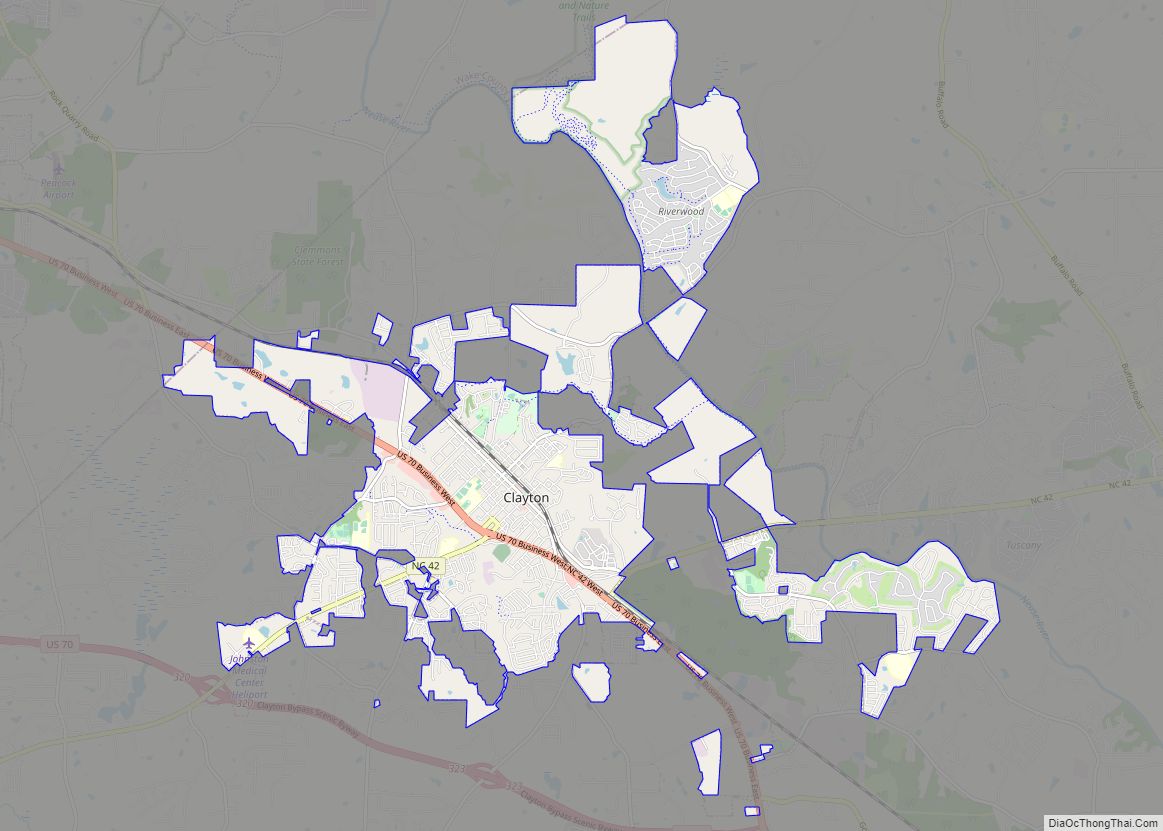
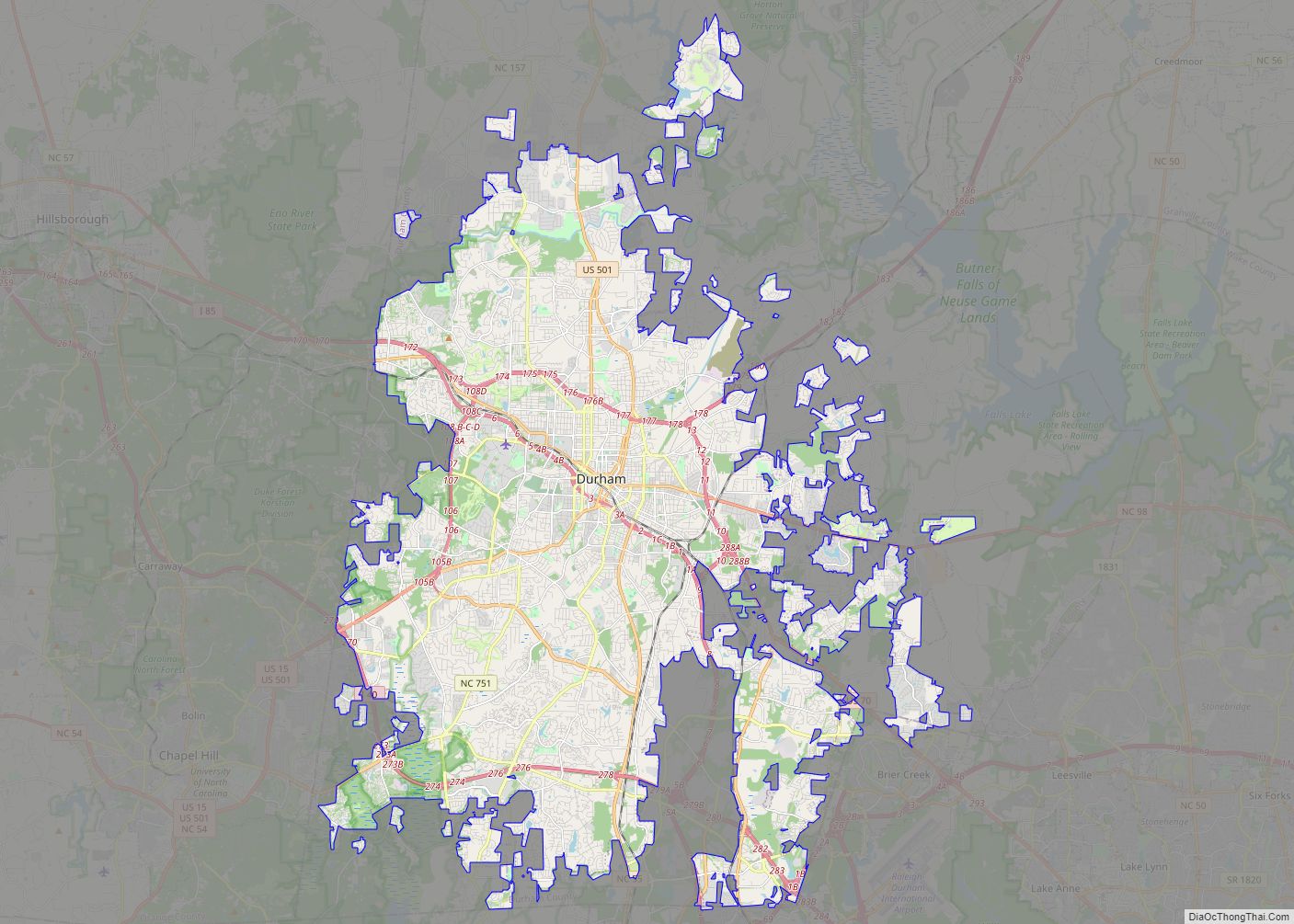
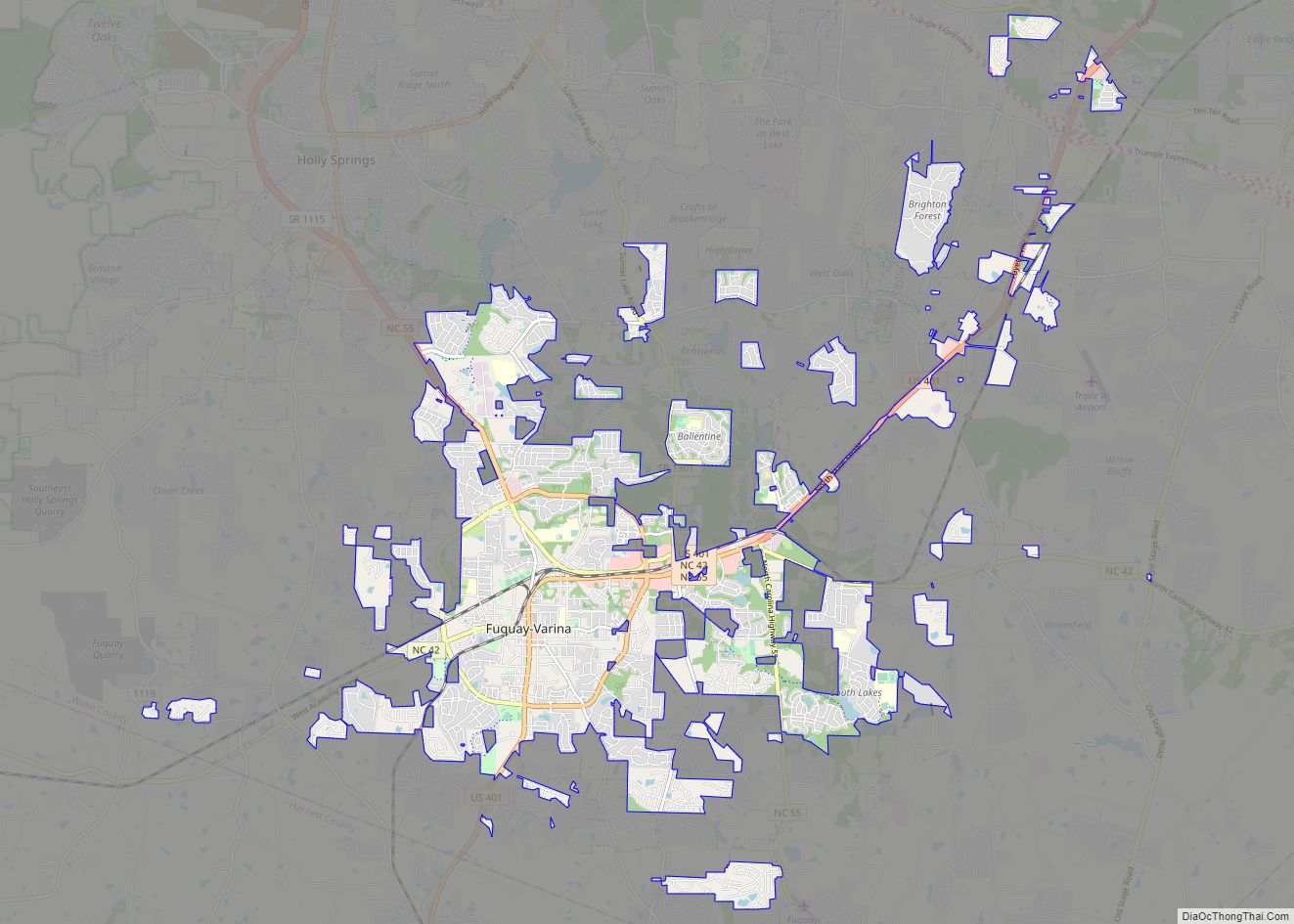
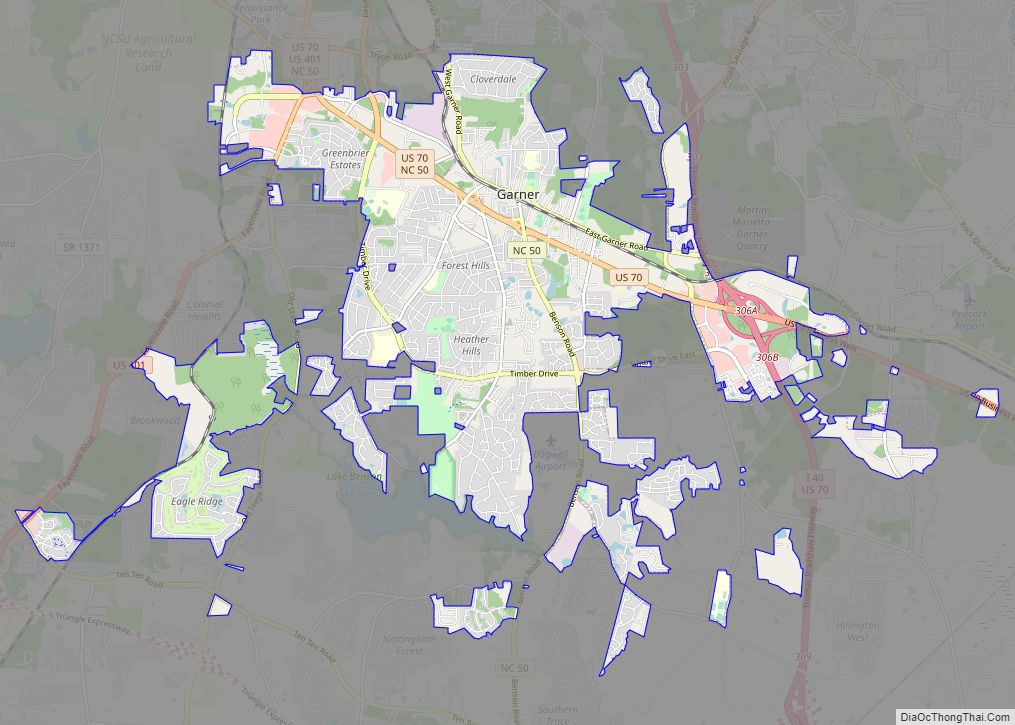
Fuquay-Varina (/ˈfjuːkweɪ vəˈriːnə/ FYUU-kway və-REE-nə) is a town in southern Wake County, North Carolina, United States, lying south of Holly Springs and southwest of Garner, and north of the Harnett County town of Angier and west of the unincorporated community of Willow Springs. The population was 17,937 at the 2010 census, and estimated at 36,736 as of July 2021. The hyphenated name attests to the town’s history as two separate towns. Fuquay Springs and Varina merged in 1963 to create the modern town. Economically, the town initially grew due to tobacco trade and agriculture, but has seen recent population growth and real estate development due to its proximity to Research Triangle Park.
| Name: | Fuquay-Varina town |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 43 |
| LSAD Description: | town (suffix) |
| State: | North Carolina |
| County: | Wake County |
| Incorporated: | 1909 |
| Elevation: | 327 ft (99 m) |
| Total Area: | 18.73 sq mi (48.51 km²) |
| Land Area: | 18.65 sq mi (48.29 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.08 sq mi (0.22 km²) |
| Total Population: | 36,736 |
| Population Density: | 1,831.60/sq mi (707.19/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 27526 |
| Area code: | 919/984 |
| FIPS code: | 3725300 |
| Website: | www.fuquay-varina.org |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
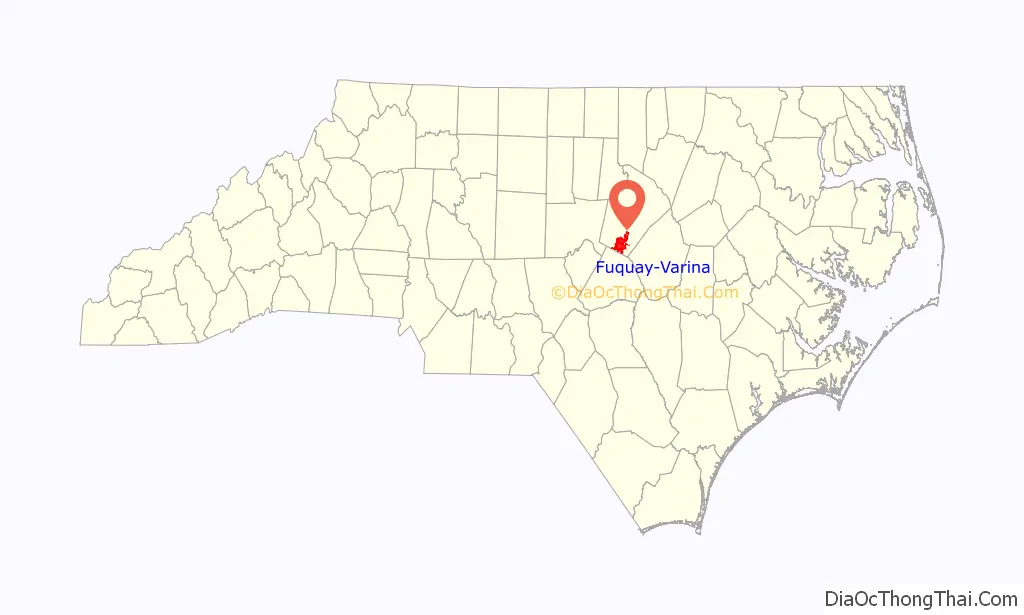
Fuquay-Varina location map. Where is Fuquay-Varina town?
History
Early history
Frenchman William Fuquay first settled in the small farming town of Sippihaw, named for the original Native American tribe that inhabited the area. Although there is no history of a tribe called Sippihaw, there are historical accounts in the area of a tribe called Susippihaw. Around 1858, while plowing the fields of the family tobacco farm, Stephen Fuquay, son of William, discovered a spring. Originally the spring was used solely for drinking water. Stephen soon came to the conclusion that the mineral water flowing from the springs had healing properties. As word spread, locals began to help the springs establish this reputation, which brought residents from neighboring communities and counties to its waters. The springs were eventually walled in to better serve the tourists coming to the area by road or rail. In 1860, Fuquay sold the springs to a group of local investors who formed the Chalybeate Springs Company to market the attraction and its waters.
At that time another Sippihaw resident, J. D. “Squire” Ballentine, was returning home from the Civil War. Ballentine had been the town’s schoolmaster before going off to fight for the Confederate Army. During his tour of duty, he had received letters from one of many southern ladies who wrote to the troops to improve their morale. Originally signing her name “Varina”, perhaps an homage to the wife of Jefferson Davis, Virginia Avery would later meet and fall in love with Ballentine. He continued to call her Varina throughout their life together. When he became the first postmaster at the new post office in town in 1880, he named it “Varina” in her honor. A community grew just south of the springs, near the post office and the couple’s Varina Mercantile Company general store. In time, it adopted the same name. Ballentine’s business success allowed him to construct the Ballentine Spence House in 1910, the first house to have plumbing and electricity in the area. This house, a local historic landmark, still stands today.
Growth around the start of the 20th century
The Fuquay Mineral Spring’s popularity grew in the 1890s and around the start of the 20th century as local businessman John Mills developed the idea to offer “Moonlight Excursions” to the springs. He fitted flat rail cars with seats and offered nighttime train trips to southern Wake County from Raleigh. As more guests came to the springs to “take the waters”, a group of small hotels sprung up in town, along with restaurants, barbecue stands, and a dance pavilion with a player piano. The town became a tourist destination and was the site of special celebrations on Fourths of July and Easter Mondays. During these events, residents of Raleigh would take the train down to watch the accompanying baseball games and participate in the dances and celebrations. Hotels like the Ben Wiley Hotel (now called the Fuquay Mineral Spring Inn & Garden) catered to the out-of-towners and became as much a center of town life as the springs. In 1902, Sippihaw was renamed “Fuquay Springs” in honor of its founding family and was officially incorporated in 1909.
When it was incorporated, the new Fuquay Springs town limits included the core of the neighboring town of Varina, consisting of its business district and the rail junction of the Cape Fear and Northern Railway and the Norfolk Southern Railway. But Varina reestablished itself the following year when the Varina Union Station was erected and a new post office was created, spurred by the lobbying of Ballentine. Four years later, the Bank of Varina was established, competing directly with the Bank of Fuquay (now Fidelity Bank). Several warehouses for the growing tobacco business were built in town over the next few years, capitalizing on the railroad connections. Another supply store and a knitting factory followed. As Varina came into its own as a hub for area agriculture, the Fuquay Springs Corporation was formed and began bottling and selling mineral water from the springs commercially. Area businesses continued to develop and, in 1927, U.S. Route 401 was paved through town, shortening travel times to Raleigh and nearby communities.
Unification and the present
By this time, Fuquay Springs and Varina had become major trading hubs for southern Wake County as well as neighboring Harnett and Johnston counties. Yet improvements to automobiles and area roads caused a decline in tourism at the springs. Rather than visiting the springs, residents in the region chose to visit the coast as travel times decreased. During this time, however, the tobacco industry continued to drive the area economy, with five warehouses, a cotton buyer, and fifteen stores established by the end of the 1920s. The shared emphasis on agricultural and industrial growth brought the towns to a shared vision, and as their residents worked, played, and attended church together, the towns merged into Fuquay-Varina in 1963.
While development in the area today includes numerous residential communities and commercial sites along the major roadways into town, many of the older structures from its past remain within the town limits. The Victorian, Craftsman, and Colonial Revival homes constructed in the late 19th century and early 20th century are contributing structures to the Fuquay Springs Historic District, while the downtown shops and businesses are part of the Varina Commercial Historic District. Area landmarks located in these districts include the Ben-Wiley Hotel, the Ballentine-Spence House, and the Dr. Wiley S. Cozart House, built across the street from the springs by the original owner and proprietor of the Ben Wiley. The springs are now contained in a small park developed on the site in 1945 which was handed over to the town in 1998 to maintain as a historic park. Lexie McLean owned and operated McLean’s Grocery on Academy Street for many years. McLean was a community leader and considered a major factor in the growth and development of the Fuquay-Varina area. Edward N. Farnell was the principal of the Fuquay Spring High School from 1952 through 1967. Farnell was an important community leader and educator; many of his students went on to become community and state leaders.
From 1970 to 2000, the population more than doubled, growing from 3,576 residents to 7,898. The population more than doubled again between 2000 and 2010, growing to 17,937 at the 2010 census. According to the NC State Data Center, Fuquay-Varina grew 23% from 2000 to 2003, making it the 26th fastest growing community in the state and the 11th fastest for those with populations over 5,000.
The mayor of Fuquay-Varina is Blake Massengill, who was elected in 2021 with 50% of the vote over Commissioner Bill Harris. Prior to being elected as mayor, Blake served as Mayor Pro-Tem for six years. The new Mayor Pro-Tem replacing Massengill is Commissioner Larry Smith.
Fuquay-Varina is also the former hometown of Internet personalities Rhett McLaughlin and Link Neal, who moved their studio there in 2010, as well as Link who until then lived in Apex, North Carolina.
In addition to the Ben-Wiley Hotel, Fuquay Springs Historic District, and Varina Commercial Historic District, the Fuquay Mineral Spring, Fuquay Springs High School, Fuquay Springs Teacherage, Fuquay-Varina Woman’s Club Clubhouse, J. Beale Johnson House, Kemp B. Johnson House, Jones-Johnson-Ballentine Historic District, and Wayland H. and Mamie Burt Stevens House are listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
Fuquay-Varina Road Map
Fuquay-Varina city Satellite Map
Geography
Fuquay-Varina is located at 35°35′31″N 78°47′19″W / 35.59194°N 78.78861°W / 35.59194; -78.78861 (35.591969, -78.788746).
According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of 12.2 square miles (31.5 km), of which 12.1 square miles (31.3 km) is land and 0.08 square miles (0.2 km), or 0.51%, is water.
Fuquay-Varina is located in the northeast central region of North Carolina, where the North American Piedmont and Atlantic Coastal Plain regions meet. This area is known as the “Fall Line” because it marks the elevation inland at which waterfalls begin to appear in creeks and rivers. Its central Piedmont location situates Fuquay-Varina approximately three hours west of Atlantic Beach by car and four hours east of the Great Smoky Mountains.
Climate
Fuquay-Varina enjoys a moderate subtropical climate, with moderate temperatures in the spring, fall, and winter. Summers are typically hot with high humidity. Winter highs generally range in the low 50s°F (10 to 13 °C) with lows in the low-to-mid 30s°F (-2 to 2 °C), although an occasional 60 °F (15 °C) or warmer winter day may occur. Spring and fall days usually reach the low-to-mid 70s°F (low 20s°C), with lows at night in the lower 50s°F (10 to 14 °C). Summer daytime highs often reach the upper 80s to low 90s°F (29 to 35 °C). The rainiest month is July.
See also
Map of North Carolina State and its subdivision:- Alamance
- Alexander
- Alleghany
- Anson
- Ashe
- Avery
- Beaufort
- Bertie
- Bladen
- Brunswick
- Buncombe
- Burke
- Cabarrus
- Caldwell
- Camden
- Carteret
- Caswell
- Catawba
- Chatham
- Cherokee
- Chowan
- Clay
- Cleveland
- Columbus
- Craven
- Cumberland
- Currituck
- Dare
- Davidson
- Davie
- Duplin
- Durham
- Edgecombe
- Forsyth
- Franklin
- Gaston
- Gates
- Graham
- Granville
- Greene
- Guilford
- Halifax
- Harnett
- Haywood
- Henderson
- Hertford
- Hoke
- Hyde
- Iredell
- Jackson
- Johnston
- Jones
- Lee
- Lenoir
- Lincoln
- Macon
- Madison
- Martin
- McDowell
- Mecklenburg
- Mitchell
- Montgomery
- Moore
- Nash
- New Hanover
- Northampton
- Onslow
- Orange
- Pamlico
- Pasquotank
- Pender
- Perquimans
- Person
- Pitt
- Polk
- Randolph
- Richmond
- Robeson
- Rockingham
- Rowan
- Rutherford
- Sampson
- Scotland
- Stanly
- Stokes
- Surry
- Swain
- Transylvania
- Tyrrell
- Union
- Vance
- Wake
- Warren
- Washington
- Watauga
- Wayne
- Wilkes
- Wilson
- Yadkin
- Yancey
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming