Mackinac Island (/ˈmækənɔː/ MAK-ə-naw, locally /ˈmækənə/ MAK-ə-nə) is a city in Mackinac County in the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2020 census, the city had a permanent population of 583. The population numbers in the tens of thousands from May 1st to October 31st due to an influx of visitors and hundreds of seasonal workers.
Established as an important fur trading center in the eighteenth century, with a predominately French-speaking population of French Canadians and Métis, after the War of 1812 the city gained more Anglo-American residents. The US put restrictions on Canadians for fur trading. From 1818 until 1882 the city served as the county seat of the former Michilimackinac County, which was later organized as Mackinac County, with St. Ignace designated as the county seat. The city includes all of Mackinac Island and it also originally included nearby Round Island which is unpopulated and now federally owned and part of the Hiawatha National Forest. The state park and the national forest make up most of the city.
A unique local ordinance passed in 1895 prohibits the use of any motor vehicles on the island. The only exceptions to this are city emergency vehicles (ambulance, police cars and fire trucks), city service vehicles and snowmobiles in the winter. Today the most common means of travel is either by foot, bicycle, horse or horse-drawn carriage. Roller skates and roller blades are also allowed, except in the downtown area. Mackinac Island is home to the Grand Hotel, built during the late nineteenth century when the island started to be a summer destination. When the 1980 movie Somewhere in Time was filmed here, the city made an exception to allow the production company to use motorized vehicles on the island.
| Name: | Mackinac Island city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Michigan |
| County: | Mackinac County |
| Incorporated: | March 25, 1847; 176 years ago (1847-03-25) (village) |
| Elevation: | 594 ft (181 m) |
| Total Area: | 18.84 sq mi (48.80 km²) |
| Land Area: | 4.35 sq mi (11.27 km²) |
| Water Area: | 14.49 sq mi (37.53 km²) 76.91% |
| Population Density: | 134.02/sq mi (51.75/km²) |
| Area code: | 906 |
| FIPS code: | 2650280 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1620659 |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
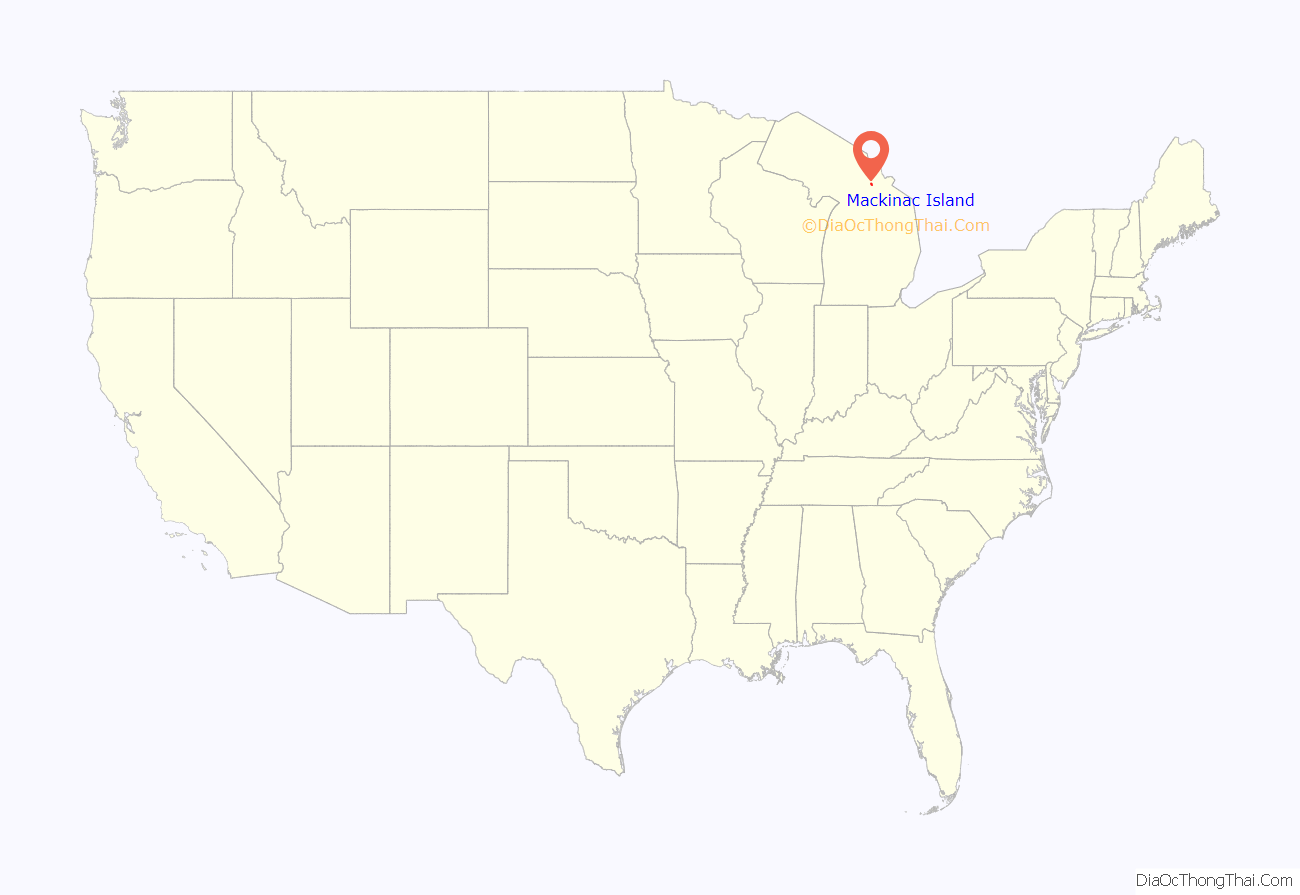
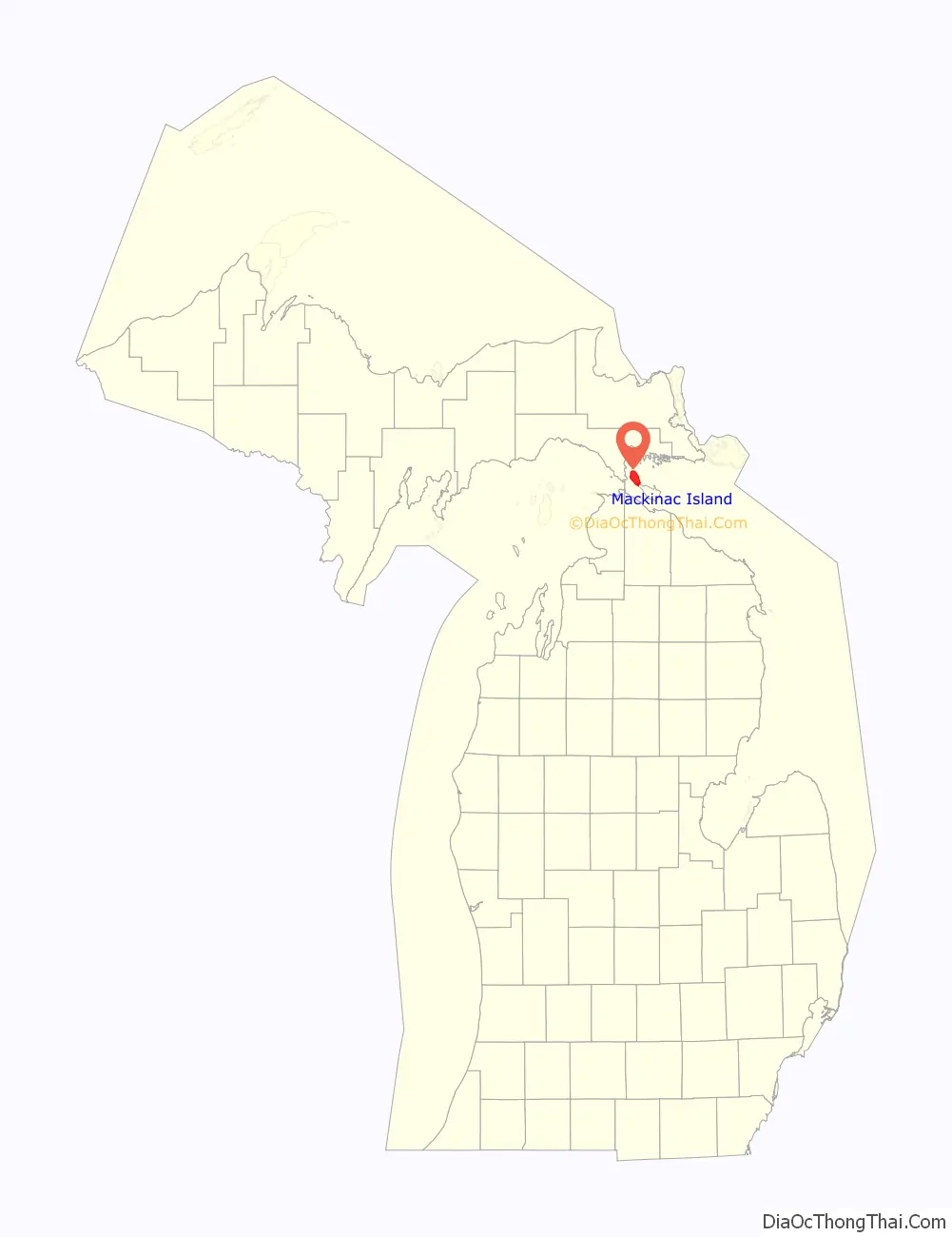
Mackinac Island location map. Where is Mackinac Island city?
History
Andrew Blackbird was the son of an Ottawa chief and served as an official interpreter for the U.S. government in the late 19th century. According to his 1887 history of the indigenous peoples of Michigan, the people of Mackinac Island had been a small independent tribe known as Mi-shi-ne-macki naw-go. They became affiliated with the larger tribe of Ottawa from Ottawa Island (now Manitoulin Island) situated north of Lake Huron.
One winter the Mi-shi-ne-macki naw-go on Mackinac were nearly annihilated by the Seneca, the westernmost nation of the Iroquois Confederacy, then based in present-day New York and Pennsylvania. Two natives escaped by hiding in one of the natural caves on the island. To commemorate this tribe, the Ottawa and Chippewa (Ojibwe) named the island as Mi-shi-ne-macki-nong, also known as Michilimackinac (meaning “Great Turtle”) by the 18th century.
In 1654 French Jesuit missionaries recorded French traders at the island, who were with a large party of Huron and Ottawa heading to Three Rivers. Another trader was said to have made a canoe voyage to the island in 1665. The French colonists continued in the fur trade, which became extremely lucrative; they operated out of Montreal and Quebec, and established posts on Mi-shi-ne-macki-nong and throughout the Great Lakes area. After the French ceded their territory in North America to the British in 1763 following defeat in the Seven Years’ War, the British established Fort St. Joseph and an installation on what was known as Michilimackinac. During the American Revolutionary War, they vacated the fort.
By 1782, the Americans established a garrison on what they called Mackinac Island, commanded by Captain Daniel Robertson; he had command until his death in 1787. In 1796 as a result of Jay’s Treaty with Great Britain, settling the northern border, the island officially became part of the United States and its Northwest Territory.
In the early 1800s Mackinac Island had a permanent population of about 250. Although it was part of the United States, most of the residents were of French-Canadian and Métis ancestry, based on its colonial history, and French was the predominant language. The fur trade was the dominant feature of the economy. Native American languages, particularly Ojibwe and Odawa, and dialects were spoken by some residents. In the summer trading season, the population could reach 4,000, attracting agents and Native Americans from the interior.
After the War of 1812, the United States prohibited British fur traders from operating in US territory, cutting off some of the relations between Canadians and Native Americans on the US side. Some fur trading families divided their operations with posts on each side of the border. The noted French writer Alexis de Tocqueville visited Mackinac Island in July 1831 on his tour of the United States. He wrote about its unique population with its strong French and Native American influence.
Under American rule, Michilimackinac (the island and adjacent areas) had a justice of the peace, supervisor of roads, and two military captains until the borough was formed. The island’s people made a request through Indian Agent William Henry Puthuff on February 2, 1817, that a borough be established on the island and for building a jailhouse. In response on March 15, 1817, Michigan Territory Secretary William Woodbridge issued a proclamation forming the Township of Michilimackinac, giving the jurisdiction’s distance from Detroit, the territorial capital. The governor and judges passed an act on April 6, 1817, forming the Borough of Michilimackinac. The borough organizational meeting was held in the Indian Council House, presided over by Puthuff on Monday, July 7, 1817. (The site was within the boundaries of the current Marquette Park). At this meeting, the residents selected the following officers, a warden, two burgesses, a clerk, a marshal and a treasurer. Puthuff was selected as warden, the chief official similar to a mayor. The American Fur Company was formed on Main Street, now Market Street.
With the 1818 formation of Michilimackinac County by Territorial Governor Lewis Cass, this borough was named as the county seat. The Borough form was later replaced with that of a village. Waren Puthuff was authorized by borough act to build a wharf at the end of Cross Street, now named Astor Street after John Jacob Astor. This wharf is the longest-lasting wharf on the island and was later used as the coal dock.
On March 16, 1847, the Michigan state legislature passed a law abolishing the borough, effective April 1. The legislature reversed this action and incorporated the island as the Village of Mackinac, effective March 25, 1847.
In the late 19th century, Mackinac Island became a popular summer resort destination for travelers from major cities such as Chicago and later Detroit, as well as more distant ones. The Grand Hotel was built as a luxury venue. The seasonal peak of population in the summer, now made up of thousands of tourists and service workers, follows the earlier cycle of the fur trade. As then, it is a time of festivities and entertainment.
In 1860, the Augustus Pond vs. The People court case was held in the county courthouse. It clarified the self-defense legal principle informally expressed as “a man’s home is his castle.” Hubbard’s Annex was platted on the former Ambrose Davenport farm west of the harbor in 1882 by Gurdon Saltonstall Hubbard. The county seat was moved from the municipality in 1882 to St. Ignace, as more population had moved into the western part of the county.
Personal motor vehicles were banned in 1895 in order to protect the health of the island horses and residents. Soon after the first automobiles made their way onto the island, members of Mackinac Island Carriage Tours petitioned the Village of Mackinac Island to ban the automobile as the “dangerous horseless carriage” startled the horses. This ban remains in effect today with only exceptions being city emergency vehicles (ambulance, police cars and fire trucks), city service vehicles and snowmobiles in winter.
The Michigan Legislature created the City of Mackinac Island on June 9, 1899, via act 437 as a special charter city, combining the Township of Holmes and Village of Mackinac. At that time, all of nearby Round Island was included in the corporate limits, for reasons not clear today.
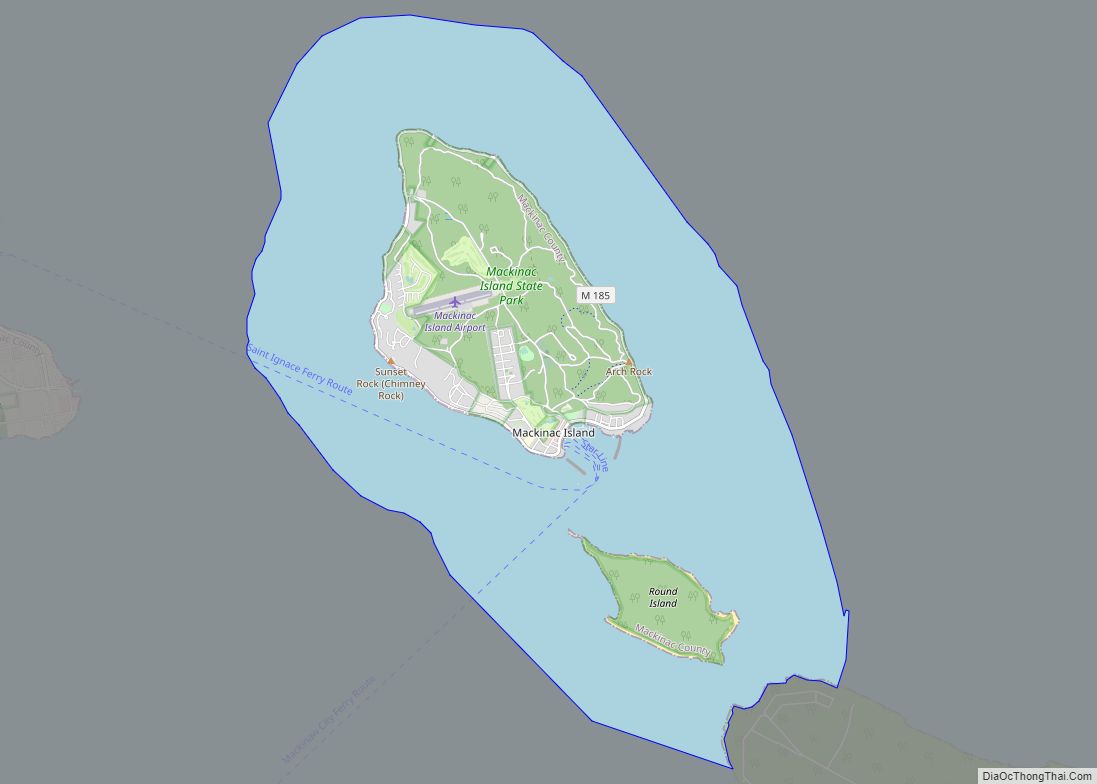
Round Island is owned and overseen by the United States Forest Service in its entirety, and is managed as part of the Round Island Wilderness Area and the Hiawatha National Forest. The city limits include all of Mackinac Island State Park, which area makes up 82 percent of Mackinac Island; it is governed by the Mackinac Island State Park Commission.
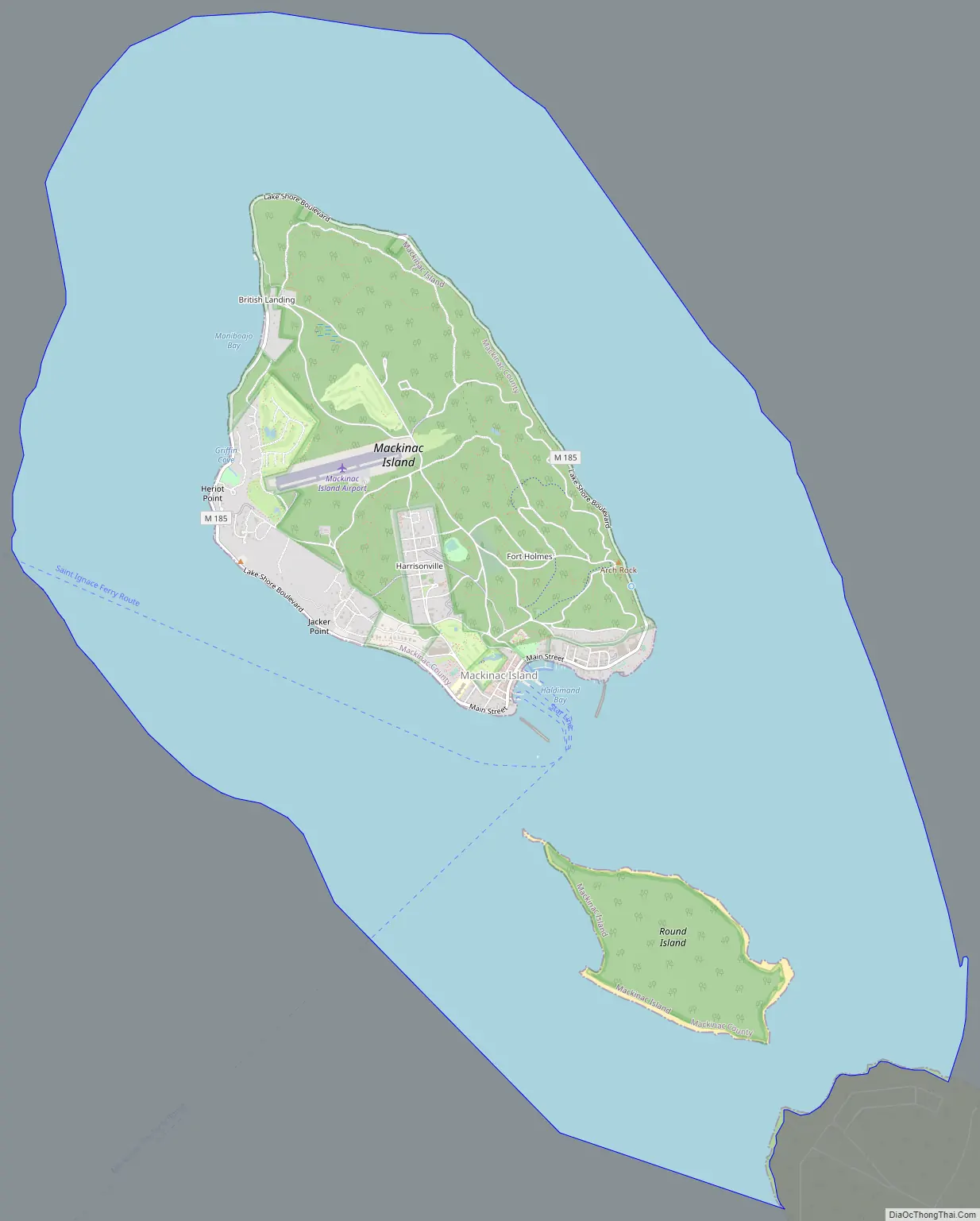
Mackinac Island Road Map
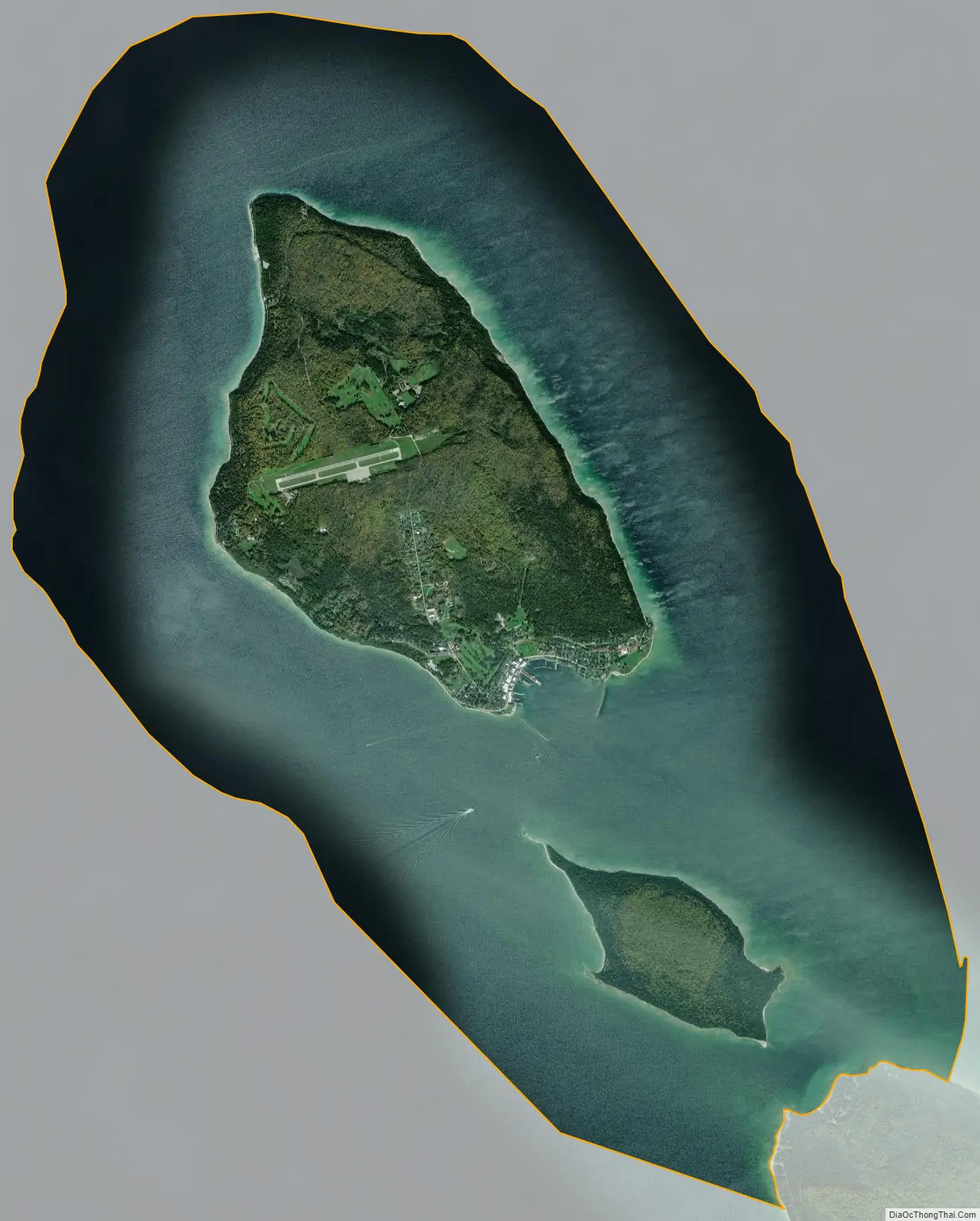
Mackinac Island city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 18.84 square miles (48.80 km), of which 4.35 square miles (11.27 km) is land and 14.49 square miles (37.53 km) is water. The City of Mackinac Island exists on the island of the same name, and it also nominally includes the entirety of nearby Round Island, situated in the Straits of Mackinac immediately to the south, which is uninhabited, and is owned and overseen by the United States Forest Service in its entirety, and is managed as part of the Round Island Wilderness Area and the Hiawatha National Forest.
While all of Mackinac Island, the landform, is located within the corporate limits of the City of Mackinac Island, today 82 percent of the island’s landmass is owned by the State of Michigan and managed by the Mackinac Island State Park Commission (MISPC). The city has direct jurisdiction over only 18 percent of the island. The City and the Commission work together on the many issues affecting both the City and the State Park, such as the longtime ban on motorized vehicles on the island.
Access to the island is by ferries across Lake Huron. The city of Mackinac Island is one of seven municipalities in the state of Michigan to consist entirely of islands, including Grosse Ile, Drummond, Bois Blanc, St. James, Peaine, and Sugar Island townships.
Neighborhoods
- Harrisonville, also referred to as “the village”, is a neighborhood of the city just past the Grand Hotel and up a hill.
- Hubbard’s Annex is a summer cottage subdivision and historical district west of the harbor platted in 1882 by Gurdon Saltonstall Hubbard. The plans included a public park referred to as the Commons and a community building lot for the Eating House. Francis B. Stockbridge purchased a cottage on the bluff top in 1882, where the Dziabis cottage is now located.
See also
Map of Michigan State and its subdivision:- Alcona
- Alger
- Allegan
- Alpena
- Antrim
- Arenac
- Baraga
- Barry
- Bay
- Benzie
- Berrien
- Branch
- Calhoun
- Cass
- Charlevoix
- Cheboygan
- Chippewa
- Clare
- Clinton
- Crawford
- Delta
- Dickinson
- Eaton
- Emmet
- Genesee
- Gladwin
- Gogebic
- Grand Traverse
- Gratiot
- Hillsdale
- Houghton
- Huron
- Ingham
- Ionia
- Iosco
- Iron
- Isabella
- Jackson
- Kalamazoo
- Kalkaska
- Kent
- Keweenaw
- Lake
- Lake Hurron
- Lake Michigan
- Lake St. Clair
- Lake Superior
- Lapeer
- Leelanau
- Lenawee
- Livingston
- Luce
- Mackinac
- Macomb
- Manistee
- Marquette
- Mason
- Mecosta
- Menominee
- Midland
- Missaukee
- Monroe
- Montcalm
- Montmorency
- Muskegon
- Newaygo
- Oakland
- Oceana
- Ogemaw
- Ontonagon
- Osceola
- Oscoda
- Otsego
- Ottawa
- Presque Isle
- Roscommon
- Saginaw
- Saint Clair
- Saint Joseph
- Sanilac
- Schoolcraft
- Shiawassee
- Tuscola
- Van Buren
- Washtenaw
- Wayne
- Wexford
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming