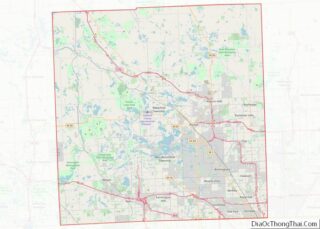
Royal Oak is a city in Oakland County in the U.S. state of Michigan. An inner-ring suburb of Detroit, Royal Oak is about 3 miles (4.8 km) north of Detroit’s city limits. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 58,211.
Royal Oak is located along the Woodward Corridor, and is served by Interstate 75 and Interstate 696. The city has one of the largest downtowns in Detroit’s suburbs, and is also home to much of the Detroit Zoo, with portions extending into neighboring Huntington Woods.
| Name: | Royal Oak city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Michigan |
| County: | Oakland County |
| Incorporated: | 1891 (village) 1921 (city) |
| Elevation: | 663 ft (202 m) |
| Land Area: | 11.79 sq mi (30.54 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km²) |
| Population Density: | 4,936.48/sq mi (1,905.96/km²) |
| Area code: | 248 |
| FIPS code: | 2670040 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 636352 |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Royal Oak location map. Where is Royal Oak city?
History
Royal Oak was named in 1819, during one of the surveying expeditions led by Territorial Governor Lewis Cass. A large oak tree at this small settlement reminded Cass of the story of the Royal Oak, where King Charles II of England, Scotland and Ireland hid to escape capture by the Roundheads after the Battle of Worcester, so he chose that name for the settlement.
Royal Oak was not incorporated as a village until 1891. It was reincorporated a city in 1921.
20th century to present
Royal Oak developed as a suburb of Detroit in the early 20th century, following Detroit’s booming growth as a result of industrialization and its auto industry.
The Royal Oak Farmers Market opened as a truck market, at the corner of 4th and Troy streets, on October 14, 1925, as a cooperative venture between the then-new City of Royal Oak and Oakland County, Michigan. There were still numerous farmers in the county. The present structure, at the corner of 11 Mile Road and Troy Street, is adjacent to the 44th District Court. It was erected in the spring of 1927 and dedicated July 1 of that year.
In the 1920s, Father Charles Coughlin, a Canadian Catholic priest who relocated to Detroit, became the founding pastor of the Shrine of the Little Flower, now a prominent landmark in the city. Through his ministry, he raised funds to build the present limestone church complex and tower. Initially he broadcast religious speeches from this site.
During the 1930s, his broadcasts became more political. He initially supported President Franklin D. Roosevelt, then opposed him and promoted the causes of the fascist leaders of Germany and Italy. The Roosevelt administration closed down his radio operation after the outbreak of World War II, with support from the Catholic hierarchy. Coughlin had developed national political influence and had an increasingly anti-semitic message, at a time when Jewish people were being severely persecuted in Germany.
In 1991, Thomas McIlvane, a postal worker, killed five people in Royal Oak’s post office, after being fired from the Postal Service for “insubordination.” This incident helped to popularize the term “going postal.”
The downtown originally had a typical mixture of small-scale retail and trade to serve the city of Royal Oak. With the development of the highway system in the postwar period, it lost business to suburban malls. Since the late 1990s and early 2000s, however, Royal Oak’s downtown has developed as an entertainment and nightlife destination. A number of large condominiums and lofts have been built in the area, increasing the density of the downtown population. In 2022, the Royal Oak City Council approved the demolition of the historic Main Art Theater, once a symbol of moviegoers in the area.
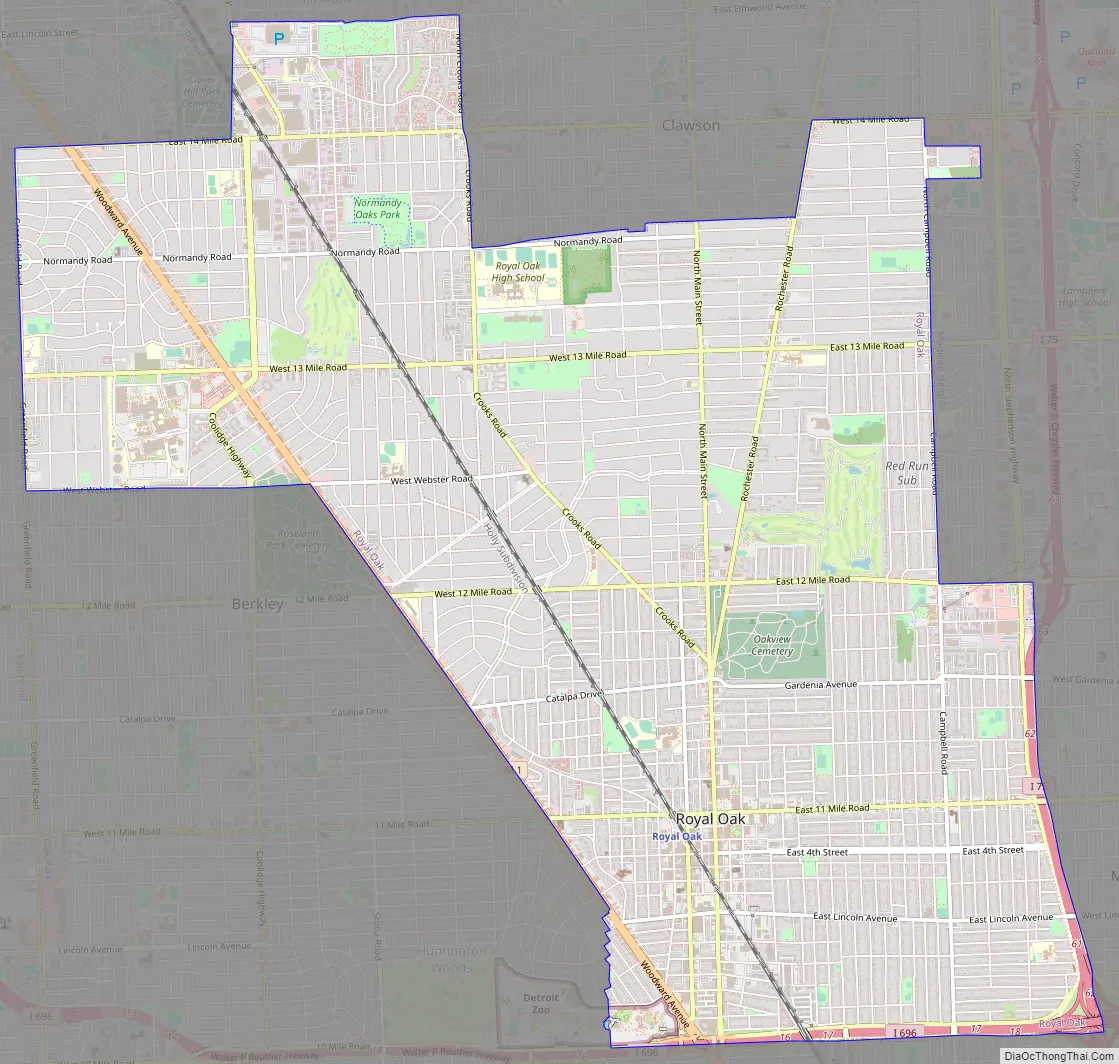
Royal Oak Road Map
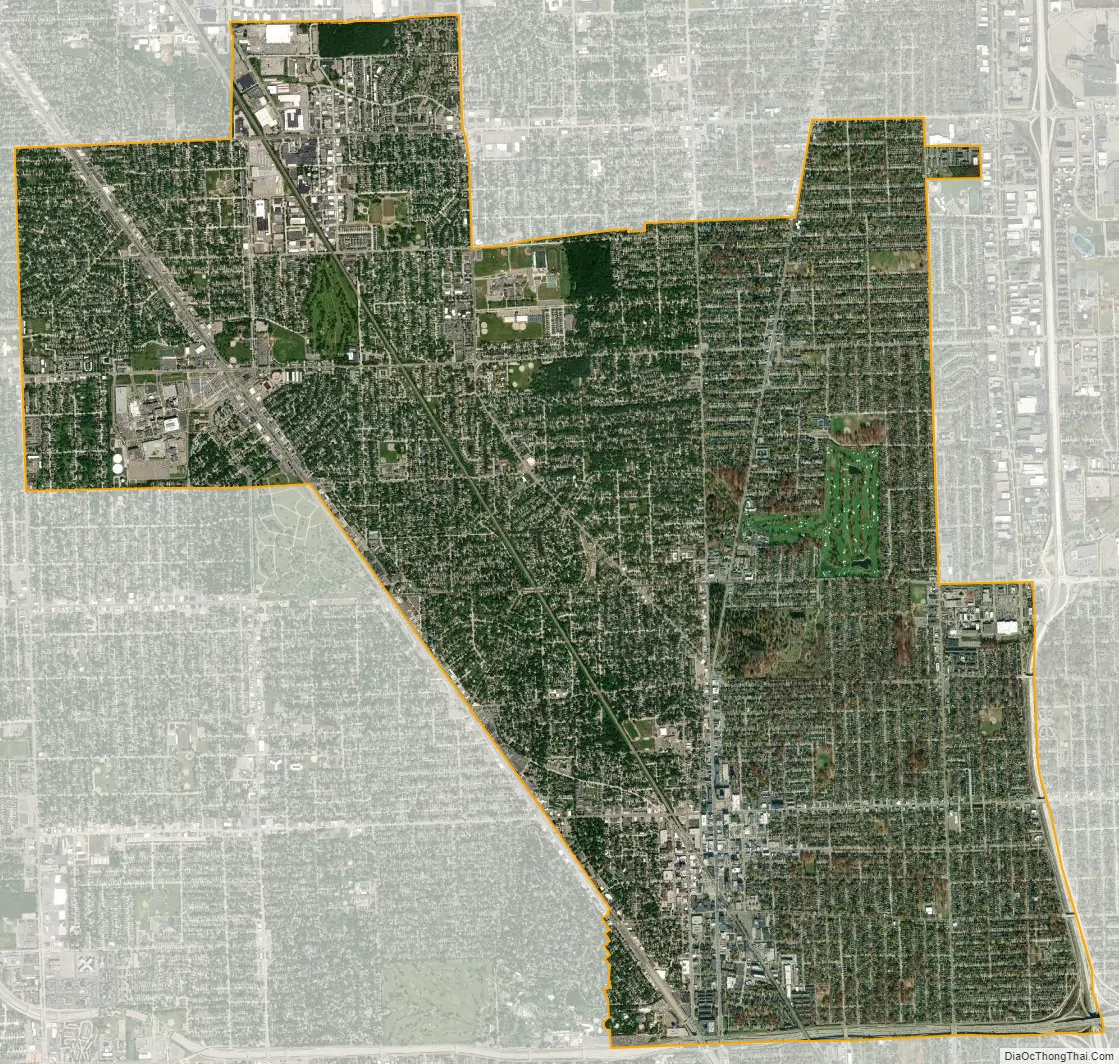
Royal Oak city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 11.79 square miles (30.54 km), of which 11.78 square miles (30.51 km) is land and 0.01 square miles (0.03 km) (0.08%) is water.
Royal Oak developed around a river, the Red Run. Vinsetta Boulevard was built skirting a source branch of the Red Run for its median. In the 1930s, Vinsetta’s entire median, along with the river and all but the tops of the bridges for the crossing streets were filled in as part of a WPA project during the Great Depression. During 1967–8, the rest of the river in Oakland County was buried within a six-foot drain pipe.
Extensive tree-planting has taken place since the 1930s, leading to the town being nicknamed “The City of Trees”, although recent increased developments have caused controversy about the maintenance of the city’s urban forest.
See also
Map of Michigan State and its subdivision:- Alcona
- Alger
- Allegan
- Alpena
- Antrim
- Arenac
- Baraga
- Barry
- Bay
- Benzie
- Berrien
- Branch
- Calhoun
- Cass
- Charlevoix
- Cheboygan
- Chippewa
- Clare
- Clinton
- Crawford
- Delta
- Dickinson
- Eaton
- Emmet
- Genesee
- Gladwin
- Gogebic
- Grand Traverse
- Gratiot
- Hillsdale
- Houghton
- Huron
- Ingham
- Ionia
- Iosco
- Iron
- Isabella
- Jackson
- Kalamazoo
- Kalkaska
- Kent
- Keweenaw
- Lake
- Lake Hurron
- Lake Michigan
- Lake St. Clair
- Lake Superior
- Lapeer
- Leelanau
- Lenawee
- Livingston
- Luce
- Mackinac
- Macomb
- Manistee
- Marquette
- Mason
- Mecosta
- Menominee
- Midland
- Missaukee
- Monroe
- Montcalm
- Montmorency
- Muskegon
- Newaygo
- Oakland
- Oceana
- Ogemaw
- Ontonagon
- Osceola
- Oscoda
- Otsego
- Ottawa
- Presque Isle
- Roscommon
- Saginaw
- Saint Clair
- Saint Joseph
- Sanilac
- Schoolcraft
- Shiawassee
- Tuscola
- Van Buren
- Washtenaw
- Wayne
- Wexford
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming