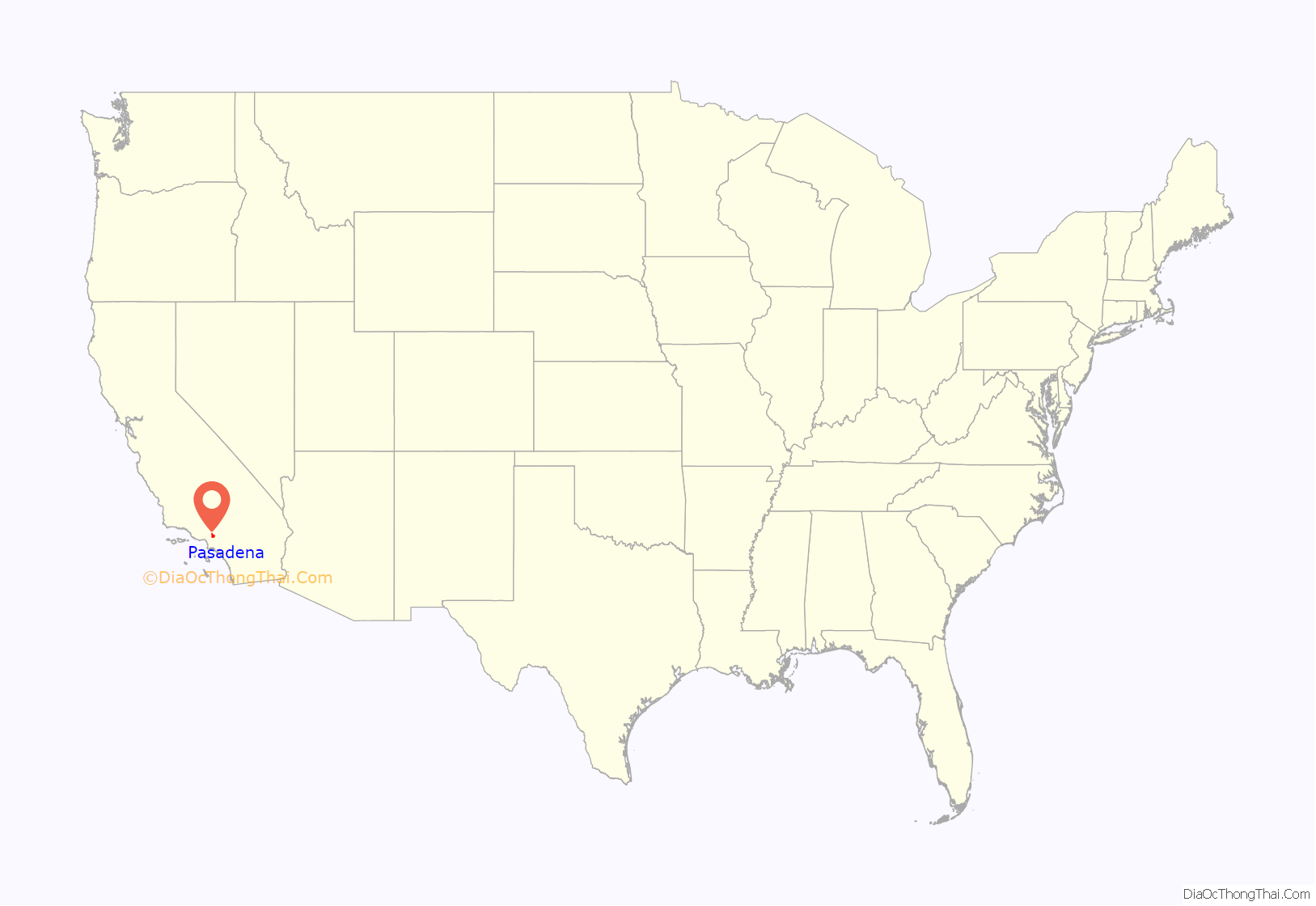
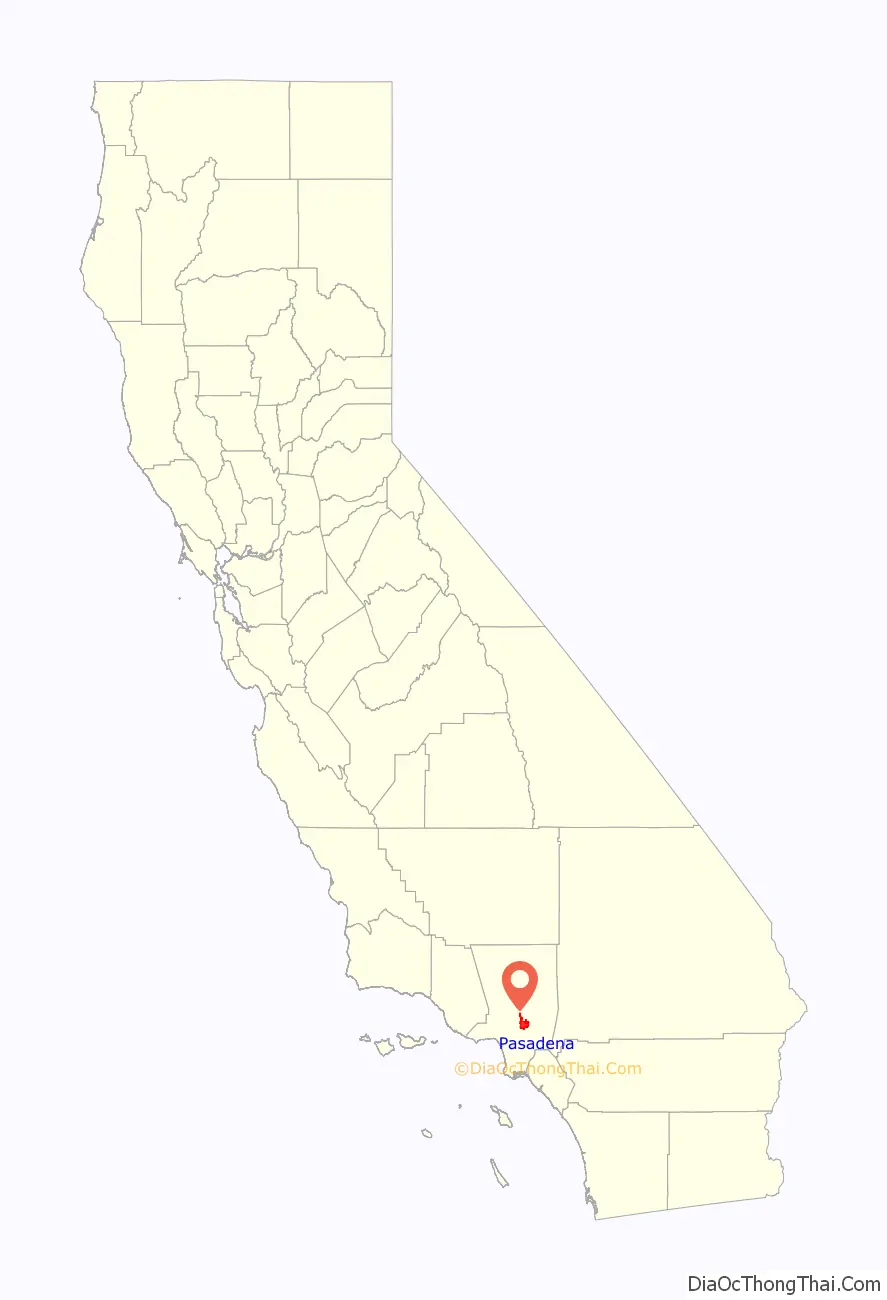
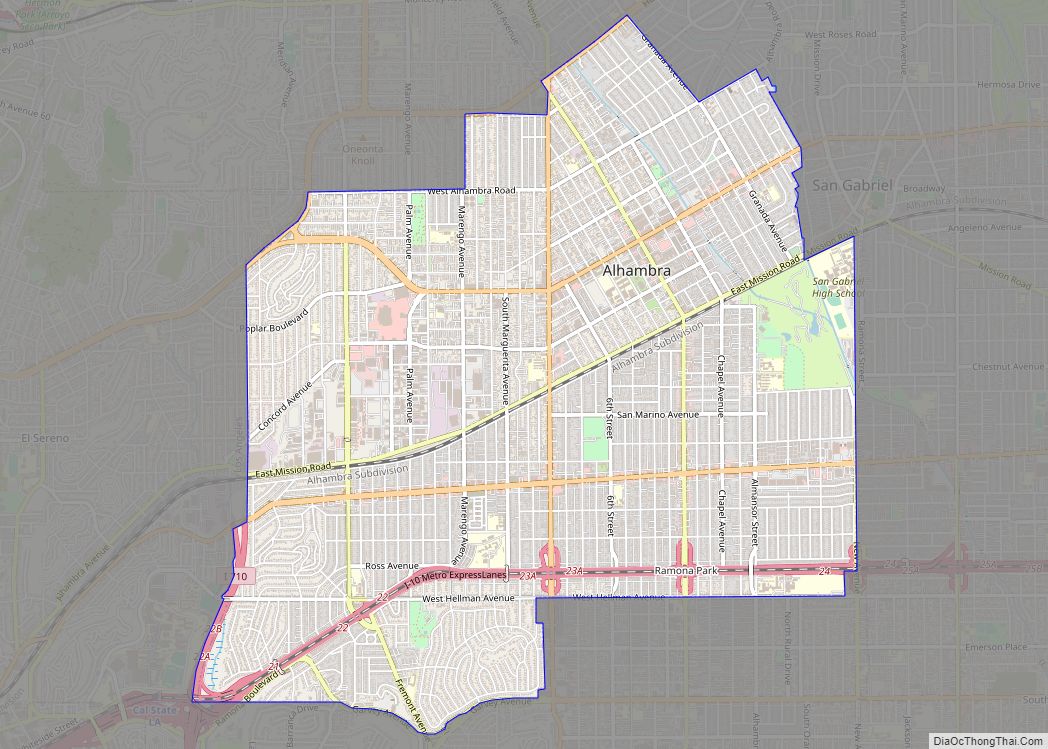
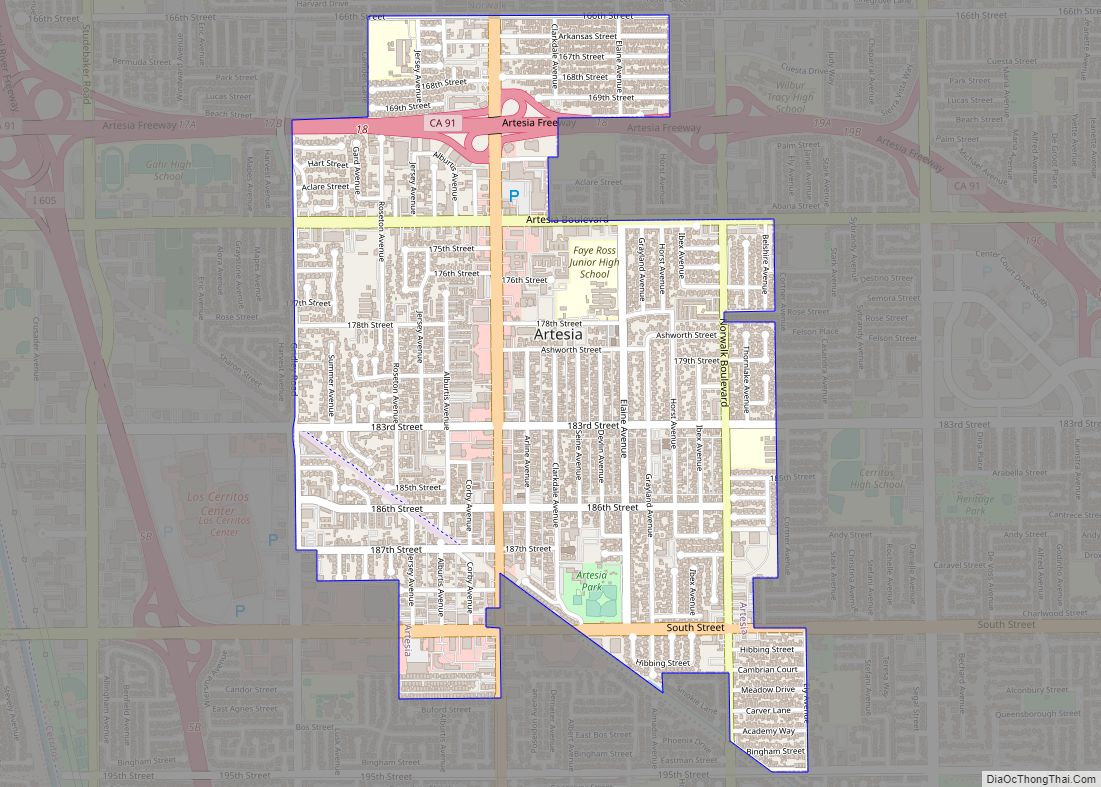
Pasadena (/ˌpæsəˈdiːnə/ PAS-ə-DEE-nə) is a city in Los Angeles County, California, United States, 11 miles (18 km) northeast of downtown Los Angeles. It is the most populous city and the primary cultural center of the San Gabriel Valley. Old Pasadena is the city’s original commercial district.
Its population was 138,699 at the 2020 census, making it the 44th largest city in California and the ninth-largest city in Los Angeles County. Pasadena was incorporated on June 19, 1886, becoming one of the first cities to be incorporated in what is now Los Angeles County, following the city of Los Angeles (April 4, 1850).
Pasadena is known for hosting the annual Rose Bowl football game and Tournament of Roses Parade. It is also home to many scientific, educational, and cultural institutions, including Caltech, Pasadena City College, Kaiser Permanente Bernard J. Tyson School of Medicine, Fuller Theological Seminary, Parsons Corporation, ArtCenter College of Design, the Pasadena Playhouse, the Ambassador Auditorium, the Norton Simon Museum, and the USC Pacific Asia Museum.
| Name: | Pasadena city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | California |
| County: | Los Angeles County |
| Incorporated: | June 19, 1886 |
| Elevation: | 863 ft (263 m) |
| Total Area: | 23.11 sq mi (59.84 km²) |
| Land Area: | 22.96 sq mi (59.47 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.14 sq mi (0.37 km²) 0.68% |
| Total Population: | 138,699 |
| Population Density: | 6,141.5/sq mi (2,371.24/km²) |
| Area code: | 626 |
| FIPS code: | 0656000 |
| Website: | www.cityofpasadena.net |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
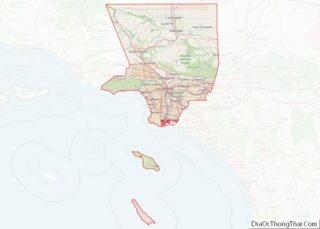
Pasadena location map. Where is Pasadena city?
History
Indigenous peoples and Spanish colonial era
The original inhabitants of Pasadena (from the Tongva language name “Pasakeg-na”) and surrounding areas were members of the Native American Hahamog-na tribe, a branch of the Tongva Nation. They spoke the Tongva language (part of the Uto-Aztecan languages group). Native Americans had lived in the Los Angeles Basin for thousands of years. Tongva dwellings lined the Arroyo Seco (Los Angeles County) in present day Pasadena and south to where it joins the Los Angeles River and along other natural waterways in the city.
The native people lived in thatched, dome-shape lodges and lived on a diet of acorn meal, seeds and herbs, venison, and other small animals as well as trading for ocean fish with the coastal Tongva. They made cooking vessels from steatite soapstone from Catalina Island. The oldest transportation route still in existence in Pasadena is the old Tongva foot trail, also known as the Gabrielino Trail, that follows the west side of the Rose Bowl and the Arroyo Seco past the Jet Propulsion Laboratory into the San Gabriel Mountains. The trail has been in continuous use for thousands of years. An arm of the trail is also still in use in what is now known as the Salvia Canyon.
The Spanish first colonized the Los Angeles Basin in the 1770s as part of the Viceroyalty of New Spain, building the San Gabriel Mission and renaming the local Tongva people “Gabrielino Indians”, after the name of the mission. Today, several bands of Tongva people live in the Los Angeles area.
Mexican rancho era and early American era
In 1821, Mexico became independent of Spain and California came under control of the Mexican government. In 1833, the mission lands were secularized and most of the lands in California were granted to private Mexican citizens in the form of ranchos. Present-day Pasadena was divided between Rancho San Rafael (lands west of the Arroyo Seco extending to present-day Burbank in the northwest to Glassell Park in the southwest), Rancho del Rincon de San Pascual, (present-day central Pasadena, Altadena, and South Pasadena), and Rancho Santa Anita (present-day east Pasadena, Arcadia, and Monrovia). Rancho del Rincon de San Pascual was so named because it was deeded on Easter Sunday to Eulalia Perez de Guillén Mariné of Mission San Gabriel Arcángel.
Before the annexation of California in 1848 by the United States at the end of the Mexican-American war, the last of the Mexican owners of Rancho del Rincon de San Pascual was Manuel Garfias who retained title to the property after statehood in 1850. Garfias sold sections of the property to the first Anglo settlers to come into the area: Dr. Benjamin Eaton, the father of Fred Eaton; and Dr. S. Griffin. Much of the property was purchased by Benjamin Wilson, who established his Lake Vineyard property in the vicinity. Wilson, known as Don Benito to the local Indians, also owned the Rancho Jurupa (Riverside, California) and was mayor of Los Angeles. He was the grandfather of WWII General George S. Patton, Jr. and the namesake of Mount Wilson.
In 1873, Wilson was visited by Dr. Daniel M. Berry of Indiana who was looking for a place in the country that could offer a mild climate for his patients, most of whom suffered from respiratory ailments. Berry was an asthmatic and claimed that he had his best three night’s sleep at Rancho San Pascual. To keep the find a secret, Berry code-named the area “Muscat” after the grape that Wilson grew. To raise funds to bring the company of people to San Pascual, Berry formed the Southern California Orange and Citrus Growers Association and sold stock in it. The newcomers were able to purchase a large portion of the property along the Arroyo Seco and on January 31, 1874, they incorporated the Indiana Colony. As a gesture of good will, Wilson added 2,000 acres (8 km) of then-useless highland property, part of which would become Altadena. Colonel Jabez Banbury opened the first school on South Orange Grove Avenue. Banbury had twin daughters, named Jennie and Jessie. The two became the first students to attend Pasadena’s first school on Orange Grove.
At the time, the Indiana Colony was a narrow strip of land between the Arroyo Seco and Fair Oaks Avenue. On the other side of the street was Wilson’s Lake Vineyard development. After more than a decade of parallel development on both sides, the two settlements merged into the City of Pasadena.
Pasadena as a resort town (1886–1941)
The popularity of the region drew people from across the country, and Pasadena eventually became a stop on the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway, which led to an explosion in growth. From the real estate boom of the 1880s until the Great Depression, as great tourist hotels were developed in the city, Pasadena became a winter resort for wealthy Easterners, spurring the development of new neighborhoods and business districts, and increased road and transit connections with Los Angeles, culminating with the opening of the Arroyo Seco Parkway, California’s first freeway. By 1940, Pasadena had become the eighth-largest city in California and was widely considered a twin city to Los Angeles.
The first of the great hotels to be established in Pasadena was the Raymond (1886) atop Bacon Hill, renamed Raymond Hill after construction. Pasadena was served by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway at the Santa Fe Depot in downtown when the Second District was opened in 1887. The original Mansard Victorian 200-room facility burned down on Easter morning of 1895, was rebuilt in 1903, and razed during the Great Depression to make way for residential development. The Maryland Hotel existed from the early 1900s and was demolished in 1934. The world-famous Mount Lowe Railway and associated mountain hotels shut down four years later due to fire damage. Three hotel structures have survived, the Green Hotel (a co-op since 1926), the Vista Del Arroyo (now used as a Federal courthouse), and a residential tower of the Maryland at 80 North Euclid Avenue (a co-op since 1953).
The American Craftsman era in art and design is well represented in Pasadena. The architectural firm Greene and Greene developed the style; many of its residences still stand. Two examples of their Ultimate bungalow are the masterpiece Gamble House, of which public tours are available, and the Robert R. Blacker House, both designated California Historical Landmarks and enrolled on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places.
World War II and aftermath (1941–1969)
The Second World War proved to be a boon to Pasadena as Southern California became a major staging area for the Pacific War. High tech manufacturing and scientific companies made the city their home, a trend which continued in the decades following the war, notably with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Tetra Tech and Ameron International.
In the 1950s, Pasadena saw a steady influx of people from the Southern United States, especially African-Americans from Texas and Louisiana. Pasadena also began hosting a large immigrant community, particularly from China, Japan, Philippines, Mexico, Guatemala, El Salvador, Italy, Armenia, and India.
Pasadena since 1970
The American Academy of Dramatic Arts, founded in 1884 in New York, opened its Pasadena campus in 1974. However, in 2001 the conservatory moved from Pasadena to Hollywood. Training actors for the stage in a two year program, the conservatory was the first school in the United States to offer professional education in the field of acting. Point Loma Nazarene University was located in Pasadena for many years before relocating to San Diego County, and retained the names Pasadena University and Pasadena College.
In 1969, the Pasadena Unified School District was desegregated, though the issue would continue to be fought in court for a decade. A year later, the 210 Freeway was built along a newly chosen route. The freeway’s construction was controversial, as it caused the demolition of over a thousand homes, many historic, and many claimed that the route was designed to cut off the city’s less wealthy neighborhoods.
Downtown Pasadena became dangerous in some parts and deserted in others, and incidences of murder and arson skyrocketed. Old Pasadena faced destruction as plans for new high-rise developments were drawn up, though they were mostly stopped by increasingly active preservation advocates. Pasadena suffered demographically as many residents decamped for the nearby suburbs or the Inland Empire, causing an overall decrease in population. Despite these setbacks, many local artists and hipsters moved in to take advantage of low property values. Their legacy can be seen today in the Doo Dah Parade which began in 1976.
In 2014, several arrests were made involving an embezzlement scheme which stole money from the UUP. The amount is estimated to be $6.4 million.
Pasadena Road Map
Pasadena city Satellite Map
Geography
The greater Pasadena area is bounded by the Raymond Fault line, the San Rafael Hills, and the San Gabriel Mountains. The Arroyo Seco, a major geographic feature and home of the Rose Bowl, flows from headwaters in Pasadena’s towering Angeles National Forest greenbelt in the San Gabriel Mountains. According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 23.1 square miles (60 km), over 99% of it land; 0.68% is water.
Climate
Pasadena has a Mediterranean climate (Köppen Csa), with typically hotter summers and slightly cooler winters than nearby coastal areas. Its location relative to the San Gabriel mountains allows the orographic lift to add several more inches of rainfall per year than nearby areas. During the first few months of the year, Pasadena experiences cool to warm highs, typically in the upper 60s (16–18 °C) to lower 70s (21–24 °C). Colder days are usually accompanied by heavier rain. By April, temperatures warm further, and rain tapers off significantly.
By May and June, rain is typically sparse, but the infamous marine layer becomes more persistent. Locals have dubbed June “June Gloom” as it is the cloudiest month despite being the 3rd driest month. By July, the marine layer subsides as inland areas cool due to an increased monsoon flow. Heatwaves from July through October can be oppressive and lengthy. In addition, it rarely rains during the summer and fall months, and only does when the remnants of hurricanes and tropical storms pass by. In fact, some days in both July and August have never recorded rainfall. It is not impossible to go 6 months without measurable precipitation.
The average highest temperature recorded each year is around 106 °F (41 °C). The hottest heatwaves of the year usually occur in mid to late September. By late October, temperatures drop off. By November, Pacific storms return to Pasadena, bringing increasingly heavy rain and cooler weather. Along with them, however, are the Santa Ana winds. The Santa Ana winds can produce heat, high winds, power outages, tree damage and an increased wildfire threat whenever they strike. By December, lows typically drop into the 40s (4–9 °C) with the occasional reading in the 30s (−1–4 °C). Highs remain around 68 °F (20 °C) with heatwaves pushing temperatures into the mid-80s (28–31 °C). A high temperature of at least 85 °F (29 °C) has been recorded on all 365 days of the year, with temperatures over 100 °F (38 °C) possible April through early November.
Pasadena averages 20.08 inches (510.0 mm) of rain a year, about 6 inches (150 mm) more than nearby Los Angeles due to the orographic effect created by the San Gabriel Mountains. The wettest “rain year” was from July 1940 to June 1941 with 46.32 inches (1,176.5 mm) and the driest from July 1960 to June 1961 with 7.18 inches (182.4 mm). Wet years are commonly associated with El Niño warm surface water in the eastern Pacific and dry years with La Niña cold water conditions. The most rainfall in one month was 19.70 inches (500.4 mm) in February 1980. The most rainfall in 24 hours was 7.70 inches (195.6 mm) on March 2, 1938.
Situated at the base of the San Gabriel Mountains, snow is known to fall occasionally in Pasadena. The heaviest snowfall in Pasadena history occurred on January 11, 1949; 8 inches (20.3 cm) fell at Pasadena’s city hall and more than 14 inches (35.6 cm) fell in the foothills above the city. The most recent snowfall in Pasadena was 1 inch (2.5 cm) on February 21, 2019.
On November 30 and December 1, 2011, Pasadena, along with surrounding communities, was struck by a major windstorm caused by Santa Ana winds. The city suffered heavy damage with trees toppled, buildings damaged and even the roof of a gas station torn off.
The official NOAA weather station for the city is located just north-west of the townhall on the other side of Garfield Avenue.
See also
Map of California State and its subdivision:- Alameda
- Alpine
- Amador
- Butte
- Calaveras
- Colusa
- Contra Costa
- Del Norte
- El Dorado
- Fresno
- Glenn
- Humboldt
- Imperial
- Inyo
- Kern
- Kings
- Lake
- Lassen
- Los Angeles
- Madera
- Marin
- Mariposa
- Mendocino
- Merced
- Modoc
- Mono
- Monterey
- Napa
- Nevada
- Orange
- Placer
- Plumas
- Riverside
- Sacramento
- San Benito
- San Bernardino
- San Diego
- San Francisco
- San Joaquin
- San Luis Obispo
- San Mateo
- Santa Barbara
- Santa Clara
- Santa Cruz
- Shasta
- Sierra
- Siskiyou
- Solano
- Sonoma
- Stanislaus
- Sutter
- Tehama
- Trinity
- Tulare
- Tuolumne
- Ventura
- Yolo
- Yuba
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming