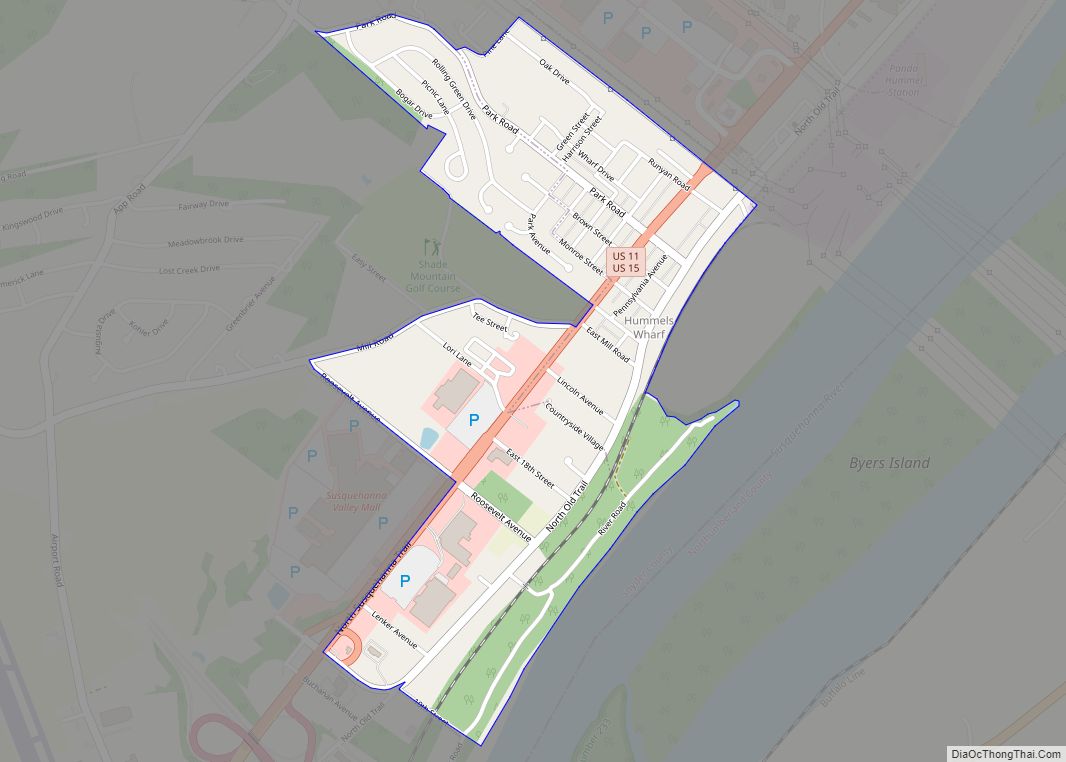
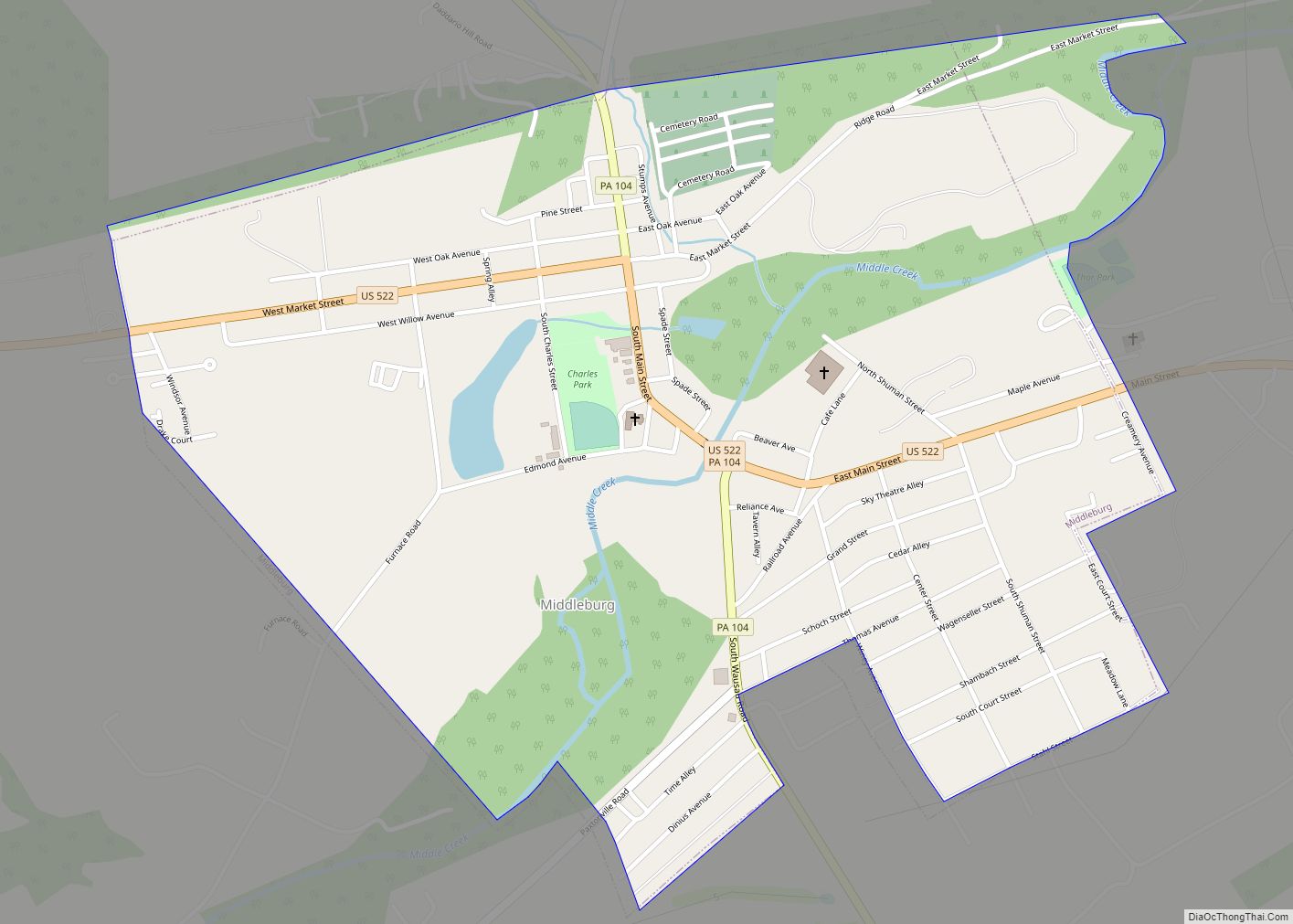
Shamokin Dam is a borough in Snyder County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 1,647 at the 2020 census.
“Shamokin” /ʃəˈmoʊkɪn/, or “Shahëmokink” in the Delaware language, and Schahamokink in another Algonquian language, means “place of eels.” The borough name is also derived from a 10-foot-tall (3.0 m) dam that was built across the Susquehanna River in the 19th century. The dam supported steamboat ferries run by Ira T. Clement, which transported goods and people between Shamokin Dam and the city of Sunbury on the Northumberland County side of the river. These ferries operated from 1772 until the Bainbridge Street Bridge was built in 1907. The dam also provided water to the Susquehanna Division of the Pennsylvania Canal System, which was constructed on the western bank of the river. The dam was destroyed by ice in March 1904. Shamokin Dam is distinct from the city of Shamokin, Pennsylvania, which is located to the east.
| Name: | Shamokin Dam borough |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 21 |
| LSAD Description: | borough (suffix) |
| State: | Pennsylvania |
| County: | Snyder County |
| Total Area: | 1.88 sq mi (4.88 km²) |
| Land Area: | 1.84 sq mi (4.78 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.04 sq mi (0.10 km²) |
| Total Population: | 1,652 |
| Population Density: | 895.39/sq mi (345.77/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 17876 |
| Area code: | 570 and 272 |
| FIPS code: | 4269616 |
| Website: | www.shamokindam.net |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
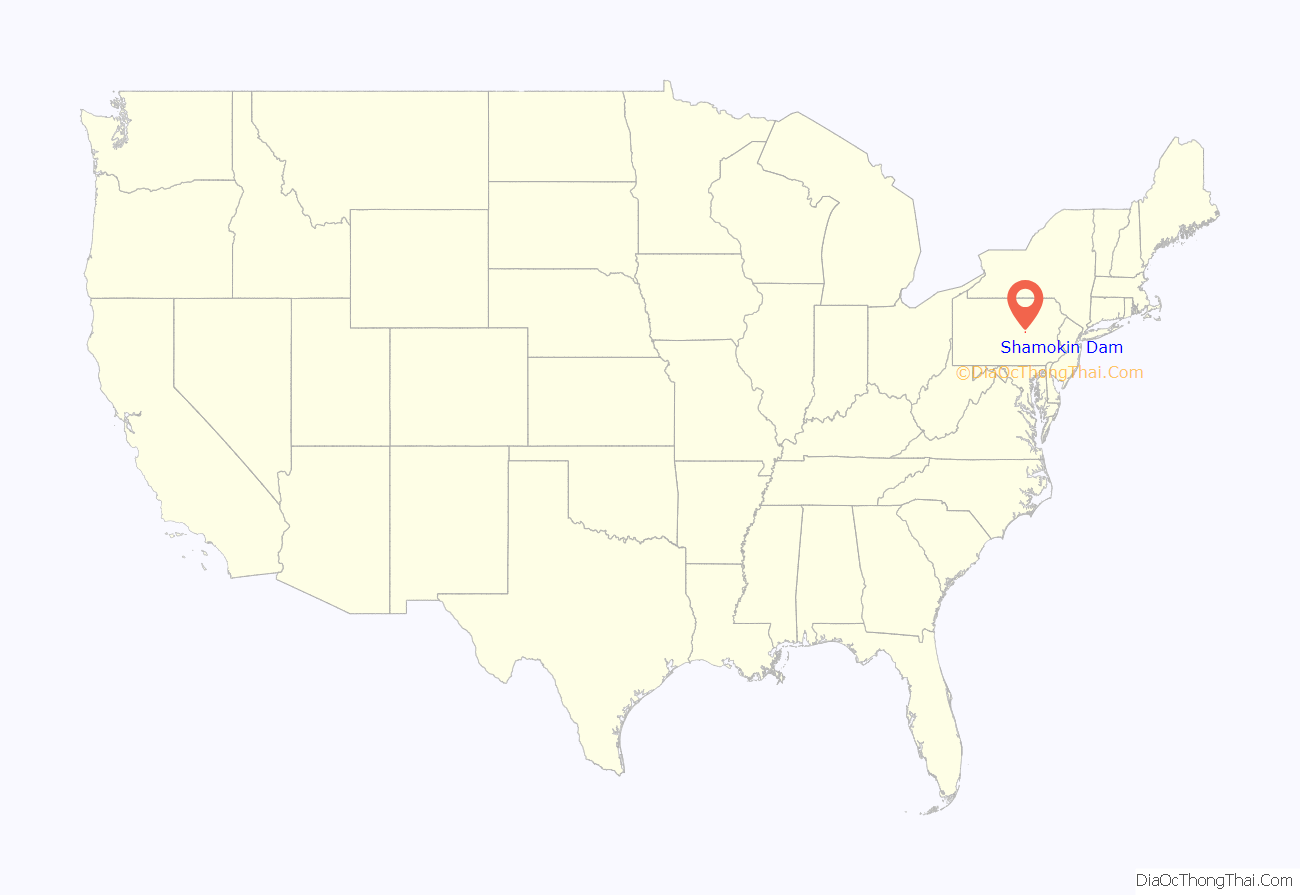
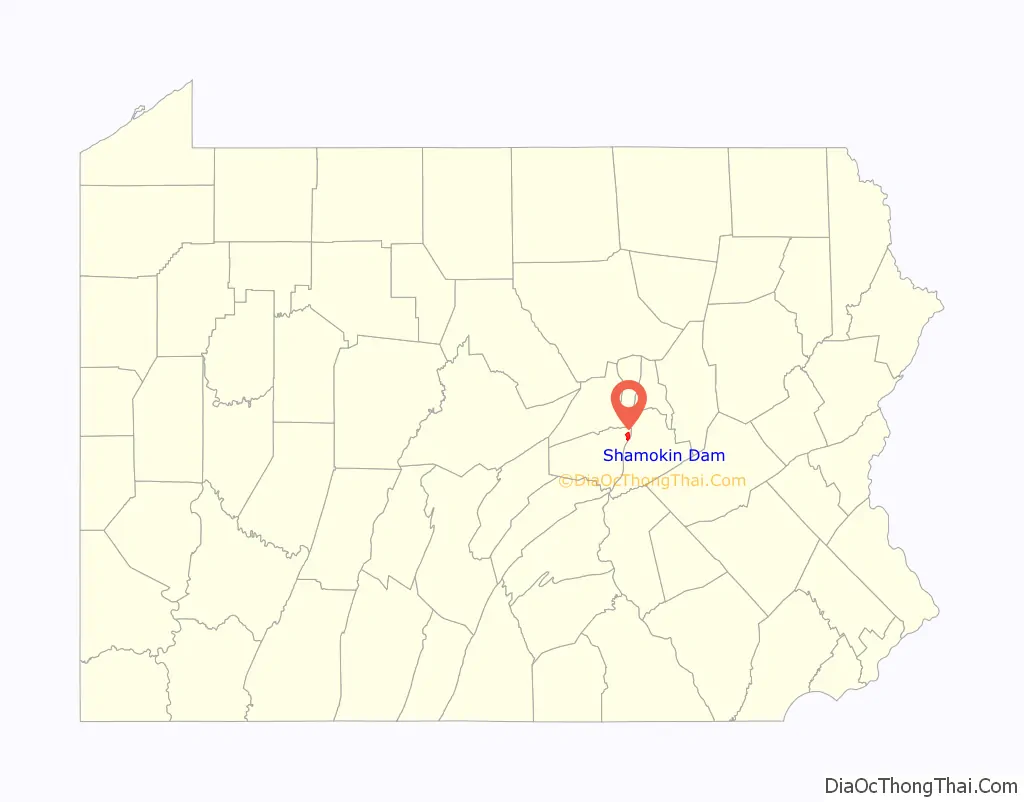
Shamokin Dam location map. Where is Shamokin Dam borough?
History
Pennsylvania was, for centuries, the home of many Native American tribes. During the 17th century the region was dominated by the Haudenosaunee Iroquois Confederacy, which at that time included the Mohawks, the Onondagas, the Cayugas, the Senecas and the Oneidas. Under the Confederacy the area was hunting grounds for the Delaware, Shawnee, Conoy, Monsey, Mohican and Nanticoke peoples. Allumapees was a Delaware chief who lived in Shamokin (now called Sunbury).
A large population of Delaware Indians was forcibly resettled in the area in the early 18th century after they lost rights to their land in the Walking Purchase. Canasatego of the Six Nations, enforcing the Walking Purchase of behalf of George Thomas, Deputy Governor of Pennsylvania, ordered the Delaware Indians to go to two places on the Susquehanna River, one of which was an area that included both present-day Sunbury, Pennsylvania and Shamokin Dam.
From 1727 to 1756, the village of Shamokin was one of the largest and most influential Indian settlements in Pennsylvania. In 1745, Presbyterian missionary David Brainerd described the city as being located on both the east and west sides of the river, and on an island, as well. Brainerd reported that the city housed 300 Indians, half of which were Delawares and the other Seneca and Tutelo.
In 1754, much of the land west of the Susquehanna was transferred from the Six Nations to Pennsylvania at the Albany Congress. However, Shamokin was not sold and was reserved by the Six Nations, “to settle such of our Nations as shall come to us from the Ohio or any others who shall deserve to be in our Alliance.” According to Weslager, “the Pennsylvania authorities had no opposition to the Six Nations reserving Wyoming and Shamokin from the sale, since friendly Delawares, including Teedyuskung (also known as Teedyuscung) and his people living in those settlements–and any other Indians who might be placed there–constituted a buffer against Connecticut.”
The French and Indian War brought fighting to much of the region. The Delaware Indian residents of Shamokin remained neutral for much of the early part of the war, in part because a drought and unseasonable frost in Shamokin in 1755 left them without provisions. However, the Delaware Indians at Shamokin joined the war against Pennsylvania and the English after the Gnadenhutten massacre in 1755. Pennsylvania Fort Augusta was built in 1756 at Shamokin. Read more about early history of Shamokin in Shamokin (village).
Shikellamy, of the Oneida people, came to the region. He negotiated with the white settlers on behalf of the native residents. In 1754, Chief Shikellamy negotiated with Conrad Weiser to set the Blue Mountains as the upper limit settlement in the native people’s home lands. Weiser told the area’s settlers they could not remain. The Six Nations Treaty of 1754 permitted settlements to move west of the Susquehanna River into lands that eventually became Snyder County. Many natives argued they had been cheated by the treaty. Conflicts between the settlers and the native peoples resulted in deaths on both sides. Eventually, the native peoples were pushed out by the white settlers after the French and Indian War.
Germans were among the first European settlers in the region. Their influence continues today in the presence of the Amish and Mennonite sects.
Shamokin Dam was founded by George Keen in 1745. At the time it was named Keensville. Most of the residents were canal workers, raftsmen, shad fishermen and eel fishermen. Restaurants and hotels provided support for the workers and travelers. A lock for the Pennsylvania Canal was located on the riverbank. Most of the local commerce revolved around transportation and supporting the canal.
In 1907 a toll bridge was completed that connected Shamokin Dam to Sunbury the county seat of Northumberland County. The cost for construction was $150,000. A full-time toll collector lived in the house that straddled the bridge. A gate closed the bridge at night. A bell was posted to summon the toll worker during the night. The bridge was used by pedestrians, buggies and motor cars. The toll was 3 cents for walkers, 4 cents for bicyclists, with 15 cents for horses, buggies and motor cars.
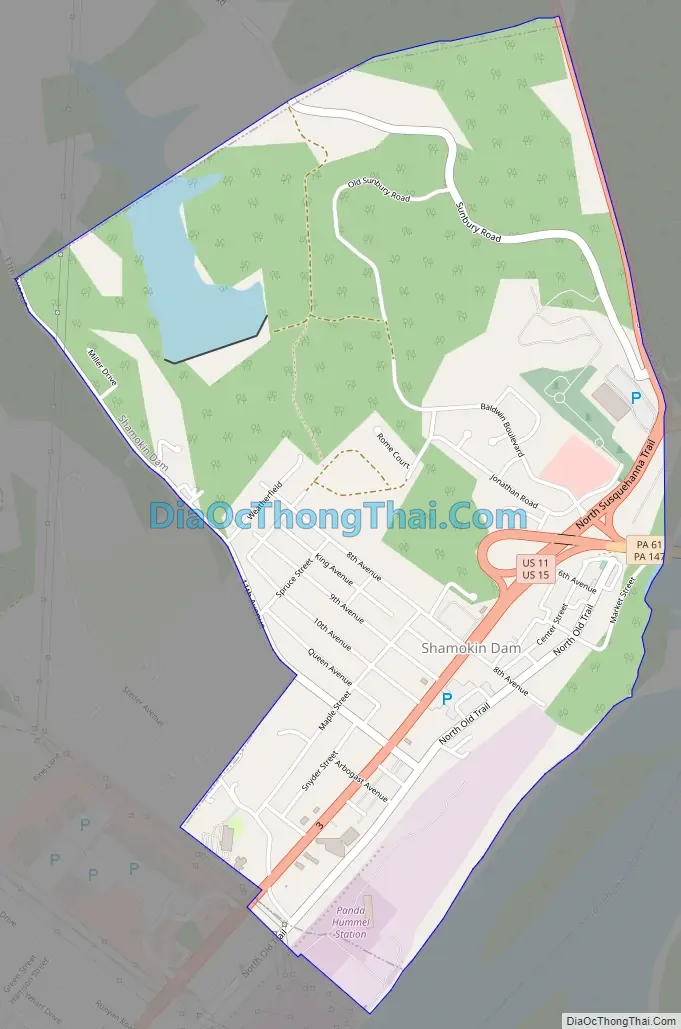
Shamokin Dam Road Map
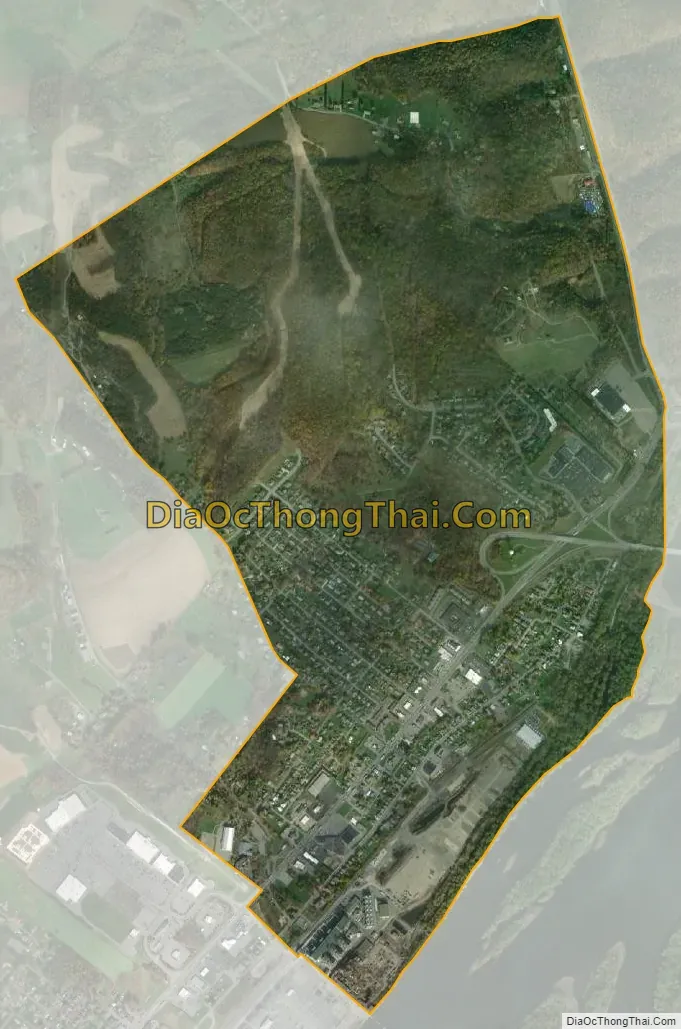
Shamokin Dam city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the borough has a total area of 1.9 square miles (4.9 km), of which 1.8 square miles (4.7 km) is land and 0.1 square miles (0.26 km) (2.66%) is water.
Shamokin Dam sits on the western bank of the Susquehanna River, just south of the confluence of the river’s west and north branches. The borough is also bordered by the community of Hummels Wharf, Monroe Township, and U.S. Route 15.
The Norfolk Southern Railway (formerly Conrail/Penn Central/Pennsylvania Railroad) passes through the borough between the Old Trail Road and the Susquehanna River.
There are several small, unnamed creeks that cross the borough, eventually draining into the Susquehanna River. Seasonal flooding occurs in the lowlands between the rail line and the river where the canal once passed. Some areas of the borough lie in the 100 year flood plain.
For many years, addresses in Shamokin Dam were listed under the same ZIP code as Selinsgrove, which was 17870. This led to confusion by delivery companies, emergency services and visitors to the region. Additionally, tax funding that should have gone to Shamokin Dam was lost. The implementation of the GIS readdressing program required that several local communities rename streets so that there were no redundancies within the Selinsgrove ZIP code. This prompted Shamokin Dam officials to appeal to the United States Postal Service for a unique ZIP code, which was awarded. Shamokin Dam addresses then became 17876.
See also
Map of Pennsylvania State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Allegheny
- Armstrong
- Beaver
- Bedford
- Berks
- Blair
- Bradford
- Bucks
- Butler
- Cambria
- Cameron
- Carbon
- Centre
- Chester
- Clarion
- Clearfield
- Clinton
- Columbia
- Crawford
- Cumberland
- Dauphin
- Delaware
- Elk
- Erie
- Fayette
- Forest
- Franklin
- Fulton
- Greene
- Huntingdon
- Indiana
- Jefferson
- Juniata
- Lackawanna
- Lancaster
- Lawrence
- Lebanon
- Lehigh
- Luzerne
- Lycoming
- Mc Kean
- Mercer
- Mifflin
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Montour
- Northampton
- Northumberland
- Perry
- Philadelphia
- Pike
- Potter
- Schuylkill
- Snyder
- Somerset
- Sullivan
- Susquehanna
- Tioga
- Union
- Venango
- Warren
- Washington
- Wayne
- Westmoreland
- Wyoming
- York
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming