Saxonburg is a borough in Butler County, Pennsylvania, United States. It is part of the Pittsburgh metropolitan area in the western part of the state. It was founded in 1832 by F. Carl Roebling and his younger brother John as a German farming colony. The population of Saxonburg was 1,525 as of the 2010 census.
The city was first named “Germania” and “Sachsenburg” before its name was Anglicized to the present one. After Roebling returned to his engineering career, he developed his innovation of wire rope in a workshop here. He became known for his design of suspension bridges, including the most famous one, the Brooklyn Bridge in New York.
| Name: | Saxonburg borough |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 21 |
| LSAD Description: | borough (suffix) |
| State: | Pennsylvania |
| County: | Butler County |
| Incorporated: | 1846 |
| Total Area: | 0.91 sq mi (2.35 km²) |
| Land Area: | 0.91 sq mi (2.35 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km²) |
| Total Population: | 1,426 |
| Population Density: | 1,573.95/sq mi (607.39/km²) |
| Area code: | 724, 878 |
| FIPS code: | 4268056 |
| Website: | www.saxonburgpa.com |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Saxonburg location map. Where is Saxonburg borough?
History
Founded in 1832 by Friedrich Carl Roebling and his younger brother John A. Roebling, the frontier farming community was initially called “Germania”. This was changed to “Sachsenburg” and later anglicized to Saxonburg. Roebling had emigrated with his brother Carl and a group of pioneers from Prussia (Germany) in 1831 to flee political unrest and oppression. ( doubtful quite from the Great Bridge by David McCullogh published 1972 “He was seeking neither religious freedom nor release from the bondage of poverty.His quest was for something else”)The two men, along with a handful of a larger group who accompanied them on the trans-Atlantic journey, bought 1,582 acres (6.40 km) of land on October 28, 1831, from Mrs. Sarah Collins.
After a few years, Roebling left farming to return to his career as an engineer. He developed a way to produce wire rope or cable, and used it in several of his projects, beginning with an aqueduct. He produced the wire rope at a workshop on his property in Saxonburg. He designed several suspension bridges, including two in Pittsburgh and one in Philadelphia. His most famous is his Brooklyn Bridge in New York. The Roebling Museum in the borough maintains several artifacts of his notable career.
In November 1920, KDKA radio, regarded as the world’s first commercial radio station, began broadcasting from East Pittsburgh. Later it located its transmitter in neighboring Clinton Township of Butler County. While the transmitter facility is no longer in Butler County, artifacts of it remain on display at the Saxonburg Museum, co-located with Roebling Park.
Saxonburg’s radio history continues with an internet-based radio station, saxonburgradio.com. The station, which is privately owned, has served the borough and surrounding southern Butler County with music and local news since October 25, 2015. The station also broadcasts over the air on micropower levels throughout Saxonburg on AM 1620 and FM 100.3 under FCC Part 15 rules.
Nuclear lab
In 1946, Fred Seitz, head of the physics department at Carnegie Tech, recruited Ed Creutz, Jack Fox, Roger Sutton and Bert Corben to the university to develop an important nuclear physics research program. By June 6, 1946, they had built a leading-edge, 450 MeV proton synchrocyclotron at the Nuclear Research Center near Saxonburg, just south of the city limits. The research program flourished up to the mid-1970s. By then the accelerator had become obsolete and was dismantled. The site was converted to industrial purposes, and is now occupied by II-VI Corporation. As of 1997, only one or two of the original Nuclear Research Center buildings remained intact, including the original laboratory building.
Murder of Police Chief Adams
On the afternoon of December 4, 1980, career criminal Donald Eugene Webb was the chief suspect in the murder of the borough police chief Gregory Adams at the Agway in Saxonburg. This was the second homicide in the borough’s nearly 150-year history and received national attention, especially as Webb was never apprehended. Webb was put on the FBI Most Wanted List, but was never captured. After the FBI found new evidence in her house in 2016, in July 2017, his wife Lillian Webb confessed to hiding her husband for 17 years, and led the FBI and police to his remains buried in the yard of her Massachusetts house. He died in 1999 after a series of strokes, at the approximate age of 68.
The first murder occurred in 1942. Christina Foertsch, sister of Albert and Wilbert Foertsch, killed Adele, Wilbert’s two-year-old daughter before killing herself.
First woman mayor
In November 2009, Jody Pflueger was elected as mayor as a write-in candidate, defeating the 12-year incumbent. She is both the city’s first Democratic and first female mayor. While in office, Mayor Pflueger had the position of Police Chief reinstated in the small city. Pflueger was succeeded by Pamela Bauman in 2013, who died in office. William Gillespie was elected in a special election to complete the remainder of Bauman’s term. As of 2023, Gillespie remains in office.
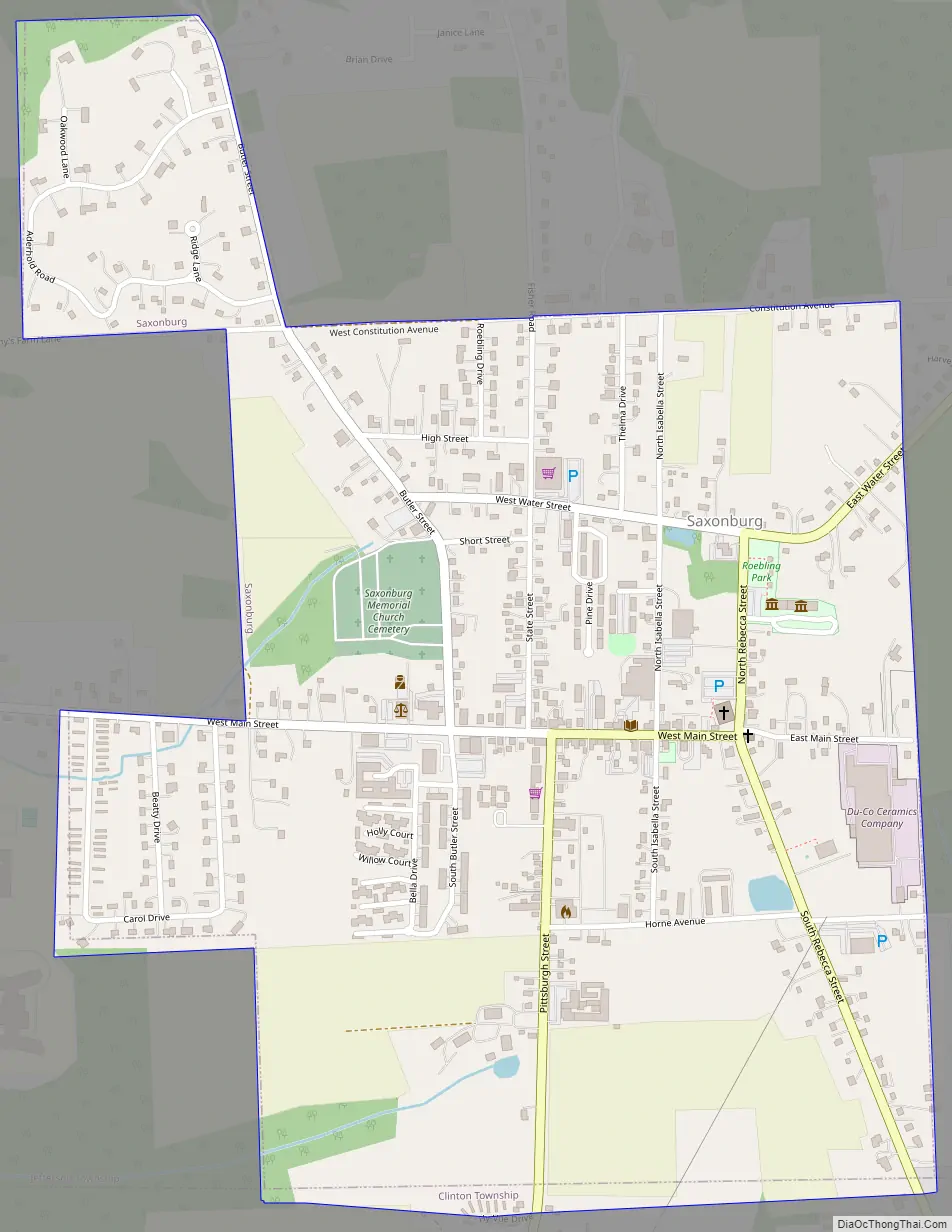
Saxonburg Road Map
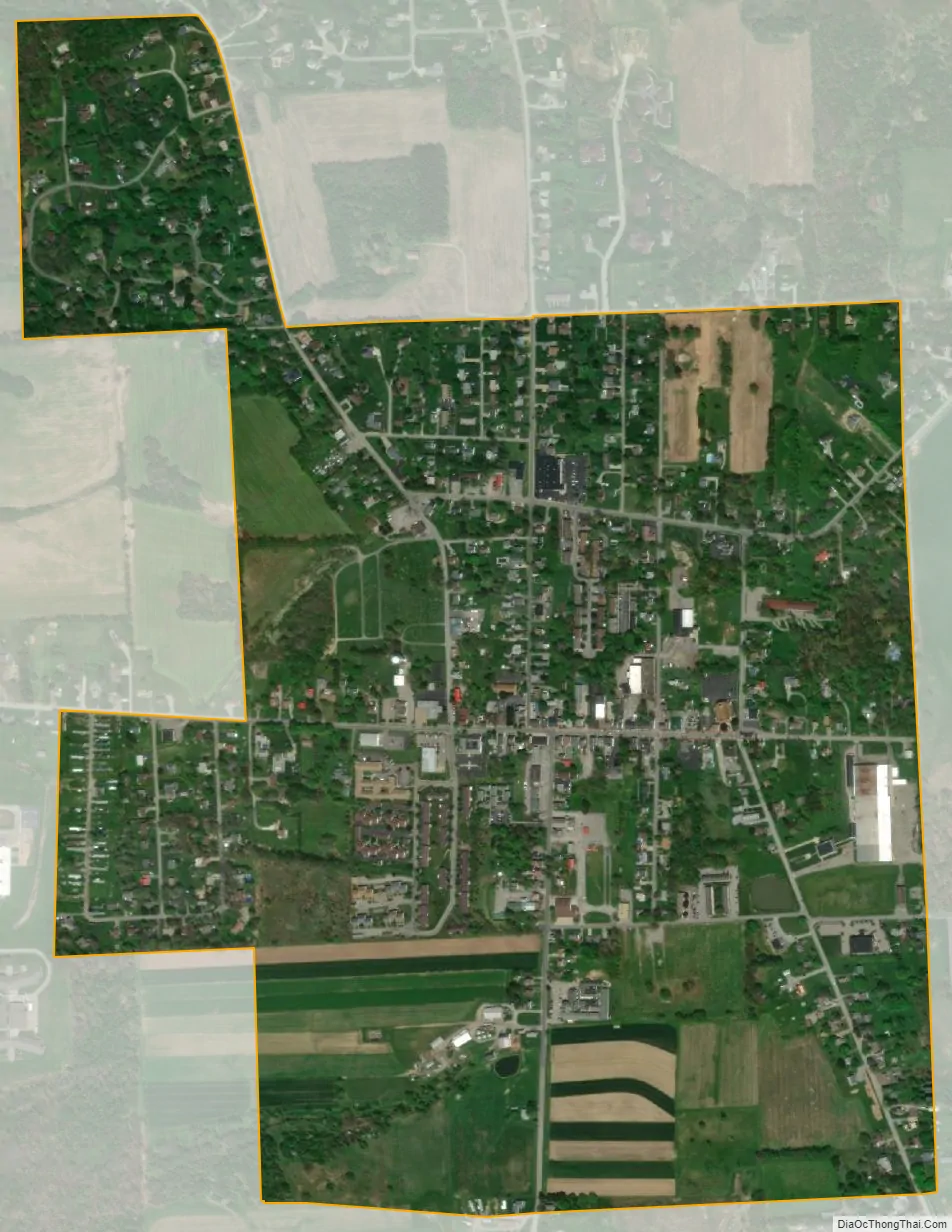
Saxonburg city Satellite Map
Geography
Saxonburg is located in southeastern Butler County at 40°45′15″N 79°48′56″W / 40.75417°N 79.81556°W / 40.75417; -79.81556 (40.754040, -79.815619). Butler, the county seat, is 9 miles (14 km) to the northwest, and Freeport, on the Allegheny River, is 10 miles (16 km) to the southeast.
According to the United States Census Bureau, Saxonburg has a total area of 0.89 square miles (2.3 km), all land.
See also
Map of Pennsylvania State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Allegheny
- Armstrong
- Beaver
- Bedford
- Berks
- Blair
- Bradford
- Bucks
- Butler
- Cambria
- Cameron
- Carbon
- Centre
- Chester
- Clarion
- Clearfield
- Clinton
- Columbia
- Crawford
- Cumberland
- Dauphin
- Delaware
- Elk
- Erie
- Fayette
- Forest
- Franklin
- Fulton
- Greene
- Huntingdon
- Indiana
- Jefferson
- Juniata
- Lackawanna
- Lancaster
- Lawrence
- Lebanon
- Lehigh
- Luzerne
- Lycoming
- Mc Kean
- Mercer
- Mifflin
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Montour
- Northampton
- Northumberland
- Perry
- Philadelphia
- Pike
- Potter
- Schuylkill
- Snyder
- Somerset
- Sullivan
- Susquehanna
- Tioga
- Union
- Venango
- Warren
- Washington
- Wayne
- Westmoreland
- Wyoming
- York
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming