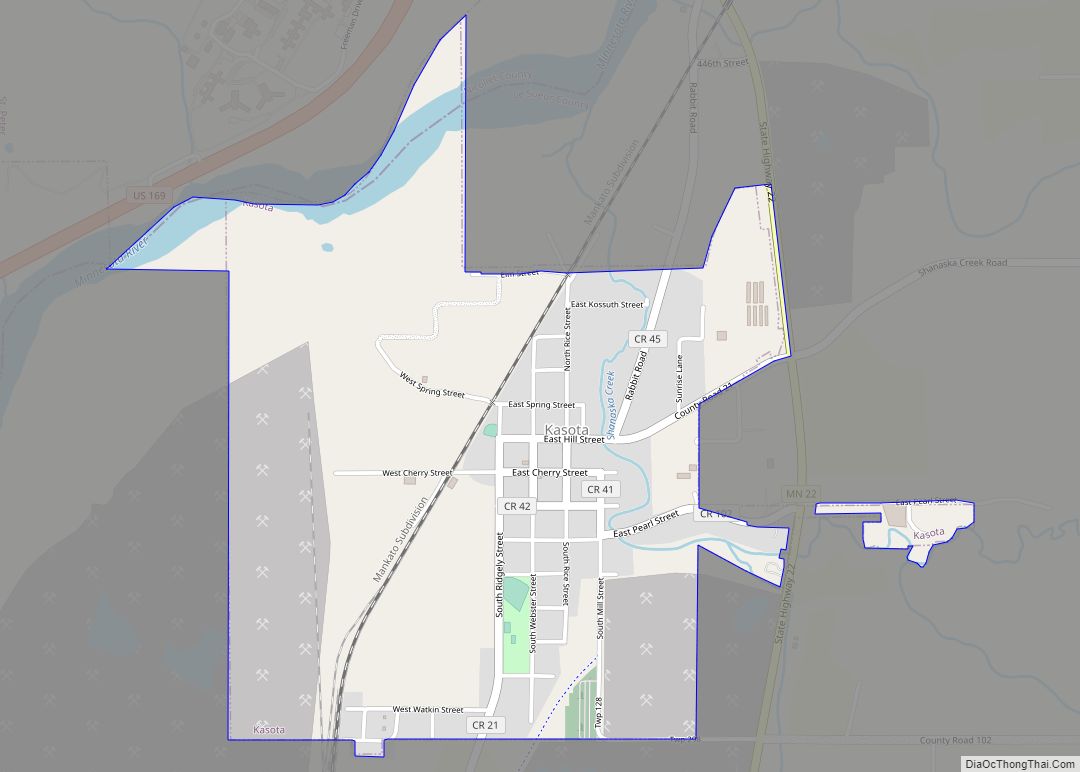
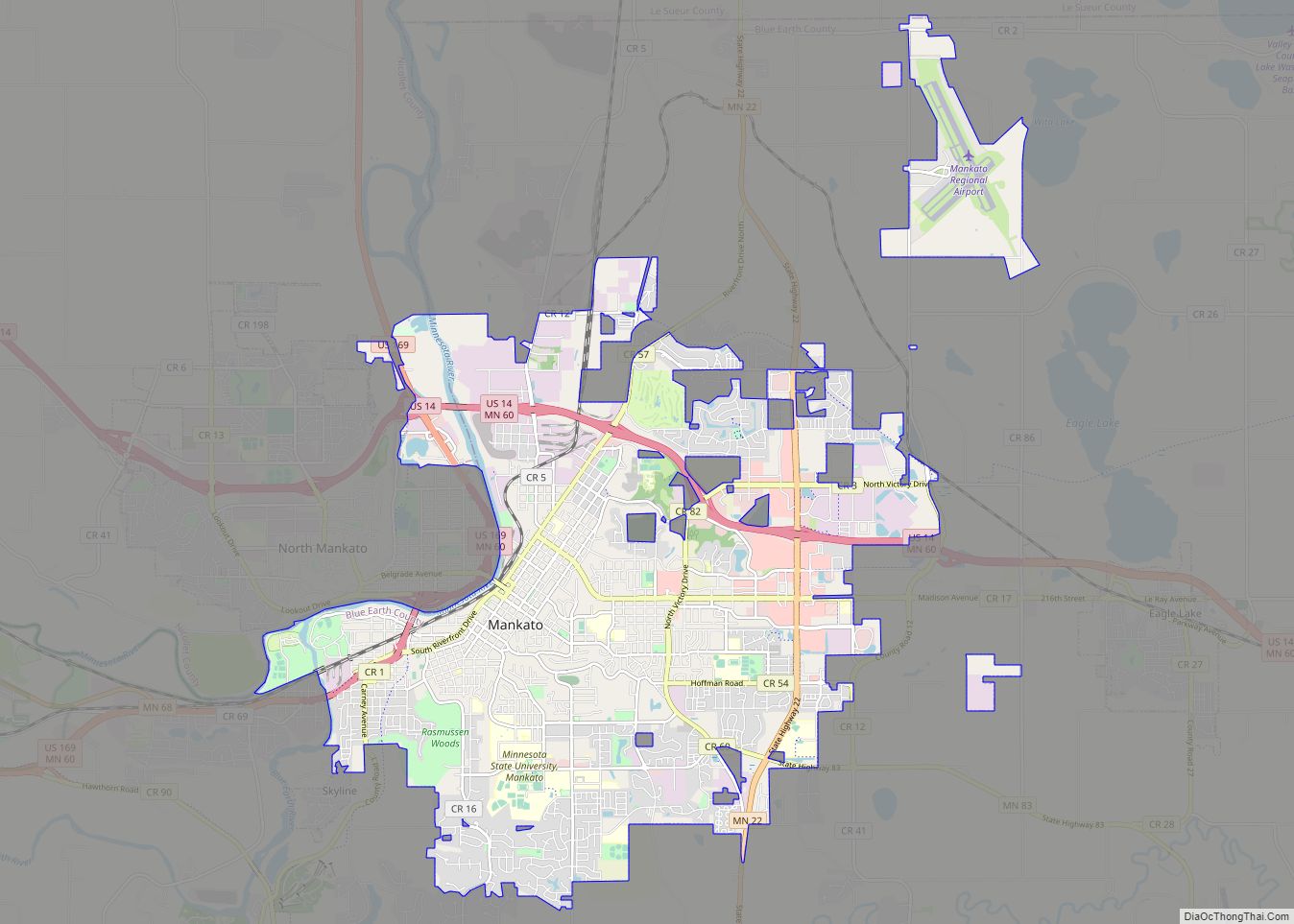
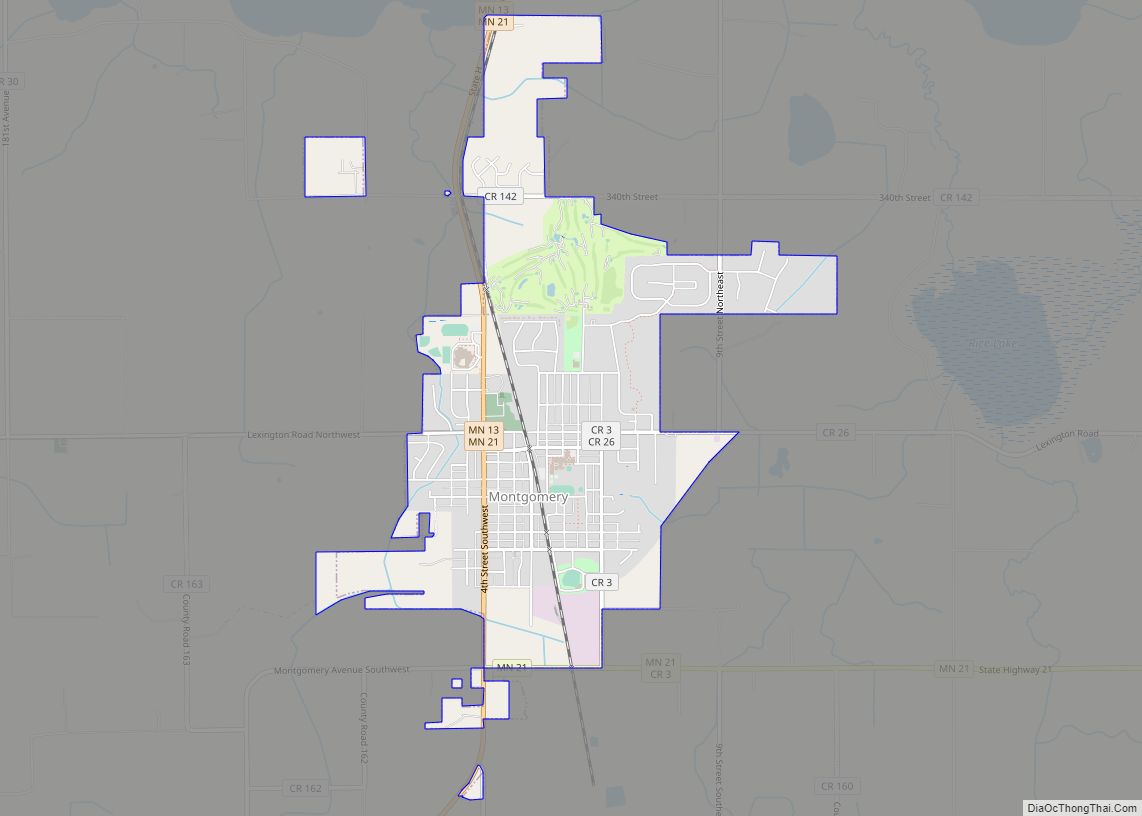
Kasota is a city within the larger Kasota Township, Le Sueur County, Minnesota, United States. The population was 714 at the 2020 census.
| Name: | Kasota city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Minnesota |
| County: | Le Sueur County |
| Elevation: | 807 ft (246 m) |
| Total Area: | 1.28 sq mi (3.32 km²) |
| Land Area: | 1.24 sq mi (3.22 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.04 sq mi (0.10 km²) |
| Total Population: | 714 |
| Population Density: | 574.88/sq mi (221.91/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 56050 |
| Area code: | 507 |
| FIPS code: | 2732462 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0646046 |
| Website: | kasotamn.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
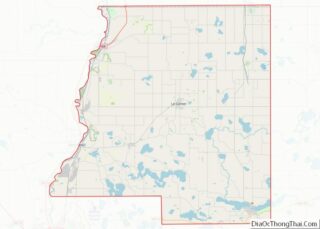
Kasota location map. Where is Kasota city?
History
Kasota was platted in 1855. “Kasota” is a name derived from the Dakota language word for “cleared off”.
On July 1, 1892, the Sontag Brothers, John Sontag and George Contant, and their partner in crime, Chris Evans, tried to rob a train between St. Peter and Kasota along the Minnesota River. The bandits acquired nothing of value, but their activities came under the review of Pinkerton detectives, and both were apprehended in June 1893.
The stone industry
During the 1880s, the stone industry experienced an unexpected boom. During this time, C.W. Babcock took over his father’s stone business. He began applying modern quarrying methods, and in 1889 formed a partnership with Tyrrell Swan Willcox, an immigrant from Rugby, England, who was instrumental in promoting the use of polished Kasota limestone for interior and exterior residential use. Much of the industry’s boom was caused by the railroads’ expansion westward, which required large quantities of stone for trestles and culverts.
Babcock also was the first to begin quarrying Kasota limestone in and around the city of Kasota. The Babcock Company was the chief stone company during the city’s early history, and the relationship between the company and the city was often contentions. At one point, the Babcock Company decided to blast within the city limits. This led to the creation of the park on County Road 21 in the town center, after the company was forced to fill in the quarry near the homes of city residents.
In the early 1980s, the Babcock Company went bankrupt. The Vetter Stone Company bought the Babcock quarries, further expanding the business, which now operates just outside the Mankato city limits. The Vetters were former employees of the Babcock Company who left to start their own company in the 1950s. The former Babcock Company plant in Kasota is now occupied by Door Engineering, which manufactures industrial doors. Much of the former Kasota quarry is occupied by Unimin Corporation, which mines silica sand for hydraulic fracturing (“fracking”).
Kasota stone was selected as the primary stone for building the National Museum of the American Indian and the Eiteljorg Museum of American Indians and Western Art in Indianapolis.
Namesakes
Kasota (Dakota for “a cleared place”) was the name of a wooden Great Lakes iron ore steamer, built in 1884. The Kasota sank after colliding with the passenger steamer The City of Detroit on the Detroit River on July 18, 1890. The Kasota was salvaged and rebuilt in 1892 but sank again after springing a leak during a storm off Grand Marais, Michigan, on September 19, 1903.
The USS Kasota was a naval tugboat, launched in 1944 and struck from the Navy list in 1961. It is believed that the Kasota (also known as the “Mighty Deuces”) was the last wooden hull tug in the Navy at the time.
Kasota Road Map
Kasota city Satellite Map
Geography
Kasota is about halfway between Mankato and St. Peter on the eastern side of the Minnesota River. According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has an area of 1.00 square mile (2.59 km), all land. The city center is about two miles north of the Kasota Prairie, designated as a Scientific and Natural Area by the state Department of Natural Resources.
Minnesota State Highway 22 serves as a main route in the community. U.S. Route 169 is nearby, on the western side of the Minnesota River.
See also
Map of Minnesota State and its subdivision:- Aitkin
- Anoka
- Becker
- Beltrami
- Benton
- Big Stone
- Blue Earth
- Brown
- Carlton
- Carver
- Cass
- Chippewa
- Chisago
- Clay
- Clearwater
- Cook
- Cottonwood
- Crow Wing
- Dakota
- Dodge
- Douglas
- Faribault
- Fillmore
- Freeborn
- Goodhue
- Grant
- Hennepin
- Houston
- Hubbard
- Isanti
- Itasca
- Jackson
- Kanabec
- Kandiyohi
- Kittson
- Koochiching
- Lac qui Parle
- Lake
- Lake of the Woods
- Lake Superior
- Le Sueur
- Lincoln
- Lyon
- Mahnomen
- Marshall
- Martin
- McLeod
- Meeker
- Mille Lacs
- Morrison
- Mower
- Murray
- Nicollet
- Nobles
- Norman
- Olmsted
- Otter Tail
- Pennington
- Pine
- Pipestone
- Polk
- Pope
- Ramsey
- Red Lake
- Redwood
- Renville
- Rice
- Rock
- Roseau
- Saint Louis
- Scott
- Sherburne
- Sibley
- Stearns
- Steele
- Stevens
- Swift
- Todd
- Traverse
- Wabasha
- Wadena
- Waseca
- Washington
- Watonwan
- Wilkin
- Winona
- Wright
- Yellow Medicine
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming