°1′4″N 117°41′24″W / 34.01778°N 117.69000°W / 34.01778; -117.69000 (34.017765, -117.689990). According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 29.7 square miles (77 km). 29.6 square miles (77 km) of it is land and 0.04% is water.
- Chino is a suburb in San Bernardino County, located 33 miles (53 km) from the county seat, San Bernardino.
- Los Angeles, 35 miles (56 km)
- Riverside, 26 miles (42 km)
- Santa Ana, 30 miles (48 km)
- Anaheim, 24 miles (39 km)
Climate
According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Chino has a hot-summer Mediterranean climate, abbreviated “Csa” on climate maps. Chino has long, hot summers with cool to mild mornings and short, mild, and wet winters with chilly mornings usually in the 40s. Precipitation peaks during the month of February.
See also
Map of California State and its subdivision:- Alameda
- Alpine
- Amador
- Butte
- Calaveras
- Colusa
- Contra Costa
- Del Norte
- El Dorado
- Fresno
- Glenn
- Humboldt
- Imperial
- Inyo
- Kern
- Kings
- Lake
- Lassen
- Los Angeles
- Madera
- Marin
- Mariposa
- Mendocino
- Merced
- Modoc
- Mono
- Monterey
- Napa
- Nevada
- Orange
- Placer
- Plumas
- Riverside
- Sacramento
- San Benito
- San Bernardino
- San Diego
- San Francisco
- San Joaquin
- San Luis Obispo
- San Mateo
- Santa Barbara
- Santa Clara
- Santa Cruz
- Shasta
- Sierra
- Siskiyou
- Solano
- Sonoma
- Stanislaus
- Sutter
- Tehama
- Trinity
- Tulare
- Tuolumne
- Ventura
- Yolo
- Yuba
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming