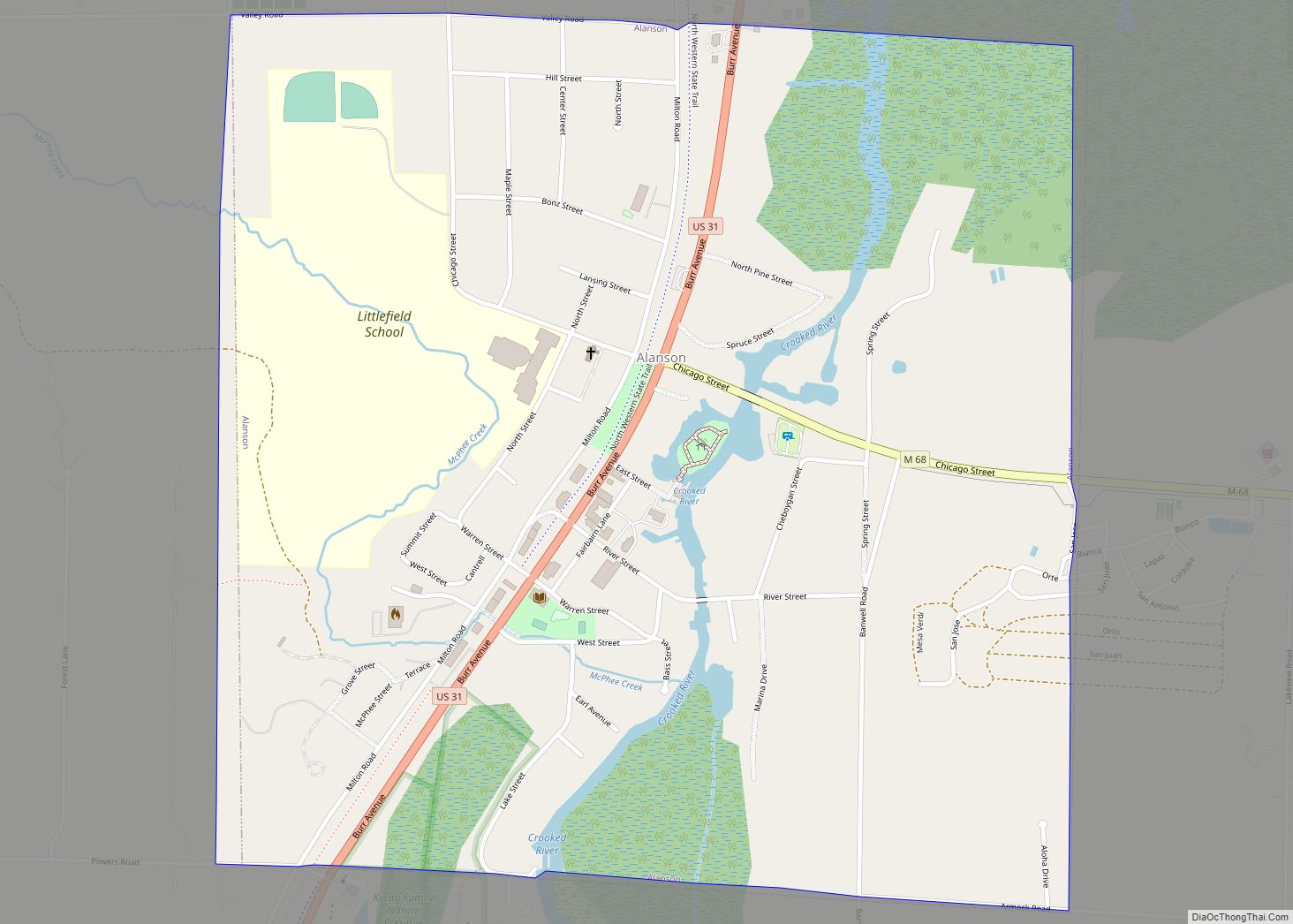
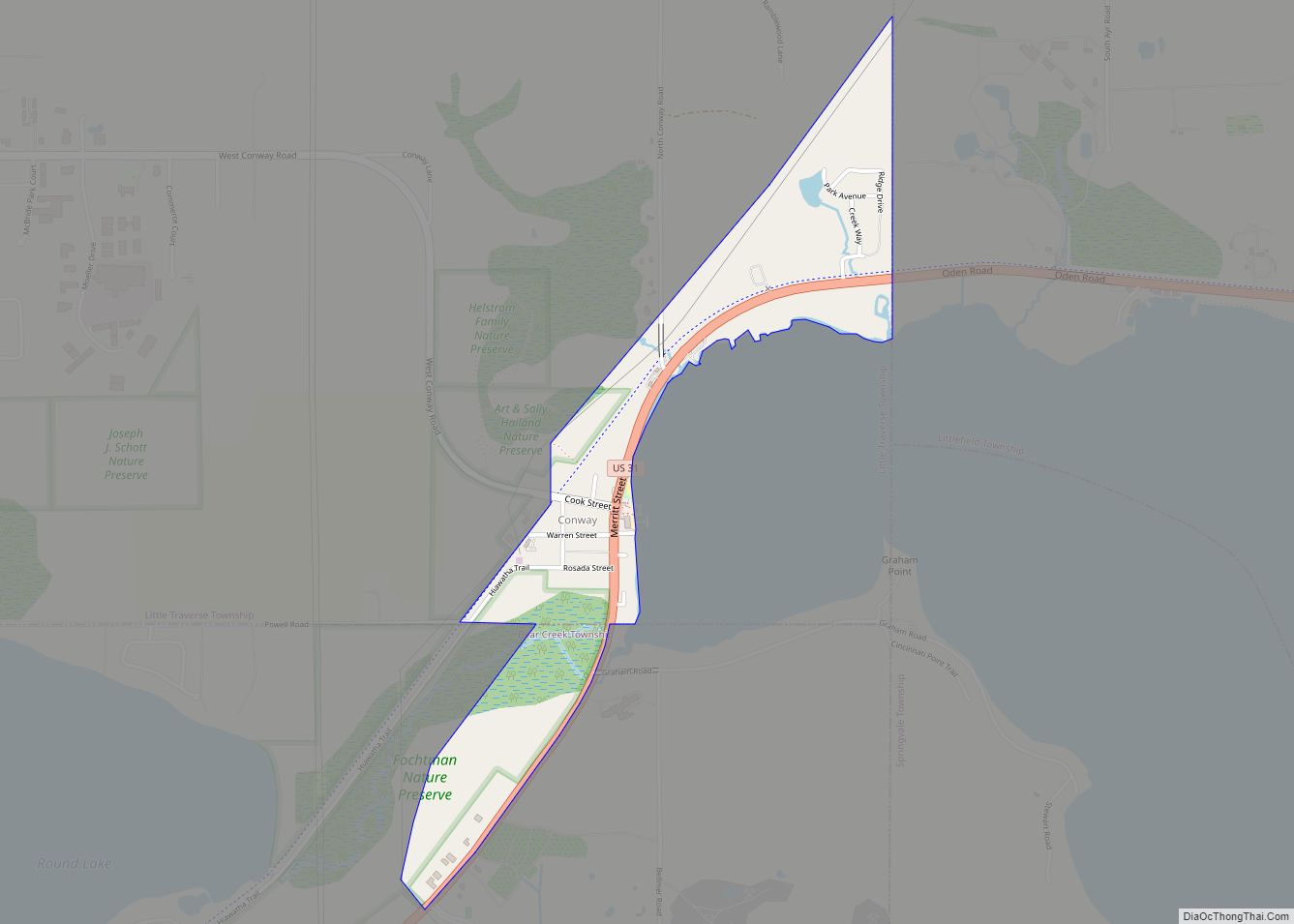
Mackinaw City (/ˈmækənɔː/ MAK-ə-naw) is a village at the northernmost point of the Lower Peninsula of Michigan. Divided between Cheboygan and Emmet counties, Mackinaw City is the located at the southern end of the Mackinac Bridge, which carries Interstate 75 over the Straits of Mackinac to the Upper Peninsula. Mackinaw City, along with St. Ignace, serves as an access point to Mackinac Island. For these reasons, Mackinaw City is considered one of Michigan’s most popular tourist attractions.
The Mackinaw City area is home to a number of historic sites, including Fort Michilimackinac, Historic Mill Creek State Park, Old Mackinac Point Light, McGulpin Point Light, and the retired US Coast Guard Icebreaker Mackinaw.
| Name: | Mackinaw City village |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 47 |
| LSAD Description: | village (suffix) |
| State: | Michigan |
| County: | Cheboygan County, Emmet County |
| Incorporated: | 1882 |
| Elevation: | 597 ft (182 m) |
| Total Area: | 7.65 sq mi (19.83 km²) |
| Land Area: | 3.44 sq mi (8.92 km²) |
| Water Area: | 4.21 sq mi (10.91 km²) |
| Total Population: | 846 |
| Population Density: | 245.72/sq mi (94.88/km²) |
| Area code: | 231 |
| FIPS code: | 2650320 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1620662 |
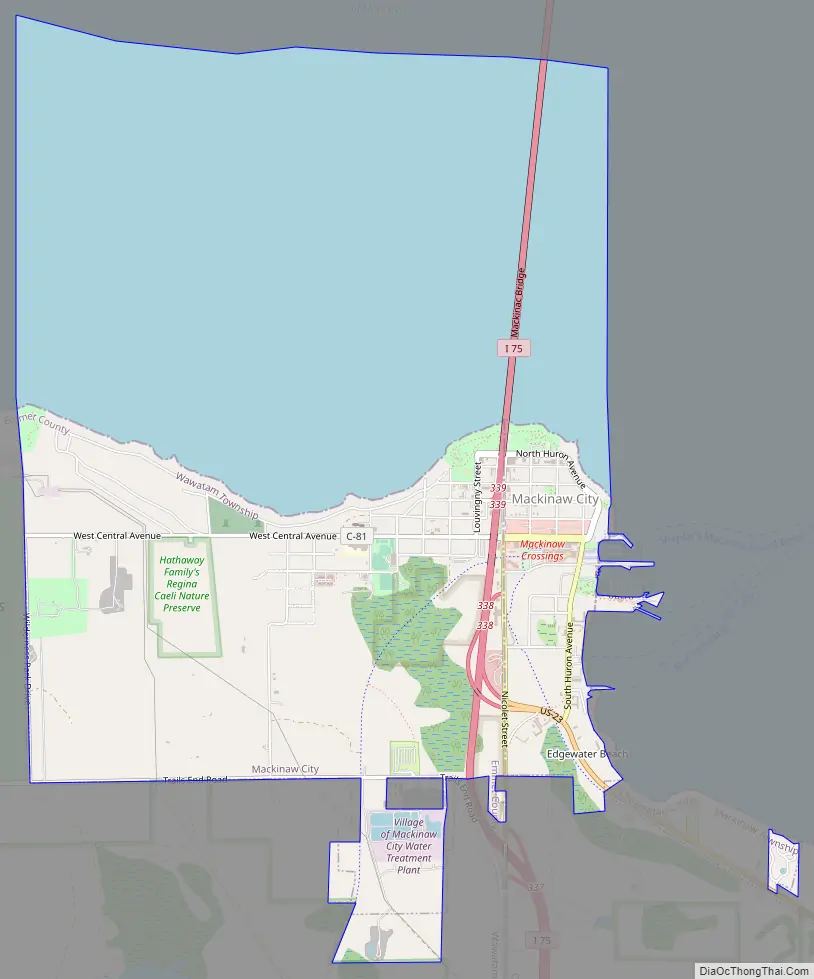
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
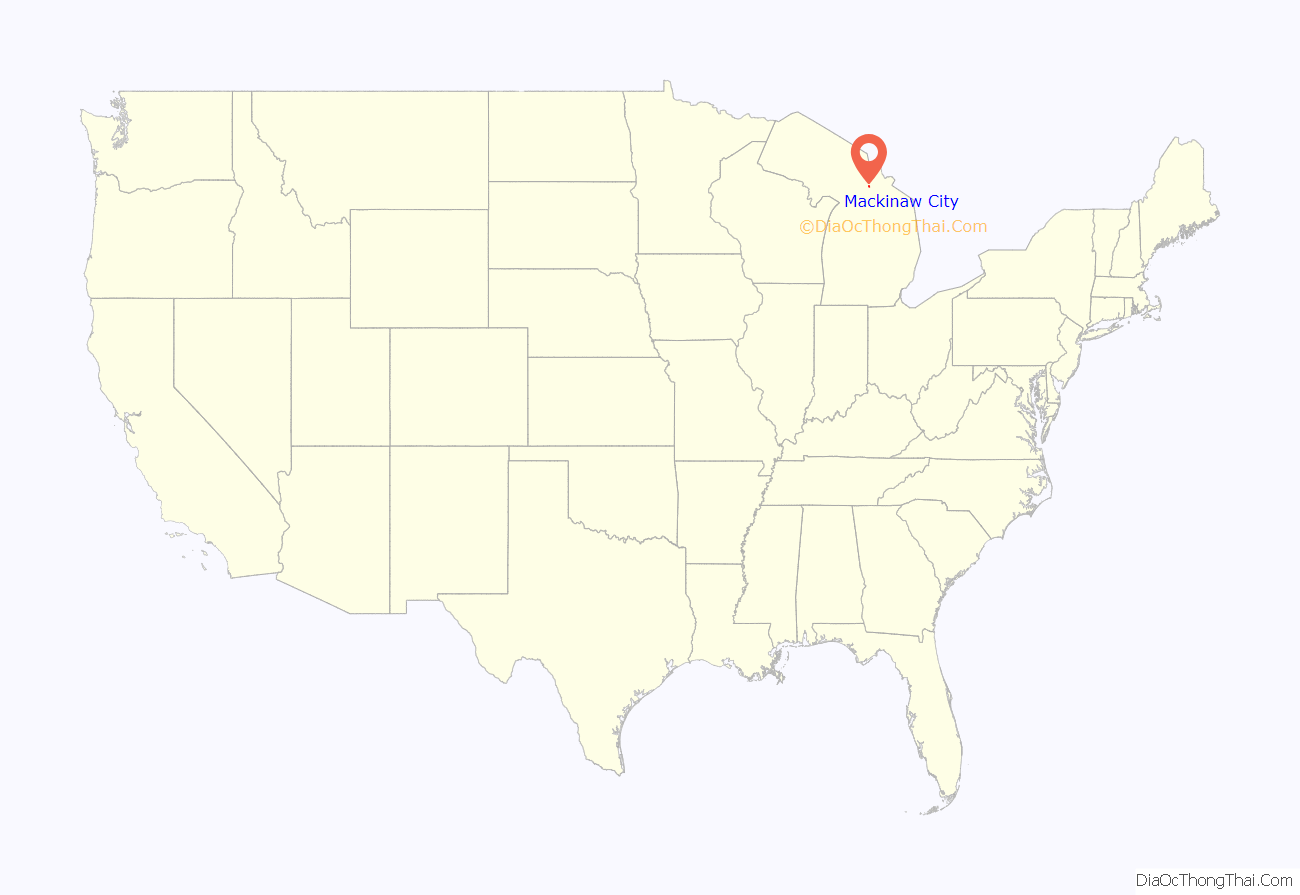
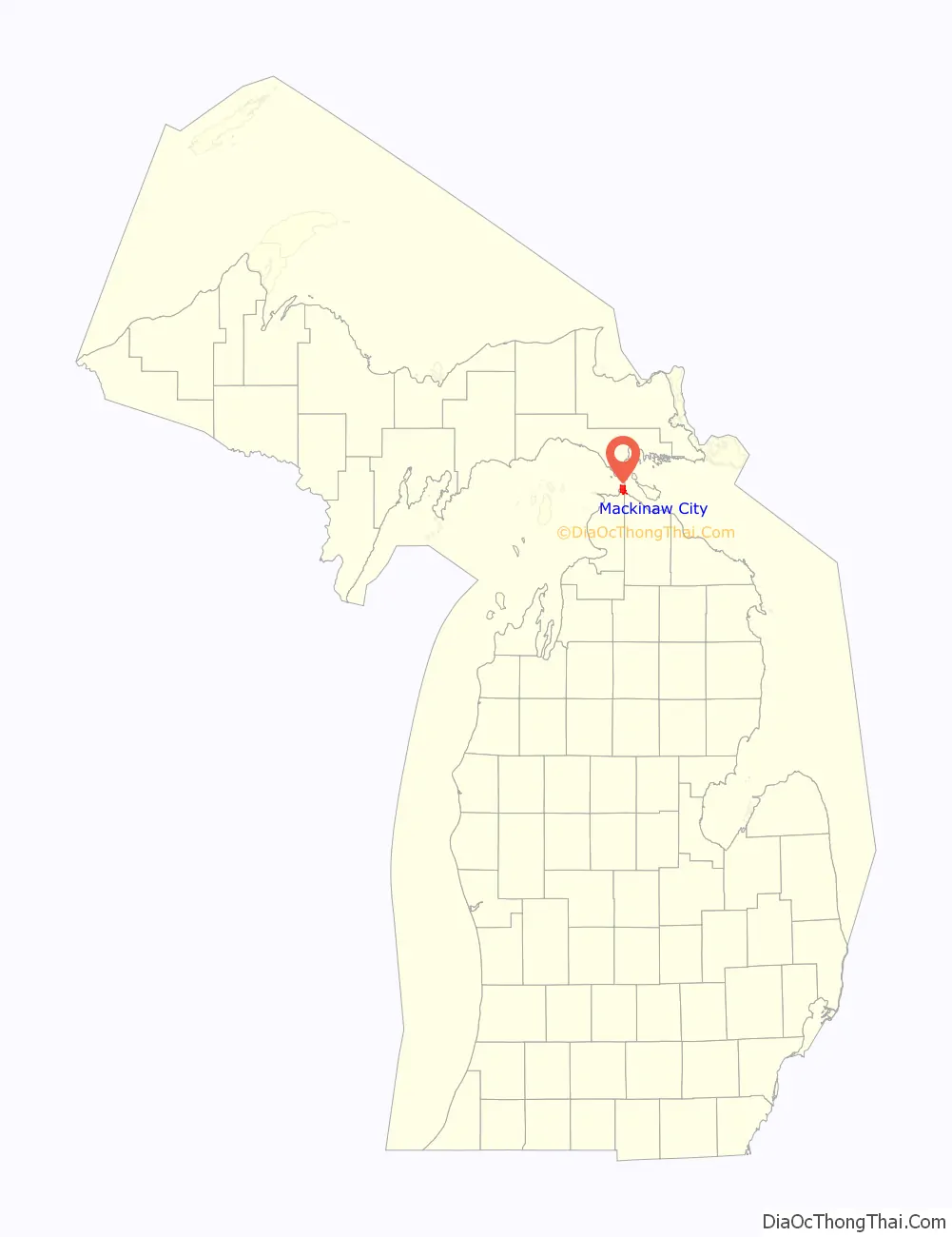
Mackinaw City location map. Where is Mackinaw City village?
History
Etymology and early settlement
The name of Mackinaw is a respelling of “Mackinac”, a strait between Lake Huron and Lake Michigan, an island in the strait, and an important trading-post on the island; ultimately from Ojibwe mishinii-makinaang (“at the place of many snapping turtles”).
The predominant historic tribes in this area were three Algonquian peoples, known collectively as the Council of Three Fires: Ojibwe (Chippewa), Ottawa (Odawa), and Potawatomi at the time of French contact in the 17th century. These peoples had long frequented the surrounding region, which they called Michilimackinac, to fish, hunt, trade, and worship. Mackinac Island in the straits appeared to have the shape of a turtle. The Native Americans here had a creation myth based on the sacred turtle. The Straits of Mackinac was the center of two routes vital to the fur trade: one to Montreal in the east, by way of Lake Nipissing and the Ottawa River valley; and the other to Detroit in the south via Lakes Huron and St. Clair.
European exploration and Fort Michilimackinac
The first European to pass the site of Mackinaw City was Jean Nicolet, sent out from Quebec City by Samuel Champlain in 1633 to explore and map the western Great Lakes, and to establish new contacts and trading partnerships with the Indian tribes of the region. His reports resulted in the French government providing funds to send settlers, missionaries, traders, and soldiers to the Great Lakes region. Father Jacques Marquette had established a mission on Mackinac Island in 1671 (which was shortly thereafter moved to St. Ignace on the Michigan peninsula, where it remained active until 1705). The construction of Fort de Buade at St. Ignace in 1681 was an attempt by the authorities of New France to establish a military presence at the Straits, but it closed in 1697.
Mackinaw City’s first European settlement came in 1715 when the French built Fort Michilimackinac. They lost it to the British during the Seven Years’ War, and the British abandoned the fort in 1783, after the American Revolutionary War resulted in independence of its Thirteen Colonies. The site of the fort in present-day Mackinaw City is a National Historic Landmark and is now preserved as an open-air historical museum. As with the forts at other settlements of the era and region such as Detroit, Michilimackinac was a fairly small post. It housed French civilians inside the fort, and allowed them to garden, hunt, and fish outside the walls. It was a trading post for the fur trade.
At the end of the French and Indian War (1754–1763), the British took possession of the fort, but continued to allow the French civilians to live within the walls, as they had good relations with the Odawa and Ojibwe for the fur trade. As a part of Pontiac’s Rebellion, Chippewa and Fox warriors captured the fort on June 2, 1763, in a surprise attack during a game of baggatiway or lacrosse; the British at the fort were taken prisoner and mostly killed.
Europeans, in the form of French and Scots-Irish traders from Detroit and elsewhere, did not return until the following spring, with the understanding that they would trade more fairly with the Native Americans. The British abandoned the vulnerable site on the mainland during the American Revolutionary War; from 1779 to 1781, the troops moved the fort, including its buildings, to Mackinac Island, where they established Fort Mackinac. What the British did not take with them, they burned; that way they could prevent the American rebels from using Michilimackinac as a base.
Mackinaw City from mid-19th century to present
In 1857, two men by the names of Conkling and Searles platted what would become Mackinaw City. The original plan reserved the northern portion as a park, to preserve the area that was once Fort Michilimackinac and to accommodate a hoped-for lighthouse. This was not built for nearly a generation after the land was set aside.
During the second half of the 1800s, the Mackinaw area (and northern Michigan in general) saw an increase in summer resort tourism. In 1875, Mackinac National Park became the second National Park in the United States after Yellowstone National Park in the Rocky Mountains.
Old Mackinac Point Lighthouse began operation in 1889 and the adjacent Fog Signal Building was built in 1906. This lighthouse, which operated until 1957, would eventually replace McGulpin Point Light, which operated between 1869 and 1906, at its location in the far western end of the village limits, with the current address of 500 Headlands Road.
The village became a vital port for train ferries crossing the Straits beginning in the 1890s, and later, for ferries for automobiles. In the 1890s, Mackinaw had one newspaper, the Mackinaw Witness, published weekly by Presbyterian missionary Rev. G. W. Wood, Jr.
Auto ferries began running in the early 1900s. Camping began in Michilimackinac State Park in 1907.
When the Mackinac Bridge was completed in 1957, the Old Mackinac Point Lighthouse was decommissioned immediately thereafter. At the same time, a grant was provided to the Mackinac Island State Park Commission, which owned the property at the Bridge’s southern terminus, to begin archeological excavations of the Michilimackinac ruins. Ultimately, a reconstruction of the fort to its 1770s appearance would be constructed.
Auto ferries, which had been running since the early 1900s, ended in 1957 after the completion of the Mackinac Bridge.
Train ferries crossed the Straits until 1984. Mackinaw City remains an important port city for tourists traveling by passenger ferry boat to Mackinac Island using Shepler’s ferry company, and Star Line services.
Through the course of time, the main industry of Mackinaw City became almost strictly tourist-oriented, with other major sources of employment being civic services such as mail, police, firefighting, schooling, and so on. Camping, which began in Michilimackinac State Park in 1907, was halted in 1971 as a Maritime Park was opened in 1972 around the lighthouse. This park was shut down in 1990, but Old Mackinac Point Lighthouse was opened to the public in 2004. Mill Creek State Park, which includes the area believed to be where Mill Creek’s sawmill once flourished when Mackinac Island was being settled, is located about five miles (8 km) southeast of the village along U.S. Highway 23 (US 23).
Mackinaw City Road Map
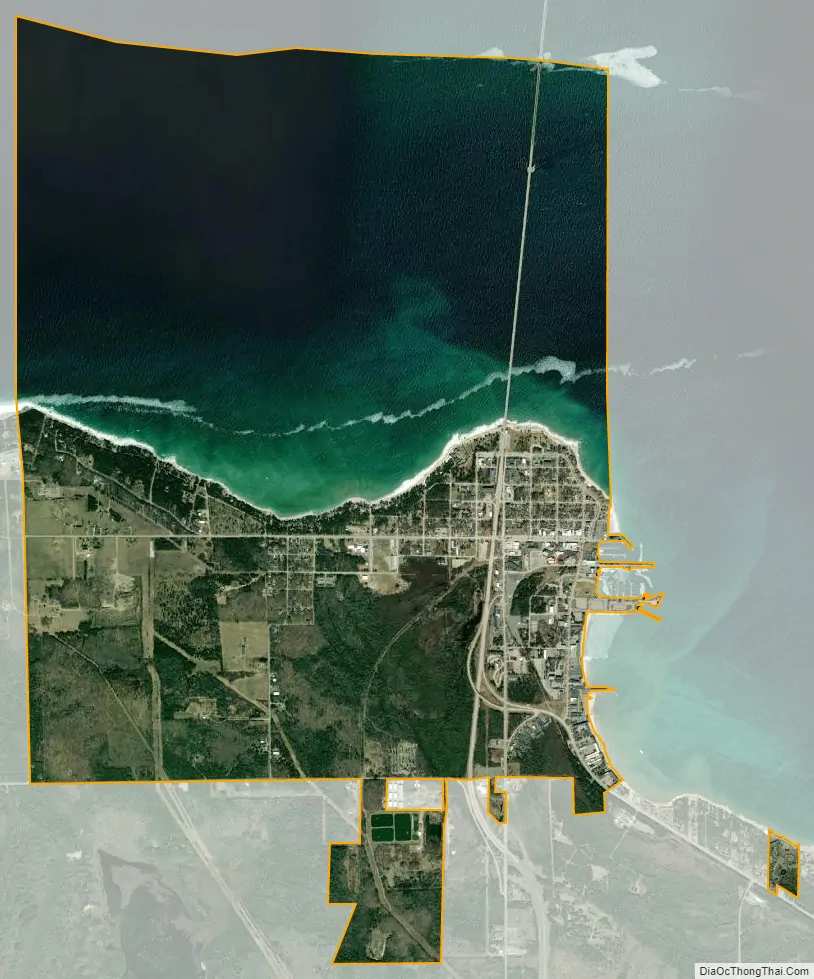
Mackinaw City city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the village has a total area of 7.65 square miles (19.81 km), of which 3.44 square miles (8.91 km) is land and 4.21 square miles (10.90 km) is water.
The village of Mackinaw City includes the northernmost point of Michigan’s Lower Peninsula. It lies along the Straits of Mackinac, and thus contains shorelines on both Lake Huron and Lake Michigan.
The southern approach of the Mackinac Bridge is located within Mackinaw City, bisecting the village.
Climate
This climatic region has large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and cold (sometimes severely cold) winters. According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Mackinaw City has a humid continental climate, abbreviated “Dfb” on climate maps.
See also
Map of Michigan State and its subdivision:- Alcona
- Alger
- Allegan
- Alpena
- Antrim
- Arenac
- Baraga
- Barry
- Bay
- Benzie
- Berrien
- Branch
- Calhoun
- Cass
- Charlevoix
- Cheboygan
- Chippewa
- Clare
- Clinton
- Crawford
- Delta
- Dickinson
- Eaton
- Emmet
- Genesee
- Gladwin
- Gogebic
- Grand Traverse
- Gratiot
- Hillsdale
- Houghton
- Huron
- Ingham
- Ionia
- Iosco
- Iron
- Isabella
- Jackson
- Kalamazoo
- Kalkaska
- Kent
- Keweenaw
- Lake
- Lake Hurron
- Lake Michigan
- Lake St. Clair
- Lake Superior
- Lapeer
- Leelanau
- Lenawee
- Livingston
- Luce
- Mackinac
- Macomb
- Manistee
- Marquette
- Mason
- Mecosta
- Menominee
- Midland
- Missaukee
- Monroe
- Montcalm
- Montmorency
- Muskegon
- Newaygo
- Oakland
- Oceana
- Ogemaw
- Ontonagon
- Osceola
- Oscoda
- Otsego
- Ottawa
- Presque Isle
- Roscommon
- Saginaw
- Saint Clair
- Saint Joseph
- Sanilac
- Schoolcraft
- Shiawassee
- Tuscola
- Van Buren
- Washtenaw
- Wayne
- Wexford
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming