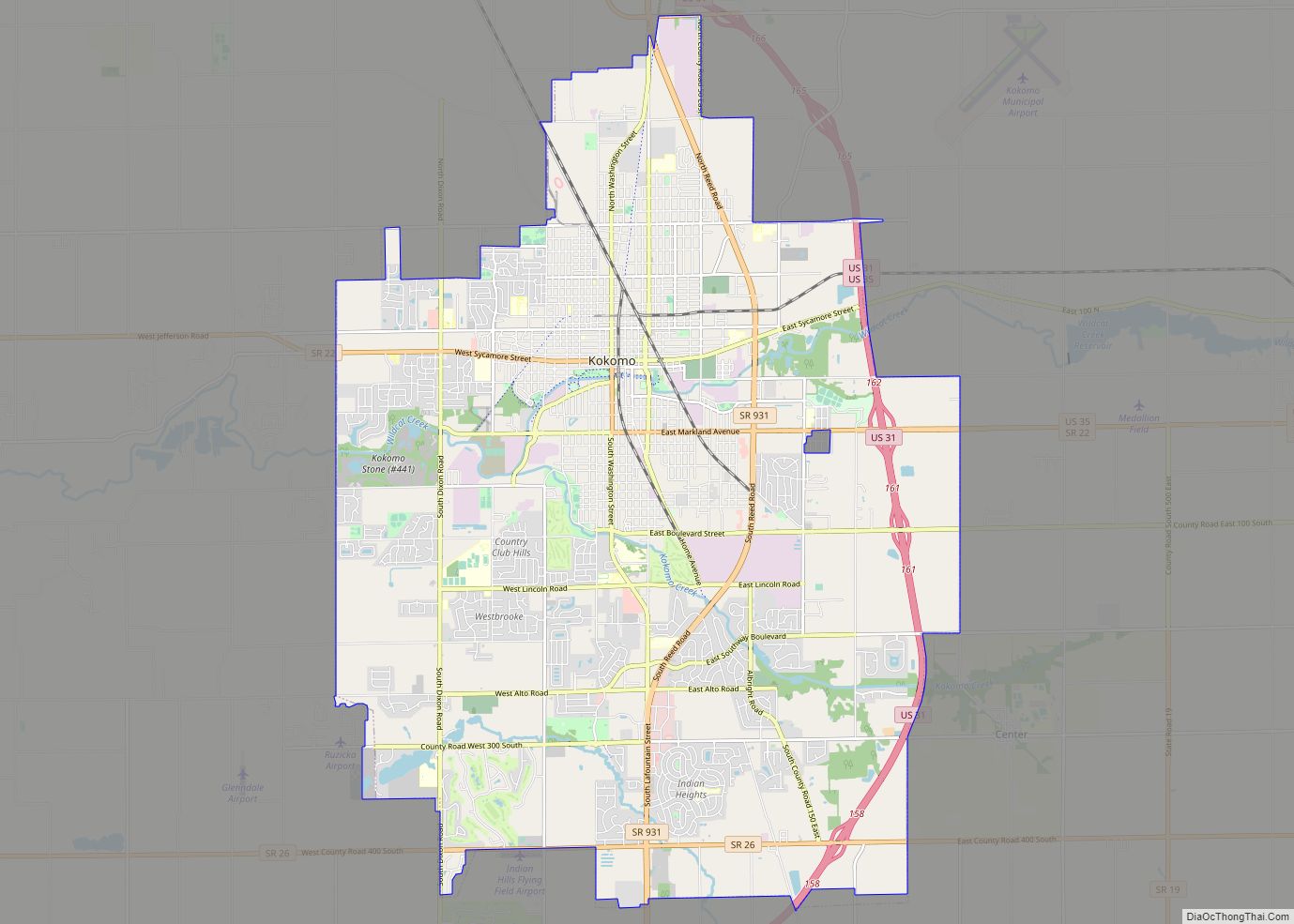
| Name: | Kokomo city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Indiana |
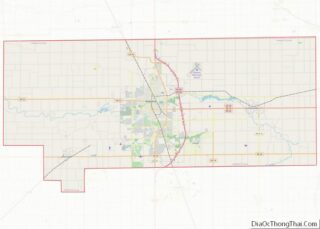
| County: | Howard County |
| Elevation: | 810 ft (250 m) |
| Total Area: | 36.79 sq mi (95.29 km²) |
| Land Area: | 36.68 sq mi (95.00 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.11 sq mi (0.29 km²) |
| Total Population: | 45,468 |
| Population Density: | 1,581.75/sq mi (610.72/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 46901-46904 |
| Area code: | 765 |
| FIPS code: | 1840392 |
| Website: | cityofkokomo.org |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Kokomo location map. Where is Kokomo city?
History
Early history and incorporation
The city of Kokomo was named after the Miami man Ma-Ko-Ko-Mo, said to have been one of the four sons of Chief Richardville, last of the chiefs of the Miami people. Tradition holds that David Foster, the “Father of Kokomo,” named the town Kokomo after the “ornriest Indian on earth” because Kokomo was “the ornriest town on earth.” Kokomo is thought to have been born in 1775 and died in 1838. The only documentary proof of his existence is a trading post record of a purchase of a barrel of flour for $12 for his “squaw.” His remains (with those of others) were reportedly discovered during the construction of a saw mill in 1848 and re-interred in the “north-east corner” of the Pioneer Cemetery. The tradition of the Peru Miami is that the town was named after a Thorntown Miami named Ko-kah-mah, whose name is rendered Co-come-wah in the Treaty at the Forks of the Wabash in 1834. That name was translated as “the diver” (an animal that could swim under water).
As a result of various removals, by 1840 the Miami population in Howard County (until 1846 known as Richardville County) was reduced to about 200. The principal settlement was the Village of Kokomo, on the south side of Wildcat Creek. Indian paths connected Kokomo with Frankfort and Thorntown (along the Wildcat) and led to Peru by way of Cassville, and to Meshingomesia by way of Greentown. At the time David Foster had a trading post in Howard County, near the intersection of the reservation boundary line and Wildcat pike, where he engaged in both legitimate trade and illegal sale of alcohol to the Miamis on government property.
Shortly after Richardville County was organized in 1844 the commissioners appointed to establish the county seat approached Foster for a donation from his substantial holdings. (In 1846 tax records show that he owned 552 acres (223 ha) of farmland and as well as 67 divided lots in the business district.) At the time of the request the only improvements in what is now Kokomo were Foster’s log house and log barn and several Miami huts. The commissioners sought a donation of the more fertile lands south of Wildcat Creek, but Foster refused, donating instead 40 acres (16 ha) north of the creek—land which was thickly forested and “swampy.” The terms of the donation required that Foster build a courthouse on the land, but he was later excused and Rufus L. Blowers was promised $28 to build it. He was penalized $2 for construction delays. The log courthouse was completed in 1845.
In June 1855, Henry A. Brouse petitioned the board of Howard county commissioners to incorporate the town of Kokomo. The original election was not held (for unspecified reasons), but another took place on October 1, 1855. After a vote of 62–3 in favor of incorporation, the board so ordered it.
On March 31, 1865, an election was held for Kokomo to assume a city government. The resolution was passed, and Nelson Purdum was elected the first mayor.
Early growth
In anticipation of business that the court would bring, Kokomo began a fairly quick growth from the time that lots were first sold on October 18, 1844. David Foster was granted the first license to sell merchandise in Kokomo at the December 1844 commissioners meeting. Two more merchants were licensed in March 1845. John Bohan, who would become a major shop owner, merchant, justice of the peace and investor, moved to Kokomo in December 1844, and erected the first two-story frame house, not only in Kokomo, but in all the county.
After the enactment of the 1846 pre-emption law, settlers rapidly attempted to secure homesteads in the surrounding lands.
In 1848 Stonebreaker’s Mill, 10 miles (16 km) west of Kokomo, began operations. By 1850 Kokomo had a newspaper, when James Beard purchased the printing equipment of the New London Pioneer and set up the Howard Tribune. By 1851 county business was so brisk that the county ordered the construction of two more court buildings, both one story brick affairs, 18 by 36 feet (5.5 by 11.0 m). The county auditor and treasurer occupied one building, and the clerk and recorder occupied the other.
On April 1, 1854, Kokomo’s first bank, the Indian Reserve Bank, was organized with David Foster, John Bohan and Harless Ashly the principal shareholders. (It only lasted a few years until a robbery impaired its capital. The loss substantially injured Foster’s fortune.)
Railroads
1854 saw the first railroad stop at Kokomo. The New London Pioneer had long advocated for a rail line to connect Kokomo with Indianapolis. Colonel C.D. Murray was the agent at Kokomo for stock subscriptions in support of the railroad. In 1852 the construction of the Peru and Indianapolis Railroad commenced. In Kokomo Samuel C. Mills and Dr. Corydon Richmond, commercial competitors of David Foster, donated several lots to the railroad in order to secure the location of the rail depot near their commercial property. The route was laid along Buckeye Street at the insistence of the merchants who hoped to reduced drayage expenses. Samuel Mills built a large frame structure at the Howard flouring mills, which served as a warehouse for the company’s freight and a passenger depot. For some time after 1854 Kokomo was the terminus of the line, but eventually the line was extended to Peru and then to Michigan City.
A short time after the construction of the Peru and Indianapolis Railroad began, the Pennsylvania Railroad announced that one of its lines would pass through Kokomo. By 1853 a line was commenced between Kokomo and Logansport (which was intended to become the hub of a network of lines for the company). Railroad service was inaugurated on that line on July 4, 1855.
The most important rail line for Kokomo became the standard-gauge Clover Leaf line. This railroad would eventually link Kokomo with both the West Coast and the Eastern Seaboard. It began as a short line linking Frankfort and Kokomo, the Frankfort and Kokomo Railroad. Henry Y. Morrison of Frankfort was the principal promoter, and A.Y. Comstock acted for him in Kokomo. A failure of the proposed subsidy caused the promoters to turn all assets over to the contractors, who promised to complete the line. Construction began in 1873 and was completed the following year. Limited freight between the two cities made the line unprofitable. After a series of acquisitions by other railroads, the line became part of the Toledo, St. Louis and Kansas City Railroad. A line connecting it to the east reached Kokomo on January 1, 1881.
Mayor Cole
In 1881, one of the most remarkable and controversial events in Kokomo’s history took place. Mayor Henry C. Cole was shot to death by a sheriff’s posse. Dr. Cole had a curious history and had stirred up a great deal of passion in the previous fifteen years. He was reputed to have been a gifted surgeon, who served in the Union Army during the Civil War and when afterwards he settled in Kokomo, he became a prominent physician. In Kokomo he married a woman, Natalie Cole, of whom he became intensely jealous. He became suspicious of one Allen, whom he warned away from Kokomo. When he discovered Allen leaving the post office one day in October 1866, he shot him dead. The fact that the killing both took place in broad daylight and showed cold-blooded rage (Cole continued shooting after Allen was down) caused the crime to receive national attention. Cole’s case was venued to Tipton County, where he retained Daniel W. Voorhees of Terre Haute to represent him. Voorhees obtained a not guilty verdict on a plea of emotional insanity. Cole divorced his wife thereafter.
Cole’s reputation for violent instability, and the cowardice in the way he killed Allen, created many enemies for him, but his generosity toward poor patients and a promise to “clean up” the town won him enough support to win a bitter election for Mayor in 1881. Shortly thereafter, on September 19, 1881, he was shot dead by a sheriff’s posse at Old Spring Mills at West Jefferson Street. According to the coroner’s inquest, he died from shotgun wounds inflicted by Deputy George Bennett (father of New York stage idol Richard Bennett). The sheriff claimed that an informant had advised him that Cole was planning to rob a flour mill, possibly to incriminate his enemies. The posse was forced to fire on Cole in self-defense (the sheriff claimed he had two revolvers) and to prevent his escape, although his injuries seemed inconsistent with that version. Cole’s supporter’s argued that no revolvers or burglary tools were produced and that the motive was implausible. Nevertheless, no action was taken against Bennett or the other members of the posse.
Natural gas boom
Natural gas had been developed in Pennsylvania and Canada for some time, and had most recently been developed around Findlay, Ohio. In March 1886, a group of citizens, led principally by A.Y. Comstock (who had promoted the Frankfort and Kokomo Railroad) and D.C. Spraker (later President of Kokomo Rubber Company), circulated a memorandum seeking subscribers (at $100 each) for the purpose of boring for gas at a distance of at least 2,000 feet (610 m) below ground. It took until September to obtain the necessary 22 subscribers. The first rig was built south of Wildcat Creek. and on October 6, 1886, natural gas erupted forth and the well was capped.
Together with the well in Eaton, which began producing slightly before Kokomo’s, the discovery led to the Indiana Gas Boom. This discovery was directly responsible for Elwood Haynes’ move to Kokomo, as a superintendent with a gas company with interests in Kokomo and Howard County. The Diamond Plate Glass Company (now part of PPG Industries) began in Kokomo in 1887, lured by the cheap and plentiful natural gas. The Kokomo Opalescent Glass Works started making stained glass in Kokomo in 1888 and has been in continuous operation ever since.
“City of Firsts”
As a result of the natural gas boom, Kokomo attracted an increasing number of industries, which resulted in significant technological innovations. For these industrial and technical achievements, Kokomo is officially known as the “City of Firsts.” Among other achievements, Kokomo was a pioneer of the United States automobile manufacturing, with Elwood Haynes test-driving his early internal combustion engine auto there on July 4, 1894. Haynes and his associates built a number of other autos over the next few years; the Haynes-Apperson Automobile Company for mass-production of commercial autos was established in Kokomo in 1898. Haynes went on to invent Stainless Steel flatware in 1912 to give his wife tarnish-free dinnerware. In 1938, the Delco Radio Division of General Motors (now Aptiv) developed the first push button car radio.
Kokomo serves as the “City of Firsts” in the food industry as well. In 1928 Walter Kemp, Kemp Brothers Canning Co. developed the first canned tomato juice because of a request by a physician in search for baby food for his clinic. Kokomo is also home to the first mechanical corn picker which was developed by John Powell in the early 1920s. Kokomo was home to the first Ponderosa Steakhouse, which opened in 1965. Kokomo opened the first McDonald’s with a diner inside, locally called “McDiner.” This McDonald’s theme failed nationally. Eventually, the “McDiner” closed and was converted back to a regular McDonald’s restaurant.
The following inventions are associated with Kokomo:
- 1894 – Elwood Haynes makes the first successful trial run of his “horseless carriage” on Pumpkinvine Pike, which is now Boulevard east of Indiana 931 (formerly U.S.31.)
- 1894 – The first pneumatic rubber tire in the US was created by D.C. Spraker at the Kokomo Rubber Tire Company.
- 1895 – The first aluminum casting was developed by William “Billy” Johnson from the Ford and Donnelly Foundry.
- 1902 – Kingston carburetor developed by George Kingston.
- 1906 – The first Stellite cobalt-base alloy was discovered by Elwood Haynes.
- 1912 – Stainless steel tableware was invented by Elwood Haynes as a response to his wife’s desire for tableware that wouldn’t tarnish.
- 1918 – The Howitzer shell, used in World War I, was created by the Superior Machine Tool Company.
- 1918 – The first aerial bomb with fins was produced by the Liberty Pressed Metal Company.
- 1920 – The mechanical corn picker was created by John Powell.
- 1923 – William Swern Sr. developed the first tire-building machine for mass production of auto tires
- 1928 – The first canned tomato juice was created by Walter Kemp from Kemp Brothers Canning Company in response to a physician’s need for baby food.
- 1938 – The first push-button car radio was created at Delco Radio Division of General Motors Corporation.
- 1941 – Globe American Stove Company manufactured the first all-metal life boats and rafts, known as Kokomo Kids in the US Navy.
- 1947 – The first signal-seeking car radio was created by the Delco Radio Division of General Motors.
- 1956 – Delco Radio Division of General Motors produced a transistorized signal-seeking car (hybrid) radio, which used both vacuum tubes and transistors in its radio’s circuitry. This transistorized car radio was available as an option on the 1956 Chevrolet Corvette car models.
- 1957 – Delco Radio Division of General Motors produced an all-transistor car radio, as standard equipment for the Cadillac Eldorado Brougham car model.
1913 Flood
On March 21–26, 1913 Kokomo suffered severe flooding when 6.59 inches (167 mm) of rainfall occurred. The Kokomo Tribune reported at the time that the Wildcat Creek over-topped its levee to reach nearly 1 mile (1.6 km) wide after rising at a rate of 3 inches (76 mm) per hour. Damage was widespread, including loss of electrical power due to the power plant being flooded. On March 26, flooding was declared over after the water level dropped 42 inches (1,100 mm) in a 24-hour period.
Continental Steel Corporation
From 1914 through 1986, the Continental Steel Corporation facility produced nails, wire and wire fence from scrap steel on a 183-acre (74 ha) facility in Kokomo. Manufacturing operations in the steel plant and on other portions of the property included the use, handling, storage and disposal of hazardous materials. Steel-making operations had included reheating, casting rolling, drawing, pickling, galvanizing, tinning and tempering.
After the company filed for bankruptcy in 1986, EPA and the Indiana Department of Environmental Management investigated the plant and property and found soil, sediments, surface water and ground water contaminated with volatile organic compounds (PCBs) and several metals, including lead, arsenic, cadmium, and chromium. Lead contamination was also detected in soils on nearby residential properties.
The site was proposed to the National Priorities List as a Superfund site in 1988 and formally added in 1989.
In April 2009, EPA received almost $6 million in American Recovery and Reinvestment Act to complete needed cleanup at two problems at the Continental Steel Superfund site: the former Slag Processing Area and the site’s contaminated ground water. The ARRA funding helped accelerate the cleanup of hazardous waste on the site. In the process, total of 15 Indiana contractors or subcontractors were involved in the ARRA-funded work, creating at least 45 temporary jobs.
In August 2010, using the ARRA funds, EPA completed the cleanup of the former slag processing area of the Superfund Site. Approximately 86,000 short tons (78,000 t) of slag were moved to the site’s acid lagoon area for use as fill on that portion of the site. Two feet (0.6 m) of clean soil were used to cap the former slag processing area, leaving it suitable for potential redevelopment. ARRA funds were also used to address contaminated groundwater at the site. This work included extensive groundwater sampling to determine the contaminated plume area and installation of groundwater extraction and monitoring wells. Three wind turbines will be used to generate much of the power needed to operate the groundwater extraction system.
Site cleanup was completed in August 2011.
In 2016 the former site was approved as the location of a Solar farm with installation of panels beginning in August 2016. The estimated cost of the project is $10M. The solar energy park began operating on December 29, 2016.
Ku Klux Klan
In the summer of 1923, record numbers attended rallies of the Ku Klux Klan in Indiana. On June 16, 1923, a crowd of 75,000 attended a Klan rally in Terre Haute. On June 21 Argos held the largest rally it had ever seen. On June 26 a large Klan rally was held in Alexandria. All of this was merely a prelude to the rally planned for Kokomo. Conceived as a “monster tristate conclave,” it was intended to charter 93 Indiana klans representing more than 300,000 members. Some doubted the prospect of 200,000 attendees, claiming it would be “without parallel in history”; others predicted attendance of 300,000. Extensive preparations for that number were made, including the scheduling of 1,000 interurban cars from around Indiana to Kokomo. The Union Traction Company, in addition to supplying 50 cars, transported three cars of white horses to Kokomo for the parade. The Kokomo Klan rented the fields surrounding its own large lot for parking, and electric amplifiers were obtained to allow the large crowd to hear the speeches.
According to historian Robert Coughlan, “literally half” of Kokomo residents were members of the Ku Klux Klan during its height in the 1920s and 1930s. On July 4, 1923, Kokomo achieved national notoriety when it hosted the largest Ku Klux Klan gathering in history. An estimated 200,000 Klan members and supporters gathered in Malfalfa Park for a massive Konklave in which D. C. Stephenson was elevated to the position of Grand Dragon of the Indiana Klan. Other estimates say the crowd was only 10,000. A huge flag was used that day to collect a reported $50,000 for construction of a local “Klan hospital” so that Klan members would not have to be treated at the only local hospital, which was Catholic. Both men’s and women’s Klans held weekly rallies and initiations in Malfalfa Park, and Kokomo’s Klanswomen held meetings at the armory, the local headquarters of the Women of the Ku Klux Klan, and churches. A speech at a Baptist church was attended by 1,000 Klanswomen.
The Kokomo rally sent shockwaves through the national GOP, which had come to believe that the re-election of President Warren G. Harding depended on the vote of Indiana. According to the Washington correspondent of the New York World, Republicans feared that the Klan had “obliterated party lines” and “virtually swallowed” the Indiana Republican Party. Since the Republicans held only a 25,000 vote plurality in the state, any serious defection of African-Americans would tip the state to the Democrats. In the event, Harding died within a month and Republican Calvin Coolidge succeeded him with a substantial electoral majority (including Indiana) against a divided opposition. The Klan, however, continued to dominate state politics especially after the election of Edward L. Jackson as governor.
Ryan White
Kokomo served to symbolize the nation’s early misunderstanding and ignorance of AIDS in the mid-to-late 1980s when Ryan White was expelled from school due to his illness. White was a teenage hemophiliac who had been infected with HIV through contaminated blood products (Factor 8). At the time blood products were often collected through state prison systems. Factor 8 was made from pooled plasma of thousands of donors. Later the plasma was screened for HIV and Hepatitis and heat treated to inactive HIV and Hepatitis. The teen had been attending Western Middle School (which is actually in Russiaville) but was ostracized by his classmates, and forced to eat lunch alone and use a separate restroom. Many parents and teachers in Kokomo rallied in support of banning White from attending the school. A lengthy administrative appeal process with the school system ensued, followed by death threats and violence against White and his family, including a bullet being fired through the window of their Kokomo home. Media coverage of the case made White into a national celebrity and spokesman for AIDS research and public education. In 1987, the White family left Kokomo for Cicero, Indiana. Ryan attended Hamilton Heights High School in nearby Arcadia, where he was welcomed by faculty and students.
Gas tower
The Kokomo Gas Tower had been a symbol of Kokomo since it was constructed in 1954. The tower was 378 feet (115 m) tall and had a capacity of 12,000,000 cubic feet (340,000 m). Due to high maintenance costs of $75,000 a year, and up to $1,000,000 to paint it, the gas company decided to demolish it in 2003. Other ideas were reviewed before settling on this decision, including a plan to turn the tower into a giant Coca-Cola advertisement. On September 7, 2003, at approximately 7:30 a.m., the Gas Tower was demolished by Controlled Demolition, Inc. (CDI). Pieces of the tower were sold to the public for $20–$30, and proceeds went to a planned Kokomo technology incubation center and Bona Vista.
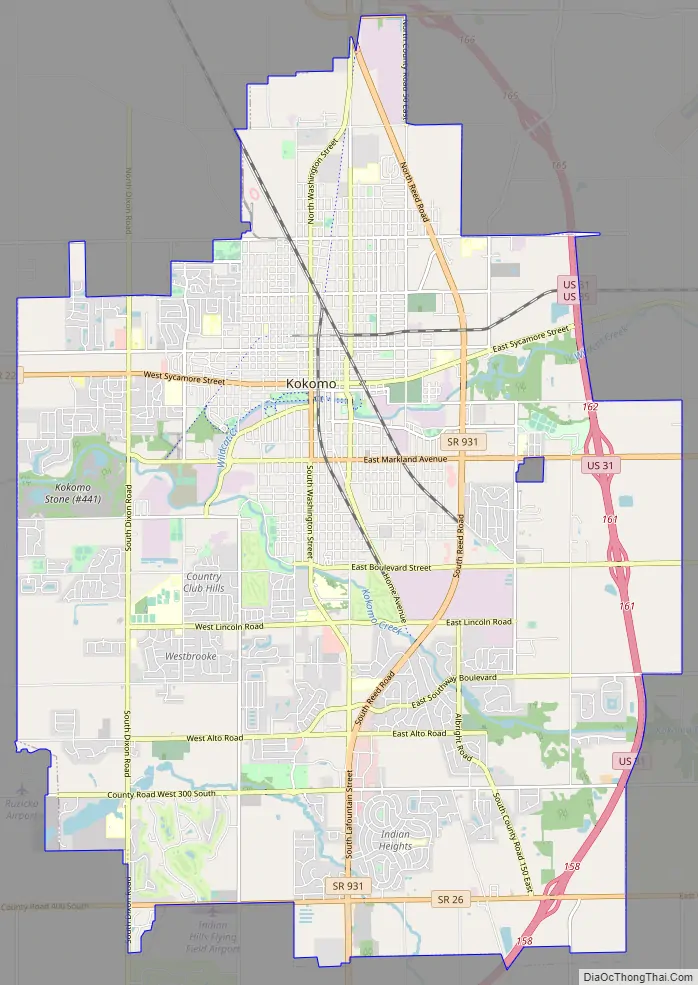
Kokomo Road Map
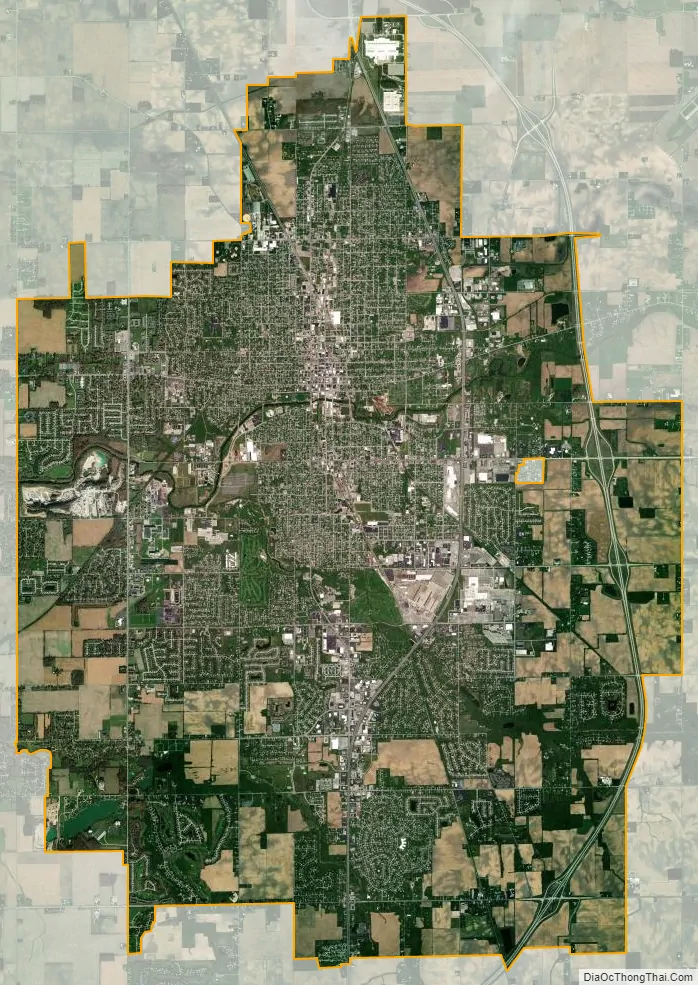
Kokomo city Satellite Map
Geography
Weather of Kokomo during December 2016
Weather of Kokomo during December 2016
U.S. 31 during winters near Kokomo
According to the 2010 census, Kokomo has a total area of 18.559 square miles (48.07 km), of which 18.5 square miles (47.91 km) (or 99.68%) is land and 0.059 square miles (0.15 km) (or 0.32%) is water.
Kokomo has a humid continental climate (Köppen Dfa).
Notable tornadoes
Kokomo has been struck by 18 tornadoes between 1950 and 2015, some of which were strong enough to claim lives.
On March 6, 1961, two F3 tornadoes struck the southern part of Kokomo, killing one person and injuring three others.
On April 11, 1965, an F4 tornado tore through portions of Russiaville, Alto, southern Kokomo, and Greentown killing 25 people and injuring hundreds of more.
On April 20, 2004, Two tornadoes struck the Northern part of Kokomo. The first tornado was rated F0 and caused little damage to homes and trees. The second tornado was rated F1 and caused a roof to collapse at the local skating rink, and damaged three other homes and a truck stop. Both tornadoes caused 1 injury and no fatalities. This was the first time ever a tornado has struck the Northern part of Kokomo.
On November 17, 2013, two EF2 tornadoes tore through the southern part of Kokomo. The first tornado Damaged over 300 homes/businesses. The second tornado touched down briefly and caused damage to the local golf course and other businesses. In all, The two tornadoes caused 0 fatalities and only five injuries.
Main #2016 tornado
On August 24, 2016, an EF3 tornado caused significant damage to the Southern part of Kokomo damaging over 1,000 homes and businesses. 80 of these homes were destroyed, 176 had their walls blown in and roofs torn off, and over 700 were damaged badly. No fatal injuries were recorded during this tornado.
See also
Map of Indiana State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Allen
- Bartholomew
- Benton
- Blackford
- Boone
- Brown
- Carroll
- Cass
- Clark
- Clay
- Clinton
- Crawford
- Daviess
- De Kalb
- Dearborn
- Decatur
- Delaware
- Dubois
- Elkhart
- Fayette
- Floyd
- Fountain
- Franklin
- Fulton
- Gibson
- Grant
- Greene
- Hamilton
- Hancock
- Harrison
- Hendricks
- Henry
- Howard
- Huntington
- Jackson
- Jasper
- Jay
- Jefferson
- Jennings
- Johnson
- Knox
- Kosciusko
- LaGrange
- Lake
- Lake Michigan
- LaPorte
- Lawrence
- Madison
- Marion
- Marshall
- Martin
- Miami
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Morgan
- Newton
- Noble
- Ohio
- Orange
- Owen
- Parke
- Perry
- Pike
- Porter
- Posey
- Pulaski
- Putnam
- Randolph
- Ripley
- Rush
- Saint Joseph
- Scott
- Shelby
- Spencer
- Starke
- Steuben
- Sullivan
- Switzerland
- Tippecanoe
- Tipton
- Union
- Vanderburgh
- Vermillion
- Vigo
- Wabash
- Warren
- Warrick
- Washington
- Wayne
- Wells
- White
- Whitley
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming