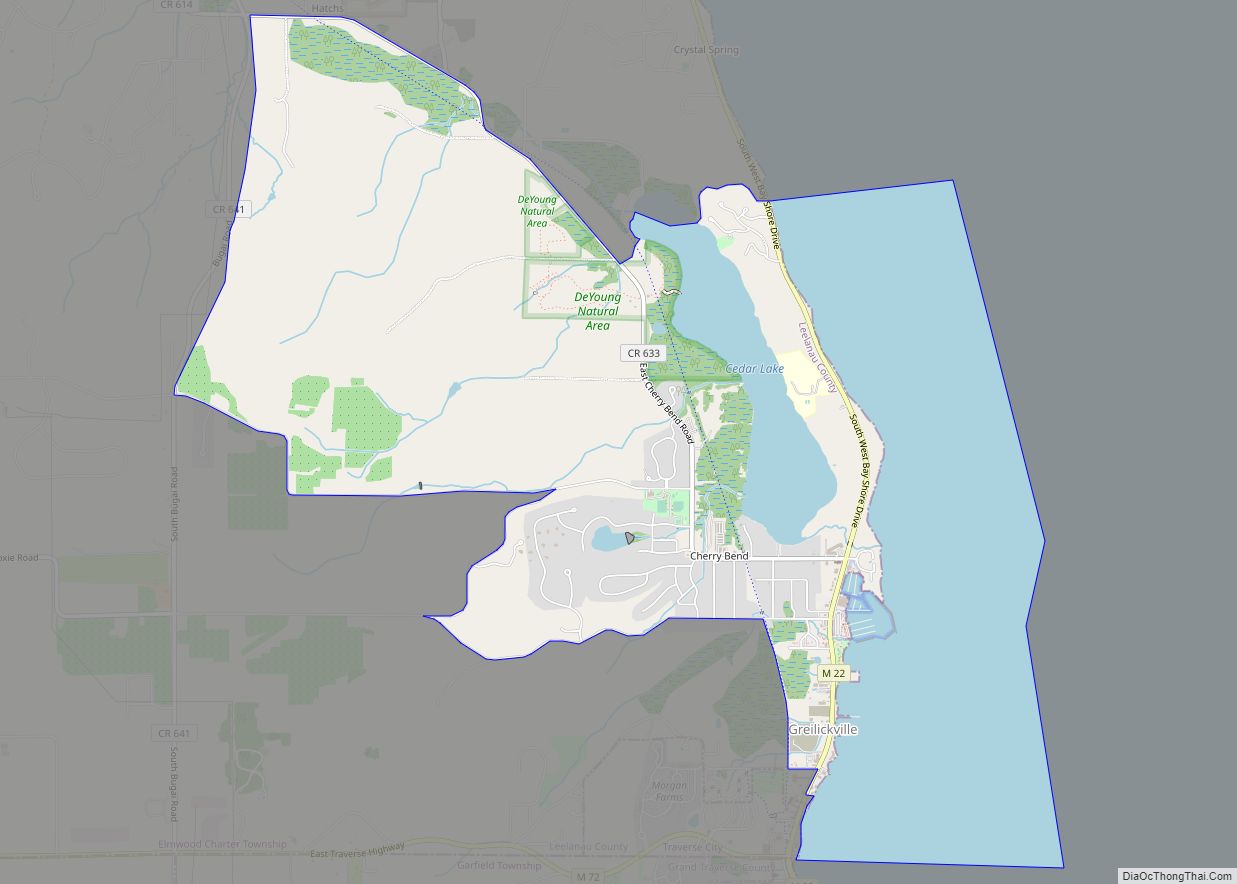
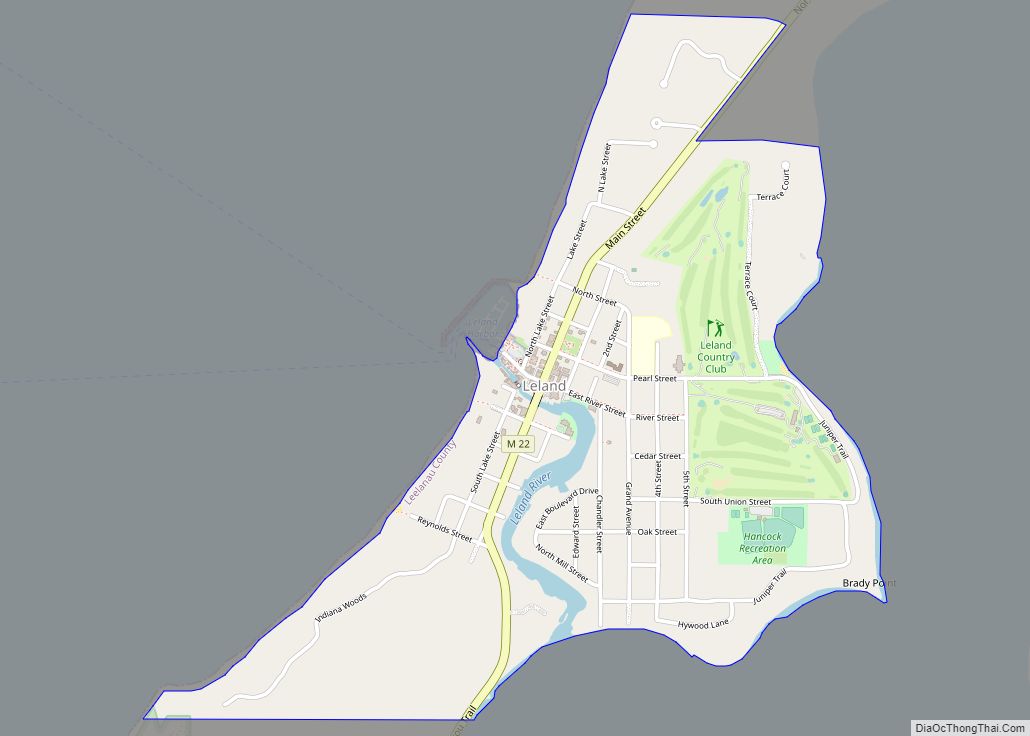
Leland (/ˈliːlənd/ LEE-lənd) is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2020 census it had a population of 410. From 1883 to 2004, Leland was the county seat of Leelanau County, which has since moved to Suttons Bay Township.
Part of Leland Township, Leland is situated on an isthmus between Lake Leelanau and Lake Michigan, and is bisected by the Leland River, flowing from the former to the latter. Leland is a significant tourism destination and summer colony, and is located nearby Sleeping Bear Dunes National Lakeshore. Leland also serves as the departure point for ferry service to North and South Manitou Islands, both of which are wholly included in the National Lakeshore.
| Name: | Leland CDP |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 57 |
| LSAD Description: | CDP (suffix) |
| State: | Michigan |
| County: | Leelanau County |
| Elevation: | 581 ft (177 m) |
| Total Area: | 1.00 sq mi (2.58 km²) |
| Land Area: | 0.98 sq mi (2.53 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.02 sq mi (0.06 km²) |
| Total Population: | 410 |
| Population Density: | 420.08/sq mi (162.26/km²) |
| Area code: | 231 |
| FIPS code: | 2646800 |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Leland location map. Where is Leland CDP?
History
Leland is built on the site of one of the oldest and largest Ottawa villages on the Leelanau Peninsula. Where the Leland (Carp) River flows into Lake Michigan, there was a natural fish ladder (which was a traditional Native American fishing grounds). The settlement was called Mishi-me-go-bing, meaning “the place where canoes run up into the river to land, because they have no harbor”, or alternatively Che-ma-go-bing or Chi-mak-a-ping.
White settlers, who began arriving in the 1830s, also took advantage of the location as a fishing settlement. White settlement increased after Antoine Manseau, with his son Antoine Jr., and John Miller, built a dam and sawmill on the river in 1854. Construction of the dam raised the water level 12 feet (3.7 m), and what had been three natural lakes in the river all became a single lake now known as Lake Leelanau (and is navigable all the way to the community of Cedar, about 13 miles (21 km) inland). The settlers built wooden docks, which allowed steamers and schooners to transport new settlers and supplies.
From 1870 to 1884, the Leland Lake Superior Iron Co. operated an iron smelter north of the river mouth, supplied with ore from the Upper Peninsula and charcoal made from local maple and beech timber; the charcoal was produced in fourteen beehive kilns near the smelting furnace, which produced up to 40 tons of iron per day. In 1884, the plant was sold to the Leland Lumber Co., which operated a sawmill on the site. Other sawmills and shingle mills operated in Leland during the years 1885–1900.
As early as 1880, commercial fishermen sailed out of the harbor to catch trout and whitefish, building wooden shacks where they processed their catch and serviced their fleet. Up to eight powered tugs once sailed out of “Fishtown”, as the buildings came to be known. Today, the historic fishing settlement and two fish tugs, Joy and Janice Sue, are owned by a non-profit organization, the Fishtown Preservation Society. Fishtown is home to a working fishery and a thriving charter fishing business. The riverfront is lined by a boardwalk and quaint shacks that have been converted into tourist shops.
Around 1900, wealthy individuals from Chicago, Detroit, and other Midwestern industrial centers began to visit Leland and build summer cottages, arriving by Lake Michigan passenger steamer or by Lake Leelanau steamer from the railhead near Traverse City. This led to the construction of resort hotels, and the growth of Leland as a summer resort town.
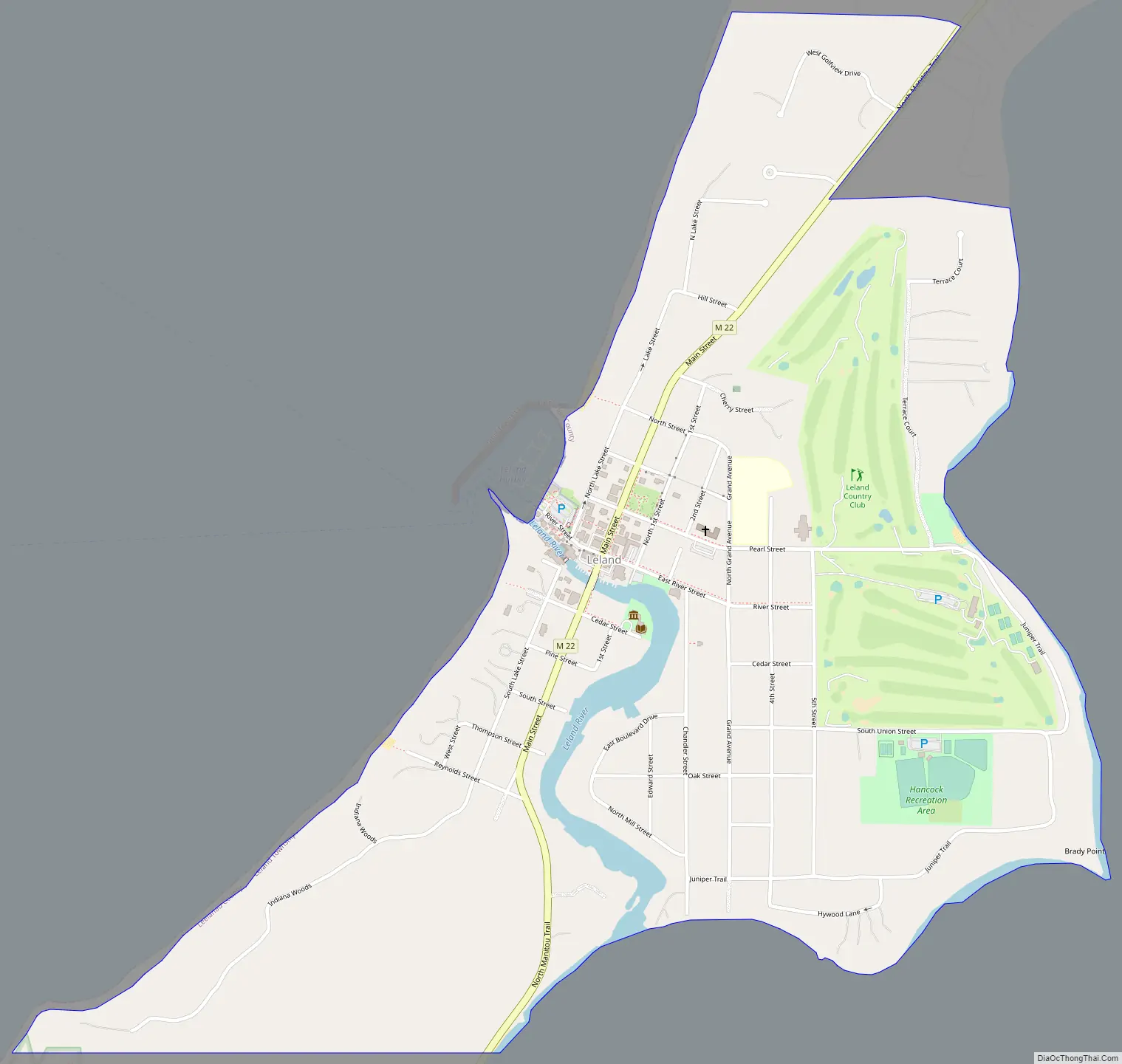
Leland Road Map
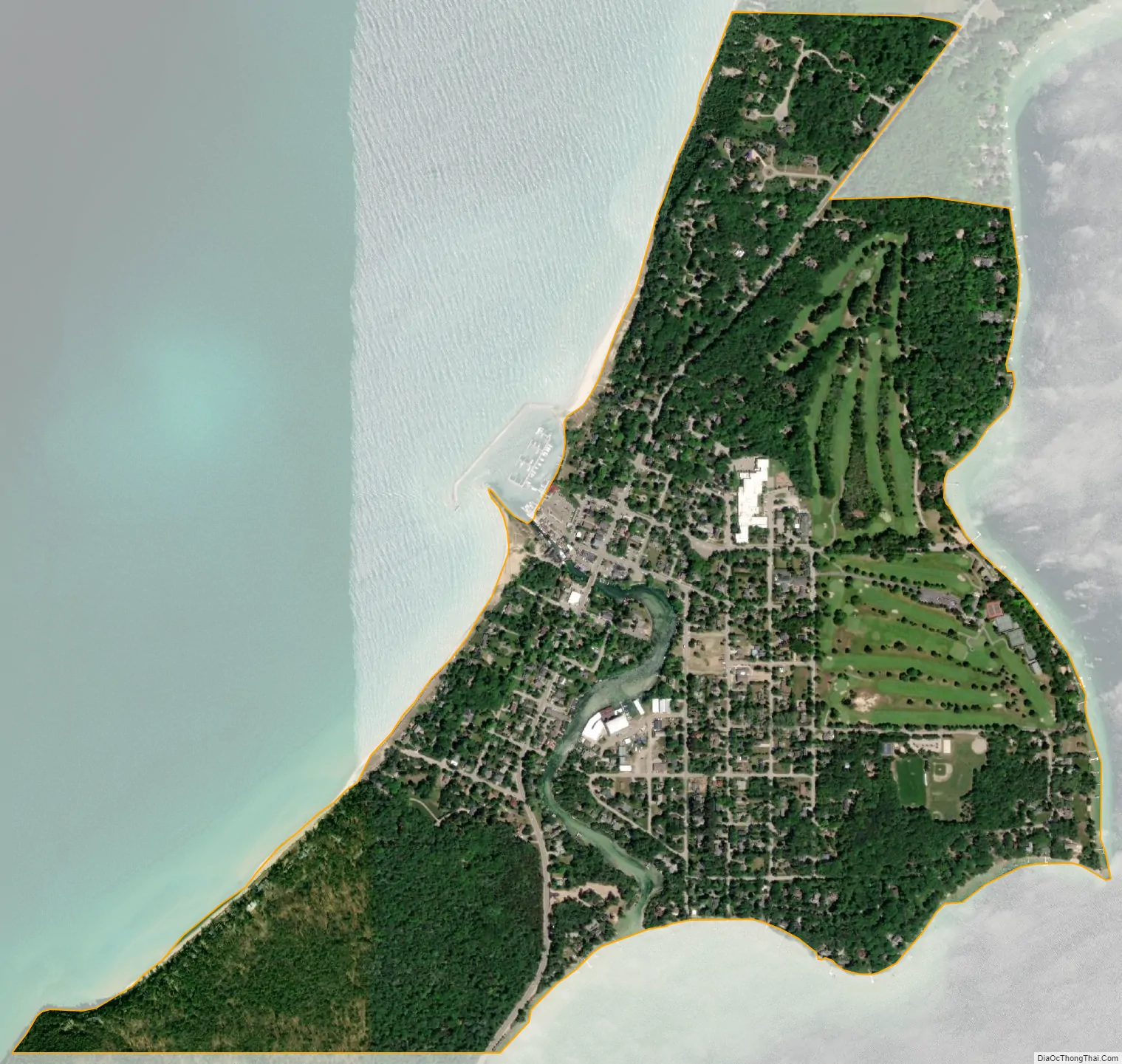
Leland city Satellite Map
Geography
Leland is in northern Leelanau County, on the west side of the Leelanau Peninsula. It is bordered to the west by Lake Michigan and to the east by the northern section of Lake Leelanau. The Leland River runs through the center of the community, connecting the two lakes. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the Leland CDP has a total area of 1.00 square mile (2.58 km), of which 0.98 square miles (2.53 km) are land and 0.02 square miles (0.06 km), or 2.22%, are water.
Leland lies just north of the 45th parallel. A sign on M-22 south of Leland reads “45th Parallel Halfway Between Equator & North Pole”.
See also
Map of Michigan State and its subdivision:- Alcona
- Alger
- Allegan
- Alpena
- Antrim
- Arenac
- Baraga
- Barry
- Bay
- Benzie
- Berrien
- Branch
- Calhoun
- Cass
- Charlevoix
- Cheboygan
- Chippewa
- Clare
- Clinton
- Crawford
- Delta
- Dickinson
- Eaton
- Emmet
- Genesee
- Gladwin
- Gogebic
- Grand Traverse
- Gratiot
- Hillsdale
- Houghton
- Huron
- Ingham
- Ionia
- Iosco
- Iron
- Isabella
- Jackson
- Kalamazoo
- Kalkaska
- Kent
- Keweenaw
- Lake
- Lake Hurron
- Lake Michigan
- Lake St. Clair
- Lake Superior
- Lapeer
- Leelanau
- Lenawee
- Livingston
- Luce
- Mackinac
- Macomb
- Manistee
- Marquette
- Mason
- Mecosta
- Menominee
- Midland
- Missaukee
- Monroe
- Montcalm
- Montmorency
- Muskegon
- Newaygo
- Oakland
- Oceana
- Ogemaw
- Ontonagon
- Osceola
- Oscoda
- Otsego
- Ottawa
- Presque Isle
- Roscommon
- Saginaw
- Saint Clair
- Saint Joseph
- Sanilac
- Schoolcraft
- Shiawassee
- Tuscola
- Van Buren
- Washtenaw
- Wayne
- Wexford
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming