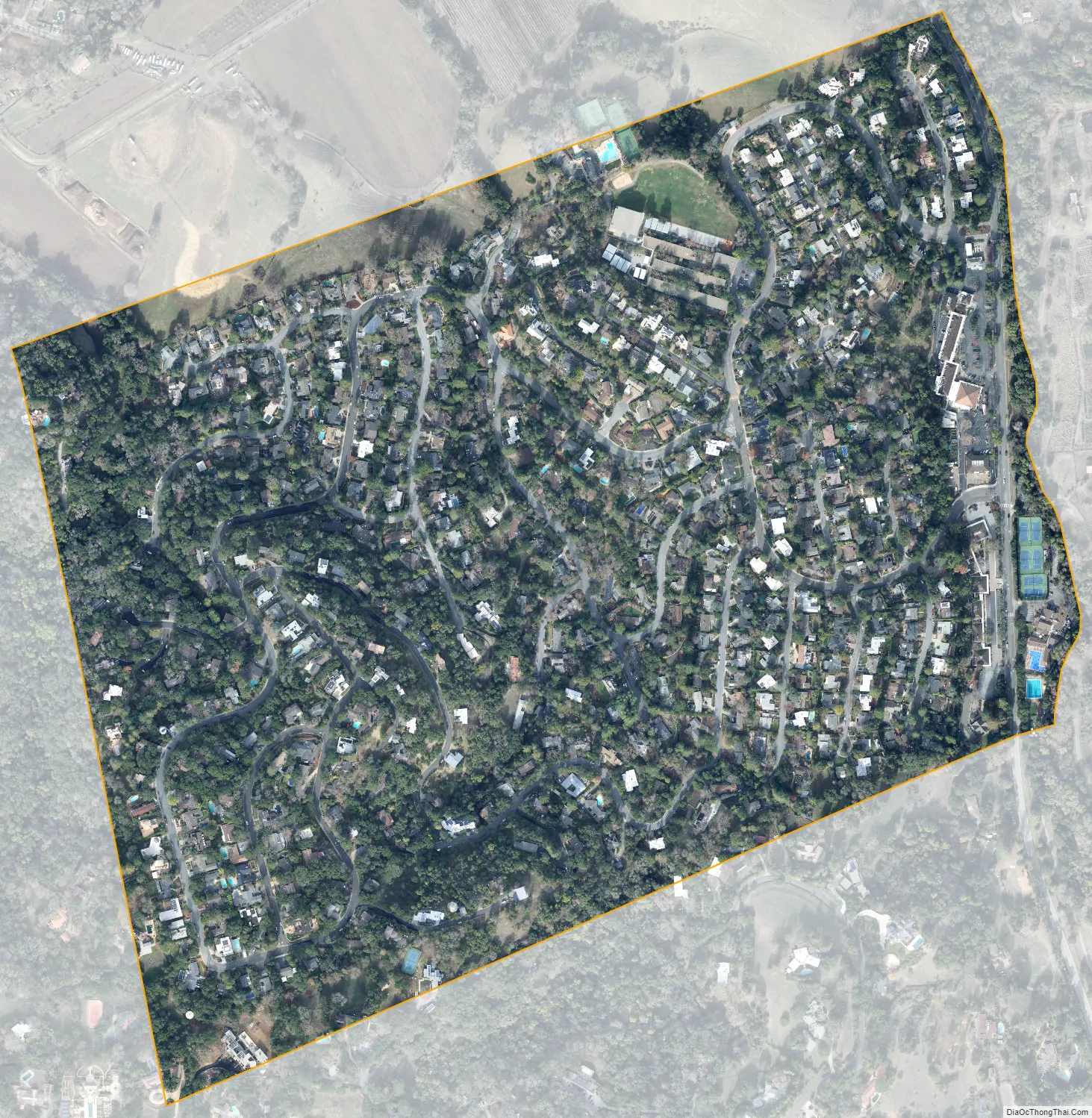
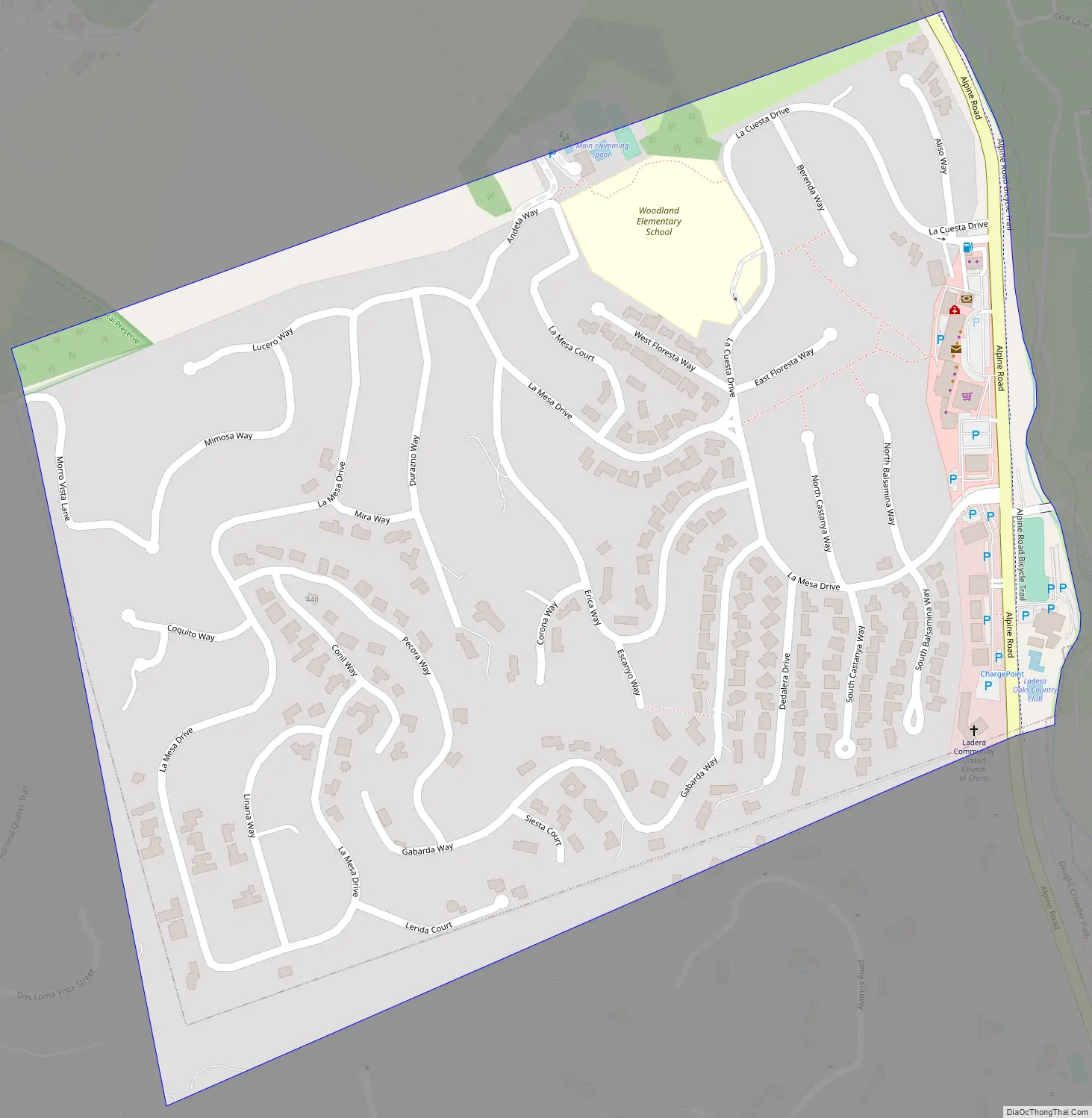
Ladera is a census-designated place (CDP) in southern San Mateo County, California, adjacent to Portola Valley. Primarily a residential community, it comprises approximately 520 homes, governed by the Ladera Community Association. The ZIP Code is 94028 and the community is inside area code 650. The population was 1,557 at the 2020 census.
| Name: | Ladera CDP |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 57 |
| LSAD Description: | CDP (suffix) |
| State: | California |
| County: | San Mateo County |
| Elevation: | 315 ft (96 m) |
| Total Area: | 0.443 sq mi (1.146 km²) |
| Land Area: | 0.443 sq mi (1.146 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0 sq mi (0 km²) 0% |
| Total Population: | 1,557 |
| Population Density: | 3,500/sq mi (1,400/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 94028 |
| Area code: | 650 |
| FIPS code: | 0639094 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 2628745 |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Ladera location map. Where is Ladera CDP?
History
The Ramaytush Ohlone peoples occupied the land that is now the community of Ladera, prior to the settlement of California by the Spanish. Ladera is located on the Rancho Corte de Madera Mexican land grant.
The land was used for grazing and timber through 1927 when it was joined to the Ormondale Ranch, owned by the Macdonough family. The Macdonoughs raised cattle and sheep, and bred racehorses; their most famous stud, Ormonde, had raced in England and never lost a race. In the 1930s, the majority of the Ormondale Ranch land was developed and incorporated into Portola Valley.
In 1944, the Peninsula Housing Association (PHA) was formed with the goal of purchasing a tract of land and developing a housing cooperative. Several prominent members of the Stanford and Palo Alto communities joined to develop the fledgling PHA co-op. It began subscribing members in 1945 and its 150 members purchased the remaining 260 acres (1.1 km) of the former Ormondale ranch for $155,000 on July 31, 1946. The co-op selected noted landscape architect Garrett Eckbo to lay out the design for the new community. Architects Joseph Allen Stein and John Funk were chosen to design several of the earliest model homes.
The members chose the name Ladera (over alternatives Lark Hills and New Rochdale) to reflect the Spanish history of the land — ladera is Spanish for hillside. Streets are Spanish phrases or botanical names. Early members of the cooperative included author Wallace Stegner and Klystron tube inventor Sigurd Varian of Varian Associates. (Varian had grown up in Halcyon, another intentional community in southern California.)
The PHA refused to place restrictive covenants on title deeds. However, the Federal Housing Administration would not insure loans to co-ops that included African American members – an example of redlining. Banks would not finance loans or issue mortgages without government approval, so the PHA failed due to financial difficulties after only a few houses had been constructed. The co-op proposed the inclusion of a quota system, promising that the proportion of African American members would not exceed the proportion of African Americans in California’s overall population. This stipulation was not sufficient for the government. The land was later sold to Hare, Brewer, and Kelley, who completed the development. Directly following completion, single family homes in the development were only sold to whites. Four non-white families were required to sell their land. These types of provisions were mostly legally unenforceable after Shelley v. Kraemer (1948) though they continued to be added and privately unenforceable after the Fair Housing Act of 1968 (see Housing discrimination in the United States).
In November 2021, following a two-and-a-half-month petition drive that achieved signatures from owners of 391 of the 534 properties in Ladera, the clause forbidding residency by people “other than those of the Caucasian or white race” was replaced by the statement: “By provisions outlined in this document the Ladera Community has formally acted to remove the Race Restriction that previously comprised this subsection, and by so doing asserts that the Ladera Community supports diversity, equity, and inclusion.”
Ladera Road Map
Ladera city Satellite Map
Geography
Ladera is located at the bottom of the eastern slope of the Peninsula Range of the Santa Cruz Mountains. It is bordered on the west by the Jasper Ridge Biological Preserve operated by Stanford University, on the east by Alpine Road, and on the north by Webb Ranch.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP covers an area of 0.4 square miles (1.1 km), all of it land.
See also
Map of California State and its subdivision:- Alameda
- Alpine
- Amador
- Butte
- Calaveras
- Colusa
- Contra Costa
- Del Norte
- El Dorado
- Fresno
- Glenn
- Humboldt
- Imperial
- Inyo
- Kern
- Kings
- Lake
- Lassen
- Los Angeles
- Madera
- Marin
- Mariposa
- Mendocino
- Merced
- Modoc
- Mono
- Monterey
- Napa
- Nevada
- Orange
- Placer
- Plumas
- Riverside
- Sacramento
- San Benito
- San Bernardino
- San Diego
- San Francisco
- San Joaquin
- San Luis Obispo
- San Mateo
- Santa Barbara
- Santa Clara
- Santa Cruz
- Shasta
- Sierra
- Siskiyou
- Solano
- Sonoma
- Stanislaus
- Sutter
- Tehama
- Trinity
- Tulare
- Tuolumne
- Ventura
- Yolo
- Yuba
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming