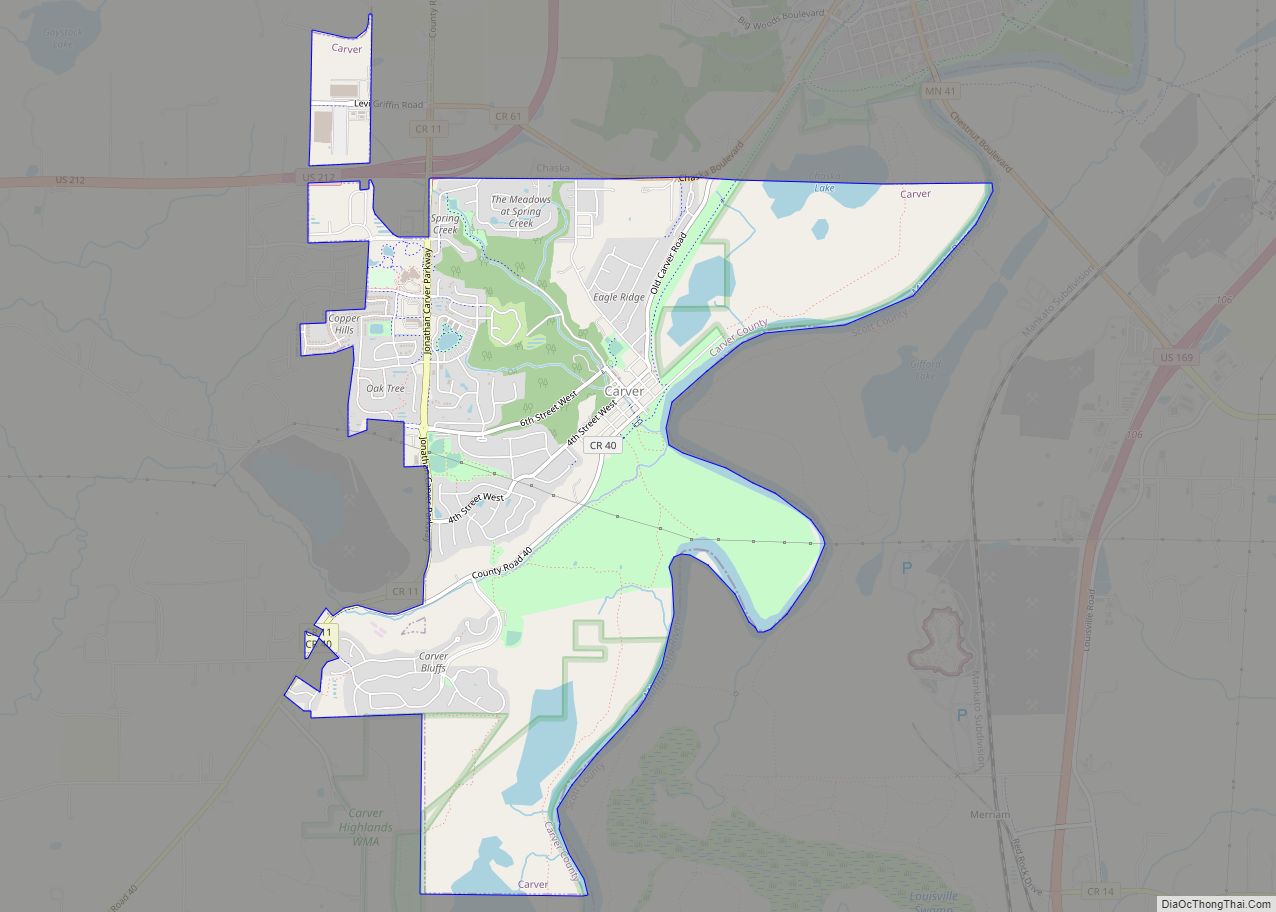
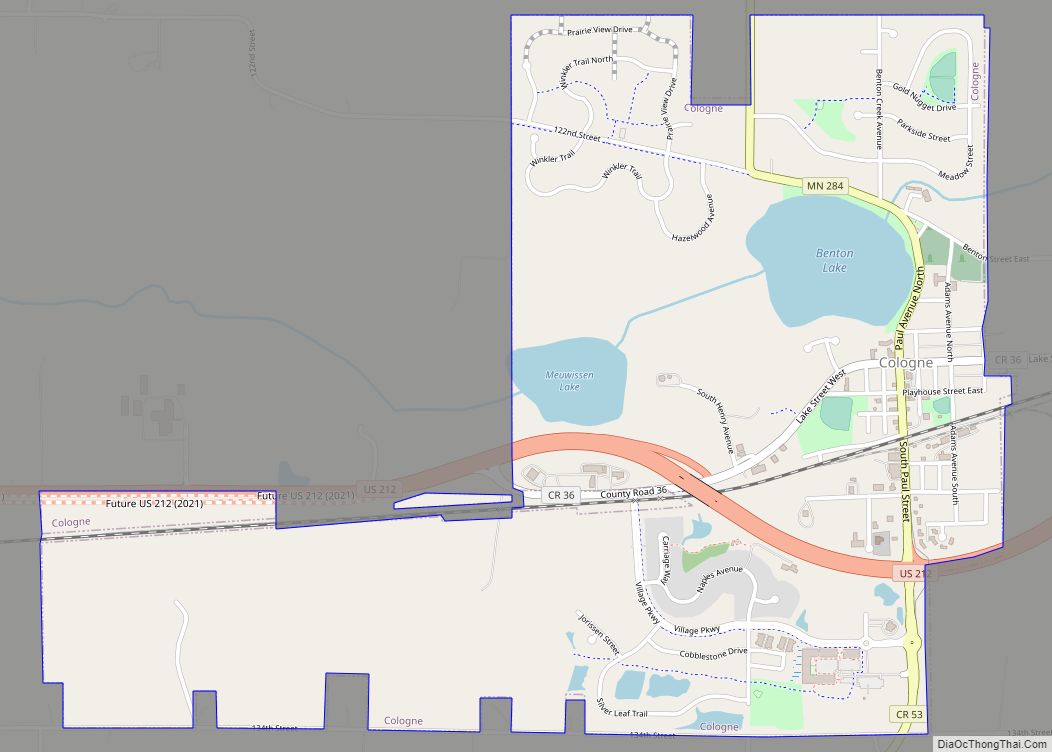
Carver is a small city in Carver County, Minnesota, United States along the banks of the Minnesota River. The city is named after early explorer Jonathan Carver. The downtown area is home to the Carver Historic District, a nationally recognized collection of historically significant local buildings.
The population was 3,724 at the 2010 census.
| Name: | Carver city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Minnesota |
| County: | Carver County |
| Elevation: | 732 ft (223 m) |
| Total Area: | 4.65 sq mi (12.05 km²) |
| Land Area: | 4.45 sq mi (11.53 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.20 sq mi (0.52 km²) |
| Total Population: | 5,829 |
| Population Density: | 1,309.01/sq mi (505.45/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 55315 |
| Area code: | 952 |
| FIPS code: | 2710144 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0640944 |
| Website: | www.cityofcarver.com |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
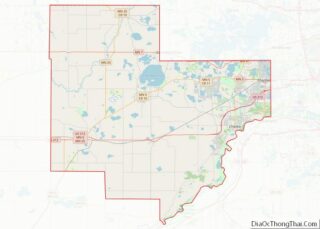
Carver location map. Where is Carver city?
History
Early history
Ten thousand years ago, the Glacial River Warren flowed through the area and left deposits of clay, sand, gravel, and fine silt soils as well as the Minnesota River. Carver and the surrounding Minnesota River Valley were occupied by a Native American, pre-Columbian Woodland Culture from approximately 1200 B.C. to A.D. 1850. In 1834, there was a Wahpeton village at the present-day location of Carver, led by Chief Mazomaini; early maps indicate it was located on either side of the mouth of Carver Creek where it meets the Minnesota River.
Pierre-Charles Le Sueur became the first European to navigate the Minnesota River, and between 1683 and 1700 made explorations of the region on behalf of King Louis XIV of France. In 1766, Jonathan Carver explored the area on behalf of the British Empire, and made maps as he searched for a western water route that flowed across North America to the Pacific Ocean. He named a small branch flowing into the Minnesota River “Carver’s River”, strongly correlated to the Carver Creek of today. In 1805, French trader Jean-Baptiste Faribault established the Little Rapids trading post just upriver of present-day Carver; the post, on behalf of the Northwest Fur Company, was visited by Voyageurs, Coureur des bois, Dakota Indians, and Christian missionaries.
Boomtown
The 1851 Treaty of Traverse de Sioux, signed between the Dakota and the U.S. Government, legally opened the area to white settlers. Before the Treaty was fully ratified, Axel Jorgenson, an immigrant from Fredrikshald, Norway, settled in the area by 1852 as a sooner. Jorgenson laid claim to 415 acres (1.68 km; 0.648 sq mi) that would become Carver. He called the area Lukenborg (or Luksenborg), but called it Fulton. In order to augment his barge transport business, to and from St. Paul, he opened a cheap hotel, the Hotel Luksenborg.
A land boom in the 1850s led to widespread speculation along key river locations. Carver’s position between navigable sections of the Minnesota River, as well as Carver and Spring Creeks, was an ideal location for a steamboat and barge terminal for transferring cargo. In 1854, Jorgenson sold his claim to the Carver Land Company, a group of seven speculators, who planned to plat and develop a town. Among the investors were Alexander Ramsey, the former Territorial Governor, and Levi Griffin, the first sheriff of Carver County. Ramsey was responsible for naming the town Carver. The Town of Carver was platted in 1857 and lots were divided up among the seven according to their investment.
By 1855, Carver already had a tailor, a hotel, a boarding house, a building designer, a carpenter, a livery stable, a blacksmith, two shoemakers, and a general store. When the town was platted in 1857, it already had 35 buildings; the school district was established the same year and was known as Minnesota School District #1 for a century. Also during this period, the steamboat The Antelope was making daily round trips between Carver and St. Paul, a one-way river run of 32 miles (51 km). Steamboats brought passengers and immigrants, who rapidly opened up the surrounding area to settlement by farmers who could buy land from the U. S. government for $1.25 an acre, as well as the supplies needed to grow these settlements.
The Panic of 1857 caused many frontier settlements to collapse. One such community, Louisville, located directly across the Minnesota River in present-day Louisville Township, collapsed and many of its buildings were moved to Carver. In 1858 Carver had a small gold rush when gold was purportedly found in Spring Creek. By 1860, immigrants who had previously come from the Eastern U.S. were supplanted by those from Sweden and Germany.
The Dakota War of 1862 erupted in the region as most of the regions soldiers were embroiled in the concurrent American Civil War. Between 400 and 500 pioneers in southern and western Minnesota were killed as war parties attacked settlements throughout the region. Many settlers sought refuge in Carver due to town’s steamboat transportation, which offered evacuation to Fort Snelling, if needed. The town was spared, but rumors of its attack caused residents of Shakopee to flee to Fort Snelling.
Decline
The arrival of the Minneapolis and St. Louis Railway in 1871 marked the decline of Carver’s importance, as cargo and passenger traffic quickly shifted to the new mode of transportation. Telegraph service quickly followed. In 1877, Carver incorporated as a village. Northwestern Bell connected the town with phone service to the Twin Cities in 1893.
Carver businesses suffered during the twin events of Prohibition and the Great Depression, causing the city to go into several decades of economic stagnation, leading to the decay of many historic houses and commercial buildings. The April 1965 flood of the Upper Mississippi River affected the lower part of old Carver and deepened the depression. The Flood Control Act of 1965 led to the creation of a floodwall to keep the Minnesota River at bay.
Restoration
On June 25, 1969, Carver-on-the-Minnesota, a non-profit historic preservation organization formed to purchase, renovate and save key properties. While some progress was made during the 1960s-70s, the deaths of founding members caused the organization to stall and several important buildings were lost. The Carver Historic District was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1980, making it one of the first historic districts in Minnesota. The years of decline had actually helped preserve a number of important historic structures from ever being redeveloped, and the historic district includes eighty-seven buildings and four structures of commercial, religious, residential and social importance.
The City of Carver created the Heritage Preservation Commission in 1989 as a supporting group of appointees to aid the City Council and Planning Commission on historic preservation issues. In 2006, Carver attained Certified Local Government status by the Minnesota State Historic Preservation Office. In summer 2007, the White House named Carver a Preserve America Community.
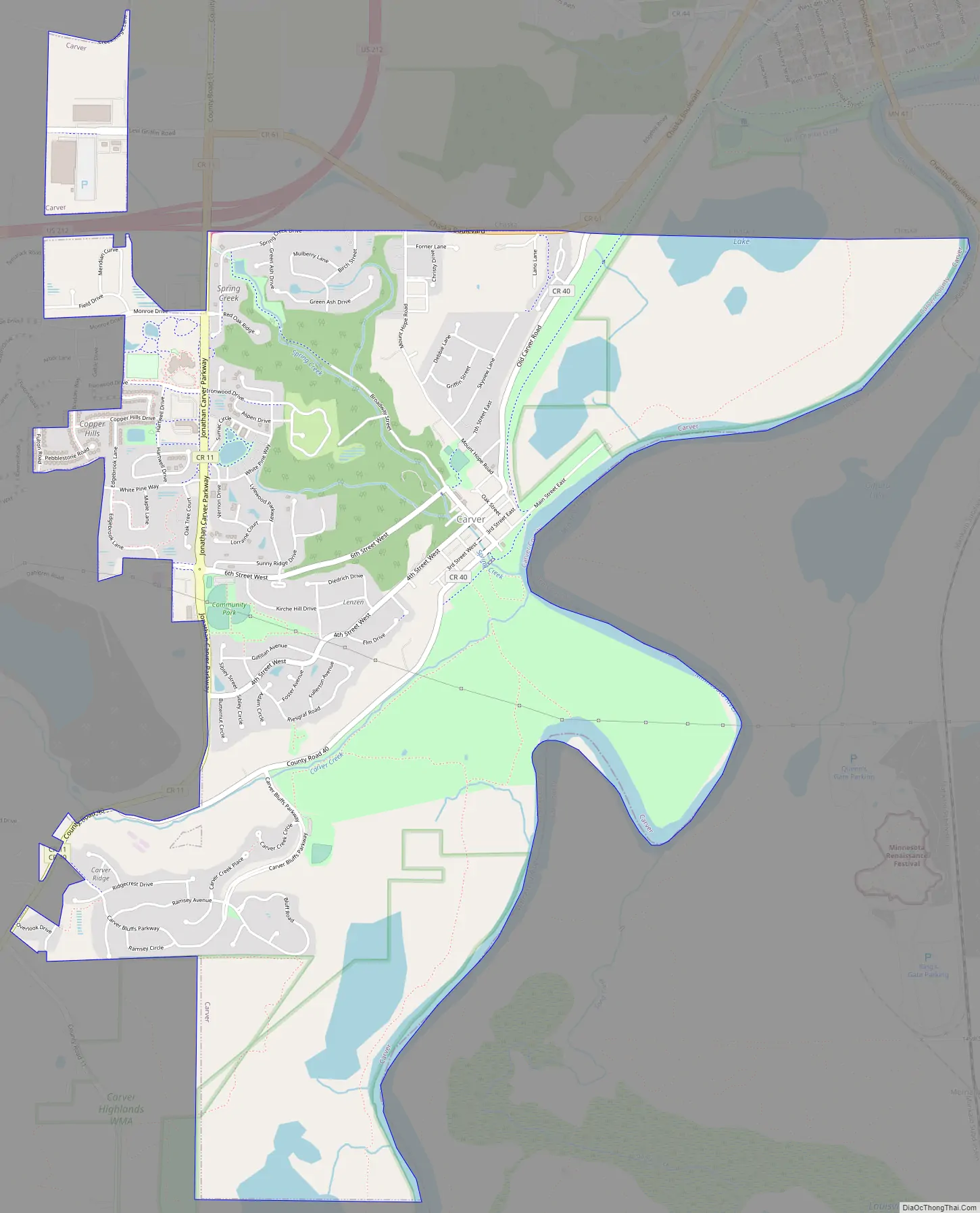
Carver Road Map
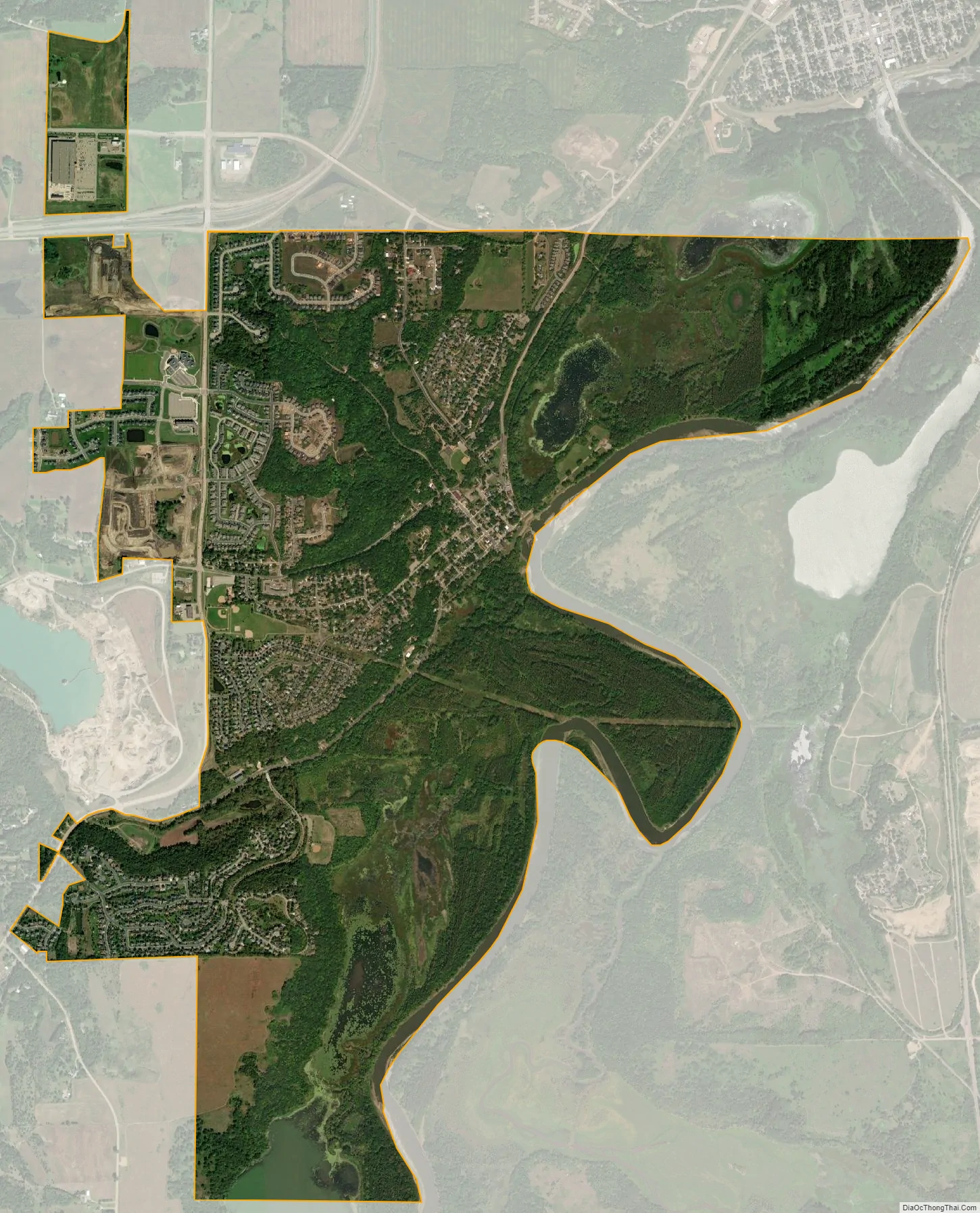
Carver city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 4.18 square miles (10.83 km), of which 4.00 square miles (10.36 km) is land and 0.18 square miles (0.47 km) is water.
U.S. Highway 212 serves as a main route in the area.
See also
Map of Minnesota State and its subdivision:- Aitkin
- Anoka
- Becker
- Beltrami
- Benton
- Big Stone
- Blue Earth
- Brown
- Carlton
- Carver
- Cass
- Chippewa
- Chisago
- Clay
- Clearwater
- Cook
- Cottonwood
- Crow Wing
- Dakota
- Dodge
- Douglas
- Faribault
- Fillmore
- Freeborn
- Goodhue
- Grant
- Hennepin
- Houston
- Hubbard
- Isanti
- Itasca
- Jackson
- Kanabec
- Kandiyohi
- Kittson
- Koochiching
- Lac qui Parle
- Lake
- Lake of the Woods
- Lake Superior
- Le Sueur
- Lincoln
- Lyon
- Mahnomen
- Marshall
- Martin
- McLeod
- Meeker
- Mille Lacs
- Morrison
- Mower
- Murray
- Nicollet
- Nobles
- Norman
- Olmsted
- Otter Tail
- Pennington
- Pine
- Pipestone
- Polk
- Pope
- Ramsey
- Red Lake
- Redwood
- Renville
- Rice
- Rock
- Roseau
- Saint Louis
- Scott
- Sherburne
- Sibley
- Stearns
- Steele
- Stevens
- Swift
- Todd
- Traverse
- Wabasha
- Wadena
- Waseca
- Washington
- Watonwan
- Wilkin
- Winona
- Wright
- Yellow Medicine
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming