Tennessee (/ˌtɛnɪˈsiː/ (listen) TEN-ih-SEE, locally /ˈtɛnɪsi/ TEN-iss-ee), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to the north, Virginia to the northeast, North Carolina to the east, Georgia, Alabama, and Mississippi to the south, Arkansas to the southwest, and Missouri to the northwest. Tennessee is geographically, culturally, and legally divided into three Grand Divisions of East, Middle, and West Tennessee. Nashville is the state’s capital and largest city, and anchors its largest metropolitan area. Other major cities include Memphis, Knoxville, Chattanooga, and Clarksville. Tennessee’s population as of the 2020 United States census is approximately 6.9 million.
Tennessee is rooted in the Watauga Association, a 1772 frontier pact generally regarded as the first constitutional government west of the Appalachian Mountains. Its name derives from “Tanasi”, a Cherokee town in the eastern part of the state that existed before the first European American settlement. Tennessee was initially part of North Carolina, and later the Southwest Territory, before its admission to the Union as the 16th state on June 1, 1796. It earned the nickname “The Volunteer State” early in its history due to a strong tradition of military service. A slave state until the American Civil War, Tennessee was politically divided, with its western and middle parts supporting the Confederacy and the eastern region harboring pro-Union sentiment. As a result, Tennessee was the last state to secede and the first readmitted to the Union after the war.
During the 20th century, Tennessee transitioned from a predominantly agrarian society to a more diversified economy. This was aided in part by massive federal investment in the Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) and the city of Oak Ridge, which was established during World War II to house the Manhattan Project’s uranium enrichment facilities for the construction of the world’s first atomic bombs. After the war, the Oak Ridge National Laboratory became a key center of scientific research. In 2016, the element tennessine was named for the state, largely in recognition of the roles played by Oak Ridge, Vanderbilt University, and the University of Tennessee in its discovery. Tennessee has also played a major role in the development of many forms of popular music, including country, blues, rock and roll, soul, and gospel.
Tennessee has diverse terrain and landforms, and from east to west, contains a mix of cultural features characteristic of Appalachia, the Upland South, and the Deep South. The Blue Ridge Mountains along the eastern border reach some of the highest elevations in eastern North America, and the Cumberland Plateau contains many scenic valleys and waterfalls. The central part of the state is marked by cavernous bedrock and irregular rolling hills, and level, fertile plains define West Tennessee. The state is twice bisected by the Tennessee River, and the Mississippi River forms its western border. Its economy is dominated by the health care, music, finance, automotive, chemical, electronics, and tourism sectors, and cattle, soybeans, corn, poultry, and cotton are its primary agricultural products. The Great Smoky Mountains National Park, the nation’s most visited national park, is in eastern Tennessee.
| Before statehood: | Southwest Territory |
|---|---|
| Admitted to the Union: | June 1, 1796; 226 years ago (June 1, 1796) (16th) |
| Capital: | Nashville |
| Capital – largest city: | largest city |
| Largest metro and urban areas: | Nashville |
| Elevation: | 900 ft (270 m) |
| Total Area: | 42,143 sq mi (109,247 km) |
| Area Rank: | 36th |
| Total Population: | 6,916,897 |
| Population Rank: | 16th |
| Population Density: | 167.8/sq mi (64.8/km) |
| Population Density Rank: | 20th |
| Median Household Income: | $54,833 |
| Income Rank: | 42nd |
| Demonym(s): | Tennessean Big Bender (archaic) Volunteer (historical significance) |
| USPS abbreviation: | TN |
| ISO 3166 code: | US-TN |
| Website: | www.tn.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
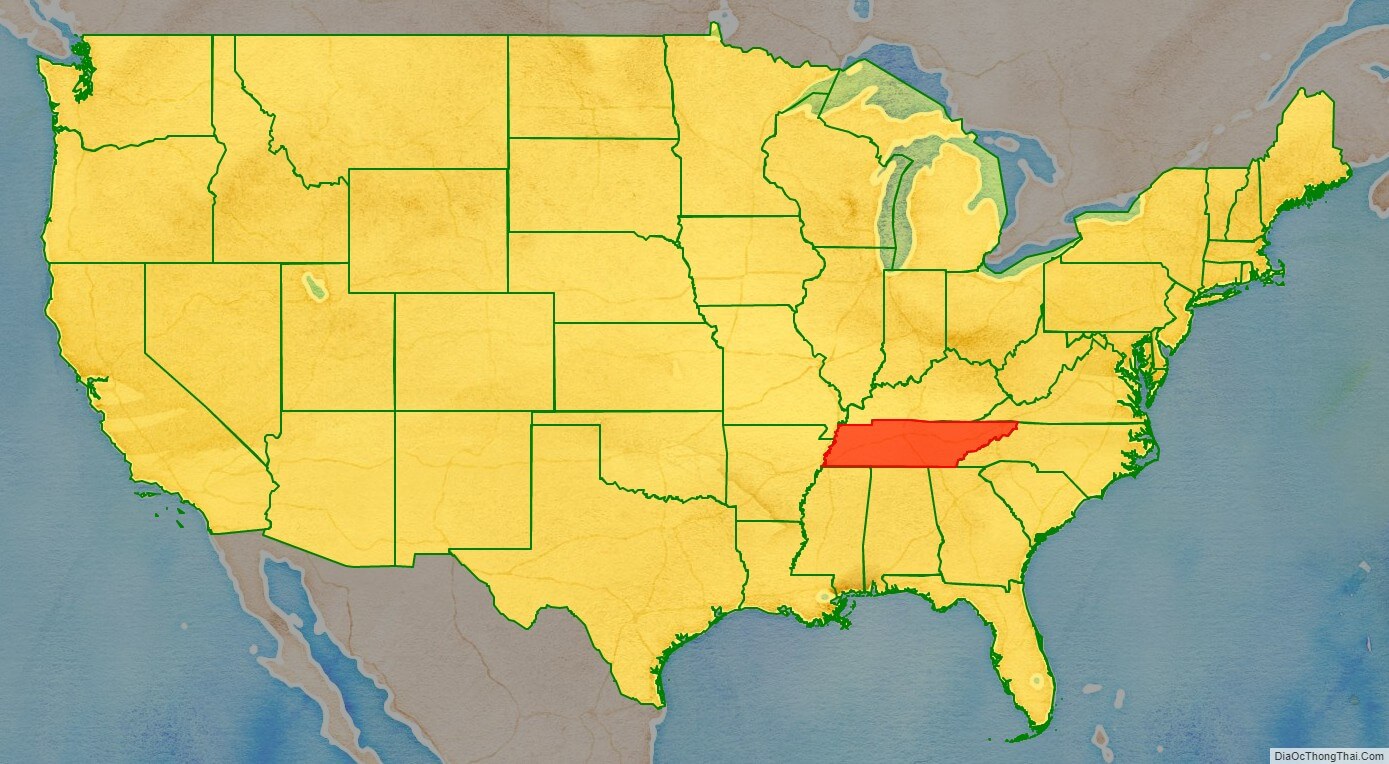
Tennessee location map. Where is Tennessee state?
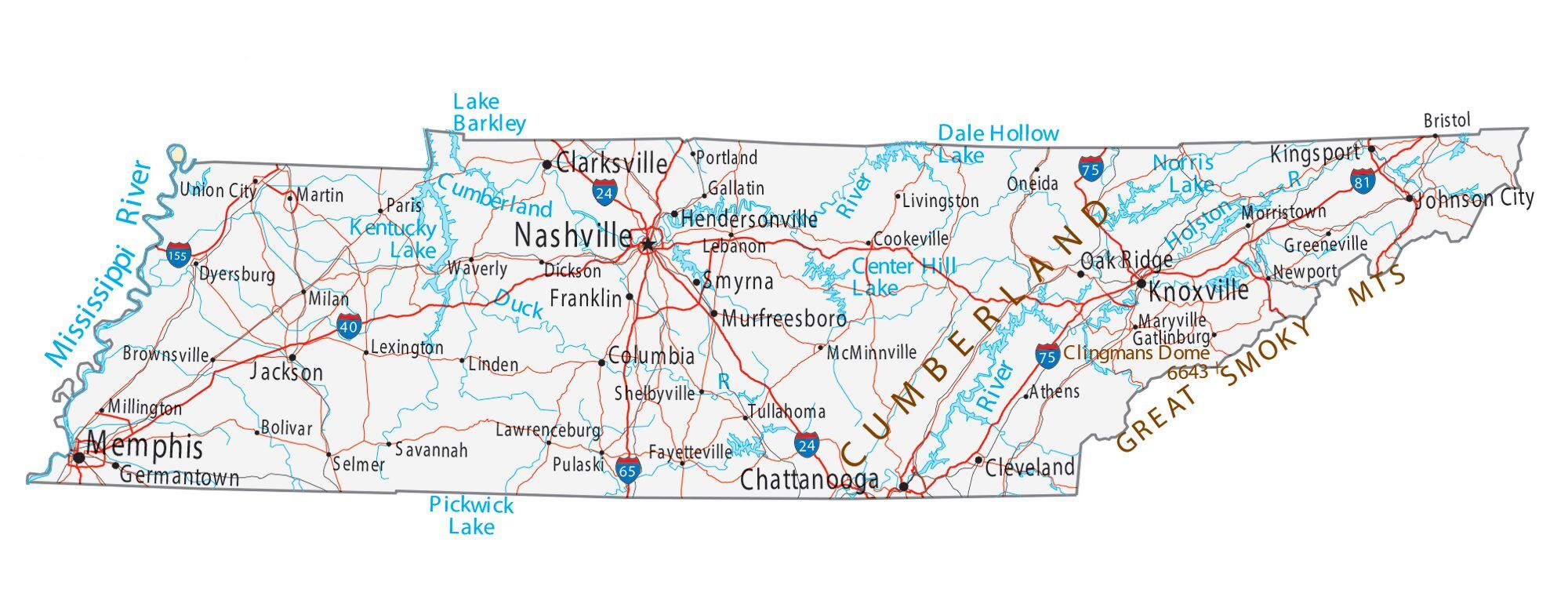
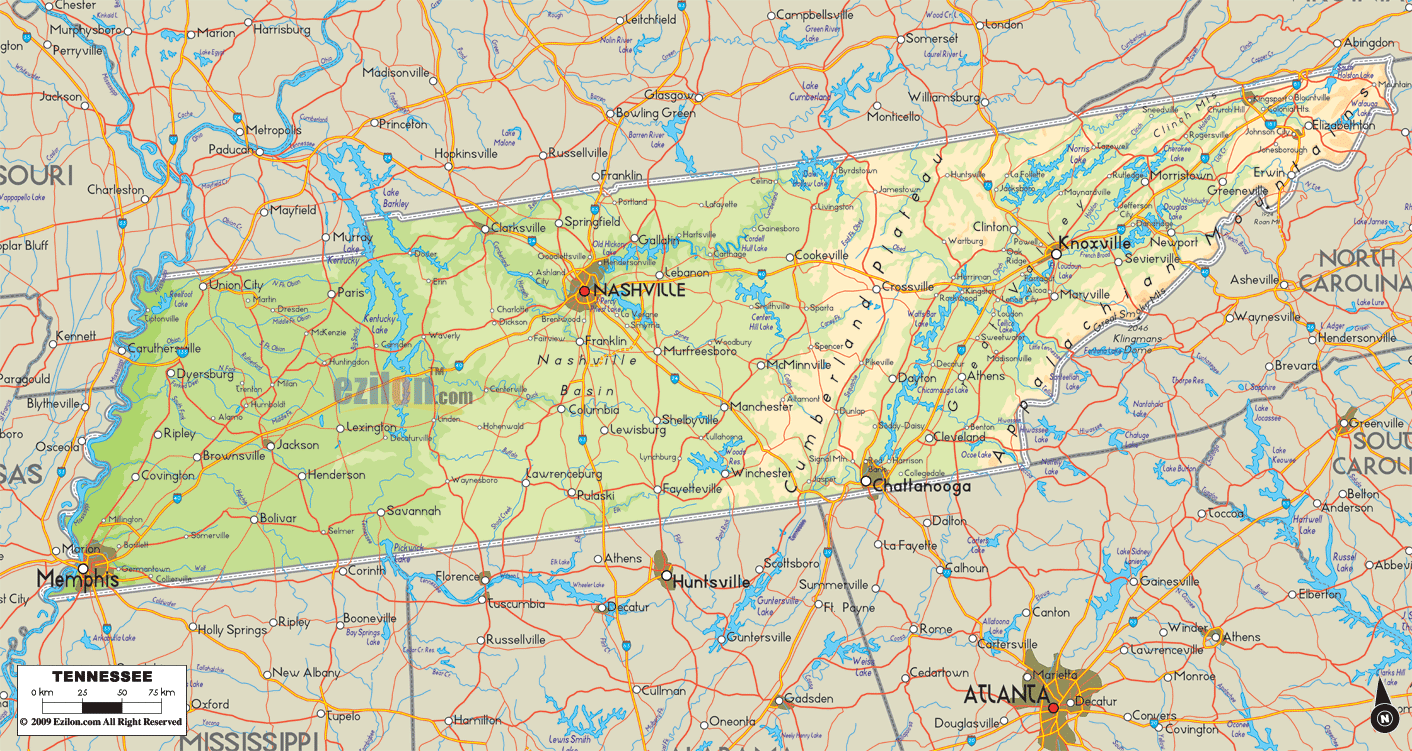
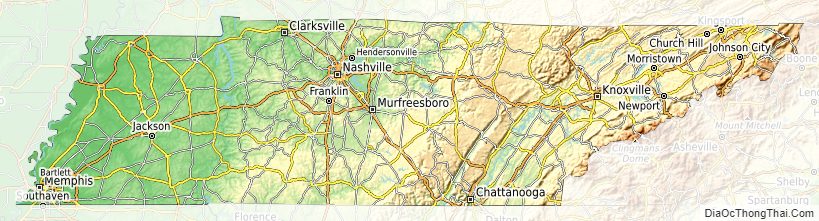
Tennessee Road Map
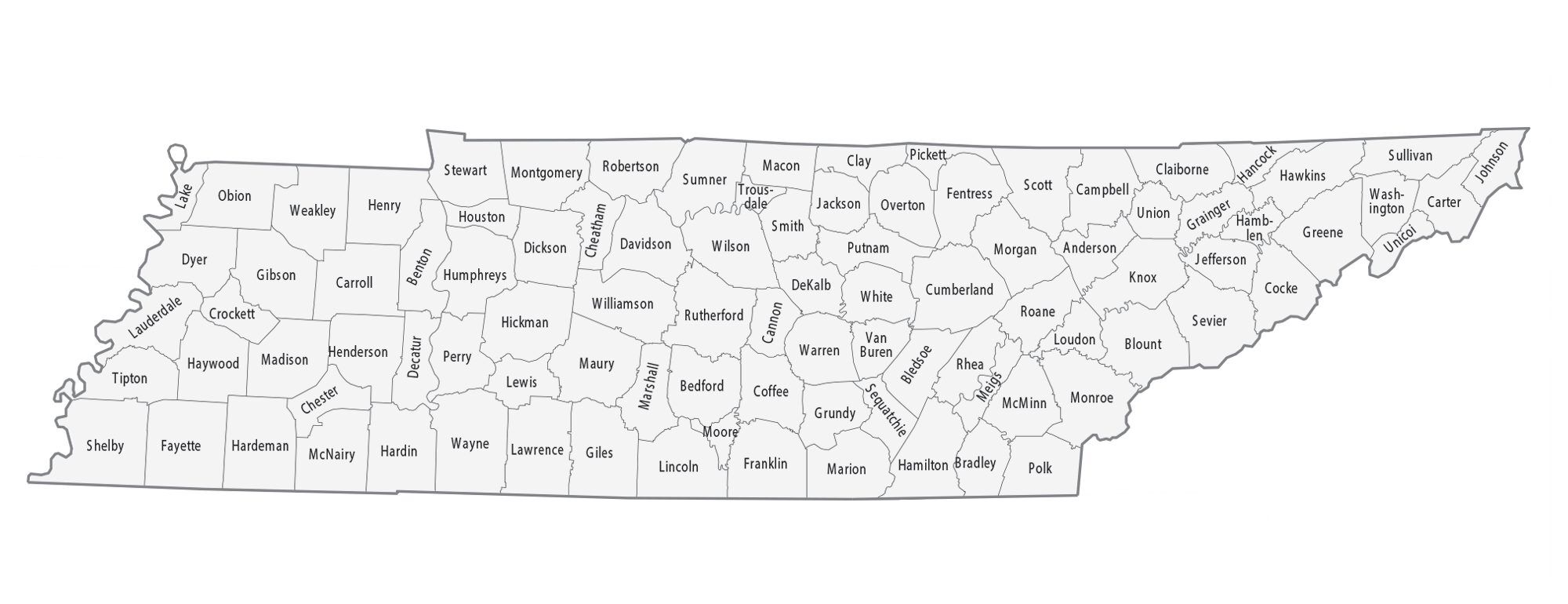
Tennessee Map – Roads & Cities
Tennessee Street Map
Tennessee State Map – Places and Landmarks
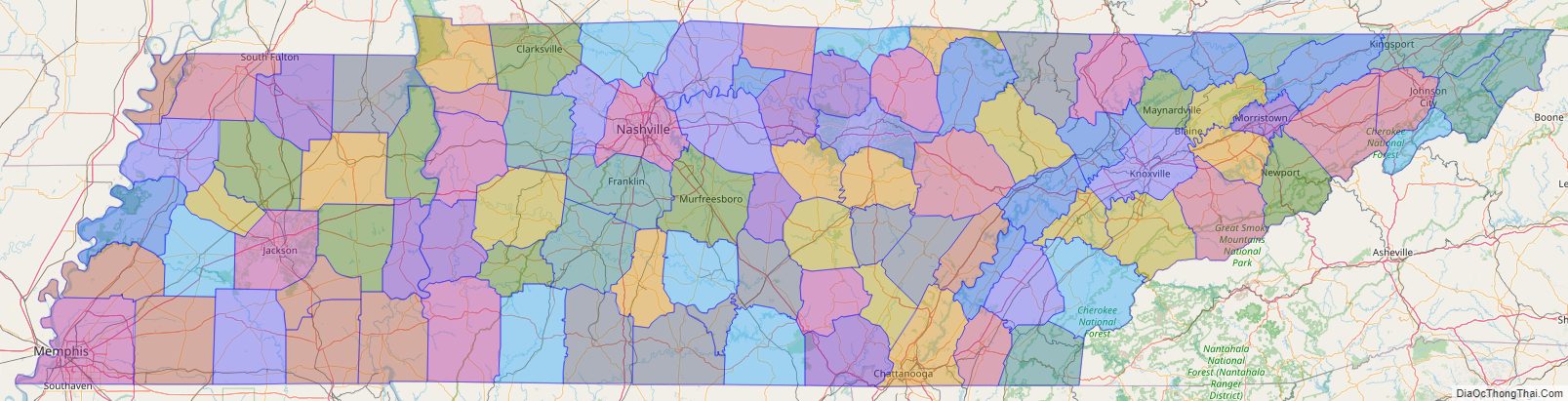
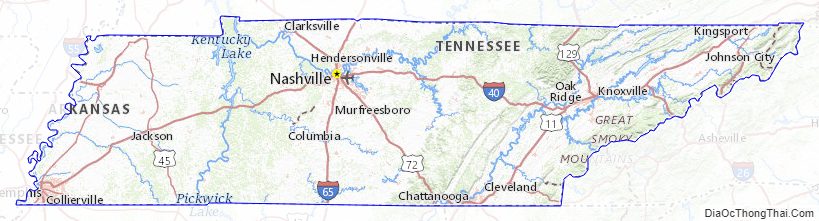
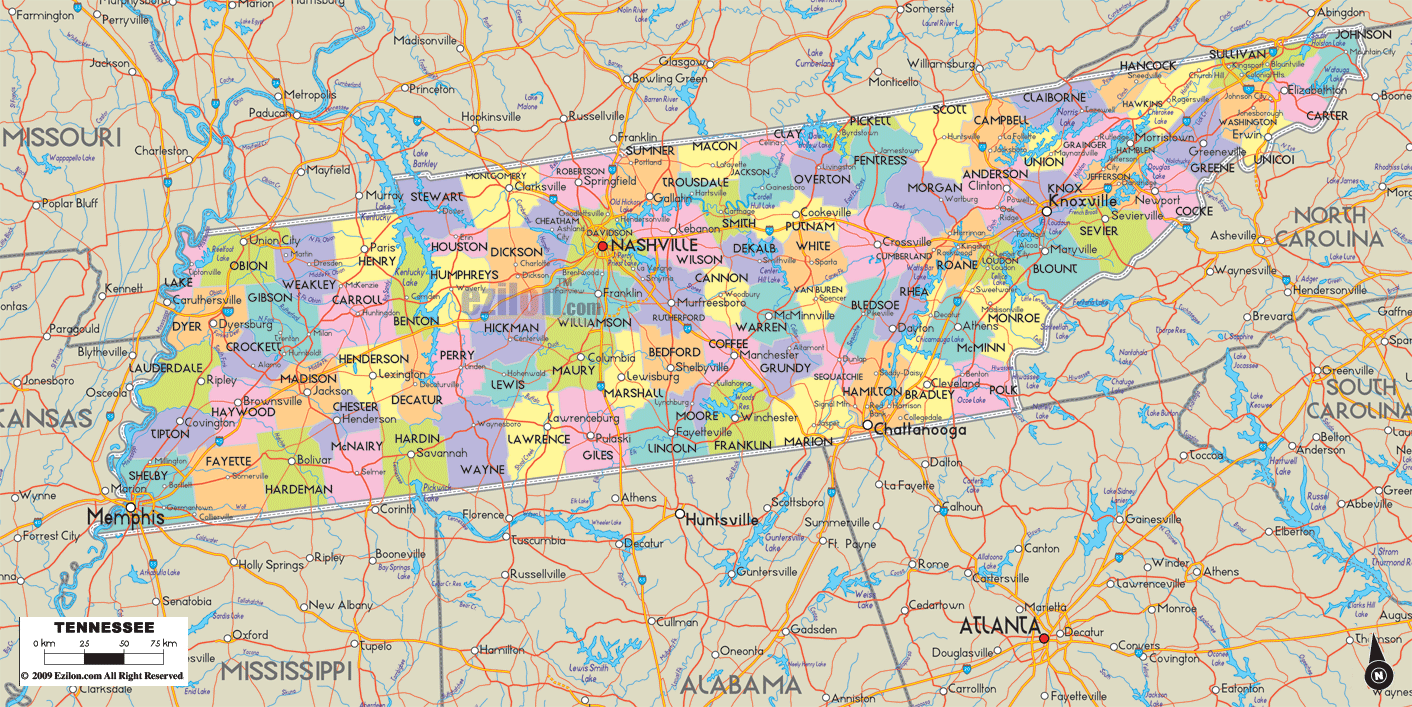
Tennessee Political Map
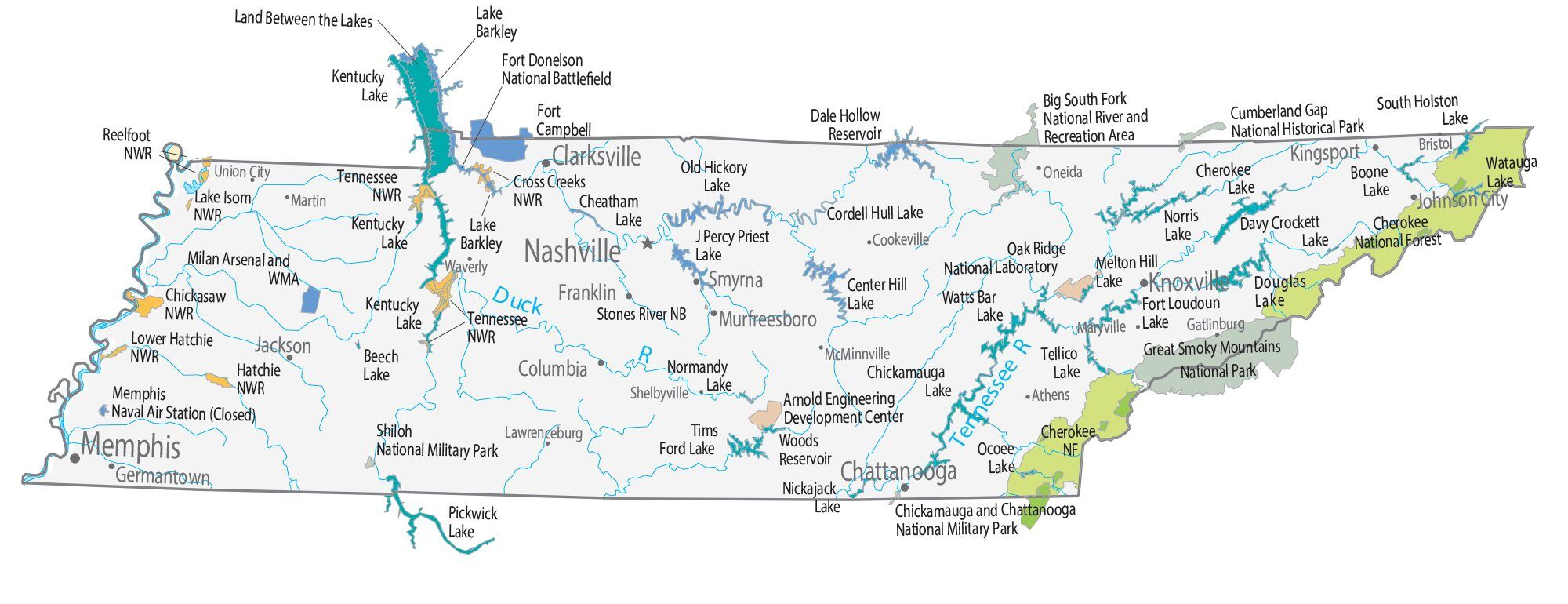
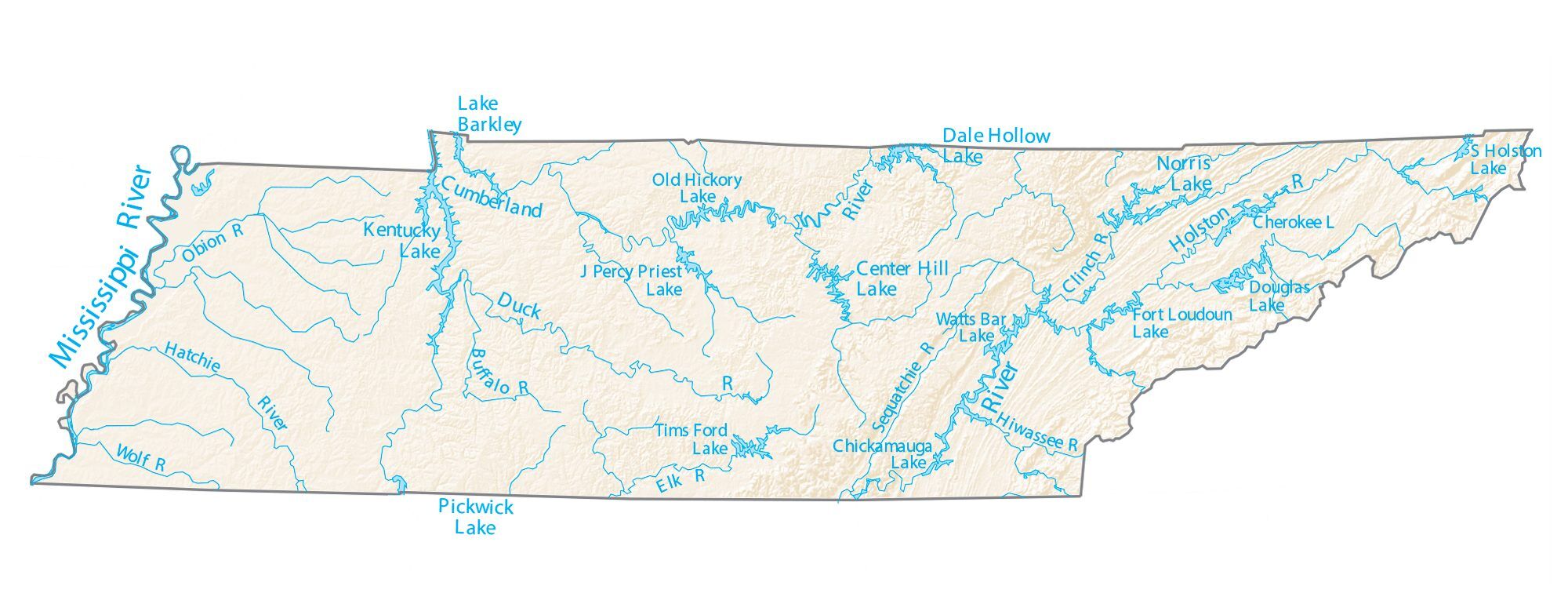
Tennessee Lakes and Rivers Map
Geography
Tennessee is in the Southeastern United States. Culturally, most of the state is considered part of the Upland South, and the eastern third is part of Appalachia. Tennessee covers roughly 42,143 square miles (109,150 km), of which 926 square miles (2,400 km), or 2.2%, is water. It is the 16th smallest state in land area. The state is about 440 miles (710 km) long from east to west and 112 miles (180 km) wide from north to south. Tennessee is geographically, culturally, economically, and legally divided into three Grand Divisions: East Tennessee, Middle Tennessee, and West Tennessee. It borders eight other states: Kentucky and Virginia to the north, North Carolina to the east, Georgia, Alabama, and Mississippi on the south, and Arkansas and Missouri on the west. It is tied with Missouri as the state bordering the most other states. Tennessee is trisected by the Tennessee River, and its geographical center is in Murfreesboro. Nearly three–fourths of the state is in the Central Time Zone, with most of East Tennessee on Eastern Time. The Tennessee River forms most of the division between Middle and West Tennessee.
Tennessee’s eastern boundary roughly follows the highest crests of the Blue Ridge Mountains, and the Mississippi River forms its western boundary. Due to flooding of the Mississippi that has changed its path, the state’s western boundary deviates from the river in some places. The northern border was originally defined as 36°30′ north latitude and the Royal Colonial Boundary of 1665, but due to faulty surveys, begins north of this line in the east, and to the west, gradually veers north before shifting south onto the actual 36°30′ parallel at the Tennessee River in West Tennessee. Uncertainties in the latter 19th century over the location of the state’s border with Virginia culminated in the U.S. Supreme Court settling the matter in 1893, which resulted in the division of Bristol between the two states. An 1818 survey erroneously placed Tennessee’s southern border 1 mile (1.6 km) south of the 35th parallel; Georgia legislators continue to dispute this placement, as it prevents Georgia from accessing the Tennessee River.
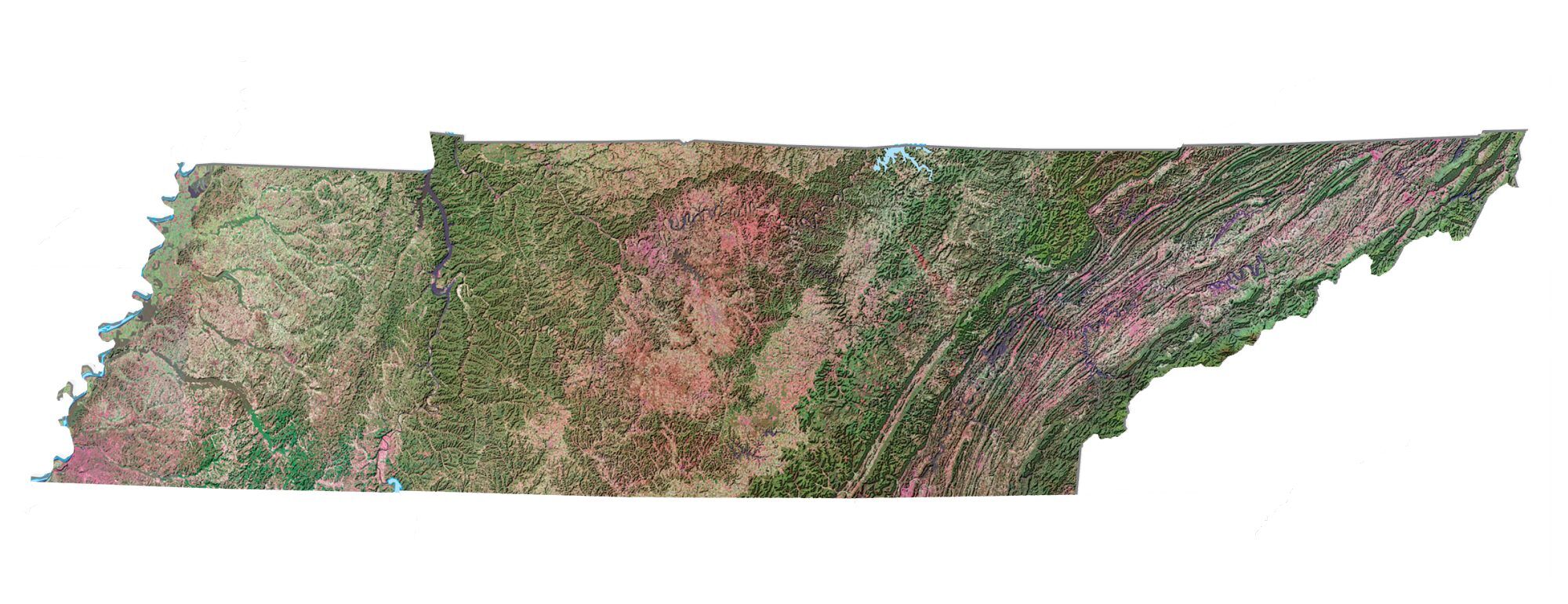
Marked by a diversity of landforms and topographies, Tennessee features six principal physiographic provinces, from east to west, which are part of three larger regions: the Blue Ridge Mountains, Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians, and Cumberland Plateau, part of the Appalachian Mountains; the Highland Rim and Nashville Basin, part of the Interior Low Plateaus of the Interior Plains; and the East Gulf Coastal Plain, part of the Atlantic Plains. Other regions include the southern tip of the Cumberland Mountains, the Western Tennessee Valley, and the Mississippi Alluvial Plain. The state’s highest point, which is also the third-highest peak in eastern North America, is Clingmans Dome, at 6,643 feet (2,025 m) above sea level. Its lowest point, 178 feet (54 m), is on the Mississippi River at the Mississippi state line in Memphis. Tennessee has the most caves in the United States, with more than 10,000 documented.
Geological formations in Tennessee largely correspond with the state’s topographic features, and, in general, decrease in age from east to west. The state’s oldest rocks are igneous strata more than 1 billion years old found in the Blue Ridge Mountains, and the youngest deposits in Tennessee are sands and silts in the Mississippi Alluvial Plain and river valleys that drain into the Mississippi River. Tennessee is considered seismically active and contains two major seismic zones, although destructive earthquakes rarely occur there. The Eastern Tennessee Seismic Zone spans the entirety of East Tennessee from northwestern Alabama to southwestern Virginia, and is considered one of the most active zones in the Southeastern United States, frequently producing low-magnitude earthquakes. The New Madrid Seismic Zone in the northwestern part of the state produced a series of devastating earthquakes between December 1811 and February 1812 that formed Reelfoot Lake near Tiptonville.
Topography
The southwestern Blue Ridge Mountains lie within Tennessee’s eastern edge, and are divided into several subranges, namely the Great Smoky Mountains, Bald Mountains, Unicoi Mountains, Unaka Mountains, and Iron Mountains. These mountains, which average 5,000 feet (1,500 m) above sea level in Tennessee, contain some of the highest elevations in eastern North America. The state’s border with North Carolina roughly follows the highest peaks of this range, including Clingmans Dome. Most of the Blue Ridge area is protected by the Cherokee National Forest, the Great Smoky Mountains National Park, and several federal wilderness areas and state parks. The Appalachian Trail roughly follows the North Carolina state line before shifting westward into Tennessee.
Stretching west from the Blue Ridge Mountains for about 55 miles (89 km) are the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians, also known as the Tennessee Valley or Great Valley of East Tennessee. This area consists of linear parallel ridges separated by valleys that trend northeast to southwest, the general direction of the entire Appalachian range. Most of these ridges are low, but some of the higher ones are commonly called mountains. Numerous tributaries join to form the Tennessee River in the Ridge and Valley region.
The Cumberland Plateau rises to the west of the Tennessee Valley, with an average elevation of 2,000 feet (610 m). This landform is part of the larger Appalachian Plateau and consists mostly of flat-topped tablelands. The plateau’s eastern edge is relatively distinct, but the western escarpment is irregular, containing several long, crooked stream valleys separated by rocky cliffs with numerous waterfalls. The Cumberland Mountains, with peaks above 3,500 feet (1,100 m), comprise the northeastern part of the Appalachian Plateau in Tennessee, and the southeastern part of the Cumberland Plateau is divided by the Sequatchie Valley. The Cumberland Trail traverses the eastern escarpment of the Cumberland Plateau and Cumberland Mountains.
West of the Cumberland Plateau is the Highland Rim, an elevated plain that surrounds the Nashville Basin, a geological dome. Both of these physiographic provinces are part of the Interior Low Plateaus of the larger Interior Plains. The Highland Rim is Tennessee’s largest geographic region, and is often split into eastern and western halves. The Eastern Highland Rim is characterized by relatively level plains dotted by rolling hills, and the Western Highland Rim and western Nashville Basin are covered with uneven rounded knobs with steep ravines separated by meandering streams. The Nashville Basin has rich, fertile farmland, and porous limestone bedrock very close to the surface underlies both the Nashville Basin and Eastern Highland Rim. This results in karst that forms numerous caves, sinkholes, depressions, and underground streams.
West of the Highland Rim is the Western Tennessee Valley, which consists of about 10 miles (16 km) in width of hilly land along the banks of the Tennessee River. West of this is the Gulf Coastal Plain, a broad feature that begins at the Gulf of Mexico and extends northward into southern Illinois. The plain begins in the east with low rolling hills and wide stream valleys, known as the West Tennessee Highlands, and gradually levels out to the west. It ends at steep loess bluffs overlooking the Mississippi embayment, the westernmost physiographic division of Tennessee, which is part of the larger Mississippi Alluvial Plain. This flat 10 to 14 miles (16 to 23 km) wide strip is commonly known as the Mississippi Bottoms, and contains lowlands, floodplains, and swamps.
Hydrology
Tennessee is drained by three major rivers, the Tennessee, Cumberland, and Mississippi. The Tennessee River begins at the juncture of the Holston and French Broad rivers in Knoxville, flows southwest to Chattanooga, and exits into Alabama before reemerging in the western part of the state and flowing north into Kentucky. Its major tributaries include the Clinch, Little Tennessee, Hiwassee, Sequatchie, Elk, Beech, Buffalo, Duck, and Big Sandy rivers. The Cumberland River flows through the north-central part of the state, emerging in the northeastern Highland Rim, passing through Nashville, turning northwest to Clarksville, and entering Kentucky east of the Tennessee River. Its principal branches in Tennessee are the Obey, Caney Fork, Stones, Harpeth, and Red rivers. The Mississippi River drains nearly all of West Tennessee. Its tributaries are the Obion, Forked Deer, Hatchie, Loosahatchie, and Wolf rivers. The Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers operate many hydroelectric dams on the Tennessee and Cumberland rivers and their tributaries, which form large reservoirs throughout the state.
About half the state’s land area is in the Tennessee Valley drainage basin of the Tennessee River. The Cumberland River basin covers the northern half of Middle Tennessee and a small portion of East Tennessee. A small part of north-central Tennessee is in the Green River watershed. All three of these basins are tributaries of the Ohio River watershed. Most of West Tennessee is in the Lower Mississippi River watershed. The entirety of the state is in the Mississippi River watershed, except for a small sliver near the southeastern corner traversed by the Conasauga River, which is part of the Mobile Bay watershed.
Ecology
Tennessee is within a temperate deciduous forest biome commonly known as the Eastern Deciduous Forest. It has eight ecoregions: the Blue Ridge, Ridge and Valley, Central Appalachian, Southwestern Appalachian, Interior Low Plateaus, Southeastern Plains, Mississippi Valley Loess Plains, and Mississippi Alluvial Plain regions. Tennessee is the most biodiverse inland state, the Great Smoky Mountains National Park is the most biodiverse national park, and the Duck River is the most biologically diverse waterway in North America. The Nashville Basin is renowned for its diversity of flora and fauna. Tennessee is home to 340 species of birds, 325 freshwater fish species, 89 mammals, 77 amphibians, and 61 reptiles.
Forests cover about 52% of Tennessee’s land area, with oak–hickory the dominant type. Appalachian oak–pine and cove hardwood forests are found in the Blue Ridge Mountains and Cumberland Plateau, and bottomland hardwood forests are common throughout the Gulf Coastal Plain. Pine forests are also found throughout the state. The Southern Appalachian spruce–fir forest in the highest elevations of the Blue Ridge Mountains is considered the second-most endangered ecosystem in the country. Some of the last remaining large American chestnut trees grow in the Nashville Basin and are being used to help breed blight-resistant trees. Middle Tennessee is home to many unusual and rare ecosystems known as cedar glades, which occur in areas with shallow limestone bedrock that is largely barren of overlying soil and contain many endemic plant species.
Common mammals found throughout Tennessee include white-tailed deer, red and gray foxes, coyotes, raccoons, opossums, wild turkeys, rabbits, and squirrels. Black bears are found in the Blue Ridge Mountains and on the Cumberland Plateau. Tennessee has the third-highest number of amphibian species, with the Great Smoky Mountains home to the most salamander species in the world. The state ranks second in the nation for the diversity of its freshwater fish species.
Climate
Most of Tennessee has a humid subtropical climate, with the exception of some of the higher elevations in the Appalachians, which are classified as a cooler mountain temperate or humid continental climate. The Gulf of Mexico is the dominant factor in Tennessee’s climate, with winds from the south responsible for most of the state’s annual precipitation. Generally, the state has hot summers and mild to cool winters with generous precipitation throughout the year. The highest average monthly precipitation usually occurs between December and April. The driest months, on average, are August to October. The state receives an average of 50 inches (130 cm) of precipitation annually. Snowfall ranges from 5 inches (13 cm) in West Tennessee to over 80 inches (200 cm) in East Tennessee’s highest mountains.
Summers are generally hot and humid, with most of the state averaging a high of around 90 °F (32 °C). Winters tend to be mild to cool, decreasing in temperature at higher elevations. For areas outside the highest mountains, the average overnight lows are generally near freezing. The highest recorded temperature was 113 °F (45 °C) at Perryville on August 9, 1930, while the lowest recorded temperature was −32 °F (−36 °C) at Mountain City on December 30, 1917.
While Tennessee is far enough from the coast to avoid any direct impact from a hurricane, its location makes it susceptible to the remnants of tropical cyclones, which weaken over land and can cause significant rainfall. The state annually averages about 50 days of thunderstorms, which can be severe with large hail and damaging winds. Tornadoes are possible throughout the state, with West and Middle Tennessee the most vulnerable. The state averages 15 tornadoes annually. They can be severe, and the state leads the nation in the percentage of total tornadoes that have fatalities. Winter storms such as in 1993 and 2021 occur occasionally, and ice storms are fairly common. Fog is a persistent problem in some areas, especially in East Tennessee.
Tennessee Physical Map
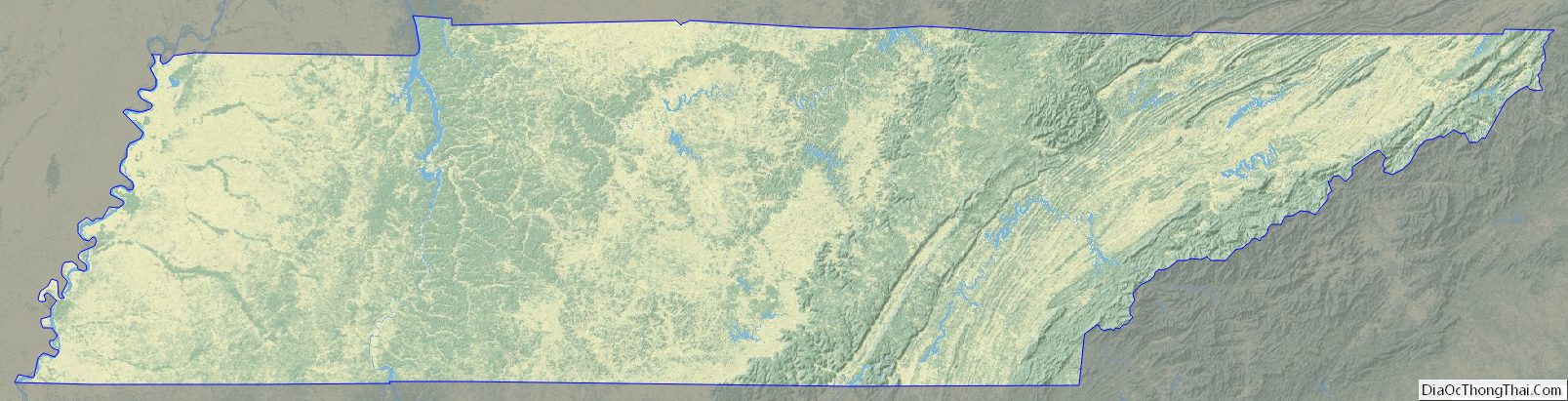
Tennessee Topographic Map
Tennessee Satellite Map
Others printable maps
Tennessee Outline Map
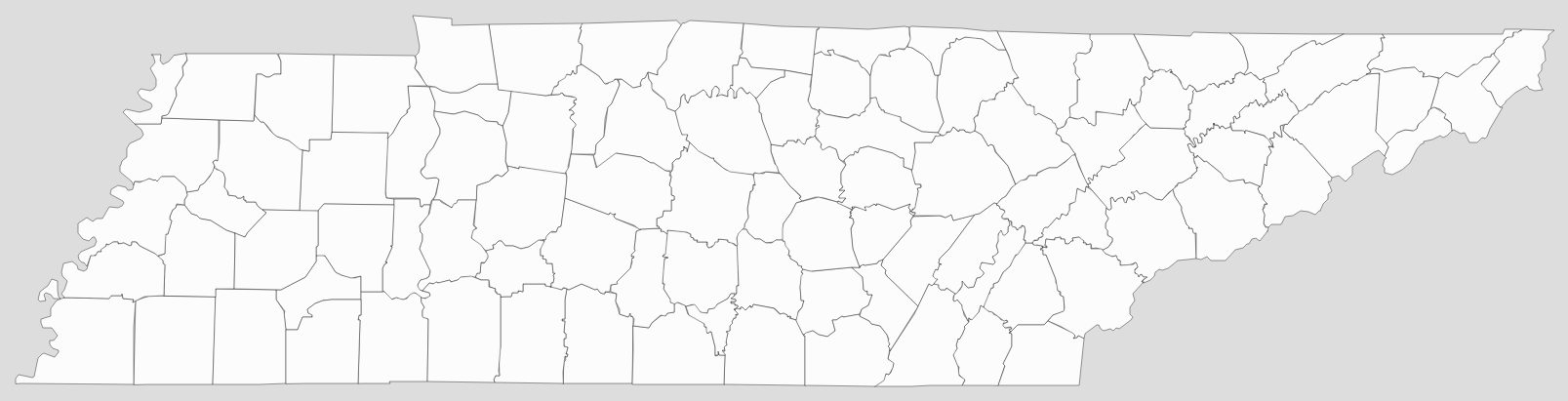
Blank Tennessee County Map
See also
Map of Tennessee State and its subdivision:- Anderson
- Bedford
- Benton
- Bledsoe
- Blount
- Bradley
- Campbell
- Cannon
- Carroll
- Carter
- Cheatham
- Chester
- Claiborne
- Clay
- Cocke
- Coffee
- Crockett
- Cumberland
- Davidson
- Decatur
- DeKalb
- Dickson
- Dyer
- Fayette
- Fentress
- Franklin
- Gibson
- Giles
- Grainger
- Greene
- Grundy
- Hamblen
- Hamilton
- Hancock
- Hardeman
- Hardin
- Hawkins
- Haywood
- Henderson
- Henry
- Hickman
- Houston
- Humphreys
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Johnson
- Knox
- Lake
- Lauderdale
- Lawrence
- Lewis
- Lincoln
- Loudon
- Macon
- Madison
- Marion
- Marshall
- Maury
- McMinn
- McNairy
- Meigs
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Moore
- Morgan
- Obion
- Overton
- Perry
- Pickett
- Polk
- Putnam
- Rhea
- Roane
- Robertson
- Rutherford
- Scott
- Sequatchie
- Sevier
- Shelby
- Smith
- Stewart
- Sullivan
- Sumner
- Tipton
- Trousdale
- Unicoi
- Union
- Van Buren
- Warren
- Washington
- Wayne
- Weakley
- White
- Williamson
- Wilson
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming