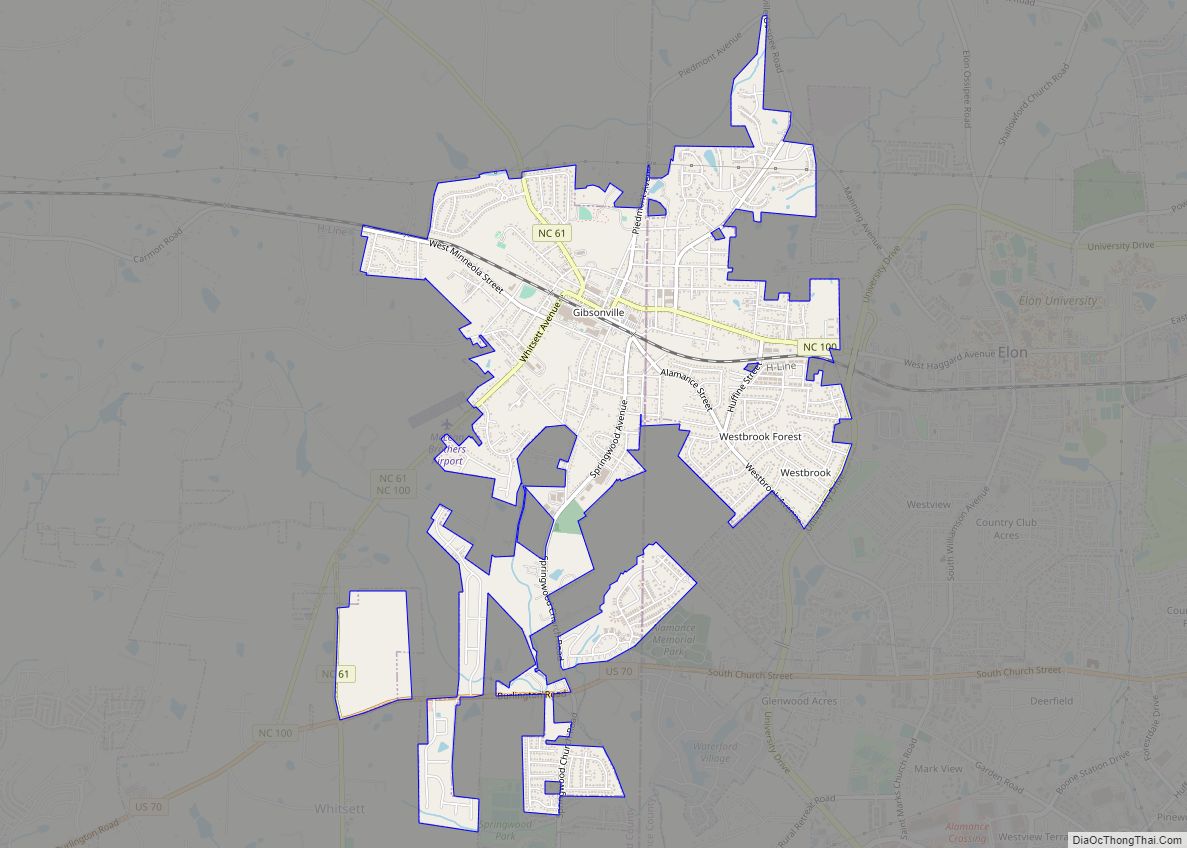
Gibsonville (“City of Roses”) is a town in both Alamance and Guilford counties in the U.S. state of North Carolina. Most of Gibsonville is situated in the Greensboro-Winston-Salem-High Point Combined Statistical Area and the eastern portion is in the Burlington, North Carolina Metropolitan Statistical Area, encompassing all of Alamance County. According to the 2020 Census, the population of Gibsonville was 8,971.
| Name: | Gibsonville town |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 43 |
| LSAD Description: | town (suffix) |
| State: | North Carolina |
| County: | Alamance County, Guilford County |
| Elevation: | 732 ft (223 m) |
| Total Area: | 3.96 sq mi (10.26 km²) |
| Land Area: | 3.94 sq mi (10.19 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.03 sq mi (0.06 km²) |
| Total Population: | 8,920 |
| Population Density: | 2,266.84/sq mi (875.13/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 27249 |
| Area code: | 336 |
| FIPS code: | 3725980 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0985675 |
| Website: | www.gibsonville.net |
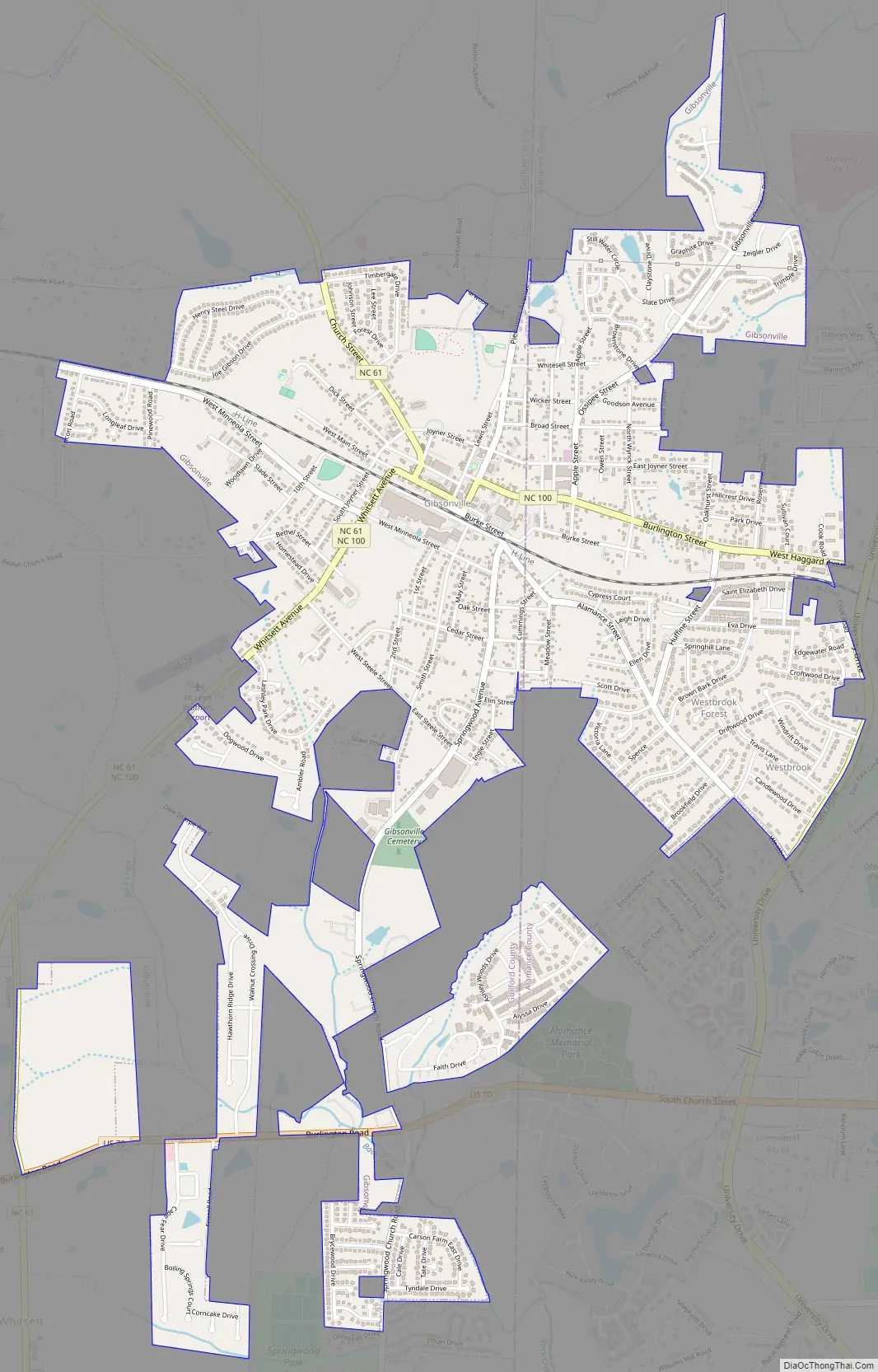
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Gibsonville location map. Where is Gibsonville town?
History
Before 1851, no official town of Gibsonville existed, only a few buildings supporting local farmers and some gold seekers.
Joseph Gibson (1785-1857), whose father established farming and gold mining operations there as early as 1775, was a local farmer who provided grading services in 1851 for the newly formed North Carolina Railroad (NCRR) Company. Shortly afterwards Gibsonville began to emerge as a commerce center.
The first train arrived on October 9, 1855, and the depot was named Gibson Station in his honor. On February 18, 1871, the state legislature issued a charter officially establishing the Town of Gibsonville.
Gold mining played a minor role here when deposits were discovered on Gibson Hill (or Gold Hill) south of town in the early 1800s. In 1888, the Chifar Consolidated Gold Mine Company began crushing ore at a mine a half mile south of the depot in Gibsonville.
The town cemetery is located in that area, but no graves have yielded gold. Captain Billy Gilmer owned one of the first stores in town built before 1860, supplying farmers and miners. His wooden general store was at the corner of Main Street and Piedmont Street where Reno’s Pizza is now. Several wooden saloons were also located downtown during the frenzied gold mining days, making Gibsonville a rough and ready town with few restrictions.
The Depot Greens served as a holding area for livestock and agricultural goods being shipped out on the railroad, which was the primary economic purpose of Gibsonville. In 1886, a local self-taught entrepreneurial mill builder, Berry Davidson, constructed the steam powered Minneola textile mill on Railroad Avenue. Subsequently, he built the Hiawatha textile mill on Eugene Street in 1893. Together, these mills transformed Gibsonville from an agricultural shipping station into a vibrant small town with an industrial base.
In 1894, Dr. Jordan built the first two-story brick building downtown on the corner of Main Street and Lewis Street, where Wade’s Jewelry is situated now. The remainder of the brick buildings facing the Greens were built between 1905 and 1920. The early 1920s were a boom time for Gibsonville when Main Street was paved, water and sewer lines installed, and street lights erected. The wooden buildings were replaced with brick structures standing today.
Prior to 1912, the Gibsonville Development Company was founded by leading citizens A. B. Owens, J.W. Burke, and D. M. Davidson (son of Berry Davidson), plus P.L. Kivett later. These civic leaders were responsible for creating the town’s telephone exchange, Bank, lumber yard, the Gibsonville Hosiery Mill on Apple Street, multiple, plus several houses. They also expanded the Rock Creek Dairy into the largest dairy in the state.
The town’s population grew slowly from 111 residents in 1890 to more than 6,410 in 2010. Most of the rapid growth occurred after 1970 when the town’s population was 2,024 residents.
When the mills closed in the 1980s the town slowly transformed itself into a commuter residential community for the Burlington and Greensboro metro area.
Gibsonville has been known as the “City of Roses” since at least 1920 when train passengers could see the large number of rose bushes along the railroad tracks at the Minneola Mill.
The Gibsonville School, Francis Marion Smith House, and Simeon Wagoner House are listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
Gibsonville Road Map
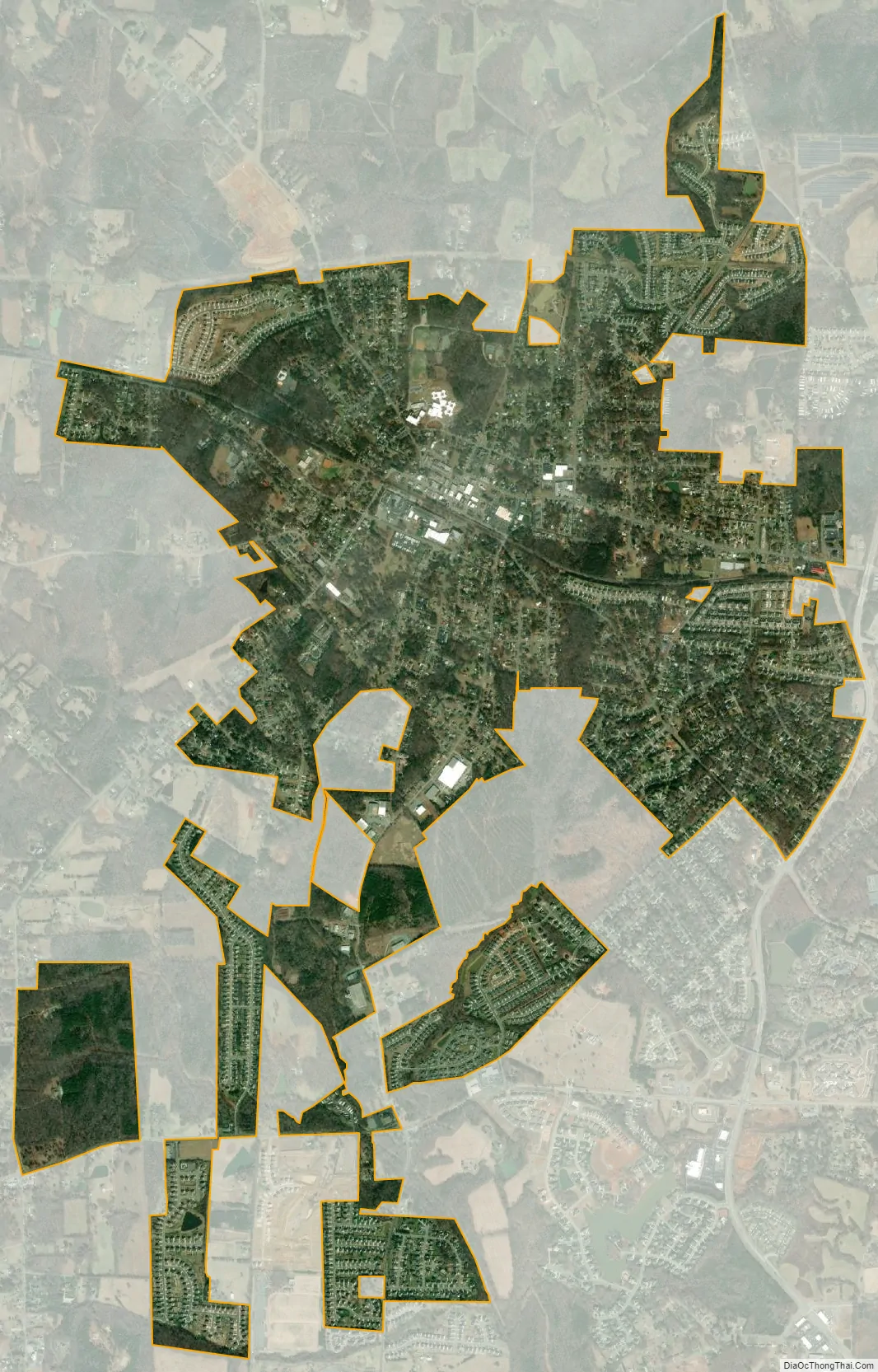
Gibsonville city Satellite Map
Geography
Gibsonville is located at 36°06′09″N 79°32′21″W / 36.102628°N 79.539078°W / 36.102628; -79.539078 (36.102628, -79.539078).
According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of 3.5 square miles (9.1 km), of which 0.012 square miles (0.03 km), or 0.28%, is water.
The town is almost evenly split between Alamance and Guilford counties, though biased towards Guilford County, but, is economically and geographically connected to the town of Elon, and Elon University in Alamance County. Gibsonville was named for Joseph Gibson, a prominent Guilford County planter of the antebellum period. Gibson’s Federal-style house remains near Gibsonville and is recognized as a Guilford County landmark property.
See also
Map of North Carolina State and its subdivision:- Alamance
- Alexander
- Alleghany
- Anson
- Ashe
- Avery
- Beaufort
- Bertie
- Bladen
- Brunswick
- Buncombe
- Burke
- Cabarrus
- Caldwell
- Camden
- Carteret
- Caswell
- Catawba
- Chatham
- Cherokee
- Chowan
- Clay
- Cleveland
- Columbus
- Craven
- Cumberland
- Currituck
- Dare
- Davidson
- Davie
- Duplin
- Durham
- Edgecombe
- Forsyth
- Franklin
- Gaston
- Gates
- Graham
- Granville
- Greene
- Guilford
- Halifax
- Harnett
- Haywood
- Henderson
- Hertford
- Hoke
- Hyde
- Iredell
- Jackson
- Johnston
- Jones
- Lee
- Lenoir
- Lincoln
- Macon
- Madison
- Martin
- McDowell
- Mecklenburg
- Mitchell
- Montgomery
- Moore
- Nash
- New Hanover
- Northampton
- Onslow
- Orange
- Pamlico
- Pasquotank
- Pender
- Perquimans
- Person
- Pitt
- Polk
- Randolph
- Richmond
- Robeson
- Rockingham
- Rowan
- Rutherford
- Sampson
- Scotland
- Stanly
- Stokes
- Surry
- Swain
- Transylvania
- Tyrrell
- Union
- Vance
- Wake
- Warren
- Washington
- Watauga
- Wayne
- Wilkes
- Wilson
- Yadkin
- Yancey
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming