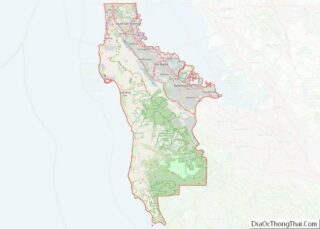
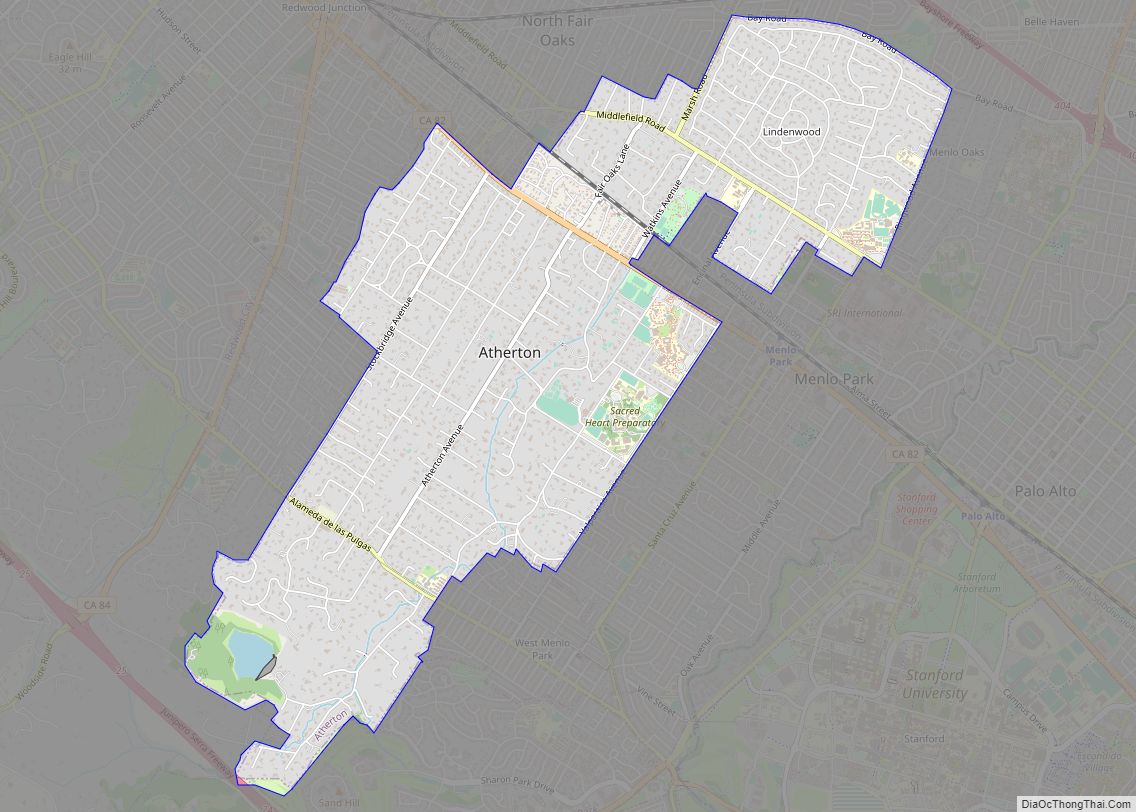
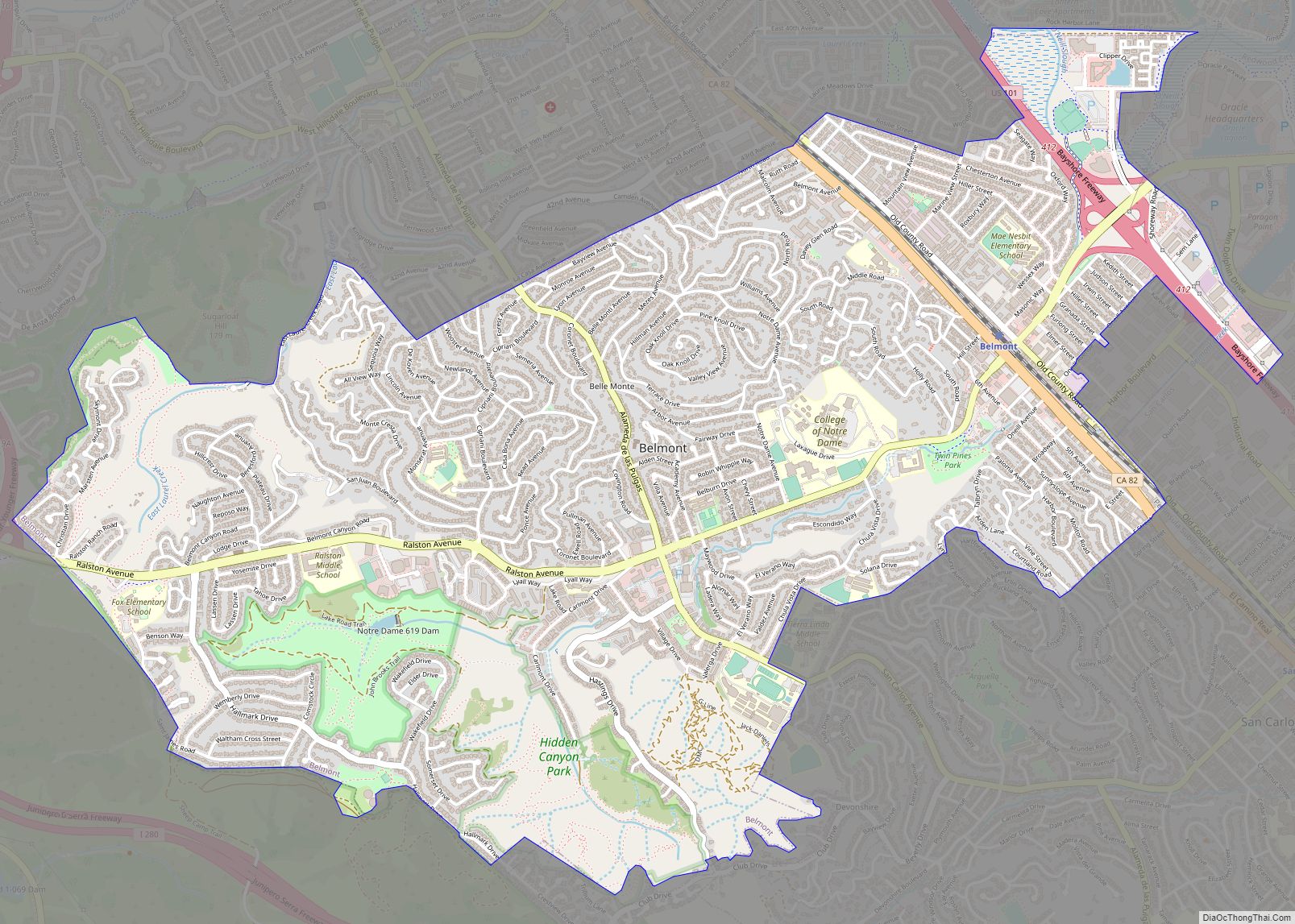
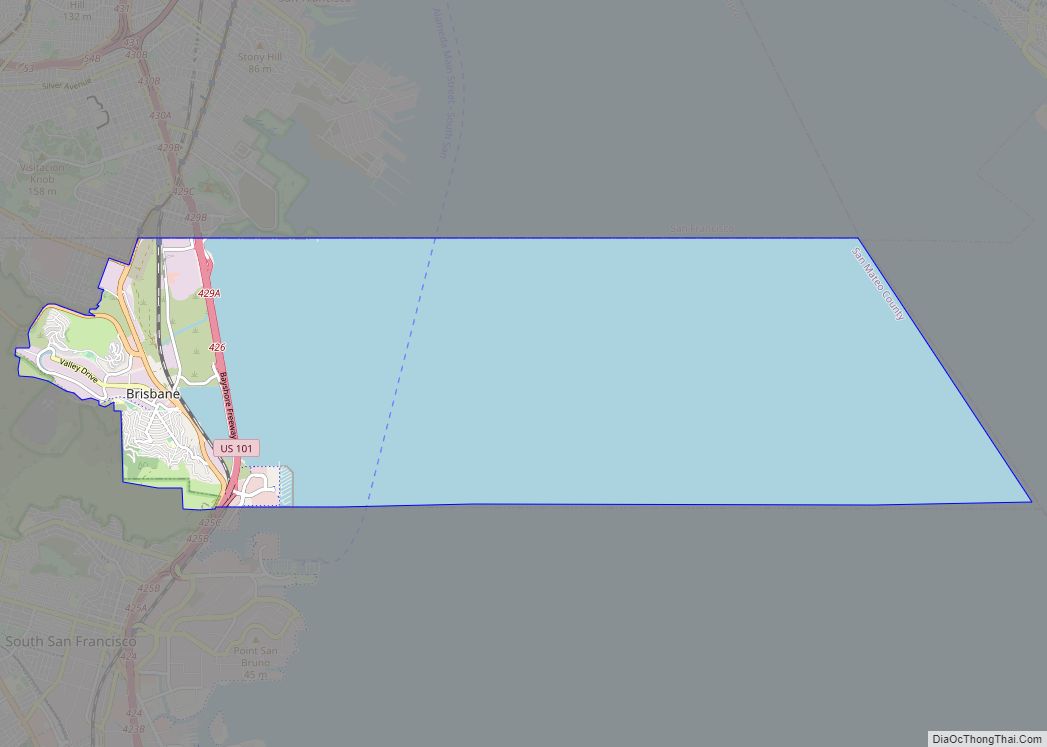
Montara (/mɒnˈtærə/) is a census-designated place (CDP) in San Mateo County, California, United States. The population was 2,833 at the 2020 census. Nearby communities include Moss Beach and Princeton-by-the-Sea.
| Name: | Montara CDP |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 57 |
| LSAD Description: | CDP (suffix) |
| State: | California |
| County: | San Mateo County |
| Elevation: | 98 ft (30 m) |
| Total Area: | 3.878 sq mi (10.045 km²) |
| Land Area: | 3.878 sq mi (10.045 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0 sq mi (0 km²) 0% |
| Total Population: | 2,833 |
| Population Density: | 730/sq mi (280/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 94037 |
| Area code: | 650 |
| FIPS code: | 0648760 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0277558 |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Montara location map. Where is Montara CDP?
History
A lighthouse was established at Point Montara in 1875. The Montara area was first settled by farmers in the late nineteenth century. A commercial flower farm, still in operation, was established in 1900. In 1905, Montara became a stop on the new Ocean Shore Railroad, then under construction. The railroad built a hotel next to the train station. The trains encouraged weekend visitors to the area, but development of the community was very slow. The railroad went bankrupt and ceased operations in 1920, but the hotel remained and, although greatly remodeled, is still standing today, between State Route 1 and Main Street, next to the remodeled train station.
The Montara Grammar School opened in 1915; the historic two-story building still stands, serving as a community center. The newer Farallone View Elementary School, a few blocks north of the original school, services the town’s children today.
California’s second paved highway, Pedro Mountain Road, was completed in 1914, providing another connection between Montara and San Francisco. This highway was replaced in 1937 by State Route 1, which followed the old railroad route through the Devil’s Slide. A tunnel was opened in 2013 to replace this dangerous route, which had been closed periodically due to landslides. The United States Navy operated an anti-aircraft training center at Point Montara during World War II.
Real growth in Montara began in the 1950s as more people moved away from San Francisco during the postwar boom. As Montara has continued to grow, the community has still maintained its generally rural image. Most of Montara’s streets were dirt or gravel until the early 1990s; the rustic quality of the town has not been lost since the streets were oiled or paved (only some of the streets are actually paved).
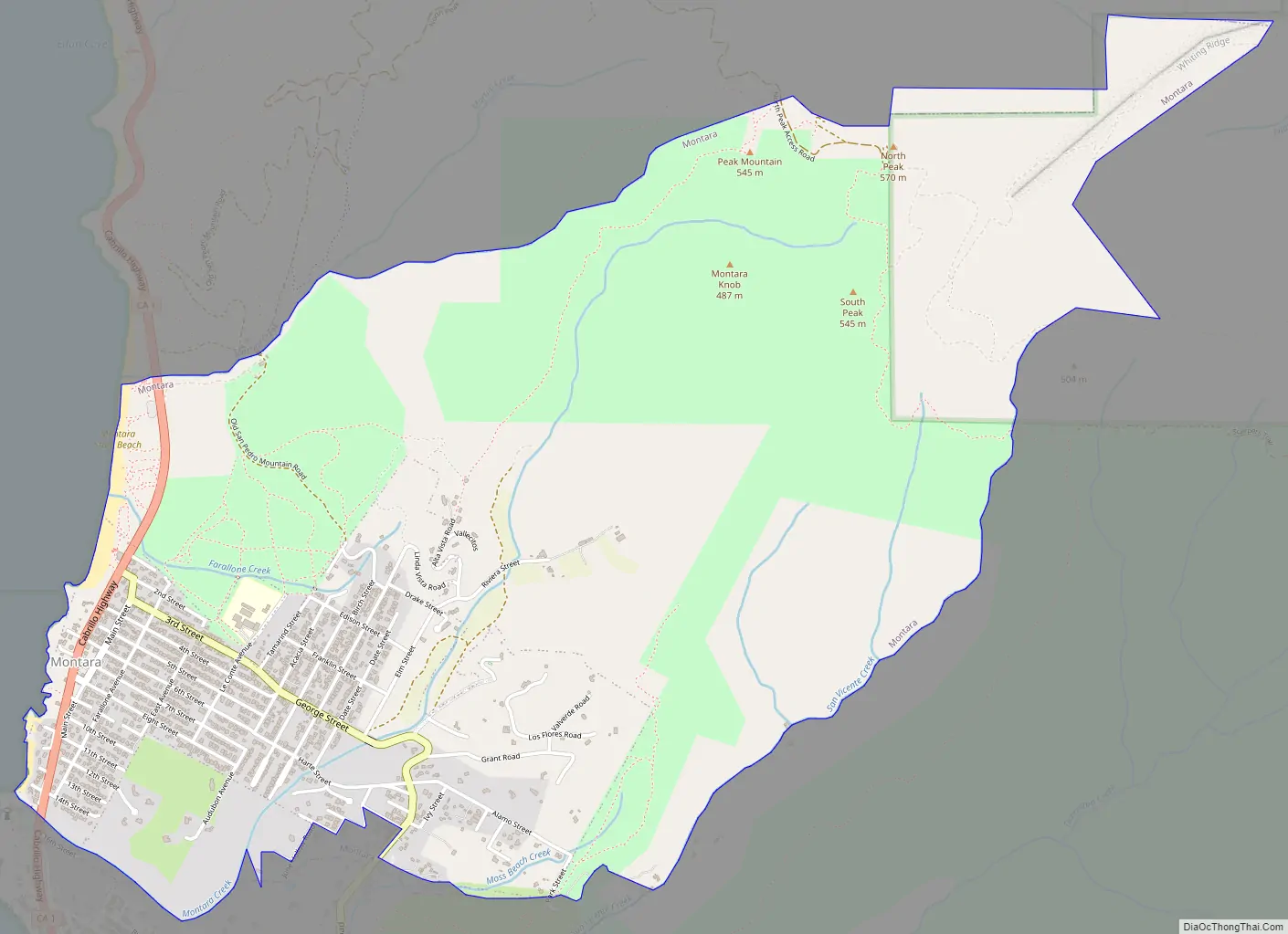
Montara Road Map
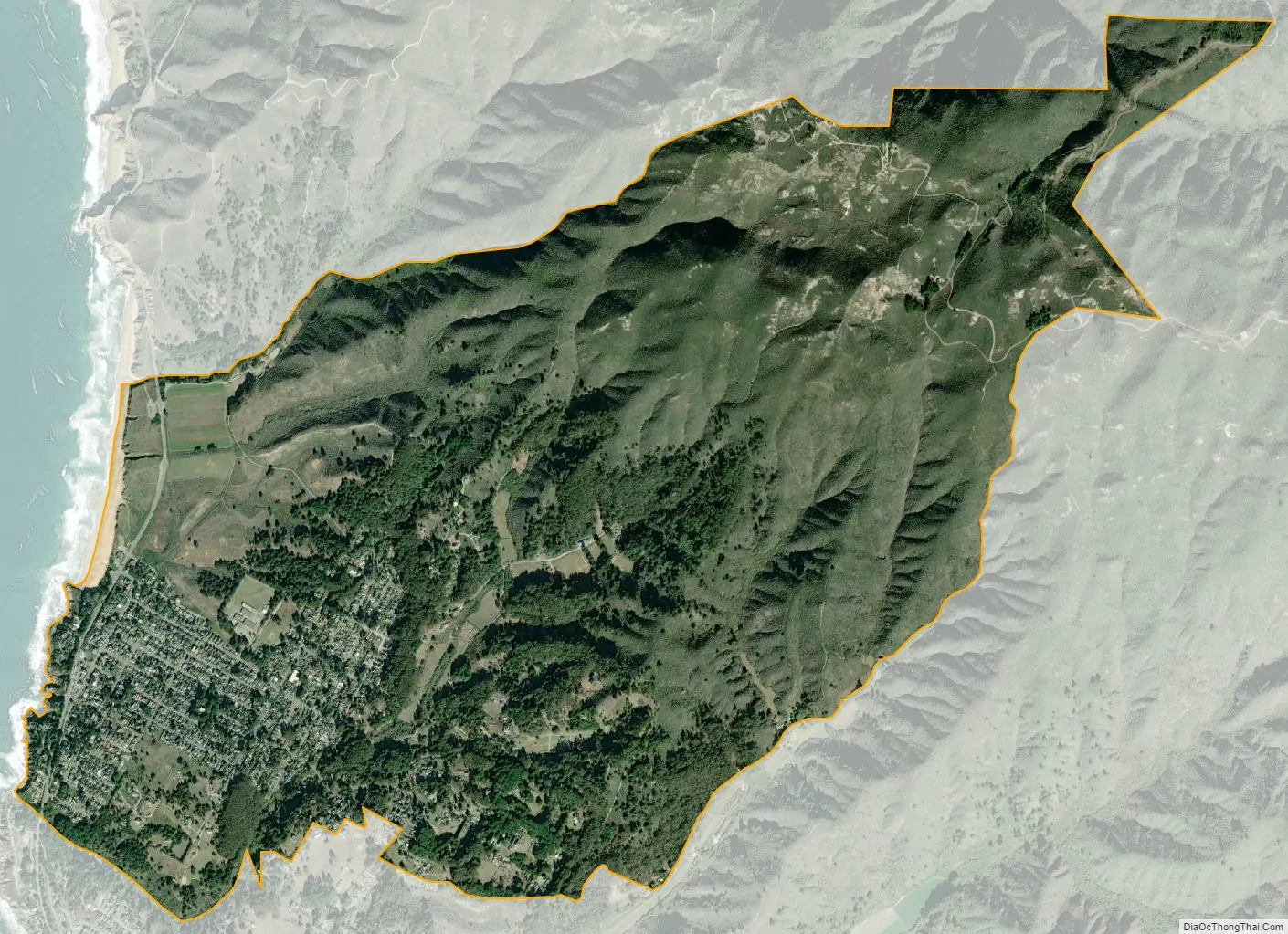
Montara city Satellite Map
Geography
Montara is located at 37°32′23″N 122°30′23″W / 37.53972°N 122.50639°W / 37.53972; -122.50639 (37.539639, -122.506426), approximately 20 miles (32 km) south of San Francisco and 50 miles (80 km) north of Santa Cruz, California. Neighboring towns include Pacifica to the north, Moss Beach, El Granada, and Half Moon Bay to the south. According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP has a total area of 3.9 square miles (10 km), all of it land.
The rare and endangered species Hickman’s potentilla occurs at the northern extremity of Montara on the slopes above Martini Creek at elevations ranging from 32 to 410 ft (9.8 to 125.0 m).
Nearby Montara Mountain, part of the Santa Cruz Mountains, rises to an elevation of 1,898 ft (579 m) above sea level. The mountain is accessible by a gravel fire road. On a few occasions light snowfall has fallen on the upper reaches of the mountain.
The town is surrounded by open space (Rancho Corral de Tierra) and a popular recreation area includes Montara State Beach. The nearly 1 mi (1.6 km) long stretch of sand drops steeply into the ocean, making this beach hazardous for swimming. It is, however, a fairly popular surfing destination for experienced surfers. Waves of at least 10–15 ft (3.0–4.6 m) can be common during winter storm swells.
Montara State Marine Reserve & Pillar Point State Marine Conservation Area extend offshore from Montara. Like underwater parks, these marine protected areas help conserve ocean wildlife and marine ecosystems.
See also
Map of California State and its subdivision:- Alameda
- Alpine
- Amador
- Butte
- Calaveras
- Colusa
- Contra Costa
- Del Norte
- El Dorado
- Fresno
- Glenn
- Humboldt
- Imperial
- Inyo
- Kern
- Kings
- Lake
- Lassen
- Los Angeles
- Madera
- Marin
- Mariposa
- Mendocino
- Merced
- Modoc
- Mono
- Monterey
- Napa
- Nevada
- Orange
- Placer
- Plumas
- Riverside
- Sacramento
- San Benito
- San Bernardino
- San Diego
- San Francisco
- San Joaquin
- San Luis Obispo
- San Mateo
- Santa Barbara
- Santa Clara
- Santa Cruz
- Shasta
- Sierra
- Siskiyou
- Solano
- Sonoma
- Stanislaus
- Sutter
- Tehama
- Trinity
- Tulare
- Tuolumne
- Ventura
- Yolo
- Yuba
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming