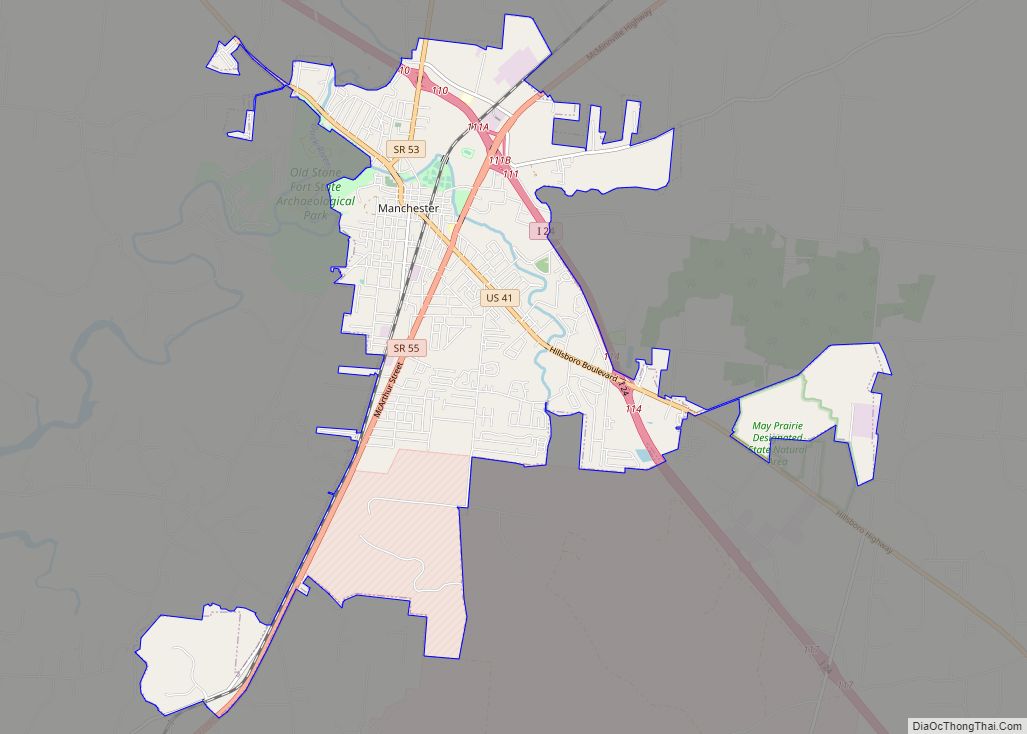
Tullahoma is a city in Coffee and Franklin counties in southern Middle Tennessee, United States. The population was 20,339 at the 2020 census. In 2019, the population was estimated to be 19,555. It is the principal city of the Tullahoma micropolitan area (a 2009 estimate placed it at 99,927), which consists of Coffee, Franklin, and Moore counties and is the second largest micropolitan area in Tennessee.
| Name: | Tullahoma city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Tennessee |
| County: | Coffee County, Franklin County |
| Incorporated: | October 4, 1852 |
| Elevation: | 1,073 ft (327 m) |
| Total Area: | 23.50 sq mi (60.85 km²) |
| Land Area: | 23.44 sq mi (60.71 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.06 sq mi (0.15 km²) |
| Total Population: | 20,339 |
| Population Density: | 867.70/sq mi (335.02/km²) |
| Area code: | 931 |
| FIPS code: | 4775320 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1272964 |
| Website: | www.tullahomatn.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Tullahoma location map. Where is Tullahoma city?
History
Tullahoma was founded in 1852 as a work camp along the new Nashville and Chattanooga Railroad. Its name is derived from the Choctaw language, and means “red rock”.
An alternative explanation (see Sam Davis Elliott’s Soldier of Tennessee and sources cited therein) of the name is that Peter Decherd, who donated the land for the railroad right-of-way (and was therefore given the right to name two stations along the line), named one station Decherd, after himself, and the other as Tulkahoma (later changed to Tullahoma). Tullahoma was the name of Decherd’s favorite horse, which had been named for a Choctaw chief captured by Decherd’s grandfather. (There was also a town called Tullahoma in Mississippi, which later changed its name to Grenada.)
The earliest settlement was by farmers from Virginia and North Carolina. Using African-American slave labor, they developed plantations for tobacco and hemp. Slaves also tended their livestock, both horses and cattle. Early families were named Moore, Decherd (pronounced as Deckerd), Anderson, Ragon, Montgomery, Ferrell, Stephenson, and Gunn.
They called a nearby spring Bottle Spring, though it was later known as John Gunn’s Spring, since it was on his property. Nowadays, it is called Big Springs. This spring provided water for the steam locomotives. Later it was exploited for health and tourist attractions, as the town developed spa facilities.
When the Civil War began in April 1861, Company B, 1st Regiment of Tennessee Volunteers, was formed in Tullahoma. It joined General Robert E. Lee’s Army of Northern Virginia. The division fought in the battles of Bull Run, Fredericksburg, Chancellorsville, Gettysburg, and Petersburg, before surrendering to Union General Ulysses S. Grant at Appomattox.
During the war, Tullahoma served in 1863 as the headquarters for the Confederate Army of Tennessee. That year the Union Army undertook the Tullahoma Campaign, defeating Confederate forces and taking control of Middle Tennessee. Federal troops occupied this area for the duration of the war. As a result of the campaign, Union forces captured Chattanooga.
Tullahoma was little more than a rough frontier outpost, and had no paved streets. 1863 was a wet year, and the place became known to the bedraggled troops of both sides as a place of endless mud. An aide on Confederate General William Hardee’s staff is said to have written his own account of the origin of the name: “It is from two Greek words – ‘Tulla’ meaning mud, and ‘Homa,’ meaning more mud.”
The selection of Tullahoma as a headquarters by Confederate General Braxton Bragg has been much criticized by military historians. Although the location was strategic with regard to the road and rail network, it had no strong natural defenses. Bragg did little to fortify it while his forces occupied the area. Eventually the town was evacuated without a battle.
After the war, Tullahoma recovered slowly, but began to prosper owing to its railroad link. It became renowned for its educational facilities, a rarity in the area at the time.
At the turn of the 20th century, Tullahoma became a popular health destination, with many spas across town to take advantage of Big Springs.
Manufacturing was developed in the area, notably of shoes, clothing, and sporting goods. In 1924, the General Shoe Corporation was established here, which eventually developed as Genesco. The diversified apparel firm is Tennessee’s oldest listed firm on the New York Stock Exchange. Since the early 1900s, a variety of sports products have been manufactured in Tullahoma, including baseballs, bats, and golf clubs by Campbell Mfg, Wilsons, Worth Sports, Tennessee Tanning Co. and Rawlings.
In 1939, U.S. Route 41A was built through town. This improved access between the town and Nashville, 71 miles (114 km) to the northwest, and Chattanooga, 77 miles (124 km) to the southeast.
The noted whiskey brand of George Dickel is made in Cascade Hollow, just north of Tullahoma near Normandy, TN. Jack Daniel’s whiskey is distilled 12 miles (19 km) southwest of Tullahoma in Lynchburg.
From the 1930s to mid-20th century, the area benefited from considerable federal investment and development: the projects of the Tennessee Valley Authority constructed dams and related facilities to generate hydroelectric power and electrify many rural areas, as well as providing needed jobs during the Great Depression. Camp Forrest was established during World War II as an infantry training center and later POW camp. The Arnold Engineering Development Complex (AEDC) was constructed near Tullahoma after WWII as a major development and test center for the Air Force and other DOD organizations, as well as NASA. It was instrumental in the development of numerous aerospace systems, as well development for the Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo space programs. It remains as the most advanced and largest complex of flight simulation test facilities in the world. Later the state established two institutions of higher learning here, the Motlow State Community College and an aerospace engineering graduate school, the University of Tennessee Space Institute.
Today manufacturing makes up a smaller part of the Tullahoma economy. The town’s growth has been steady though slow since the late 20th century, based on a mixture of education, services, tourism, and retail. The area is a major hub for aerospace, particularly aerospace ground testing, due to the presence of AEDC and the Space Institute. The former Sverdrup Technology Inc., now a subsidy of Jacobs Engineering, is a major supplier of wind tunnels, test equipment and support. Microcraft, Inc., which built the first air-breathing flight vehicles to reach Mach 7-10 under the NASA X-43a program, is located near the downtown square. A national aircraft preservation museum, Beechcraft Heritage Museum, was established on grounds south of the city’s municipal airport.
Tullahoma celebrated its 150th (sesquicentennial) anniversary on October 4, 2002.
Rock pioneer Little Richard Penniman died in Tullahoma in 2020.
The town was featured in the song, “Tullahoma Dancing Pizza Man” by Eddie Rabbitt off of the album “Rocky Mountain Music.”
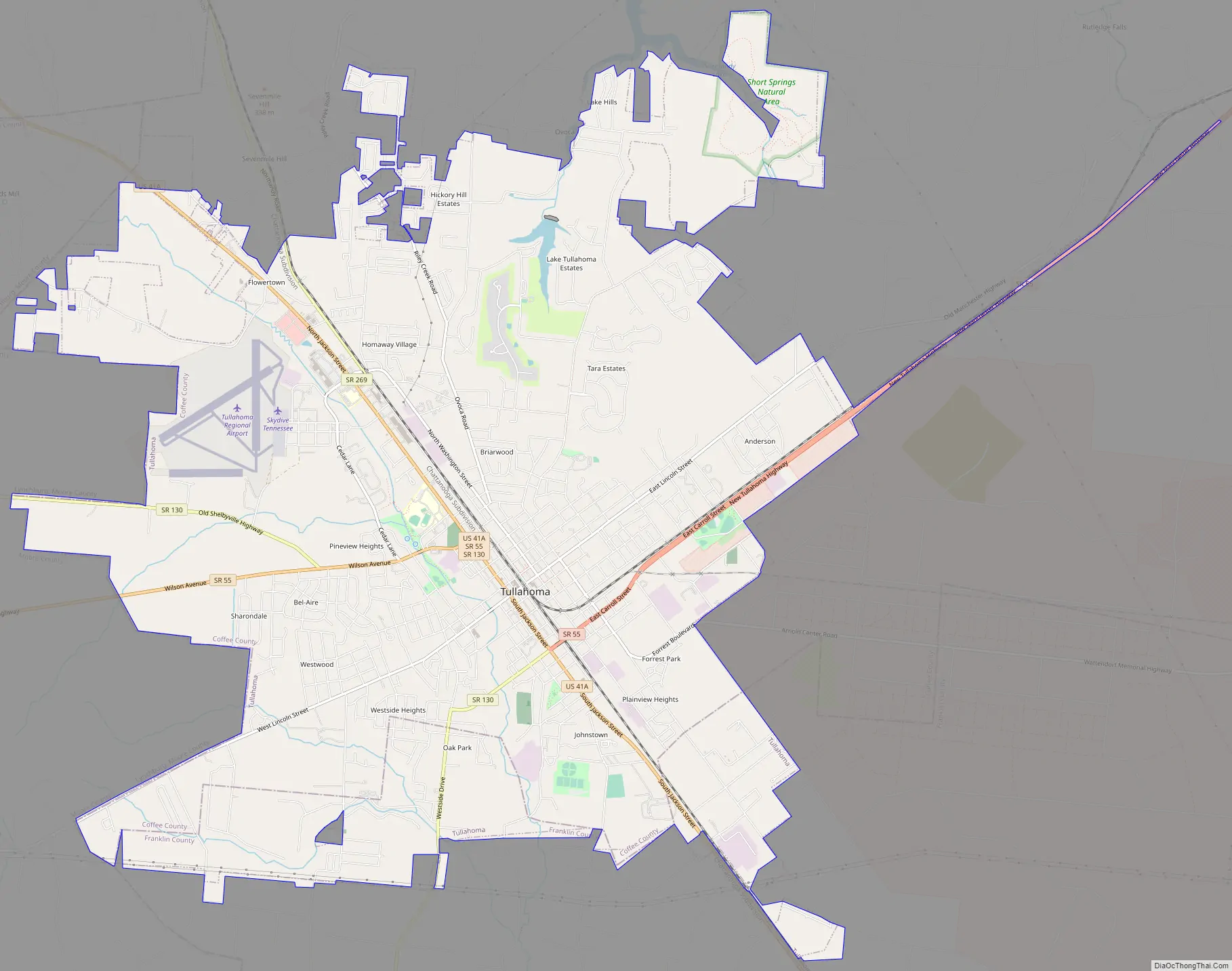
Tullahoma Road Map
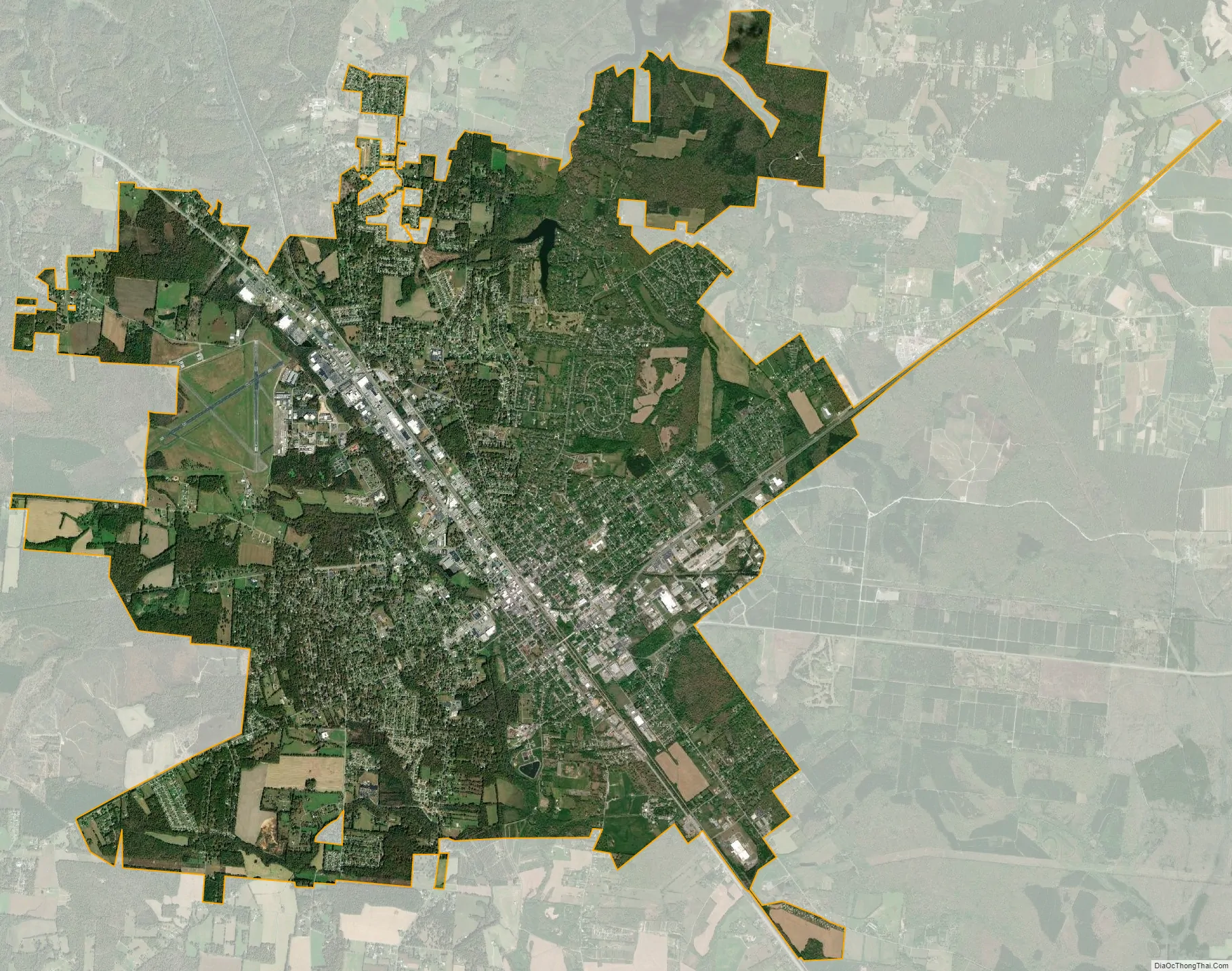
Tullahoma city Satellite Map
Geography
Tullahoma is located in the southwest corner of Coffee County at 35°22′7″N 86°12′48″W / 35.36861°N 86.21333°W / 35.36861; -86.21333 (35.368511, -86.213258), and extends south into Franklin County. It is situated at the edge of the Highland Rim, with flatter topography than in the surrounding area. The region was known as “the Barrens” to the first settlers.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 23.6 square miles (61.0 km), of which 23.5 square miles (60.8 km) is land and 0.1 square miles (0.2 km), or 0.30%, is water.
Climate
Climate is characterized by relatively high temperatures and evenly distributed precipitation throughout the year. The Köppen Climate Classification subtype for this climate is “Cfa” (Humid Subtropical Climate).
See also
Map of Tennessee State and its subdivision:- Anderson
- Bedford
- Benton
- Bledsoe
- Blount
- Bradley
- Campbell
- Cannon
- Carroll
- Carter
- Cheatham
- Chester
- Claiborne
- Clay
- Cocke
- Coffee
- Crockett
- Cumberland
- Davidson
- Decatur
- DeKalb
- Dickson
- Dyer
- Fayette
- Fentress
- Franklin
- Gibson
- Giles
- Grainger
- Greene
- Grundy
- Hamblen
- Hamilton
- Hancock
- Hardeman
- Hardin
- Hawkins
- Haywood
- Henderson
- Henry
- Hickman
- Houston
- Humphreys
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Johnson
- Knox
- Lake
- Lauderdale
- Lawrence
- Lewis
- Lincoln
- Loudon
- Macon
- Madison
- Marion
- Marshall
- Maury
- McMinn
- McNairy
- Meigs
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Moore
- Morgan
- Obion
- Overton
- Perry
- Pickett
- Polk
- Putnam
- Rhea
- Roane
- Robertson
- Rutherford
- Scott
- Sequatchie
- Sevier
- Shelby
- Smith
- Stewart
- Sullivan
- Sumner
- Tipton
- Trousdale
- Unicoi
- Union
- Van Buren
- Warren
- Washington
- Wayne
- Weakley
- White
- Williamson
- Wilson
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming