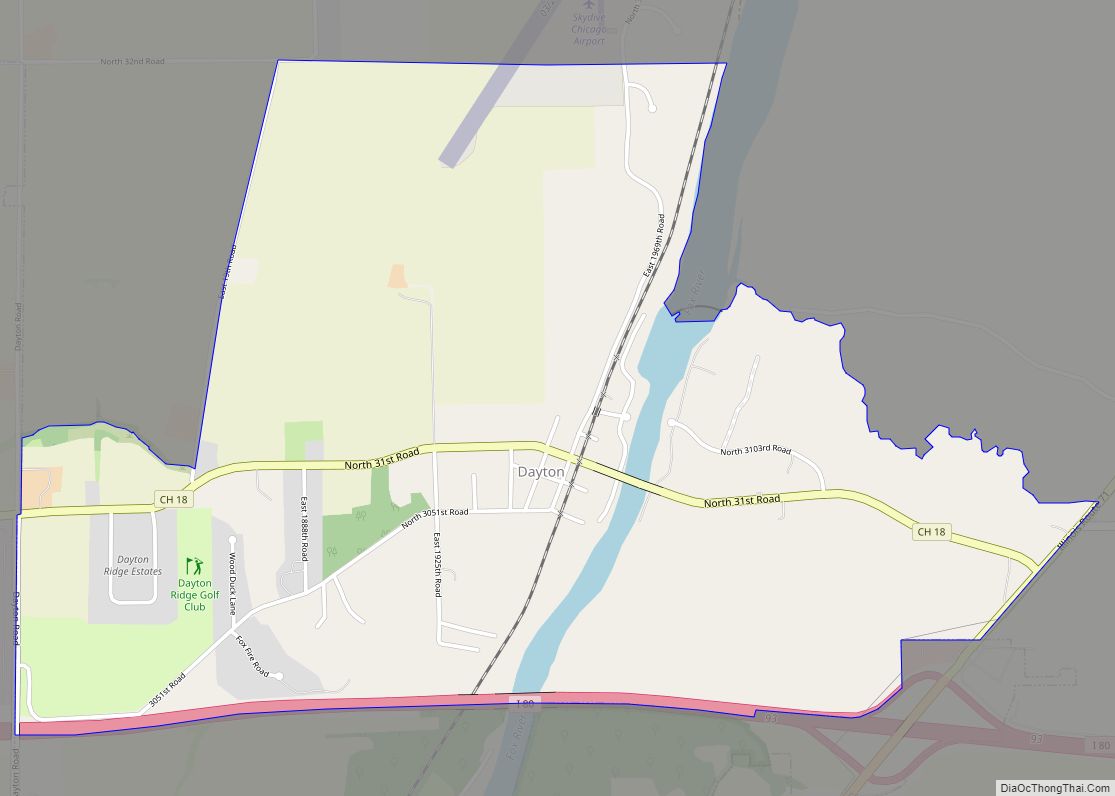
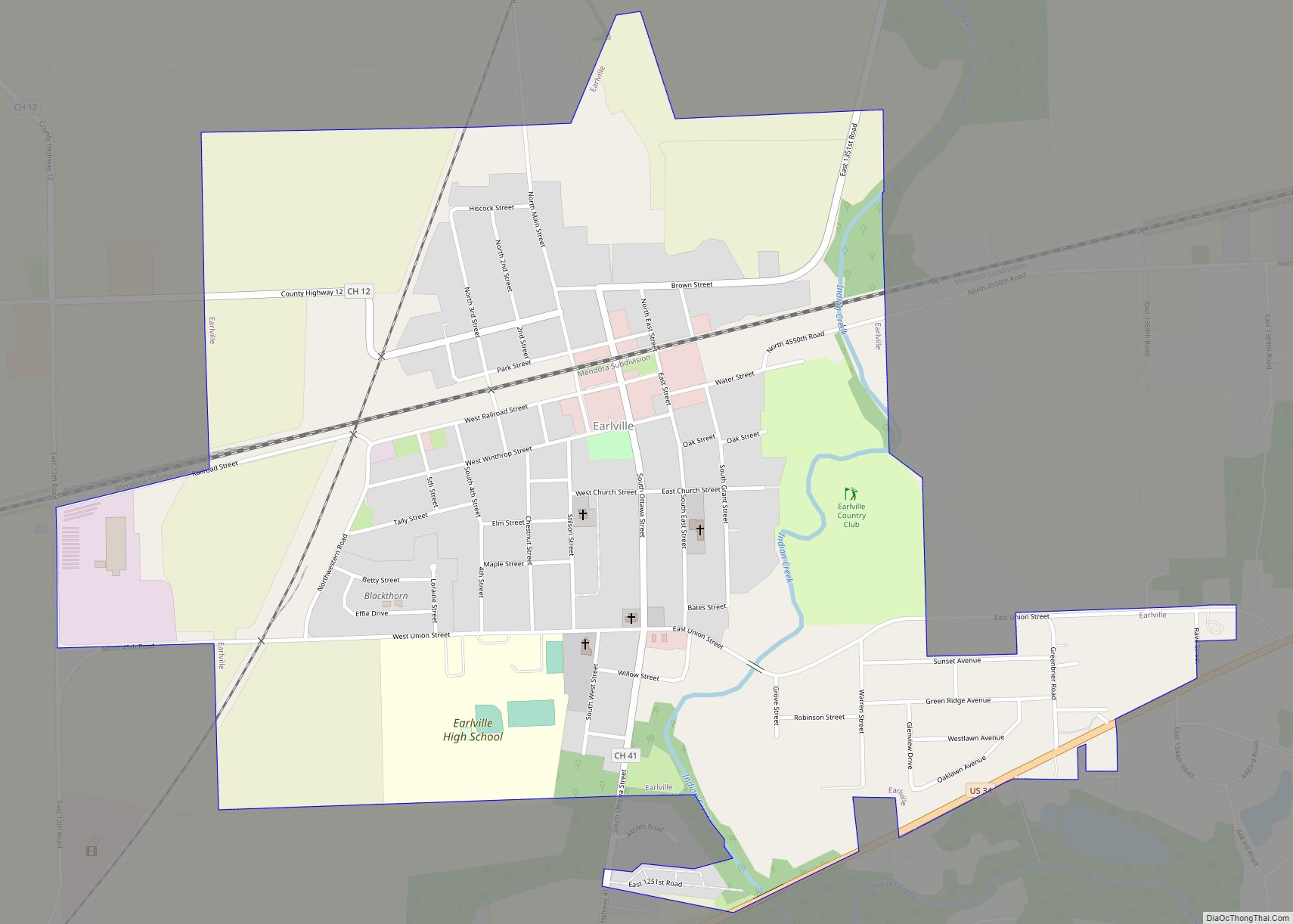
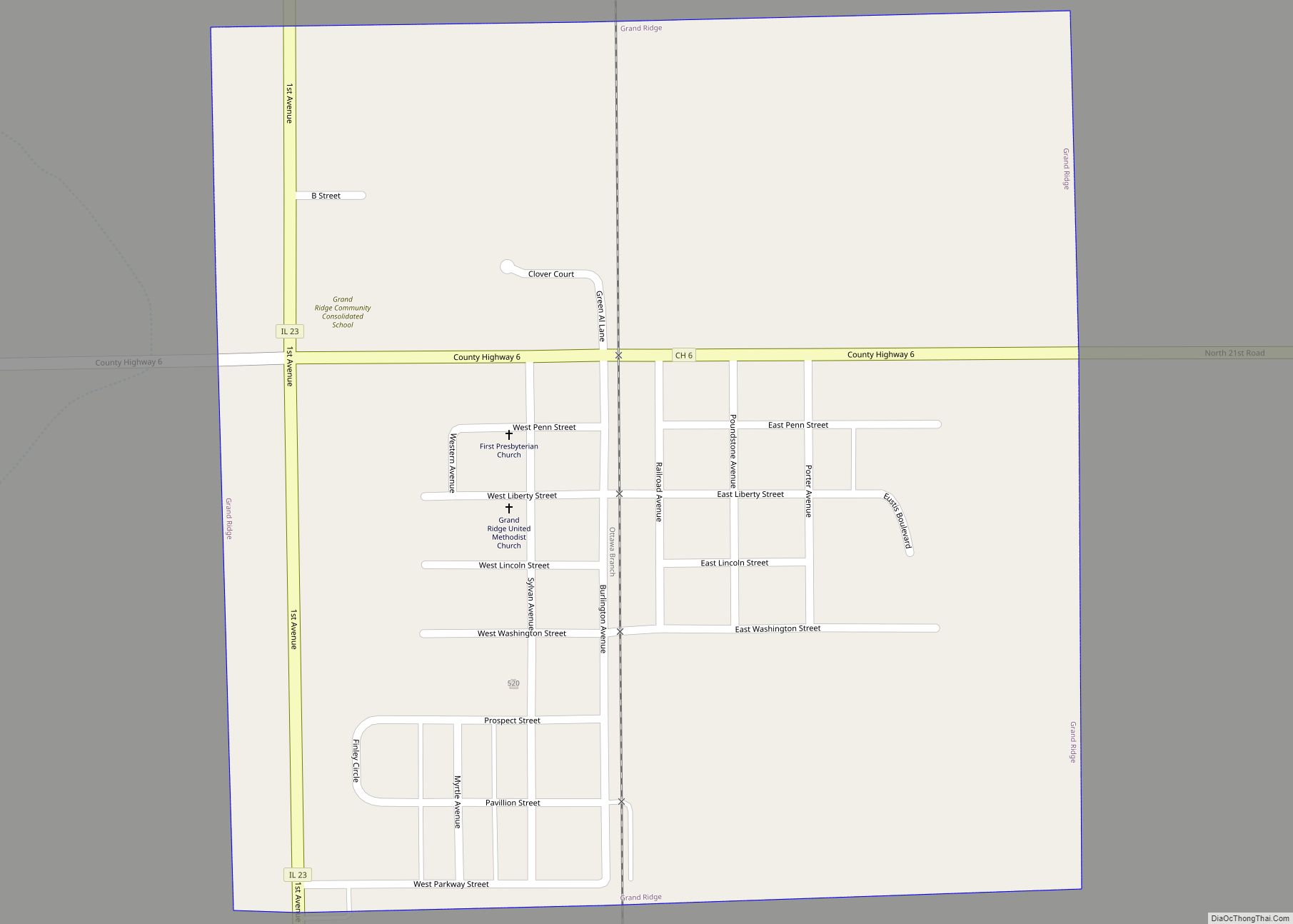
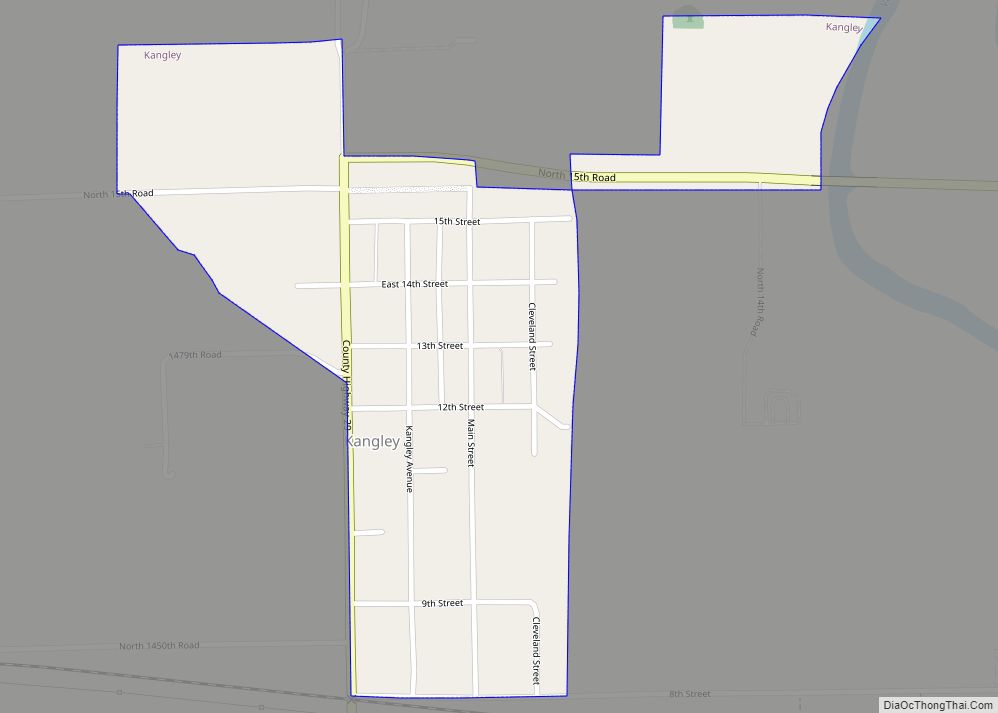
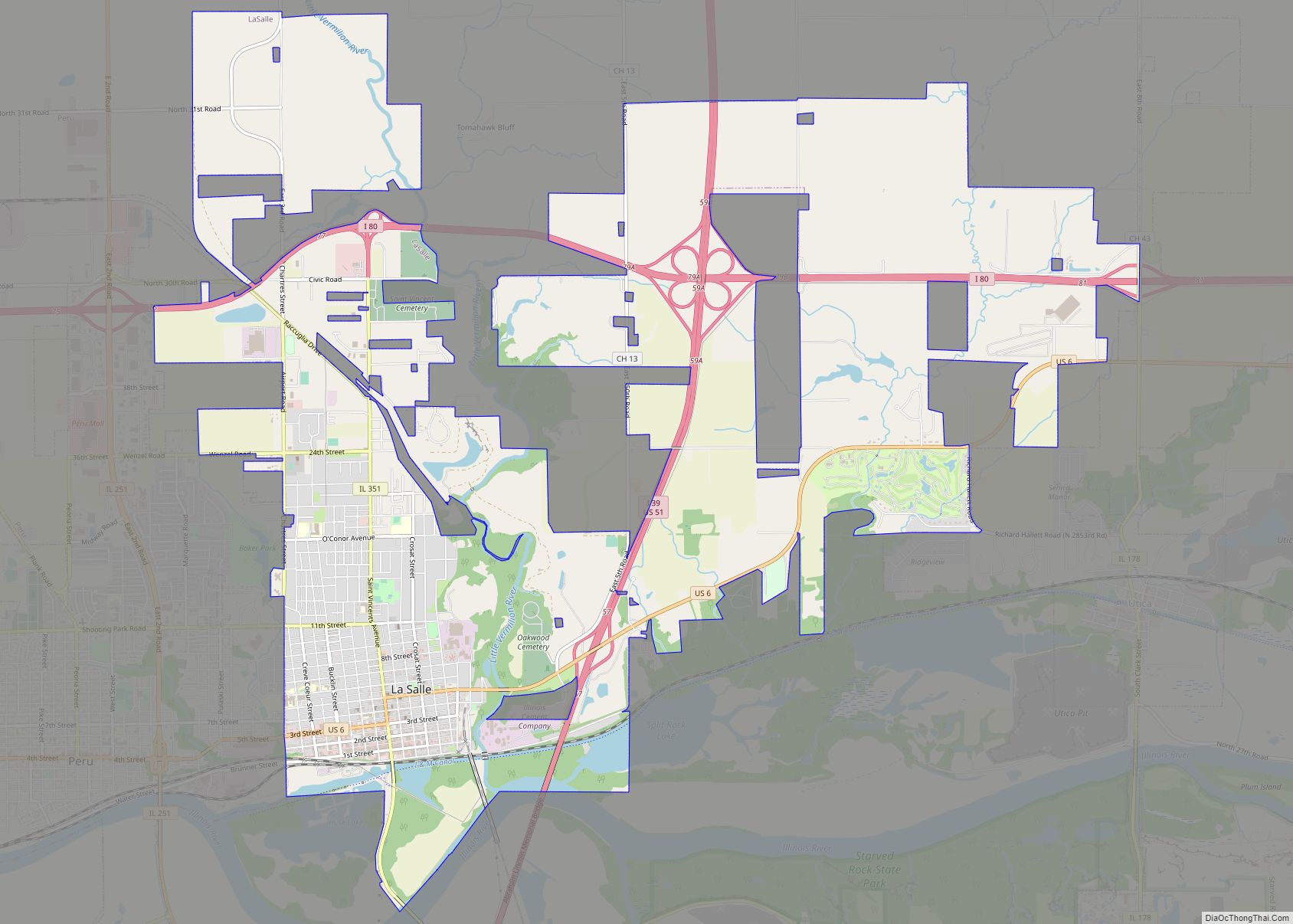
Ottawa is a city in and the county seat of LaSalle County, Illinois, United States. It is located at the confluence of the navigable Fox River and Illinois River, the latter being a conduit for river barges and connects Lake Michigan at Chicago, to the Mississippi River, and North America’s 25,000 mile river system. The population estimate was 18,742, as of 2020. It is the principal city of the Ottawa, IL Micropolitan Statistical Area.
| Name: | Ottawa city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Illinois |
| County: | LaSalle County |
| Incorporated: | 1853 |
| Elevation: | 472 ft (144 m) |
| Total Area: | 15.52 sq mi (40.19 km²) |
| Land Area: | 14.66 sq mi (37.96 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.86 sq mi (2.22 km²) |
| Total Population: | 18,840 |
| Population Density: | 1,281.98/sq mi (494.98/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 61350 |
| FIPS code: | 1756926 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 2396106 |
| Website: | cityofottawa.org |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Ottawa location map. Where is Ottawa city?
History
Ottawa occupies a place on the Illinois River that has long been one end of a portage trail between the Mississippi River and Lake Michigan. Here the river was reliably deep enough for canoes. The North Portage Trail connected the site over land and water to the Chicago River.
Ottawa was the site of the first of the Lincoln–Douglas debates on August 21, 1858. During the Ottawa debate, Stephen A. Douglas, leader of the Democratic Party, openly accused Abraham Lincoln of forming a secret bipartisan group of Congressmen to bring about the abolition of slavery.
The John Hossack House was a “station” on the Underground Railroad, and Ottawa was a major stop because of its rail, road, and river transportation. Citizens in the city were active within the abolitionist movement. Ottawa was the site of a famous 1859 extrication of a runaway slave named Jim Gray from a courthouse by prominent civic leaders of the time. Three of the civic leaders, John Hossack, Dr. Joseph Stout and James Stout, later stood trial in Chicago for violating the Fugitive Slave Act of 1850.
Ottawa was also important in the development of the Illinois and Michigan Canal, which terminates in LaSalle, Illinois, 12 miles to the west. In 1838, workmen from the canal project were causing public unrest. During a citizens’ meeting, a local political leader, Washington Armstrong, suggested that farmer William Reddick be elected sheriff. Reddick was a popular choice due to his large stature and courageous manner. Reddick was elected by a large majority and held the office of sheriff for four consecutive two-year terms. In 1855, while serving in the Illinois State Senate, Reddick commissioned the construction of a large Italianate house for the then-large sum of $25,000. Reddick Mansion is now one of the largest surviving homes in Illinois to predate the Civil War. In 1973, the mansion was added to the National Register of Historic Places, as part of the Washington Park Historic District.
On February 8, 1910, William Dickson Boyce, then a resident of Ottawa, incorporated the Boy Scouts of America. Five years later, also in Ottawa, Boyce incorporated the Lone Scouts of America. Boyce is buried in Ottawa Avenue Cemetery. The Ottawa Scouting Museum, on Canal Street, opened to the public on December 6, 1997. The museum features the history of Boy Scouting, Girl Scouting and Camp Fire.
In 1922, the Radium Dial Company (RDC) moved from Peru, Illinois to a former high school building in Ottawa. The company employed hundreds of young women who painted watch dials using a paint called “Luna”, which contained ionizing radion, for watch maker Westclox. RDC went out of business in 1936, two years after the company’s president, Joseph Kelly Sr., left to start a competing company, Luminous Processes Inc., a few blocks away. The employees of the company suffered radiation toxicity, as chronicled in the 1986 documentary, Radium City.
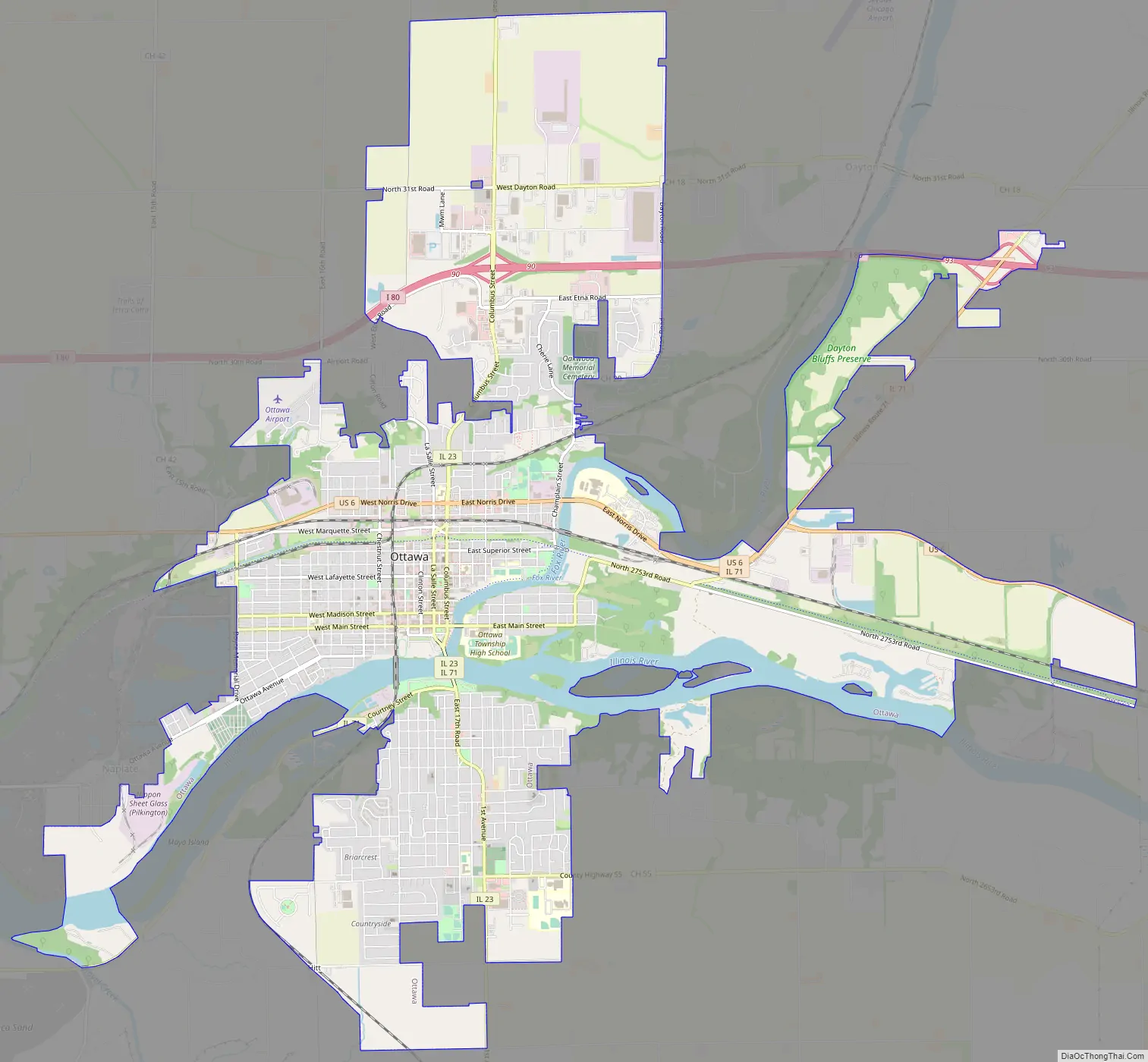
Ottawa Road Map
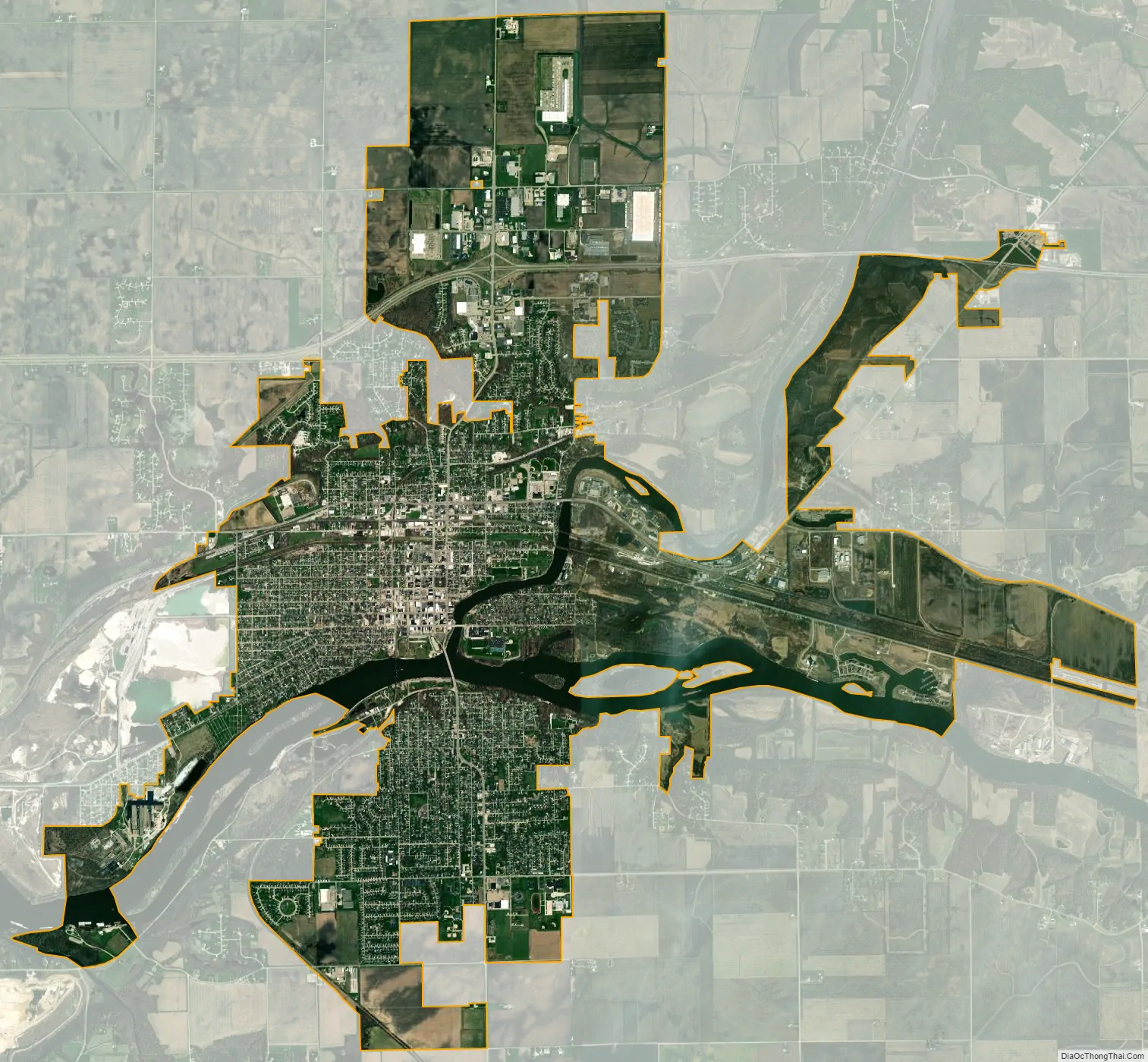
Ottawa city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the 2021 census gazetteer files, Ottawa has a total area of 15.516 square miles (40.19 km), of which 14.657 square miles (37.96 km) (or 94.46%) is land and 0.859 square miles (2.22 km) (or 5.54%) is water.
Climate
See also
Map of Illinois State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Alexander
- Bond
- Boone
- Brown
- Bureau
- Calhoun
- Carroll
- Cass
- Champaign
- Christian
- Clark
- Clay
- Clinton
- Coles
- Cook
- Crawford
- Cumberland
- De Kalb
- De Witt
- Douglas
- Dupage
- Edgar
- Edwards
- Effingham
- Fayette
- Ford
- Franklin
- Fulton
- Gallatin
- Greene
- Grundy
- Hamilton
- Hancock
- Hardin
- Henderson
- Henry
- Iroquois
- Jackson
- Jasper
- Jefferson
- Jersey
- Jo Daviess
- Johnson
- Kane
- Kankakee
- Kendall
- Knox
- La Salle
- Lake
- Lake Michigan
- Lawrence
- Lee
- Livingston
- Logan
- Macon
- Macoupin
- Madison
- Marion
- Marshall
- Mason
- Massac
- McDonough
- McHenry
- McLean
- Menard
- Mercer
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Morgan
- Moultrie
- Ogle
- Peoria
- Perry
- Piatt
- Pike
- Pope
- Pulaski
- Putnam
- Randolph
- Richland
- Rock Island
- Saint Clair
- Saline
- Sangamon
- Schuyler
- Scott
- Shelby
- Stark
- Stephenson
- Tazewell
- Union
- Vermilion
- Wabash
- Warren
- Washington
- Wayne
- White
- Whiteside
- Will
- Williamson
- Winnebago
- Woodford
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming