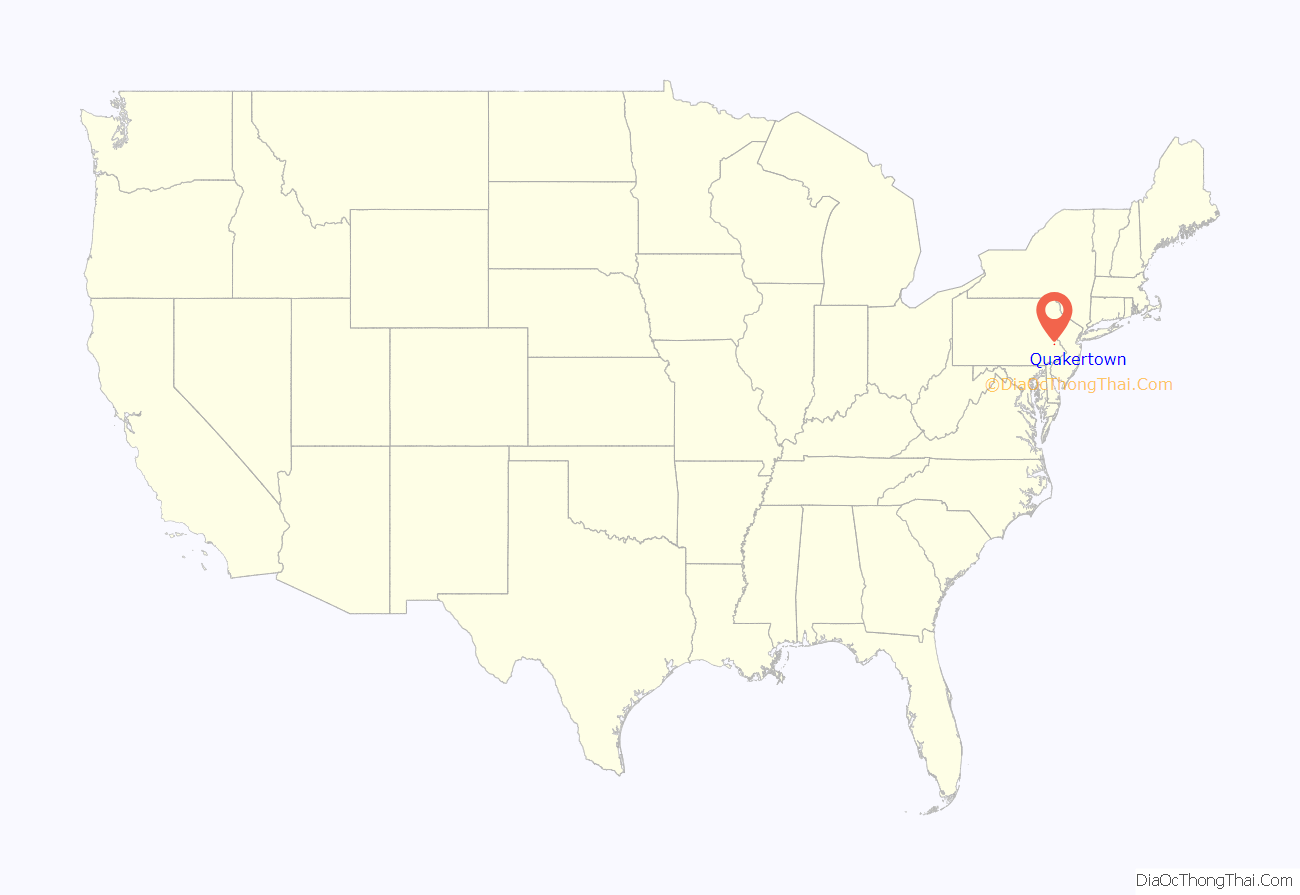
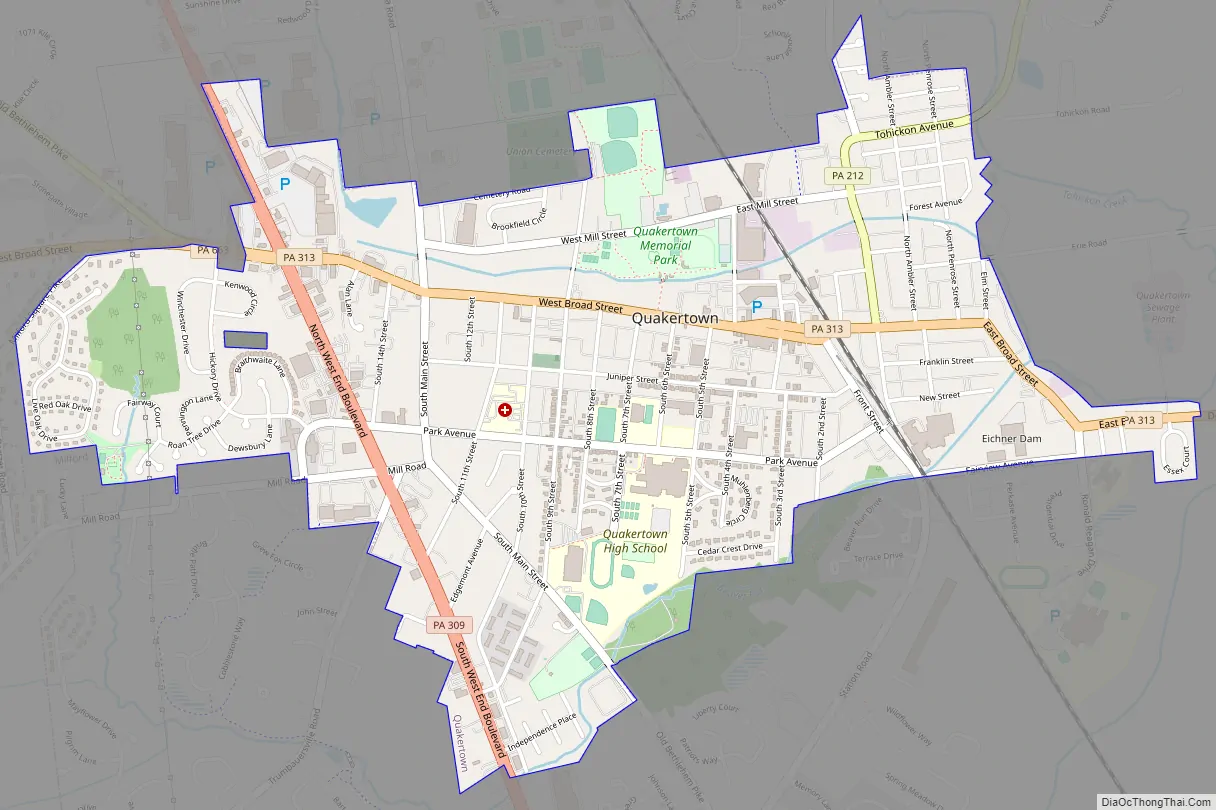
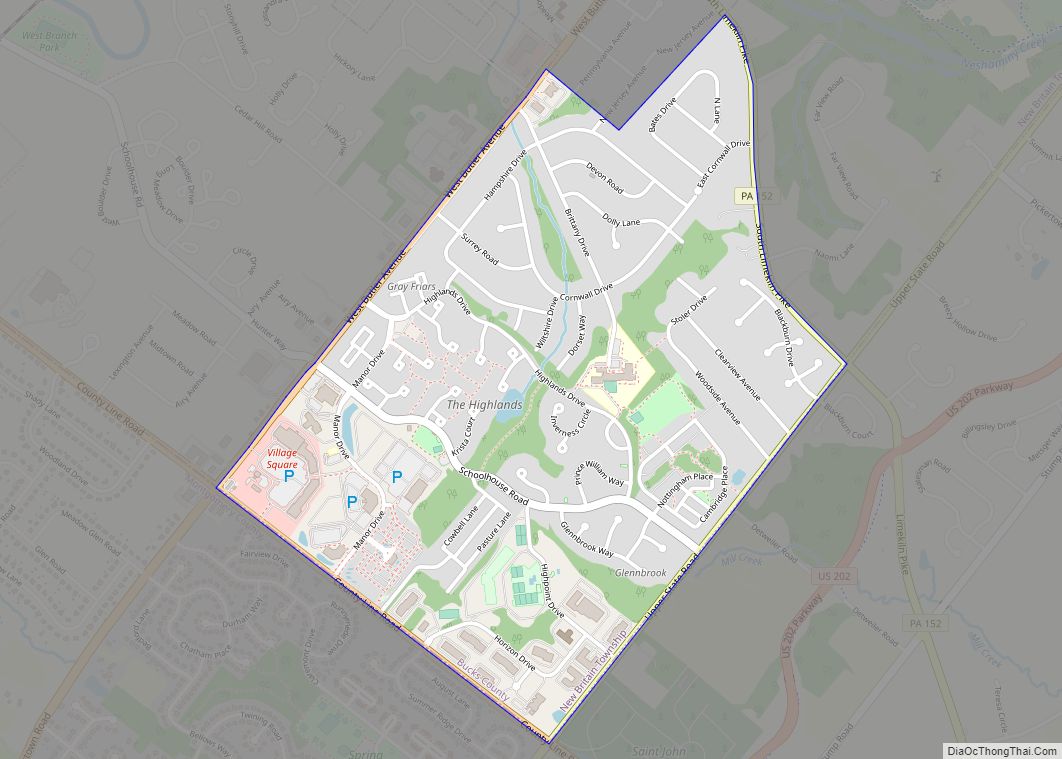
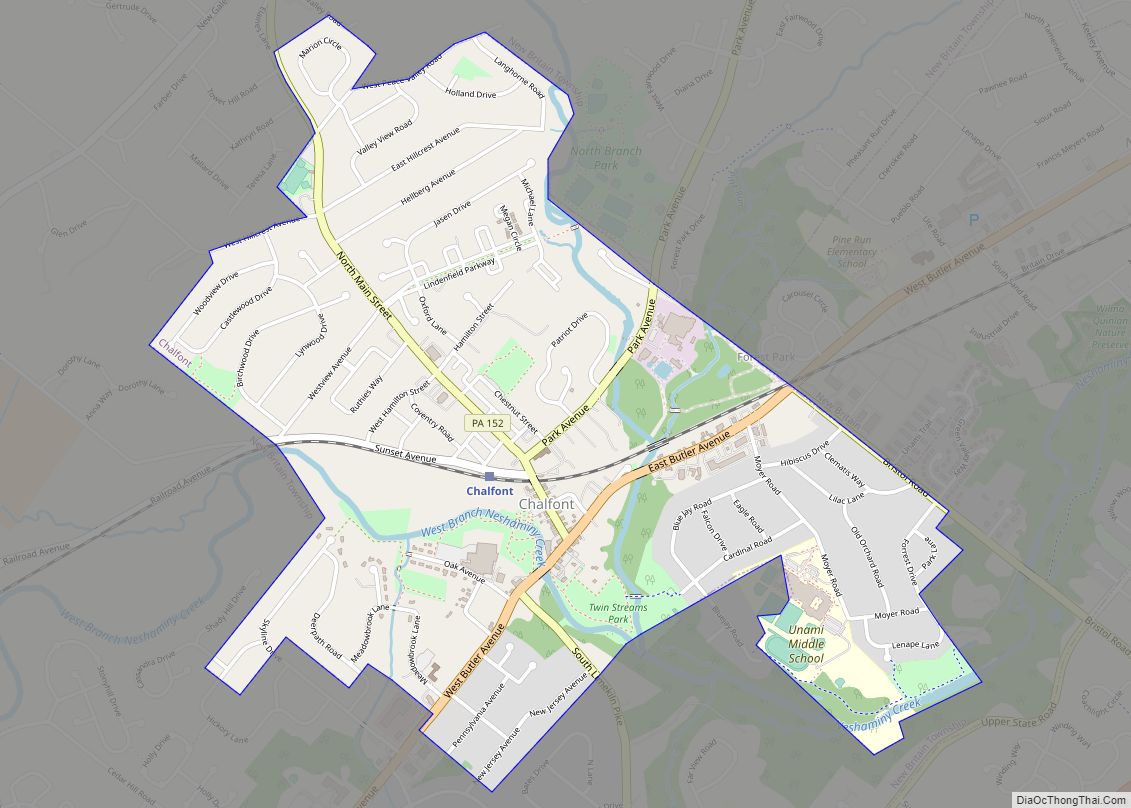
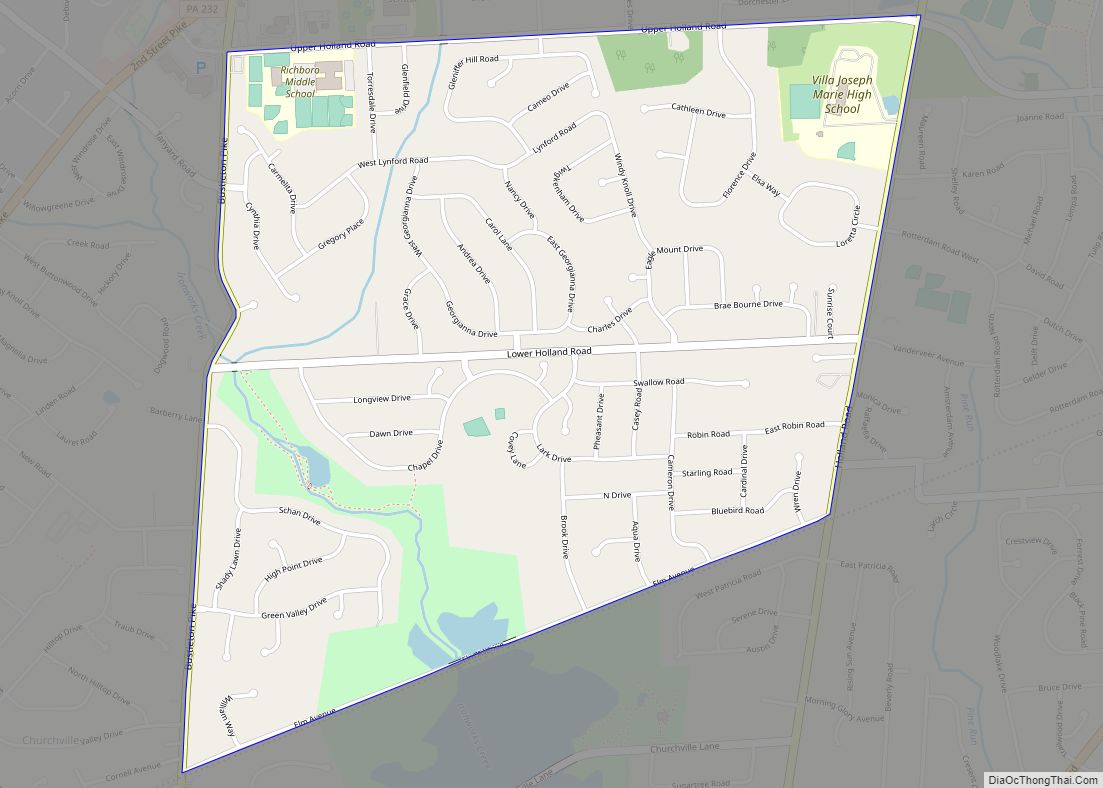
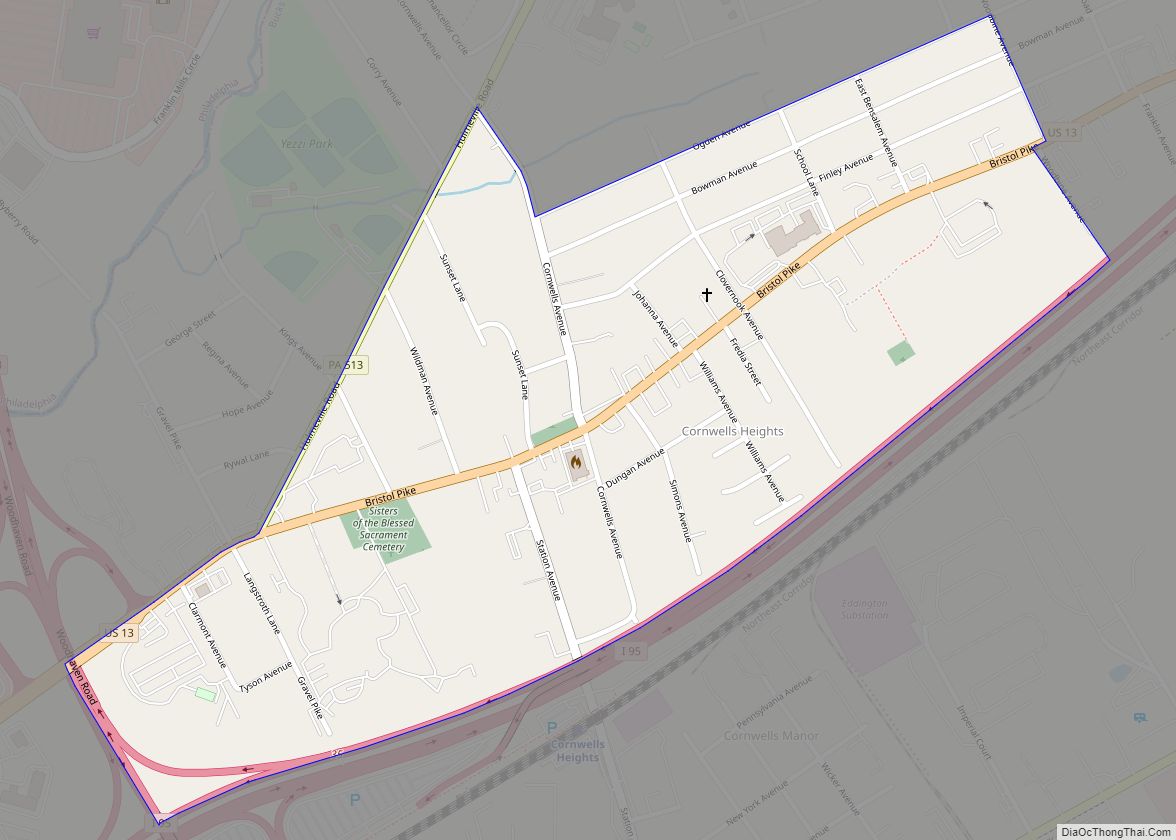
Quakertown is a borough in Bucks County, Pennsylvania, United States. As of 2020, it had a population of 9,359. The borough is 15 miles (24 km) south of Allentown and Bethlehem and 40 miles (64 km) north of Philadelphia, making Quakertown a border town of both the Delaware Valley and Lehigh Valley metropolitan areas.
Quakertown is considered part of the United States Census Bureau’s Philadelphia−Camden−Wilmington (PA−NJ−DE-MD) MSA and the Delaware Valley. Quakertown is surrounded by Richland Township.
Quakertown is located 15.7 miles (25.3 km) south of Allentown and 47.4 miles (76.3 km) northwest of Philadelphia.
| Name: | Quakertown borough |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 21 |
| LSAD Description: | borough (suffix) |
| State: | Pennsylvania |
| County: | Bucks County |
| Elevation: | 505 ft (154 m) |
| Total Area: | 2.04 sq mi (5.27 km²) |
| Land Area: | 2.04 sq mi (5.27 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km²) |
| Total Population: | 9,359 |
| Population Density: | 4,599.02/sq mi (1,775.87/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 18951 |
| FIPS code: | 4263048 |
| Website: | quakertown.org |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Quakertown location map. Where is Quakertown borough?
History
Quaker settlement
Quakertown was originally settled by members of the Religious Society of Friends, or Quakers. The settlement was not officially known as Quakertown until its first post office opened in 1803.
Liberty Bell moved
On September 18, 1777, during the American Revolutionary War, a convoy of wagons carrying the Liberty Bell from Philadelphia to Allentown, under the command of Col. Thomas Polk of Charlotte, North Carolina, stopped in Quakertown. The Liberty Bell was stored overnight behind the home of Evan Foulke (1237 West Broad Street), and the entourage stayed at the Red Lion Inn. The John Fries’ Rebellion was also started in the Red Lion Inn in 1799.
1800s growth
In 1854, Quakertown elected its first Burgess. The North Pennsylvania Railroad facilitated access to the area, which brought about a great increase in population, and by 1880, the population of Quakertown had almost reached 1,800.
Liberty Hall, Quakertown Historic District, Quakertown Passenger and Freight Station, and Enoch Roberts House are listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
Industry and population
The Civil War, along with national economic expansion, changed Quakertown from a tiny village to a commercial manufacturing center. In the nineteenth century, local industrial establishments included cigar and cigar box factories, silk mills, harness factories, and stove foundries. Until 1969, Quakertown generated its own electrical power. As of 2022, Quakertown has extensive mall development along Pennsylvania Route 309 that includes many restaurants, businesses, and retail outlets. The population of Quakertown in 1900 was 3,014; it rose to 3,801 in 1910. By 1940, the population had reached 5,150 people. At the 2010 census, the borough’s population was 8,979.
Interurban to Allentown and Philadelphia
From 1901 to 1951, Quakertown was an hourly stop on the Lehigh Valley Transit Company’s electric interurban trolley line from Allentown and Coopersburg through Quakertown then south through Perkasie, Sellersville, Souderton, Lansdale, and Norristown to Philadelphia. With car use limited during World War II due to gasoline rationing, the trolley line moved a very large number of passengers. After the war, as was the case with many other railways, its business collapsed, and it ceased operation in 1951. The LVT station at the northwestern corner of Main and Broad streets, across from the Red Lion Inn, still stands and is marked on one wall for that history. It ran in the center of Main Street as it progressed southbound to Perkasie.
Quakertown Road Map
Quakertown city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the borough has a total area of 2.0 square miles (5.2 km), all land. Licking Run begins in passes through Quakertown from the west to the east and drains into the Tohickon Creek. Tohickon Creek, which drains into the Delaware River, flows past the northeastern edge of the borough.
Climate
According to the Köppen climate classification system, Quakertown has a Hot-summer, Humid continental climate (Dfa). Dfa climates are characterized by at least one month having an average mean temperature ≤ 32.0 °F (0.0 °C), at least four months with an average mean temperature ≥ 50.0 °F (10.0 °C), at least one month with an average mean temperature ≥ 71.6 °F (22.0 °C) and no significant precipitation difference between seasons. Although most summer days are slightly humid in Quakertown, episodes of heat and high humidity can occur with heat index values > 104 °F (40 °C). Since 1981, the highest air temperature was 101.9 °F (38.8 °C) on July 22, 2011, and the highest daily average mean dew point was 74.4 °F (23.6 °C) on August 1, 2006. The average wettest month is July which corresponds with the annual peak in thunderstorm activity. Since 1981, the wettest calendar day was 6.50 inches (165 mm) on September 30, 2010. During the winter months, the average annual extreme minimum air temperature is −1.9 °F (−18.8 °C). Since 1981, the coldest air temperature was −13.7 °F (−25.4 °C) on January 22, 1984. Episodes of extreme cold and wind can occur with wind chill values < −13 °F (−25 °C). The average annual snowfall (Nov-Apr) is between 30 inches (76 cm) and 36 inches (91 cm). Ice storms and large snowstorms depositing ≥ 12 inches (30 cm) of snow occur once every few years, particularly during nor’easters from December through February.
Ecology
According to the A. W. Kuchler U.S. potential natural vegetation types, Quakertown has a dominant vegetation type of Appalachian Oak (104) with a dominant vegetation form of Eastern Hardwood Forest (25). The plant hardiness zone is 6b with an average annual extreme minimum air temperature of −1.9 °F (−18.8 °C). The spring bloom typically begins by April 12 and fall color usually peaks by October 28.
See also
Map of Pennsylvania State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Allegheny
- Armstrong
- Beaver
- Bedford
- Berks
- Blair
- Bradford
- Bucks
- Butler
- Cambria
- Cameron
- Carbon
- Centre
- Chester
- Clarion
- Clearfield
- Clinton
- Columbia
- Crawford
- Cumberland
- Dauphin
- Delaware
- Elk
- Erie
- Fayette
- Forest
- Franklin
- Fulton
- Greene
- Huntingdon
- Indiana
- Jefferson
- Juniata
- Lackawanna
- Lancaster
- Lawrence
- Lebanon
- Lehigh
- Luzerne
- Lycoming
- Mc Kean
- Mercer
- Mifflin
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Montour
- Northampton
- Northumberland
- Perry
- Philadelphia
- Pike
- Potter
- Schuylkill
- Snyder
- Somerset
- Sullivan
- Susquehanna
- Tioga
- Union
- Venango
- Warren
- Washington
- Wayne
- Westmoreland
- Wyoming
- York
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming