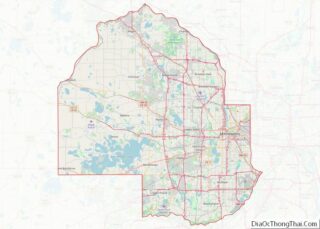
St. Louis Park is a city in Hennepin County, Minnesota, United States. The population was 50,010 at the 2020 census. It is a first-ring suburb immediately west of Minneapolis. Other adjacent cities include Edina, Golden Valley, Minnetonka, Plymouth, and Hopkins.
The Pavek Museum of Broadcasting, which has a major collection of antique radio and television equipment, is also in the city. Items range from radios produced by local manufacturers to the Vitaphone system used to cut discs carrying audio for the first “talkie”, The Jazz Singer.
The Coen brothers set their 2009 film A Serious Man in St. Louis Park circa 1967. It was important to the Coens to find a neighborhood of original-looking suburban rambler homes as they would have appeared in St. Louis Park in the mid-1960s, and after careful scouting they opted to film scenes in a neighborhood of nearby Bloomington, as well as at St. Louis Park’s B’nai Emet Synagogue, which was later sold and converted into a school.
| Name: | St. Louis Park city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Minnesota |
| County: | Hennepin County |
| Founded: | 1852 |
| Incorporated: | November 19, 1886 |
| Elevation: | 899 ft (274 m) |
| Land Area: | 10.63 sq mi (27.53 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.22 sq mi (0.56 km²) |
| Population Density: | 4,705.49/sq mi (1,816.82/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 55416, 55424, 55426 |
| Area code: | 952 |
| FIPS code: | 2757220 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0650797 |
| Website: | stlouispark.org |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
St. Louis Park location map. Where is St. Louis Park city?
History
Early developments
The 1860s village that became St. Louis Park was originally known as Elmwood, which today is a neighborhood inside the city. In August 1886, 31 people signed a petition asking county commissioners to incorporate the Village of St. Louis Park. The petition was officially registered on November 19, 1886.
The name “St. Louis Park” was derived from the Minneapolis and St. Louis Railway that ran through the area; the word “Park” was added to avoid confusion with St. Louis, Missouri.
In 1892, lumber baron Thomas Barlow Walker and a group of wealthy Minneapolis industrialists incorporated the Minneapolis Land and Investment Company to focus industrial development in Minneapolis. Walker’s company also began developing St. Louis Park for industrial, commercial and residential use.
Generally, development progressed outward from the original village center at the intersection of the Minneapolis and St. Louis Railway with Wooddale Avenue. But Minneapolis soon expanded as far west as France Avenue, and its boundary may have continued to move westward had it not been for St. Louis Park’s 1886 incorporation.
By 1893, St. Louis Park’s downtown, then located along Broadway (current-day Walker Street) near Lake Street, had three hotels and several fraternal meeting halls, and many newly arrived companies surrounded downtown. Around 1890, the village had more than 600 industrial jobs, mostly associated with agriculture implement manufacturing at the massive Moline Plow Company factory once located just south of downtown.
The financial panic of 1893 altered developers’ plans and put a damper on the village’s growth. Walker left St. Louis Park to pursue other business ventures.
In 1899, St. Louis Park became the home to the Peavey–Haglin Experimental Concrete Grain Elevator, the world’s first concrete, tubular grain elevator, which provided an alternative to combustible wooden elevators. Despite being nicknamed “Peavey’s Folly” and dire predictions that the elevator would burst like a balloon when the grain was drawn off, the experiment worked and concrete elevators have been used ever since.
Suburban boom
At the end of World War I, only seven scattered retail stores operated in St. Louis Park because streetcars provided easy access to shopping in Minneapolis. Between 1920 and 1930, the population doubled from 2,281 to 4,710. Vigorous homebuilding occurred in the late 1930s to accommodate the pent-up need created during the Depression. With America’s involvement in World War II, however, all development came to a halt.
Explosive growth came after World War II. In 1940, 7,737 people lived in St. Louis Park. By 1955, more than 30,000 new residents had joined them. From 1940 to 1955, growth averaged 6.9 persons moving into St. Louis Park every day. Sixty percent of St. Louis Park’s homes were built in a single burst of construction from the late 1940s to the early 1950s.
Residential development was closely followed by commercial developers eager to bring goods and services to these new households. In the late 1940s, Minnesota’s first shopping center — the 30,000-square-foot (2,800 m) Lilac Way — was constructed on the northeast corner of Excelsior Boulevard and Highway 100. (The Lilac Way shopping center was torn down in the late 1980s to make way for redevelopment.) Miracle Mile shopping center, built in 1950, and Knollwood Mall, which opened in 1956, remain open today.
In the late 1940s, a group of 11 former army doctors opened the St. Louis Park Medical Center in a small building on Excelsior Boulevard. The medical center merged with Methodist Hospital and today is Park Nicollet Health Services, part of HealthPartners, the second-largest medical clinic in Minnesota (after Rochester’s Mayo Clinic).
During the period between 1950 and 1956, 66 new subdivisions were recorded to make room for 2,700 new homes. In 1953 and 1954, the final two parcels — Kilmer and Shelard Park — were annexed. These parcels (originally in Minnetonka) came to St. Louis Park because of their ability to provide sewer and water service. According to Al Franken, whose mother was a realtor there, in the Twin Cities the area was nicknamed St. Jewish Park, given that 20% of its residents were of Jewish background. He states also that there appeared to be a tacit agreement between bankers, developers and real estate agents to ensure redlining, in order to prevent the spread of Jewish and Afro-American families across streets like Texas Avenue into areas with a different ethnic composition.
From village to city
In 1954, voters approved a home rule charter that gave an overwhelmed St. Louis Park the status of a city. That enabled the city to hire a city manager to assume some of the duties handled by the part-time city council. Several bridges built during that time are now being repaired or razed.
In those days, the primary concerns were the physical planning of St. Louis Park, updating zoning and construction codes, expanding sewer and water systems, paving streets, acquiring park land and building schools.
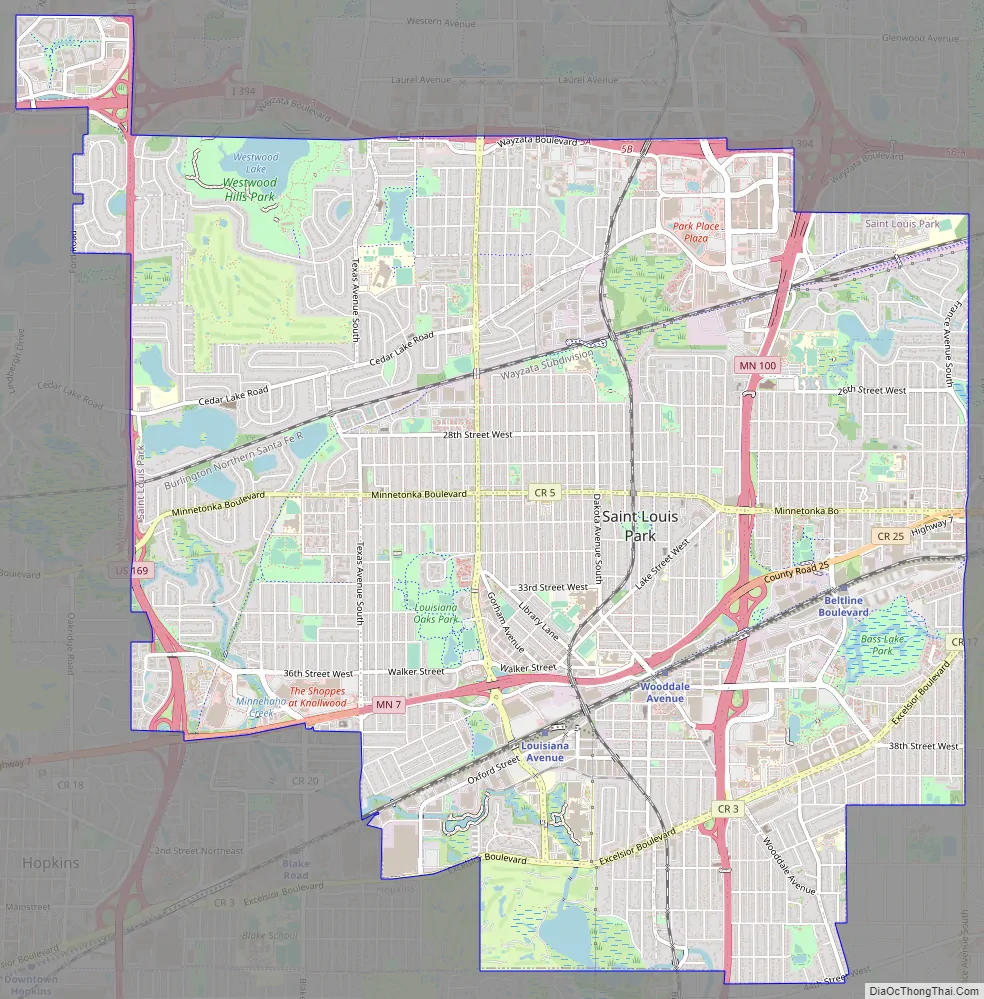
St. Louis Park Road Map
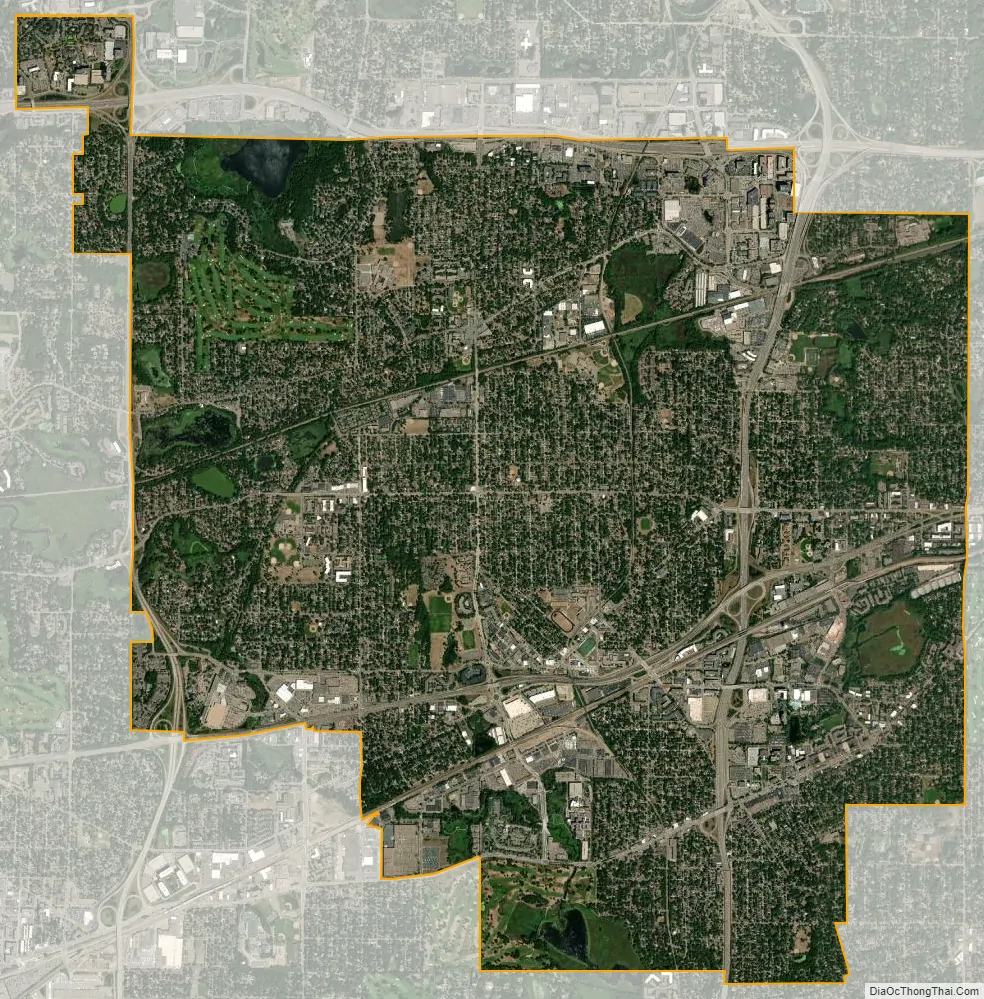
St. Louis Park city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 10.86 square miles (28.13 km), of which 10.64 square miles (27.56 km) is land and 0.22 square miles (0.57 km) is water.
Interstate 394, U.S. Highway 169, and Minnesota State Highways 7 and 100 are four of the main routes in St. Louis Park.
See also
Map of Minnesota State and its subdivision:- Aitkin
- Anoka
- Becker
- Beltrami
- Benton
- Big Stone
- Blue Earth
- Brown
- Carlton
- Carver
- Cass
- Chippewa
- Chisago
- Clay
- Clearwater
- Cook
- Cottonwood
- Crow Wing
- Dakota
- Dodge
- Douglas
- Faribault
- Fillmore
- Freeborn
- Goodhue
- Grant
- Hennepin
- Houston
- Hubbard
- Isanti
- Itasca
- Jackson
- Kanabec
- Kandiyohi
- Kittson
- Koochiching
- Lac qui Parle
- Lake
- Lake of the Woods
- Lake Superior
- Le Sueur
- Lincoln
- Lyon
- Mahnomen
- Marshall
- Martin
- McLeod
- Meeker
- Mille Lacs
- Morrison
- Mower
- Murray
- Nicollet
- Nobles
- Norman
- Olmsted
- Otter Tail
- Pennington
- Pine
- Pipestone
- Polk
- Pope
- Ramsey
- Red Lake
- Redwood
- Renville
- Rice
- Rock
- Roseau
- Saint Louis
- Scott
- Sherburne
- Sibley
- Stearns
- Steele
- Stevens
- Swift
- Todd
- Traverse
- Wabasha
- Wadena
- Waseca
- Washington
- Watonwan
- Wilkin
- Winona
- Wright
- Yellow Medicine
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming