Grand Rapids is a city and county seat of Kent County in the U.S. state of Michigan. At the 2020 census, the city had a population of 198,917 which ranks it as the second most-populated city in the state after Detroit. Grand Rapids is the central city of the Grand Rapids metropolitan area, which has a population of 1,087,592 and a combined statistical area population of 1,383,918.
Situated along the Grand River approximately 25 miles (40 km) east of Lake Michigan, it is the economic and cultural hub of West Michigan, as well as one of the fastest-growing cities in the Midwest. A historic furniture manufacturing center, Grand Rapids is home to five of the world’s leading office furniture companies and is nicknamed “Furniture City”. Other nicknames include “River City” and more recently, “Beer City” (the latter given by USA Today and adopted by the city as a brand). The city and surrounding communities are economically diverse, based in the health care, information technology, automotive, aviation, and consumer goods manufacturing industries, among others.
Grand Rapids was the childhood home of U.S. President Gerald Ford, who is buried with his wife Betty on the grounds of the Gerald R. Ford Presidential Museum in the city. The city’s Gerald R. Ford International Airport and Gerald R. Ford Freeway are named after him.
| Name: | Grand Rapids city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Michigan |
| County: | Kent County |
| Founded: | 1826 |
| Incorporated: | 1838 (village) 1850 (city) |
| Elevation: | 640 ft (200 m) |
| Land Area: | 44.78 sq mi (115.97 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.86 sq mi (2.22 km²) 1.92% |
| Population Density: | 4,442.49/sq mi (1,715.26/km²) |
| Area code: | 616 |
| FIPS code: | 2634000 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0627105 |
| Website: | GrandRapidsMI.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
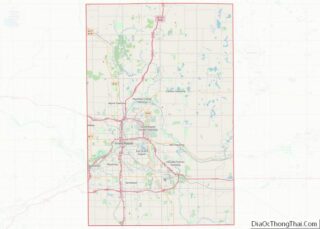
Grand Rapids location map. Where is Grand Rapids city?
Grand Rapids Road Map
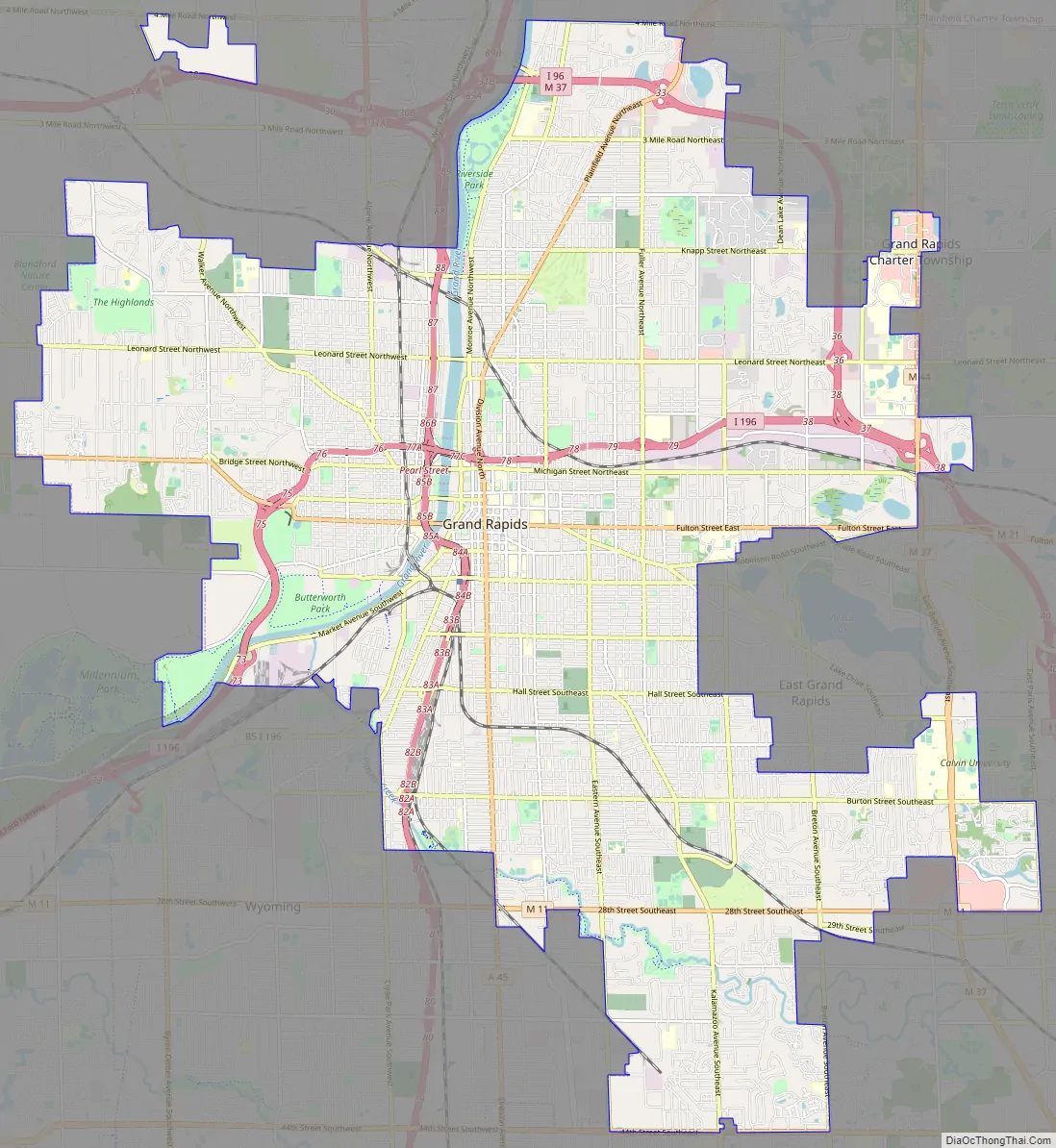
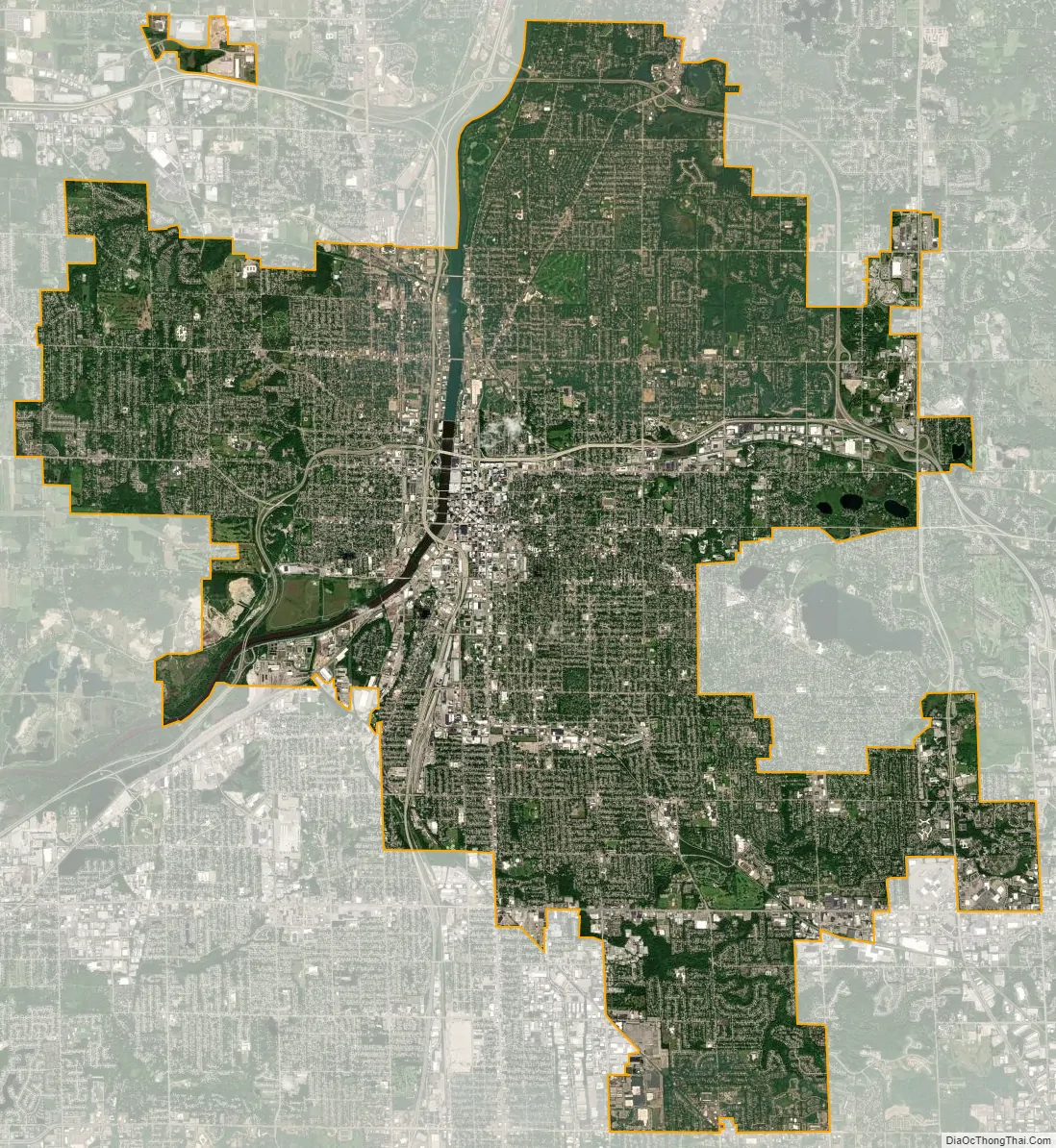
Grand Rapids city Satellite Map
Geography
Neighborhoods
According to city government data, Grand Rapids has 37 distinct neighborhoods:
- Alger Heights
- Baxter
- Belknap Lookout
- Black Hills
- Creston
- Downtown
- East Hills
- Eastern-Burton
- Eastgate
- Eastown
- Fulton Heights
- Garfield Park
- Grandville
- Heartside
- Heritage Hill
- Highland Park
- John Ball Park
- Ken-O-Sha Park
- Lake Eastbrook
- Leffingwell-Twin Lakes
- Michigan Oaks
- Midtown
- Millbank
- North End
- North Park
- Northeast
- Ottawa Hills
- Richmond-Oakleigh
- Ridgemoor Park
- Roosevelt Park
- Shangrai-La
- Shawmut Hills
- Shawnee Park
- Southeast Community
- Southeast End
- Southwest
- West Grand
Topography
Grand Rapids developed on the banks of the Grand River, where there was once a set of rapids, at an altitude of 610 feet (186 m) above sea level. Ships could navigate on the river up to this fall line, stopping because of the rapids. The river valley is flat and narrow, surrounded by steep hills and bluffs. The terrain becomes more rolling hills away from the river. The countryside surrounding the metropolitan area consists of mixed forest and farmland, with large areas of orchards to the northwest. It is approximately 25 mi (40 km) east of Lake Michigan. The state capital of Lansing lies about 60 mi (97 km) to the east-by-southeast, and Kalamazoo is about 50 mi (80 km) to the south.
Grand Rapids is divided into four quadrants, which form a part of mailing addresses in Kent County. The quadrants are NE (northeast), NW (northwest), SE (southeast), and SW (southwest). Fulton Street serves as the north–south dividing line, while Division Avenue serves as the east–west dividing line separating these quadrants.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 45.27 square miles (117.25 km), of which, 44.40 square miles (115.00 km) of it is land and 0.87 square miles (2.25 km) is water.
Climate
Grand Rapids has a humid continental climate (Köppen Dfa), with very warm and humid summers, cold and snowy winters, and short and mild springs and autumns.
Even though it is in the middle of the continent, the city experiences some maritime effects due to its location east of Lake Michigan, including a high number of cloudy days during the late fall and winter, delayed heating in the spring, delayed cooling in fall, somewhat moderated temperatures during winter and lake effect snow. The city averages 75.6 in (192 cm) of snow a year, making it one of the snowiest major cities in the United States. The area often receives quick and sudden lake effect snowstorms, producing significant amounts of snowfall.
The months of March, April, October and November are transitional months and the weather can vary. March has experienced a record high of 87 °F (31 °C) and record low of −13 °F (−25 °C). The average last frost date in spring is May 1, and the average first frost in fall is October 11, giving the area a growing season of 162 days. The city is in plant hardiness zone 6a, while outlying areas are 5b. Some far western suburbs closer to the insulating effect of Lake Michigan are in zone 6b. Summers are warm or hot, and heat waves and severe weather outbreaks are common during a typical summer.
The average temperature of the area is 49 °F (9 °C). The highest temperature in the area was recorded on July 13, 1936, at 108 °F (42 °C), and the lowest was recorded on February 13–14, 1899, at −24 °F (−31 °C). During an average year, sunshine occurs in 46% of the daylight hours. On 138 nights, the temperature dips to below 32 °F (0 °C). On average, 9.2 days a year have temperatures that meet or exceed the 90 °F (32 °C) mark, and 5.6 days a year have lows that are 0 °F (−18 °C) or colder.
The coldest maximum temperature on record was −6 °F (−21 °C) in 1899, whereas the most recent subzero Fahrenheit daily maximum was −2 °F (−19 °C) in 1994. During the reference period of 1991 to 2020, the coldest daily maximum on average was 11 °F (−12 °C). Summer nights influenced by the lake can be hot and muggy on occasion. The warmest night on record was 82 °F (28 °C) in 1902 and lows above 72 °F (22 °C) have been measured in every month between April and October. On average, the warmest low of the year stood at 74 °F (23 °C) for the 1991–2020 normals.
In April 1956, the western and northern portions of the city and its suburbs were hit by a violent tornado which locally produced F5 damage and killed 18 people.
With the Grand River flowing through the center of Grand Rapids, the city has been prone to floods. From March 25 to 29, 1904, more than one-half of the entire populated portion of the city lying on the west side of the river was completely underwater, over twenty-five hundred houses, affecting fourteen thousand persons, being completely surrounded. On March 28, the river registered at 19.6 feet (6.0 m), more than two feet (0.61 m) above its highest previous mark.
More than one-hundred years later, the 2013 Grand Rapids flood occurred from April 12 to 25, 2013, with the river cresting at 21.85 feet (6.66 m) on the 21st, causing thousands of residents to evacuate their homes and over $10 million in damage.
Cityscape
The city skyline shows the Amway Grand Plaza Hotel, formerly the Pantlind, which reopened in 1981 after extensive renovations by Marvin DeWinter & Associates. This work included the addition of a 29–story glass tower offering panoramic views of the city, river and surrounding area. The Pantlind Hotel’s original architects, Warren & Wetmore, were inspired by the work of the Scottish neoclassical architect Robert Adam. In its prime, the hotel was rated as one of the top ten hotels in the US. The hotel features several restaurants well known in Grand Rapids. The hotel is owned by Amway Hotel Collection, a subsidiary of Amway’s holding company Alticor.
Other prominent large buildings include the JW Marriott Grand Rapids, the first JW Marriott Hotel in the Midwest. It is themed from cityscapes of Grand Rapids’ sister cities: Omihachiman, Japan; Bielsko-Biała, Poland; Perugia, Italy; Ga District, Ghana; and Zapopan, Mexico. When the hotel opened, Amway Hotel corporation hired photographer Dan Watts to travel to each of the sister cities and photograph them for the property. Each floor of the hotel features photography from one of the cities, which is unique to that floor. Cityscapes of these five cities are alternated in order, up the 23 floors.
The city’s tallest building is the River House Condominiums, a 34-story (123.8 m) condominium tower completed in 2008 that stands as the tallest all-residential building in the state of Michigan.
Grand Rapids is also home to two large urban nature centers. The Calvin Ecosystem Preserve and Native Gardens, operated by Calvin University on the city’s southeast side, is 104 acres (42 ha). It is home to over 44 acres (18 ha) of public-access nature trails, a 60-acre (24 ha), restricted-access wildlife preserve, as well as the Bunker Interpretive Center, which hosts university classes and educational programs for the wider community. The Blandford Nature Center, located on the city’s northwest side, opened in 1968 and contains extensive nature trails, an animal hospital, and a “heritage village” made up of several well-preserved 19th-century buildings, including a log cabin, schoolhouse, and barn. The nature center is also home to Blandford School, a highly selective environmental education program for sixth graders from the metropolitan region, which is run by Grand Rapids Public Schools and serves as a feeder school for City High-Middle School. At 264 acres (107 ha), Blandford is one of the largest urban nature centers in the United States.
See also
Map of Michigan State and its subdivision:- Alcona
- Alger
- Allegan
- Alpena
- Antrim
- Arenac
- Baraga
- Barry
- Bay
- Benzie
- Berrien
- Branch
- Calhoun
- Cass
- Charlevoix
- Cheboygan
- Chippewa
- Clare
- Clinton
- Crawford
- Delta
- Dickinson
- Eaton
- Emmet
- Genesee
- Gladwin
- Gogebic
- Grand Traverse
- Gratiot
- Hillsdale
- Houghton
- Huron
- Ingham
- Ionia
- Iosco
- Iron
- Isabella
- Jackson
- Kalamazoo
- Kalkaska
- Kent
- Keweenaw
- Lake
- Lake Hurron
- Lake Michigan
- Lake St. Clair
- Lake Superior
- Lapeer
- Leelanau
- Lenawee
- Livingston
- Luce
- Mackinac
- Macomb
- Manistee
- Marquette
- Mason
- Mecosta
- Menominee
- Midland
- Missaukee
- Monroe
- Montcalm
- Montmorency
- Muskegon
- Newaygo
- Oakland
- Oceana
- Ogemaw
- Ontonagon
- Osceola
- Oscoda
- Otsego
- Ottawa
- Presque Isle
- Roscommon
- Saginaw
- Saint Clair
- Saint Joseph
- Sanilac
- Schoolcraft
- Shiawassee
- Tuscola
- Van Buren
- Washtenaw
- Wayne
- Wexford
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming