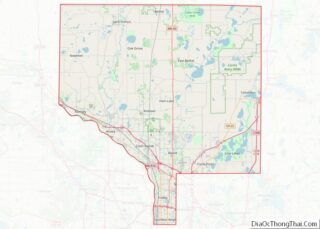
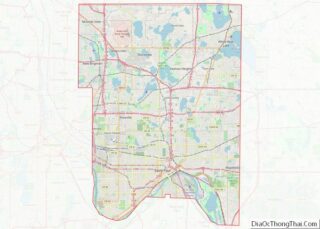
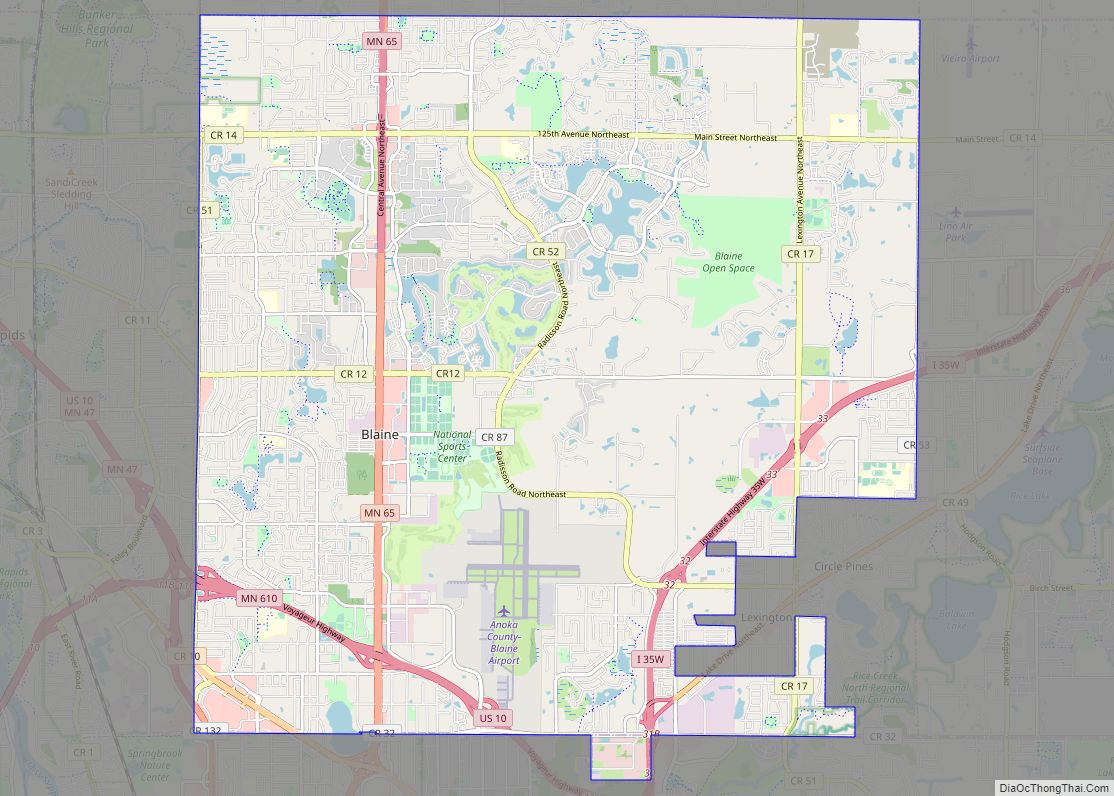
Blaine is a suburban city in Anoka and Ramsey counties in the State of Minnesota, United States. Once a rural town, Blaine’s population has increased significantly in the last 60 years. For several years, Blaine led the Twin Cities metro region in new home construction. The population was 70,222 at the 2020 census. The city is located mainly in Anoka County, and is part of the Minneapolis–Saint Paul metropolitan area.
Interstate 35W, U.S. Highway 10, and Minnesota State Highway 65 are three of the main routes in the city.
| Name: | Blaine city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Minnesota |
| County: | Anoka County, Ramsey County |
| Founded: | 1877 |
| Incorporated: | January 29, 1954 |
| Elevation: | 906 ft (276 m) |
| Land Area: | 32.91 sq mi (85.22 km²) |
| Water Area: | 1.12 sq mi (2.91 km²) |
| Population Density: | 2,134.08/sq mi (823.98/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 55014, 55434, 55449 |
| Area code: | 763 |
| FIPS code: | 2706382 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 2394183 |
| Website: | blainemn.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
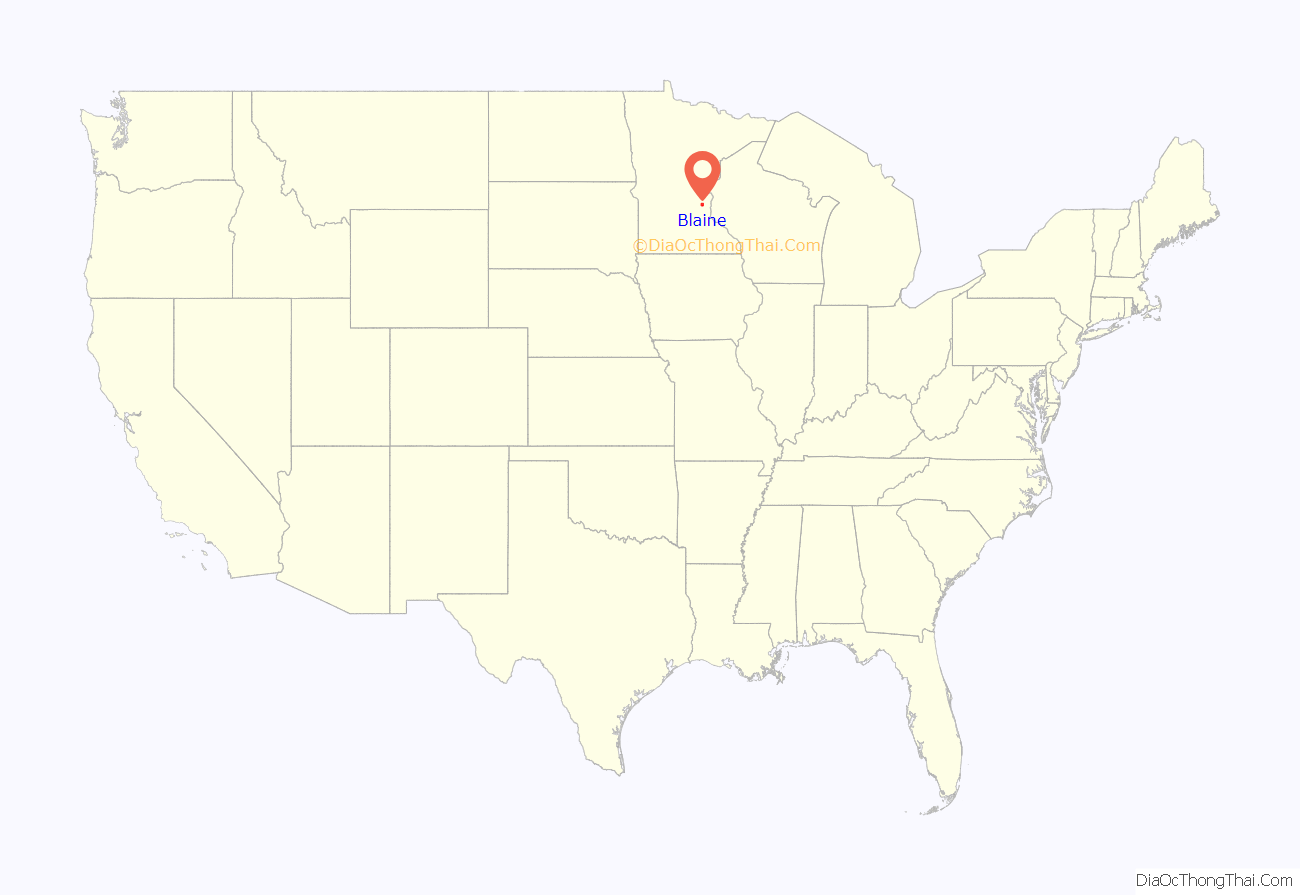
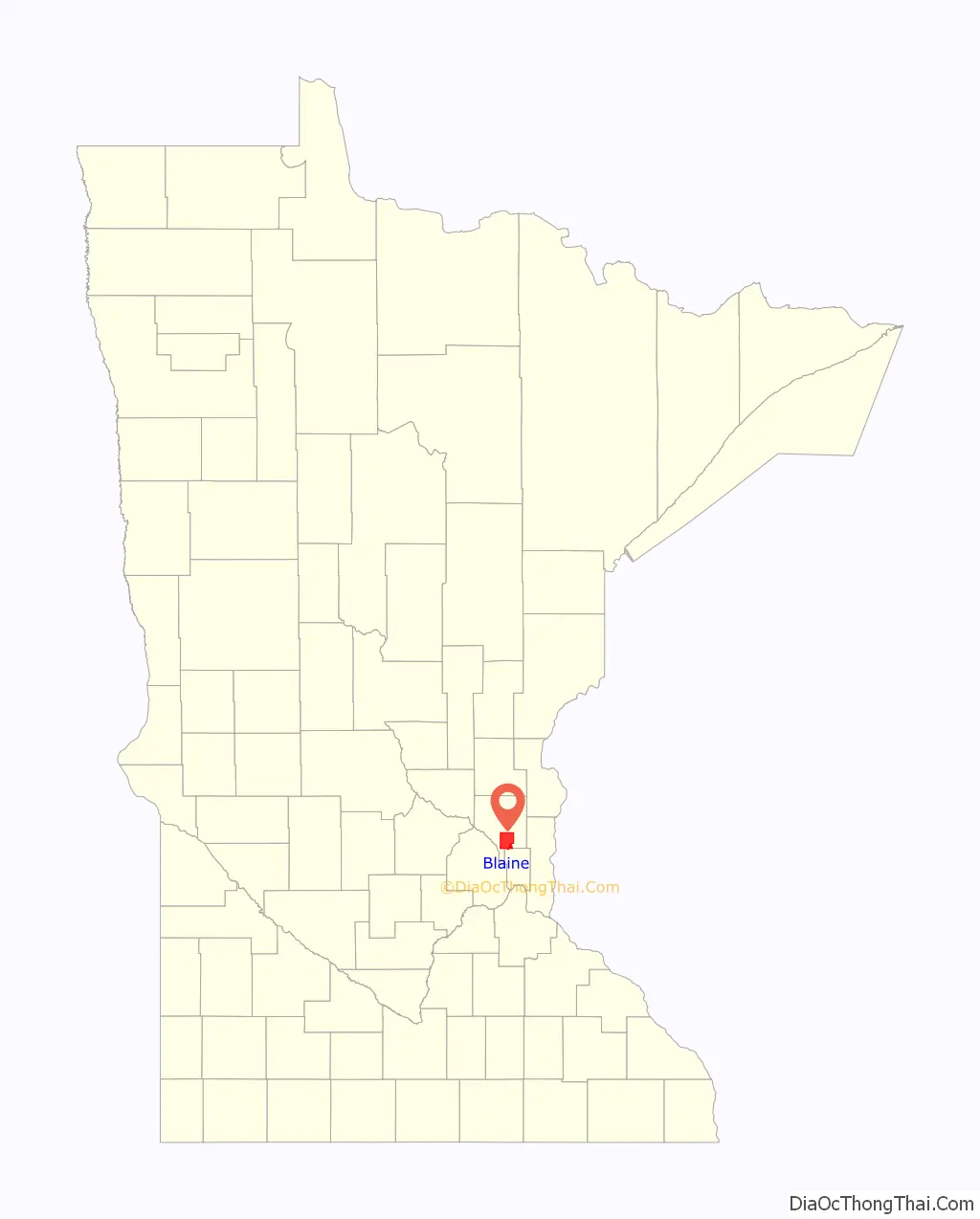
Blaine location map. Where is Blaine city?
History
Phillip Leddy, a native of Ireland, was recorded in the 1857 census as having settled in the township of Anoka until his death in 1872, on land that later became Blaine. In 1862, he moved near a lake that now bears his misspelled name, Laddie Lake. Another early settler was the Englishman George Townsend, who lived for a short time near what today is Lever St. and 103rd Ave.
It was not until 1865 that Blaine’s first permanent resident, Greenberry Chambers, settled on the old Townsend claim. Chambers was a former slave who moved north from Barren County, Kentucky, after the American Civil War. Around 1884, Chambers and his family moved to St. Paul.
In 1870, George Wall, Joseph Gagner, and others soon settled in the area and it began to grow.
In 1877, Blaine separated from Anoka and organized as a township of its own. That year the first election was held and Moses Ripley was elected the first Chairman of the Board of Supervisors. By 1880, Blaine’s population had reached 128.
While many other Anoka County communities experienced growth due to farming, Blaine’s sandy soil and abundant wetlands discouraged farmers and it remained a prime hunting area. Blaine’s growth remained slow until after World War II, when housing developments began in the southern part of town and the community became more suburban. Blaine’s population has grown from 1,694 in 1950 to 20,573 in 1970 to 57,186 in 2010 to 70,222 in 2020. By 2022, the population was over 72,000.
Furthermore, the land development technique of sand mining opened thousands of acres of peat sod farms up for development. Beginning with the development of the Knoll Creek, Club West, Pleasure Creek and TPC Twin Cities, the existing land was modified through extensive grading efforts with the result in the large open water areas. The sand from the excavation of those ponds was used to raise the level of the site. These site modifications are needed to accommodate the development of the homes and neighborhoods. The success of mining sand allowed for further development in the city. The centerpiece of those developments is The Lakes of Blaine. Corporate residents include the Aveda Corporation, Infinite Campus, PTC Inc, MagnetStreet, the parking lot portion of a Medtronic Development, and Dayton Rogers Manufacturing.
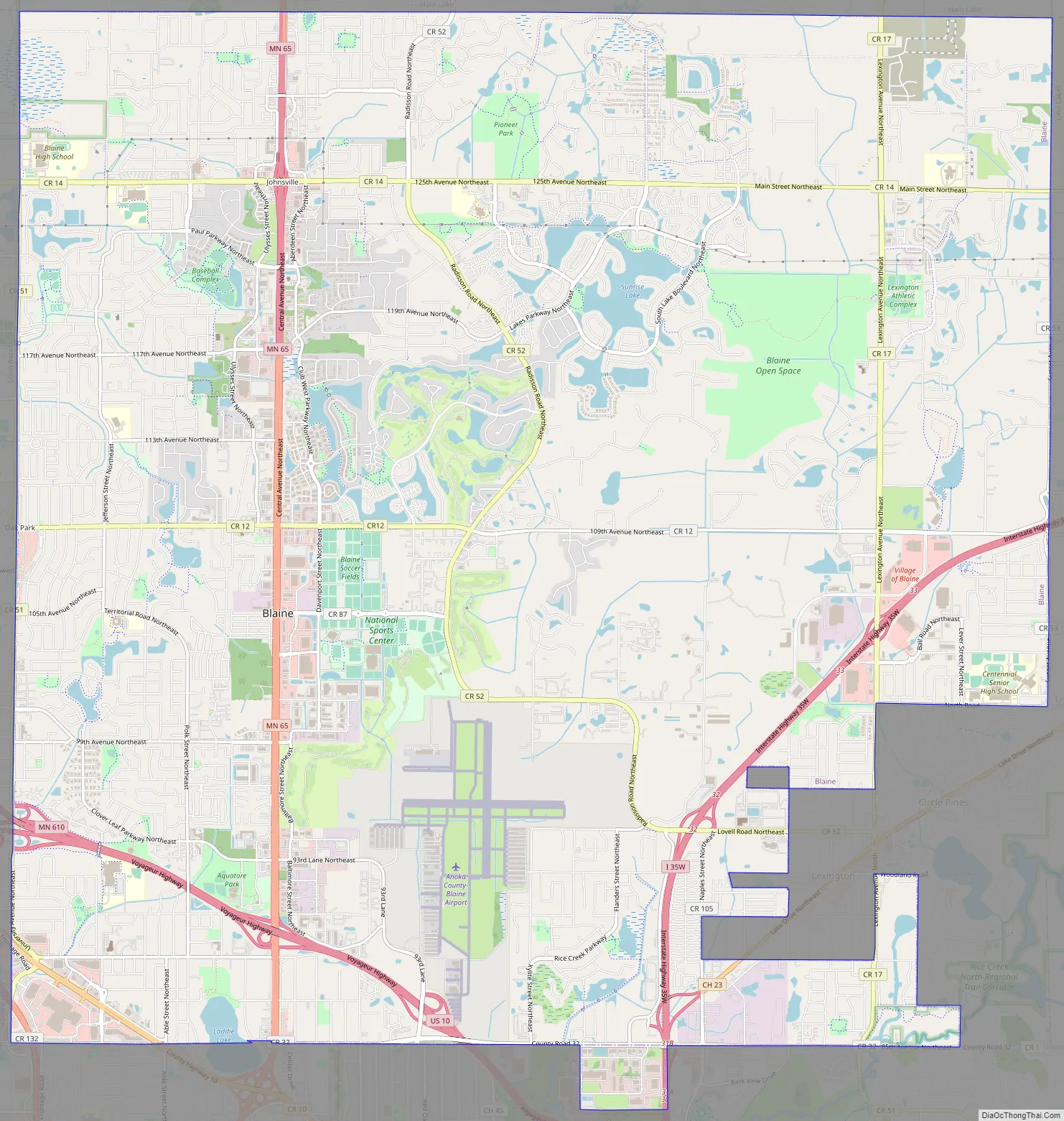
Blaine Road Map
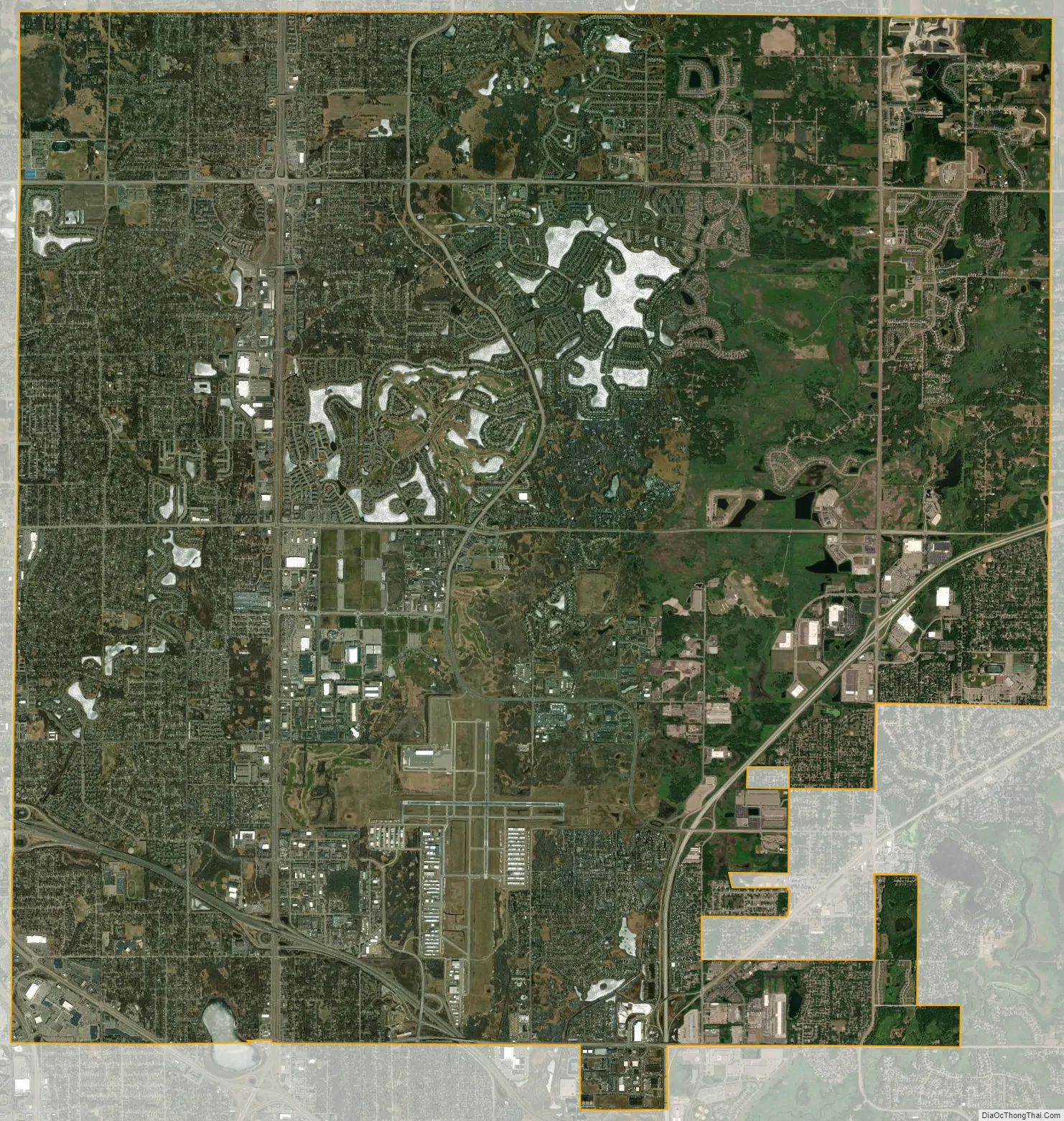
Blaine city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 34.05 square miles (88.19 km), of which 33.85 square miles (87.67 km) is land and 0.20 square miles (0.52 km) is water. Blaine is 13 miles (21 kilometers)) from Minneapolis and 20 mi (32 km) from St. Paul.
Blaine can be accessed from several major roadways in the Twin Cities, including Minnesota State Highway 65, Interstate 35W, University Avenue, Lexington Avenue, Hamline Avenue, U.S. Highway 10 and Minnesota State Highway 610.
Major landforms
The Blaine area was covered by a large glacier that shaped the landscape during the late Wisconsinan glaciation. The land used to be covered by river valleys 200 feet deep. The valleys filled with sediment. One valley ran northeast to southwest under Lino Lakes. As the glaciers retreated, the water gathered into a lake that covered much of Anoka County. Huge ice chunks were left in the glacier’s wake. They melted and formed depressions that filled with water. This became the chain of lakes between Lino Lakes and Circle Pines.
There are four major named water bodies partially or completely within the city limits. Sunrise Lake as part of The Lakes housing development is the largest body at 158 acres in size, and going down to depths of near 40 feet in some places. The next largest body is Laddie Lake, the only naturally occurring lake in Blaine, which is also partially in Spring Lake Park at 77 acres in size, reaching maximum depth of 6 ft in some locations. The next largest body is Club West Lake at 39 acres and depths up to 25 ft, also man-made, located in the Club West Housing development. The last named body of water in the city is Loch Ness; at 11 acres in size it is managed by the city and has a provided fishing dock. There are several other large bodies of water within the city that are not classified as lakes found around the TPC of the Twin Cities, Pleasure Creek Neighborhood, Knoll Creek Development, Crescent Ponds.
Blaine is also in the process of creating a 500-acre open space plan. The city started acquiring portions of the property in the late 1990s, but most of it was acquired after Blaine voters approved a $3.5 million referendum in 2000. A tentative long-range plan calls for the construction of a nature center by 2020. The 70-acre Kane Meadows Park also acquired next to The Lakes development has been the centerpiece of this open space program.
See also
Map of Minnesota State and its subdivision:- Aitkin
- Anoka
- Becker
- Beltrami
- Benton
- Big Stone
- Blue Earth
- Brown
- Carlton
- Carver
- Cass
- Chippewa
- Chisago
- Clay
- Clearwater
- Cook
- Cottonwood
- Crow Wing
- Dakota
- Dodge
- Douglas
- Faribault
- Fillmore
- Freeborn
- Goodhue
- Grant
- Hennepin
- Houston
- Hubbard
- Isanti
- Itasca
- Jackson
- Kanabec
- Kandiyohi
- Kittson
- Koochiching
- Lac qui Parle
- Lake
- Lake of the Woods
- Lake Superior
- Le Sueur
- Lincoln
- Lyon
- Mahnomen
- Marshall
- Martin
- McLeod
- Meeker
- Mille Lacs
- Morrison
- Mower
- Murray
- Nicollet
- Nobles
- Norman
- Olmsted
- Otter Tail
- Pennington
- Pine
- Pipestone
- Polk
- Pope
- Ramsey
- Red Lake
- Redwood
- Renville
- Rice
- Rock
- Roseau
- Saint Louis
- Scott
- Sherburne
- Sibley
- Stearns
- Steele
- Stevens
- Swift
- Todd
- Traverse
- Wabasha
- Wadena
- Waseca
- Washington
- Watonwan
- Wilkin
- Winona
- Wright
- Yellow Medicine
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming