Williamston is a city in Ingham County in the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 3,854 at the 2010 census. Williamston is located east of the city of Lansing and borders Williamstown Township to the north and Wheatfield Township to the south. The Red Cedar River and M-43 run through the center of the city.
| Name: | Williamston city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Michigan |
| County: | Ingham County |
| Incorporated: | 1871 (village) 1945 (city) |
| Elevation: | 892 ft (272 m) |
| Total Area: | 2.52 sq mi (6.54 km²) |
| Land Area: | 2.45 sq mi (6.35 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.07 sq mi (0.18 km²) |
| Total Population: | 3,819 |
| Population Density: | 1,556.87/sq mi (600.99/km²) |
| Area code: | 517 |
| FIPS code: | 2687420 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1627274 |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
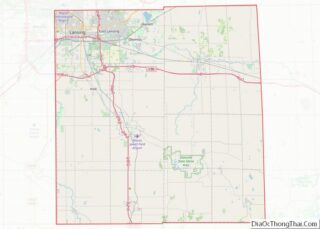
Williamston location map. Where is Williamston city?
History
The location that was later to become Williamston started as the cross-road of the Grand River and Saginaw Indian Trails. It was first occupied by a small band of the Saginaw tribe of the Chippewa People which by the mid-19th century used the area as a ‘summer village’ (it was not used by them year-round, but they ‘wintered’ in the area that is now Meridian Township). They used Williamston for planting crops, burying their dead, and holding an annual spring gathering, primarily using the land just north of the Red Cedar River.
The area was settled by Europeans in 1834 when Hiram and Joseph Putnam moved briefly to the area from Jackson. They spent less than one full year in the area, planting and then harvesting one crop of oats. Today, inside the city limits, Williamston Road becomes Putnam Street, having been named in their honor. (For many years, several street signs inside the city were misspelled as “Putman Street”, leading to confusion about the correct spelling.)
In 1839, the Putnams sold their land to Oswald B., James M., and Horace B. Williams, three brothers from Batavia, New York. James M. “Miles” Williams, who built a dam, saw mill and later a grist mill in town, eventually platted the land in 1845 and named the town “Williamstown” after himself. It is unknown how it lost the “w” in its name.
The town was a popular stop on the Grand River trail (that later became a plank road) from Detroit to Lansing in the 19th century. That trail is now Grand River Avenue (M-43) which runs through downtown Williamston. Because the primary means of transportation at that time was the horse and buggy and because the trip from Detroit to Lansing took more than one day, Williamston became a convenient overnight stop.
The town was incorporated as a village in 1871, and later as a city on April 1, 1945. A later revised City Charter was adopted by the people effective in April 1963. This charter has been amended several times, but remains in effect today.
A history of the area was published for the City’s centennial celebration in 1971. It included many photographs and stories of the early city and its inhabitants. There were earlier histories, as well, published in 1880, the 1930s, and in 1963.
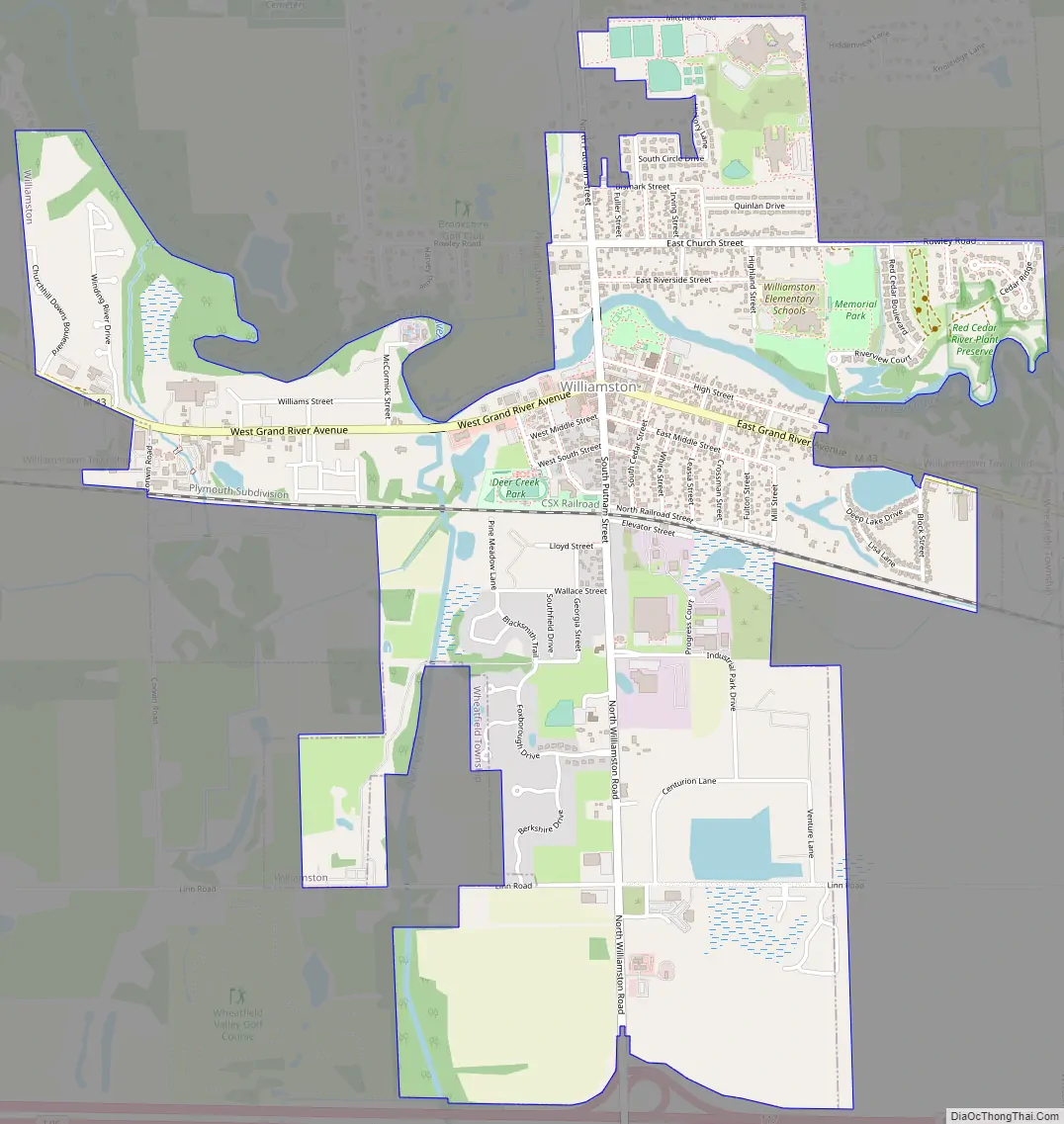
Williamston Road Map
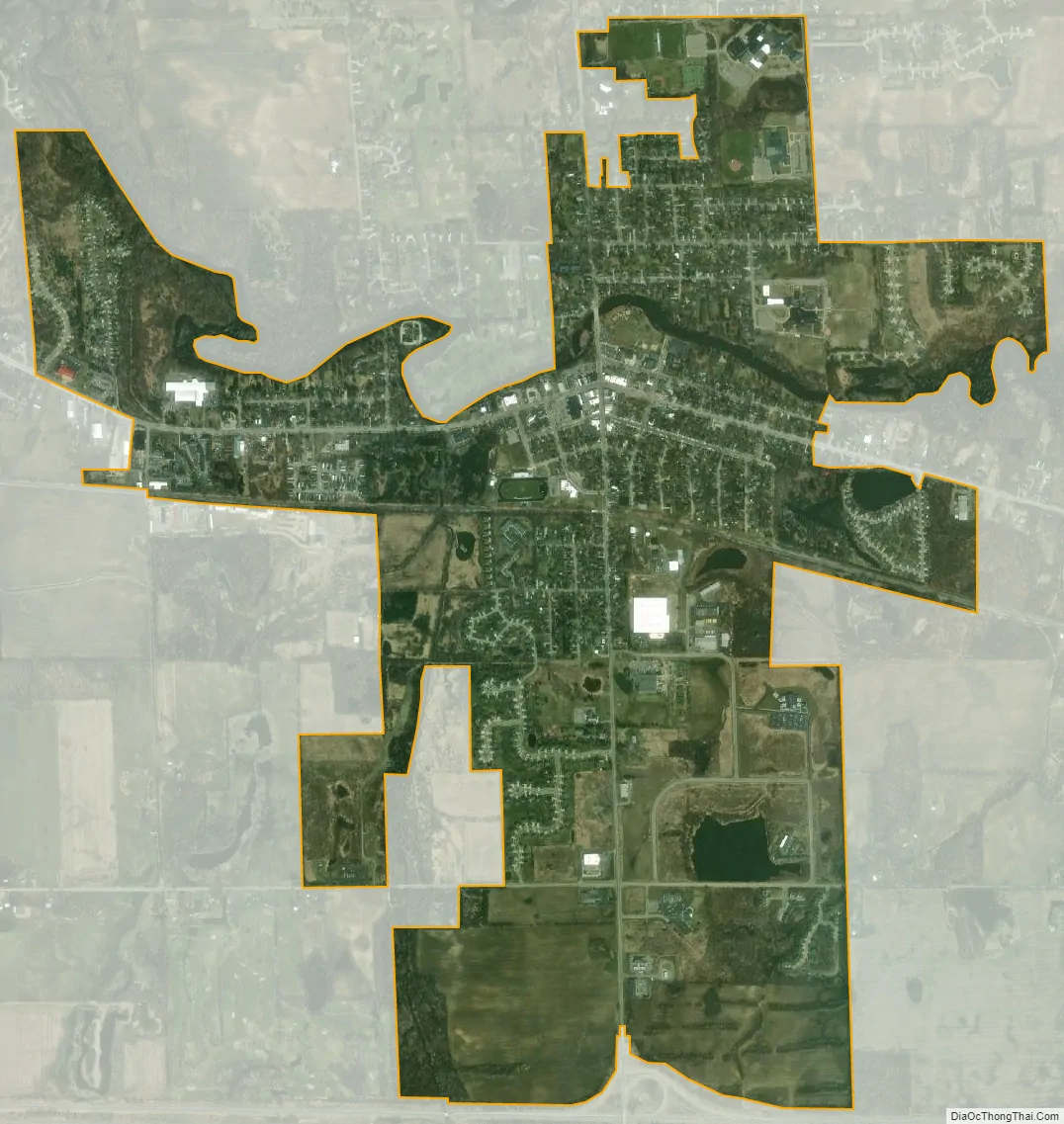
Williamston city Satellite Map
Geography
Williamston is located 15 miles east of Lansing, the state capital city of Michigan, and 11 miles east of East Lansing, the home of Michigan State University. The city is located two miles north of I-96, which provides access to Lansing and Detroit.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 2.52 square miles (6.53 km), of which 2.45 square miles (6.35 km) is land and 0.07 square miles (0.18 km) (0.02%) is water.
The Red Cedar River, a tributary of the Grand River, passes just north of the center of town. Lake Lansing is also located in nearby Haslett and is approximately 500 acres (2.0 km) in size.
Climate
This climatic region is typified by large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and cold (sometimes severely cold) winters. According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Williamston has a humid continental climate, abbreviated “Dfb” on climate maps.
See also
Map of Michigan State and its subdivision:- Alcona
- Alger
- Allegan
- Alpena
- Antrim
- Arenac
- Baraga
- Barry
- Bay
- Benzie
- Berrien
- Branch
- Calhoun
- Cass
- Charlevoix
- Cheboygan
- Chippewa
- Clare
- Clinton
- Crawford
- Delta
- Dickinson
- Eaton
- Emmet
- Genesee
- Gladwin
- Gogebic
- Grand Traverse
- Gratiot
- Hillsdale
- Houghton
- Huron
- Ingham
- Ionia
- Iosco
- Iron
- Isabella
- Jackson
- Kalamazoo
- Kalkaska
- Kent
- Keweenaw
- Lake
- Lake Hurron
- Lake Michigan
- Lake St. Clair
- Lake Superior
- Lapeer
- Leelanau
- Lenawee
- Livingston
- Luce
- Mackinac
- Macomb
- Manistee
- Marquette
- Mason
- Mecosta
- Menominee
- Midland
- Missaukee
- Monroe
- Montcalm
- Montmorency
- Muskegon
- Newaygo
- Oakland
- Oceana
- Ogemaw
- Ontonagon
- Osceola
- Oscoda
- Otsego
- Ottawa
- Presque Isle
- Roscommon
- Saginaw
- Saint Clair
- Saint Joseph
- Sanilac
- Schoolcraft
- Shiawassee
- Tuscola
- Van Buren
- Washtenaw
- Wayne
- Wexford
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming