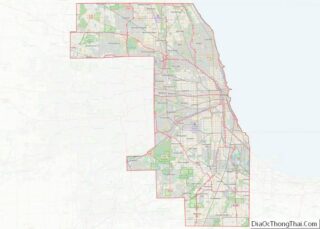
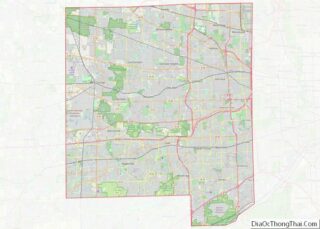
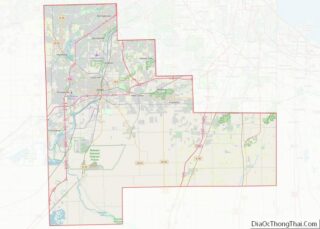
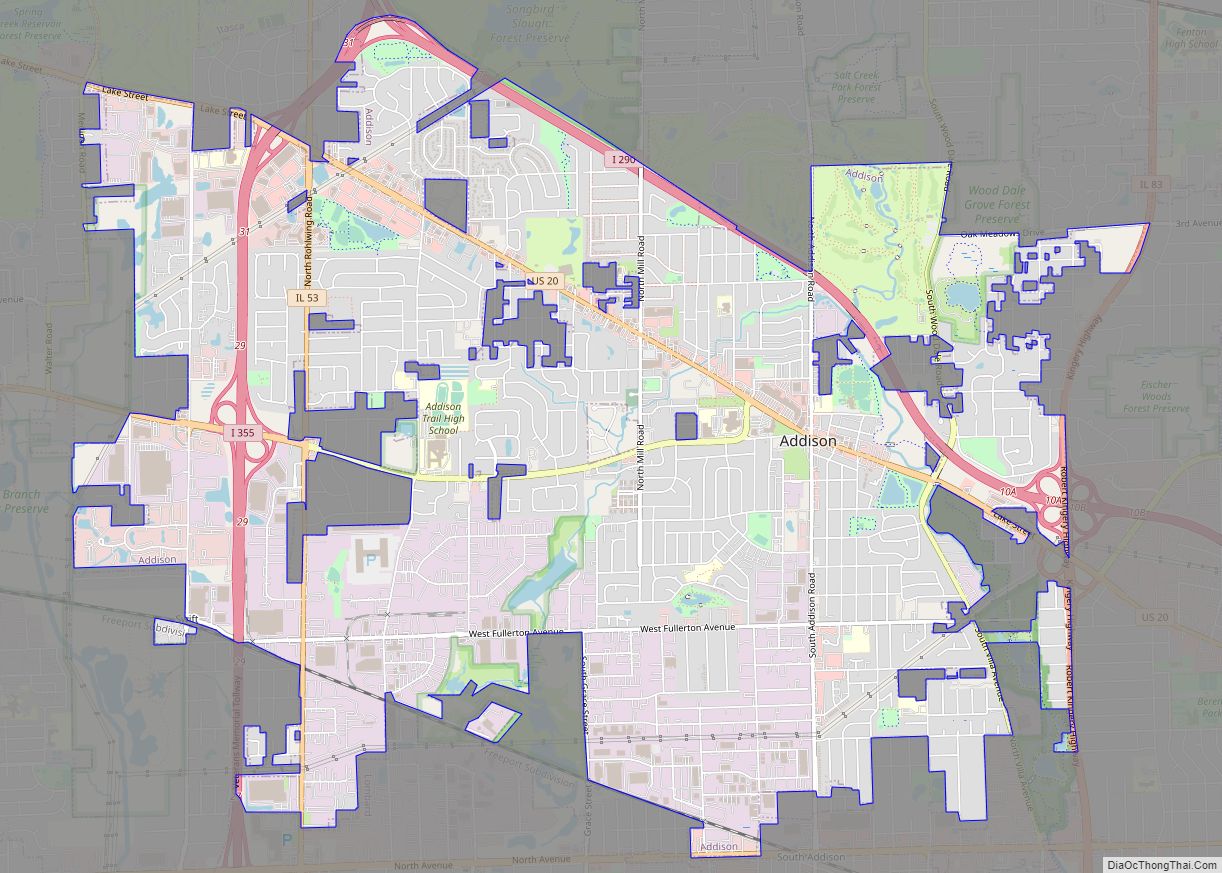
Lemont is a village located in Cook, DuPage, and Will counties in the U.S. state of Illinois, and is a south-west suburb of Chicago. The population was 17,629 as of the 2020 census. The village is situated on a hillside along the south banks of the Des Plaines River. It overlooks Waterfall Glen’s Midwestern Bluff Savanna on the opposite side. Lemont is home to Argonne National Laboratory and other heavy industrial sites, and has a substantial European immigrant population.
| Name: | Lemont village |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 47 |
| LSAD Description: | village (suffix) |
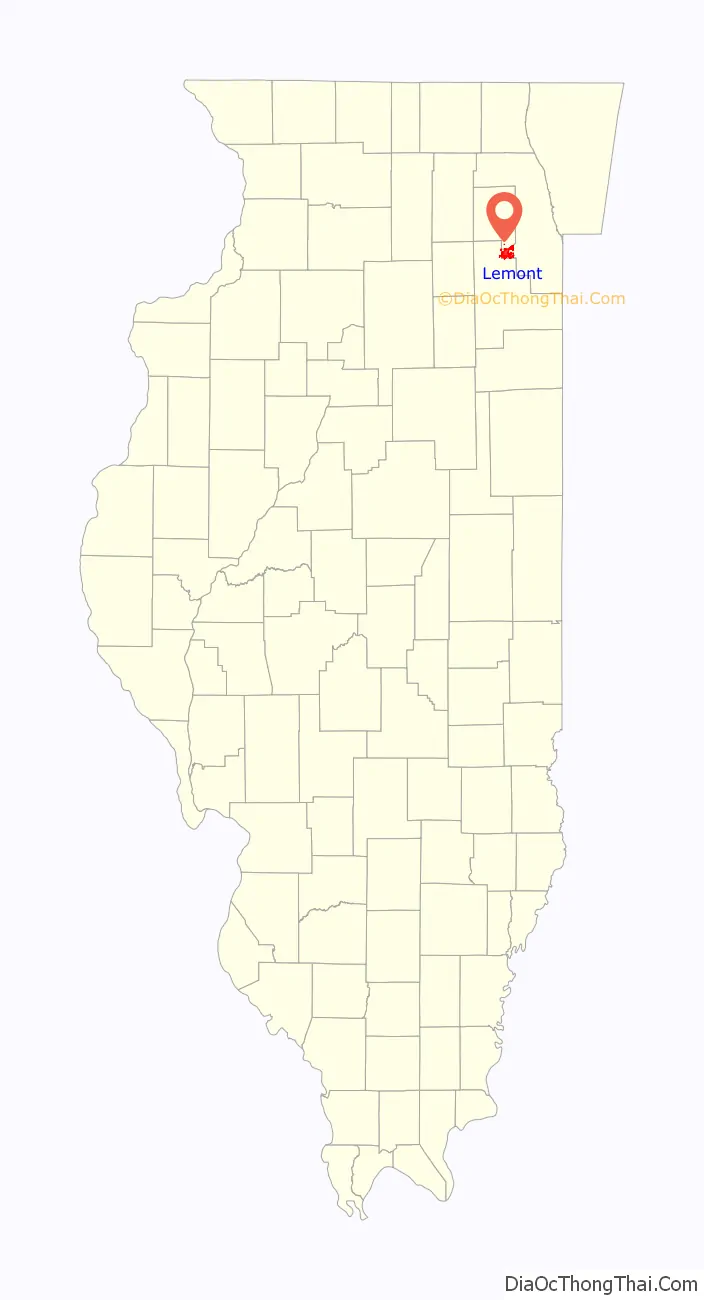
| State: | Illinois |
| County: | Cook County, DuPage County, Will County |
| Incorporated: | June 9, 1873 |
| Total Area: | 8.74 sq mi (22.64 km²) |
| Land Area: | 8.37 sq mi (21.67 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.38 sq mi (0.97 km²) |
| Total Population: | 17,629 |
| Population Density: | 2,107.47/sq mi (813.70/km²) |
| FIPS code: | 1742795 |
| Website: | lemont.il.us |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
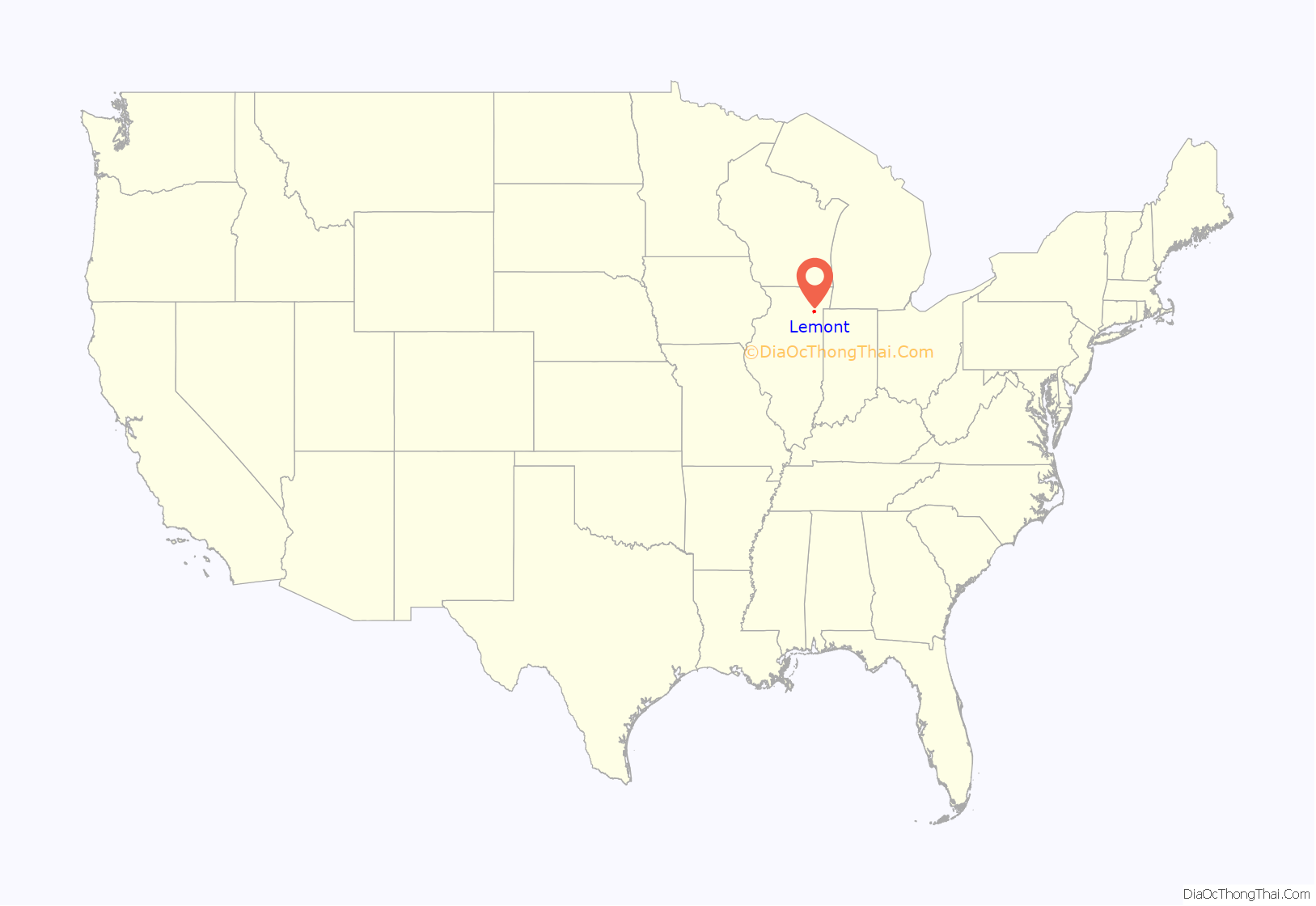
Lemont location map. Where is Lemont village?
History
Before white settlers arrived in Lemont, Native Americans traveled the Des Plaines River in birch bark canoes on trading trips between the Mississippi River and Lake Michigan. The native Potawatomi lived off the land in this area, directly using natural resources for food, shelter, clothing and medicine. In the 18th century, French voyageurs traveled down the Des Plaines River, trading Native Americans metal, beads and cloth for animal furs.
Lemont was originally known as Keepataw (after a Potawatomi chief) and a post office was established in 1840 as Keepatau. After that, it was named Athens and then Palmyra. The name Lemont (literally, ‘the mountain’ in French) was chosen in 1850 at the suggestion of Lemuel Brown, the postmaster and justice of the peace, or perhaps by his brother Nathaniel Brown.
Established in 1836, the village of Lemont stands as one of the oldest American communities in northeastern Illinois. It is historically significant for its role in transforming the northern region of the state from a sparsely settled frontier to a commercial, agricultural, and industrial region that supplied Chicago and areas beyond with commodities. Lemont is also unique in boasting an authentic historic district that remains intact and has been continually used since the 19th century. In 2016, the Lemont Downtown Historic District was listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
Both Lemont’s history and architectural uniqueness connect to the Illinois and Michigan Canal (I&M Canal). Construction of the I&M Canal began in 1837 and stands as one of the last major canal undertakings in the United States (the Hennepin Canal opened in 1907). When it was completed in 1848, it provided a continuous waterway stretching from New York (through the Erie Canal, Lake Erie, Lake Huron and Lake Michigan to Chicago, then through the I&M Canal for 97 miles (156 km) entering the Illinois River at LaSalle, Illinois, to the Mississippi River, to New Orleans) to the Gulf of Mexico.
Immigrant workers, mostly Irish, settled in Lemont to work on the canal and later moved along the corridor of the canal, improving farms within the many communities that sprang up along it. They also were for the most part responsible for the many Lemont brothels during that time.
In digging, workers discovered Lemont yellow dolomite, a harder and finer grained version of limestone. This delayed digging of the canal, but was the start of the area’s second industry, quarrying. By the mid-19th century, limestone quarrying took over as the main economic factor in Lemont and sustained its growth. The town’s important major buildings were faced with the Lemont limestone, abundant in local quarries. Today, 38 of those buildings remain as the Lemont downtown district. Lemont limestone was used to build the Chicago Water Tower, a building that “gained special significance as one of the few buildings to survive the destructive path of the Great Chicago Fire of 1871”. In the early years, this stone was known as “Athens Marble” as a nod to its place of origin. An 1859 item in the Chicago Daily Tribune had this to say: “The Athens and DesPlaines quarries, situated on the Illinois and Michigan canal, embrace 335 acres of the finest stone in the West, known as “Athens Marble”. This stone has a high reputation for color, durability and beauty, which renders it quite an article of commerce”.
Cargo and passengers were transported on the I&M until the early 20th century, when the wider, deeper Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal was built parallel to it. The Sanitary Canal is still used today as part of the Illinois Waterway system.
Lemont’s motto is “Village of Faith”, and its church spires reflect the many ethnic groups who came here to quarry stone, dig the Sanitary and Ship Canal and work in other industries.
Lemont is credited with being the largest recruiting station for the Union Army during the American Civil War, and the Old Stone Church, built in 1861 of limestone, was used as a recruiting depot. It served as the Lemont Methodist Episcopal Church for 100 years, from 1861 until 1970, when it became home to the Lemont Area Historical Society. The oldest building in Lemont, it now serves as a museum and is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
During the Civil War, Lemont was required to sign up 33 soldiers, the village recruited 293 soldiers; only 63 returned. The Lemont Civil War Memorial Committee was formed to build a memorial to honor Lemont’s Civil War veterans. The monument was dedicated in 2008 in Legion Park at the east end of Main Street, opposite the Metra Station. Of the 293 soldiers sent to fight in the war, only 243 names of the enlisted soldiers are known. Among them is Cpl. John Warden, the only Lemont resident ever awarded the Medal of Honor.
By 1854, railroads transported goods faster than water, and the I&M became obsolete as Lemont evolved into a railroad community; the village was incorporated on June 9, 1873.
Increasingly, the canal was used to carry wastes away from Chicago. In 1900, the larger Sanitary and Ship Canal went into operation, carrying both wastes and larger, more modern barges. All use of the I&M Canal ended in 1933, with the opening of the canal’s modern successor – the Illinois Waterway.
By about 1920, the quarries declined as styles changed and builders began to use Bedford limestone from Indiana and less expensive materials like concrete.
During World War II, the Metallurgical Laboratory of the University of Chicago moved into Red Gate Woods to carry out Enrico Fermi’s work on nuclear reactors for the Manhattan Project. After the war, Argonne National Laboratory was designated as the first national laboratory in the United States on July 1, 1946.
In 1984, President Ronald Reagan signed legislation establishing the Illinois & Michigan Canal National Heritage Corridor as the nation’s first National Heritage Corridor. The status recognizes the historic importance of this region and the waterway that connected Lake Michigan and the Illinois River. Today, it is a 100-mile-long (160 km) cultural park between Chicago and LaSalle/Peru, representing an ongoing partnership between the public and private sectors created to achieve a successful mixture of preservation, public use and industrial activity.
Sacred architecture is a strong suit of Lemont, whose skyline is dominated by two landmark religious edifices: the Hindu Temple of Greater Chicago and SS. Cyril and Methodius church in the Polish Cathedral style. Both are situated on the sides of hills, giving an even more dramatic backdrop to their monumental architecture.
Tornadoes
On June 13, 1976, at 5:18 PM, a killer tornado struck Lemont and took three lives. 23 were injured, 87 homes were destroyed and 82 more were damaged. Damage to the high school alone was estimated at $500,000 (equivalent to $2,380,000 in 2021). Many people reported watching neighbors’ homes explode, implode, shattering before their eyes. Cited as an unusual tornado, it backed up on its path before heading North, somewhat parallel to its path of origin. See Tornadoes of 1976 for more information on the outbreak.
On March 27, 1991, Lemont was again hit by a tornado. See Tornadoes of 1991 for more information on the outbreak.
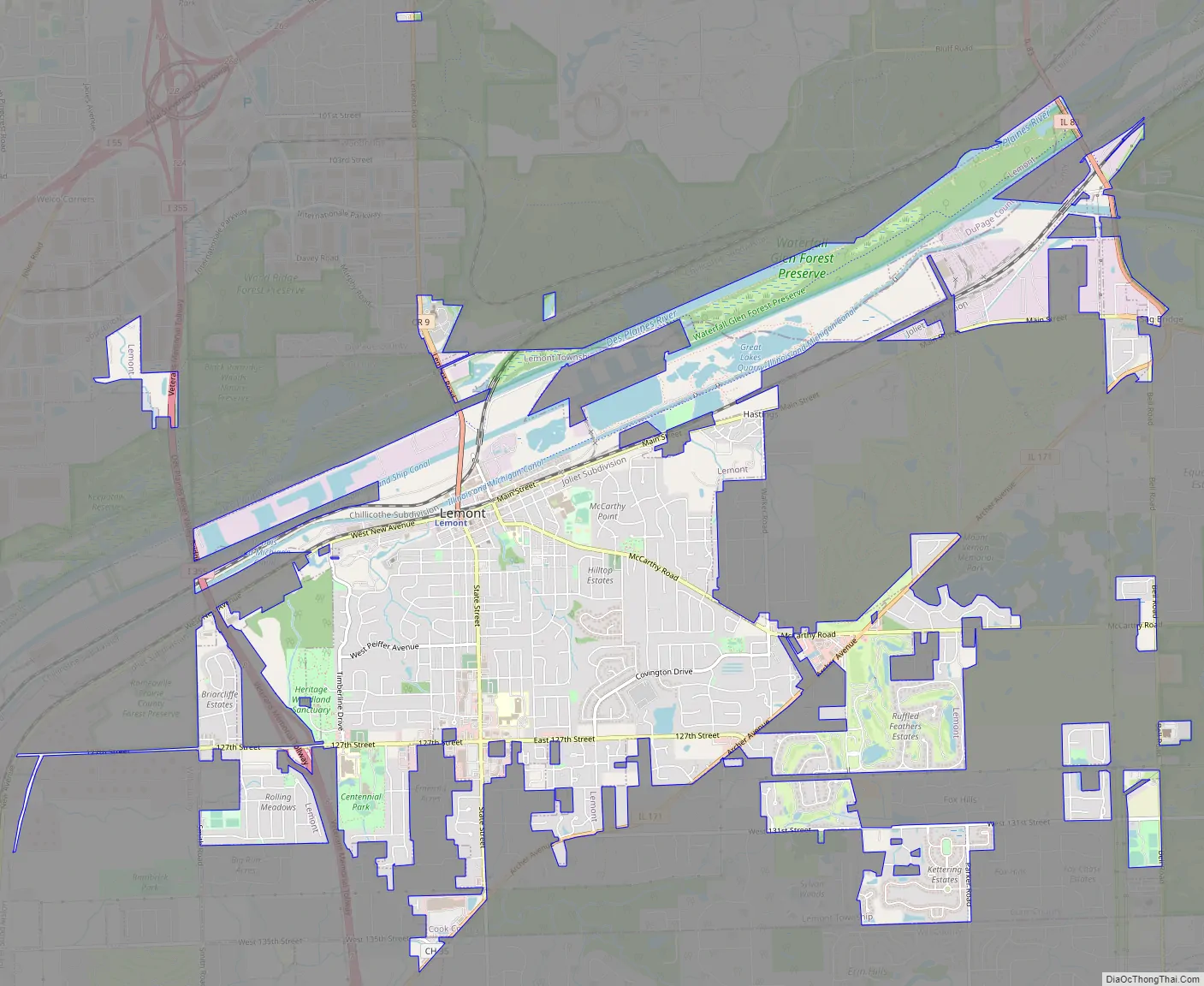
Lemont Road Map
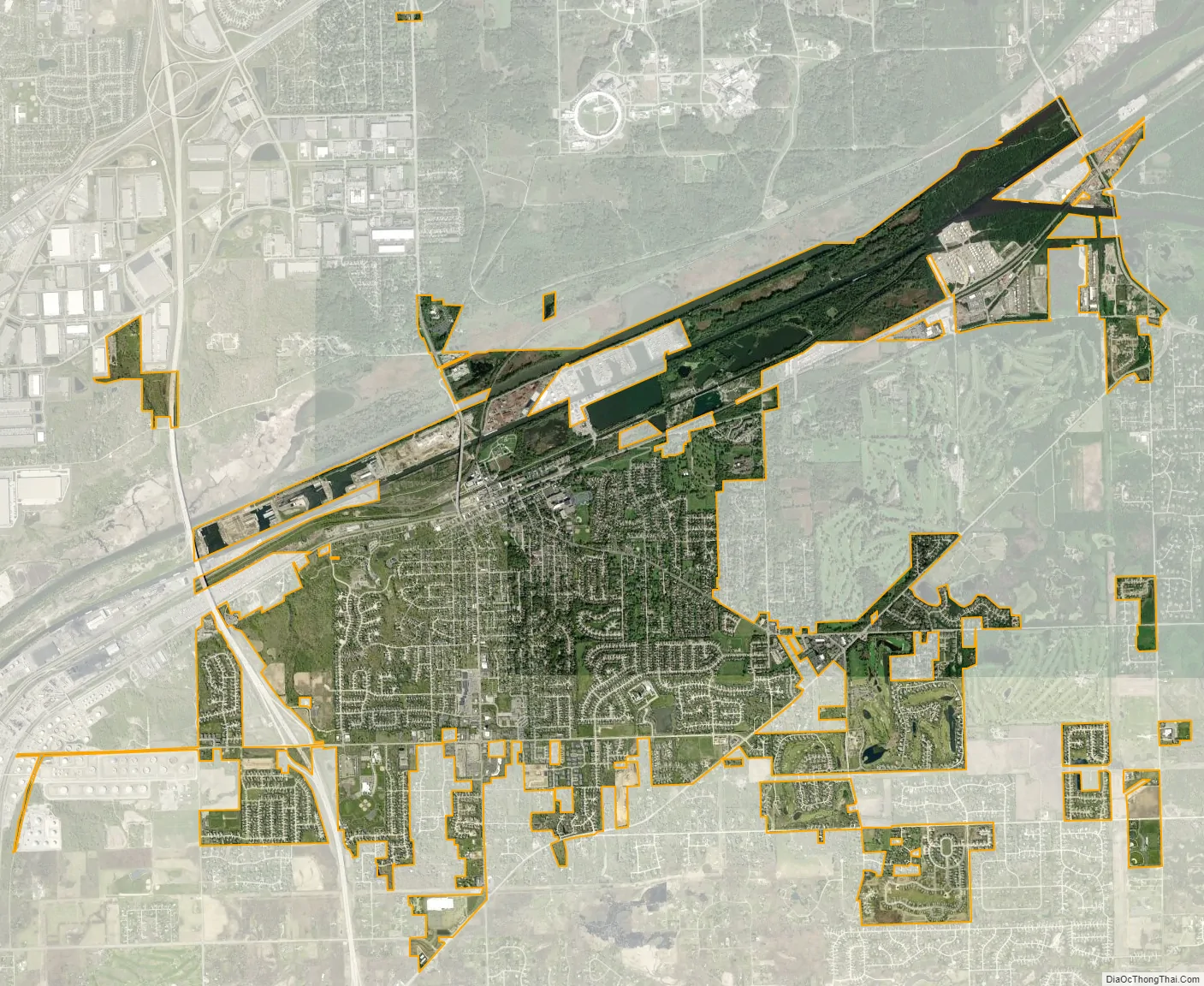
Lemont city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the 2021 census gazetteer files, Lemont has a total area of 8.74 square miles (22.64 km), of which 8.37 square miles (21.68 km) (or 95.71%) is land and 0.38 square miles (0.98 km) (or 4.29%) is water.
The village has 10 exclaves.
See also
Map of Illinois State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Alexander
- Bond
- Boone
- Brown
- Bureau
- Calhoun
- Carroll
- Cass
- Champaign
- Christian
- Clark
- Clay
- Clinton
- Coles
- Cook
- Crawford
- Cumberland
- De Kalb
- De Witt
- Douglas
- Dupage
- Edgar
- Edwards
- Effingham
- Fayette
- Ford
- Franklin
- Fulton
- Gallatin
- Greene
- Grundy
- Hamilton
- Hancock
- Hardin
- Henderson
- Henry
- Iroquois
- Jackson
- Jasper
- Jefferson
- Jersey
- Jo Daviess
- Johnson
- Kane
- Kankakee
- Kendall
- Knox
- La Salle
- Lake
- Lake Michigan
- Lawrence
- Lee
- Livingston
- Logan
- Macon
- Macoupin
- Madison
- Marion
- Marshall
- Mason
- Massac
- McDonough
- McHenry
- McLean
- Menard
- Mercer
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Morgan
- Moultrie
- Ogle
- Peoria
- Perry
- Piatt
- Pike
- Pope
- Pulaski
- Putnam
- Randolph
- Richland
- Rock Island
- Saint Clair
- Saline
- Sangamon
- Schuyler
- Scott
- Shelby
- Stark
- Stephenson
- Tazewell
- Union
- Vermilion
- Wabash
- Warren
- Washington
- Wayne
- White
- Whiteside
- Will
- Williamson
- Winnebago
- Woodford
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming