Alcoa is a city in Blount County, Tennessee, United States, south of Knoxville. Its population was 10,978 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Knoxville, Tennessee Metropolitan Statistical Area.
As its name suggests, Alcoa was the site of a large aluminum smelting plant owned and operated by the Alcoa corporation (Aluminum Company of America). Formerly known as North Maryville, the town was incorporated under its present name in 1919.
| Name: | Alcoa city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Tennessee |
| County: | Blount County |
| Incorporated: | 1919; 104 years ago (1919) |
| Elevation: | 843 ft (257 m) |
| Total Area: | 15.92 sq mi (41.22 km²) |
| Land Area: | 15.00 sq mi (38.85 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.92 sq mi (2.37 km²) |
| Total Population: | 10,978 |
| Population Density: | 731.82/sq mi (282.56/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 37701, 37777, 37801 & 37804 |
| Area code: | 865 |
| FIPS code: | 4700540 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1304784 |
| Website: | www.cityofalcoa-tn.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
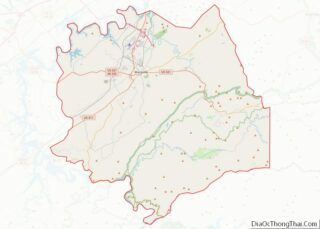
Alcoa location map. Where is Alcoa city?
History
Early company town
Shortly after the Pittsburgh Reduction Company changed its name to the Aluminum Company of America in 1907, the company began investigating the possibility of establishing a large smelting operation in East Tennessee. The hydroelectric potential of the Little Tennessee River, which exits the mountains about 20 miles (32 km) southwest of Alcoa, was one of the primary incentives, as the company’s aluminum smelting operation would require massive amounts of electricity. In 1910, the company established a base camp at what is now known as Calderwood, initially known as “Alcoa”, and was known as such until the name was reapplied to the company’s operations in North Maryville a few years later.
The company considered several potential plant sites in Knoxville, Etowah, and Monroe County, but chose North Maryville due in part to the influence of Maryville mayor Samuel Everett (1864−1941). By 1914, the company had completed the initial purchase of 700 acres (280 ha) in North Maryville, and had initiated construction of the smelting plant and 150 houses for company employees. ALCOA’s chief engineer Edwin Fickes and hydraulic engineer Robert Ewald drew up plans for the town to house the plant’s workers. The town design initially called for the acquisition of 7,500 acres (3,000 ha), and included four sections— Vose and Springbrook in the north (around what is now Springbrook Park) and Bassel and Hall in the south (around what is now the South Plant). Hall, named for the inventor of the aluminum electrolytic process, was originally a segregated community for the plant’s African-American workers. Oldfield, a small community between the planned town and Maryville, would later be annexed by the city of Alcoa.
World War I brought about a spike in the demand for aluminum, and the company quickly expanded its North Maryville operations. In 1919, a rolling mill (now West Plant) was completed, and the company purchased the Knoxville Power Company for its Little Tennessee Valley holdings. That same year, the company’s town officially incorporated as “Alcoa”. C.L. Babcock was the town’s first mayor, and Victor Hultquist was the first city manager. Hultquist, who was also ALCOA’s superintendent of construction, remained city manager until 1948, and oversaw much of the town’s early development. In 1920, Alcoa had a population of 3,358 people living in 700 houses.
The Great Depression and World War II
Early Alcoa was a classic “company town”, with the company maintaining a paternalistic relationship with the city. The city’s welfare was almost wholly dependent upon the company’s fortunes. This presented a problem for the company, which feared that its workforce would leave to look for jobs elsewhere during times of low production. Thus, during the Great Depression, the company maintained steady production levels in spite of the lack of demand for aluminum. Managers sought to cut workers’ hours— which at one point dropped to 30 hours per week— rather than slash jobs. By the end of the decade, the company had stockpiled 42,000 tons of aluminum.
The Depression (and accompanying New Deal legislation) also brought about increased labor union activity in Alcoa. A strike in 1934 was forcibly ended when Hultquist deployed a large police force. A second strike in 1937 was broken in a similar fashion, with two striking workers shot and killed and the National Guard forced to intervene.
World War II proved immensely profitable for ALCOA, as aluminum was needed for aircraft construction. Production increased 600% during the war, and the company’s Alcoa operations workforce swelled to 12,000. In the early 1940s, the company built its North Plant, which at the time of its completion was the world’s largest plant under a single roof.
Modern Alcoa
After World War II, the city of Alcoa became less and less dependent upon its parent company. Alcoa’s public image had suffered due to its hardline stance toward labor unions, and in response, it launched a series of public relations initiatives, including the donation of land for schools, parks, and airport construction. The company also desegregated its facilities during this period. In the early 1950s, the company began selling off company housing to employees. In 1956, Ross Walker became the first city manager who was not employed by the company, and toward the end of the decade, the company had relinquished ownership of city utilities. The completion of the Hall Road Viaduct in the 1940s and the continued development of McGhee Tyson Airport over subsequent decades led to commercial expansion and helped the city diversify its economy.
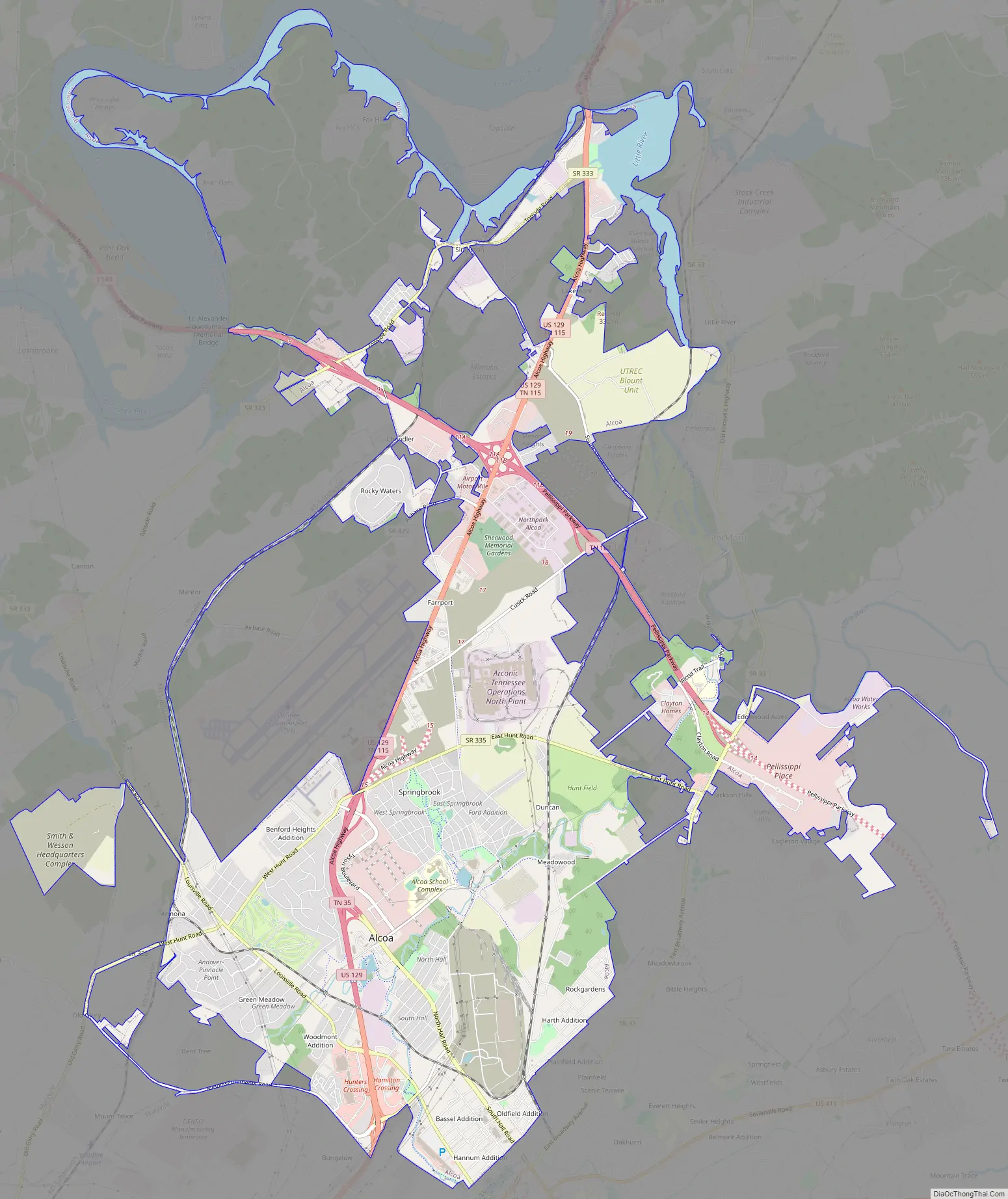
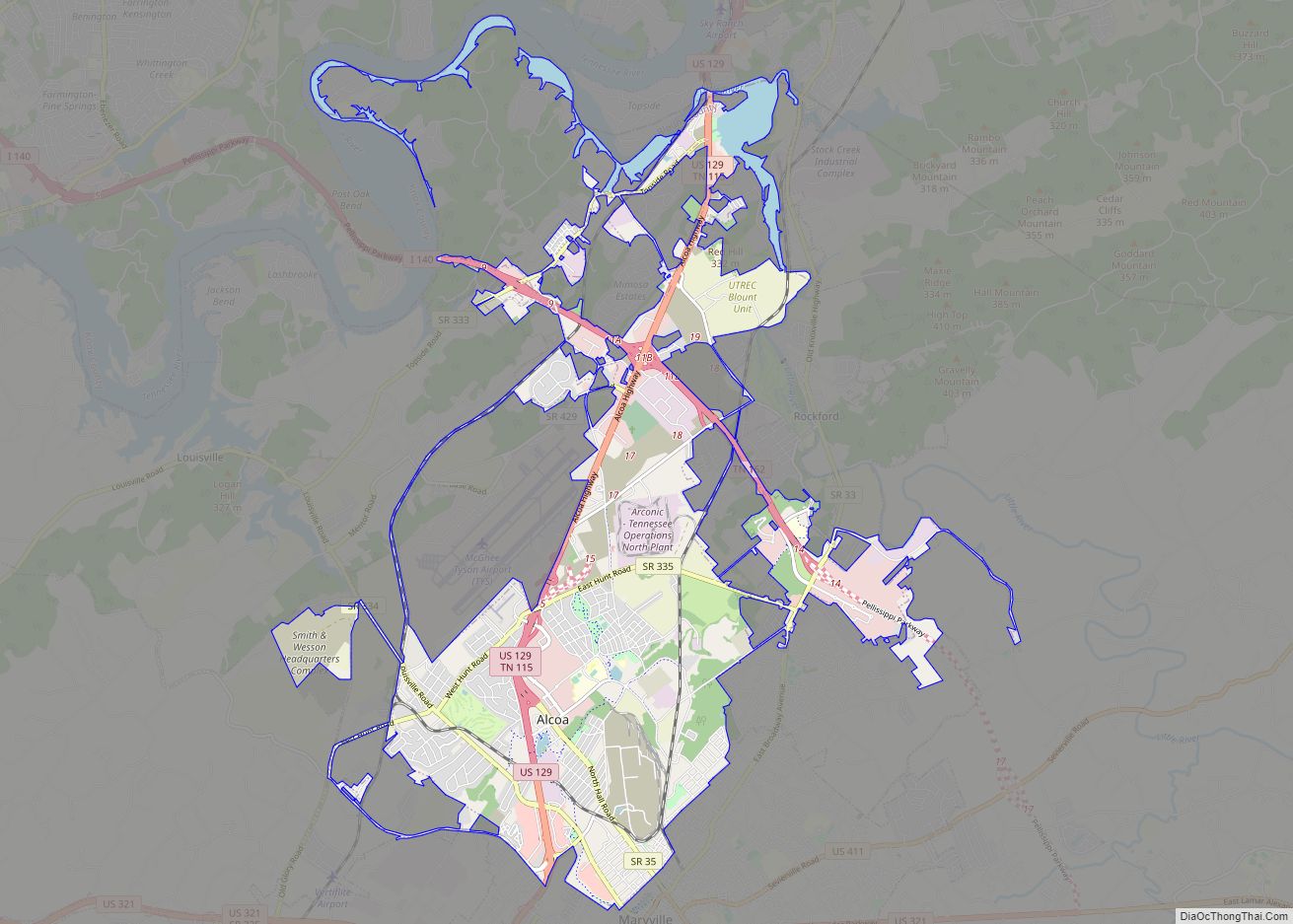
Alcoa Road Map
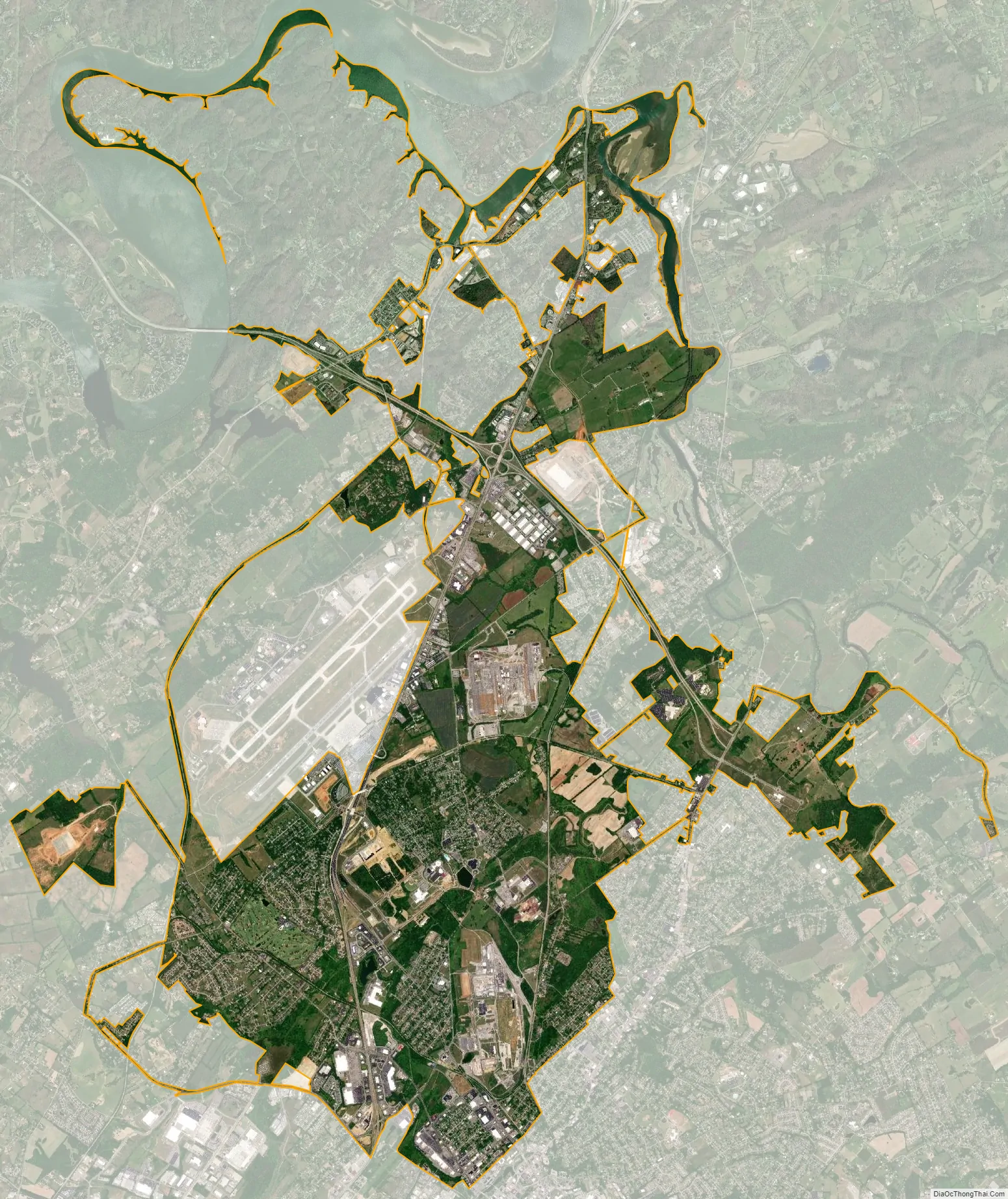
Alcoa city Satellite Map
Geography
The city is situated in the foothills of the Great Smoky Mountains, the outermost of which, Chilhowee Mountain, rises just a few miles to the south. Large sections of the north-central and northeastern parts of the range are visible from Alcoa Highway. The Little River, which rises near the heart of the Smokies, flows through the eastern section of Alcoa before emptying into the Tennessee River near Louisville.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 15.6 square miles (40.5 km), of which 14.7 square miles (38.2 km) is land and 0.93 square miles (2.4 km), or 5.90%, is water.
See also
Map of Tennessee State and its subdivision:- Anderson
- Bedford
- Benton
- Bledsoe
- Blount
- Bradley
- Campbell
- Cannon
- Carroll
- Carter
- Cheatham
- Chester
- Claiborne
- Clay
- Cocke
- Coffee
- Crockett
- Cumberland
- Davidson
- Decatur
- DeKalb
- Dickson
- Dyer
- Fayette
- Fentress
- Franklin
- Gibson
- Giles
- Grainger
- Greene
- Grundy
- Hamblen
- Hamilton
- Hancock
- Hardeman
- Hardin
- Hawkins
- Haywood
- Henderson
- Henry
- Hickman
- Houston
- Humphreys
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Johnson
- Knox
- Lake
- Lauderdale
- Lawrence
- Lewis
- Lincoln
- Loudon
- Macon
- Madison
- Marion
- Marshall
- Maury
- McMinn
- McNairy
- Meigs
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Moore
- Morgan
- Obion
- Overton
- Perry
- Pickett
- Polk
- Putnam
- Rhea
- Roane
- Robertson
- Rutherford
- Scott
- Sequatchie
- Sevier
- Shelby
- Smith
- Stewart
- Sullivan
- Sumner
- Tipton
- Trousdale
- Unicoi
- Union
- Van Buren
- Warren
- Washington
- Wayne
- Weakley
- White
- Williamson
- Wilson
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming