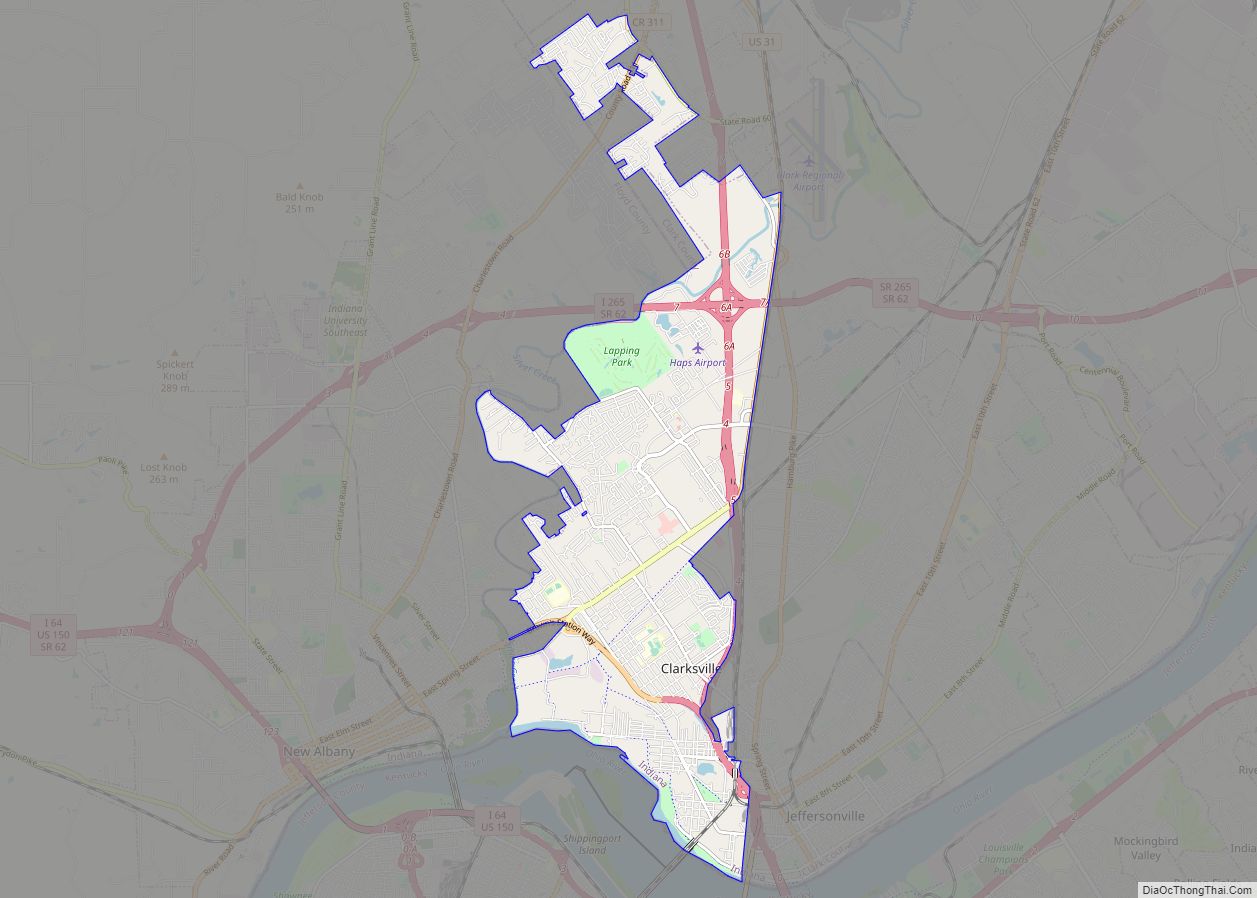
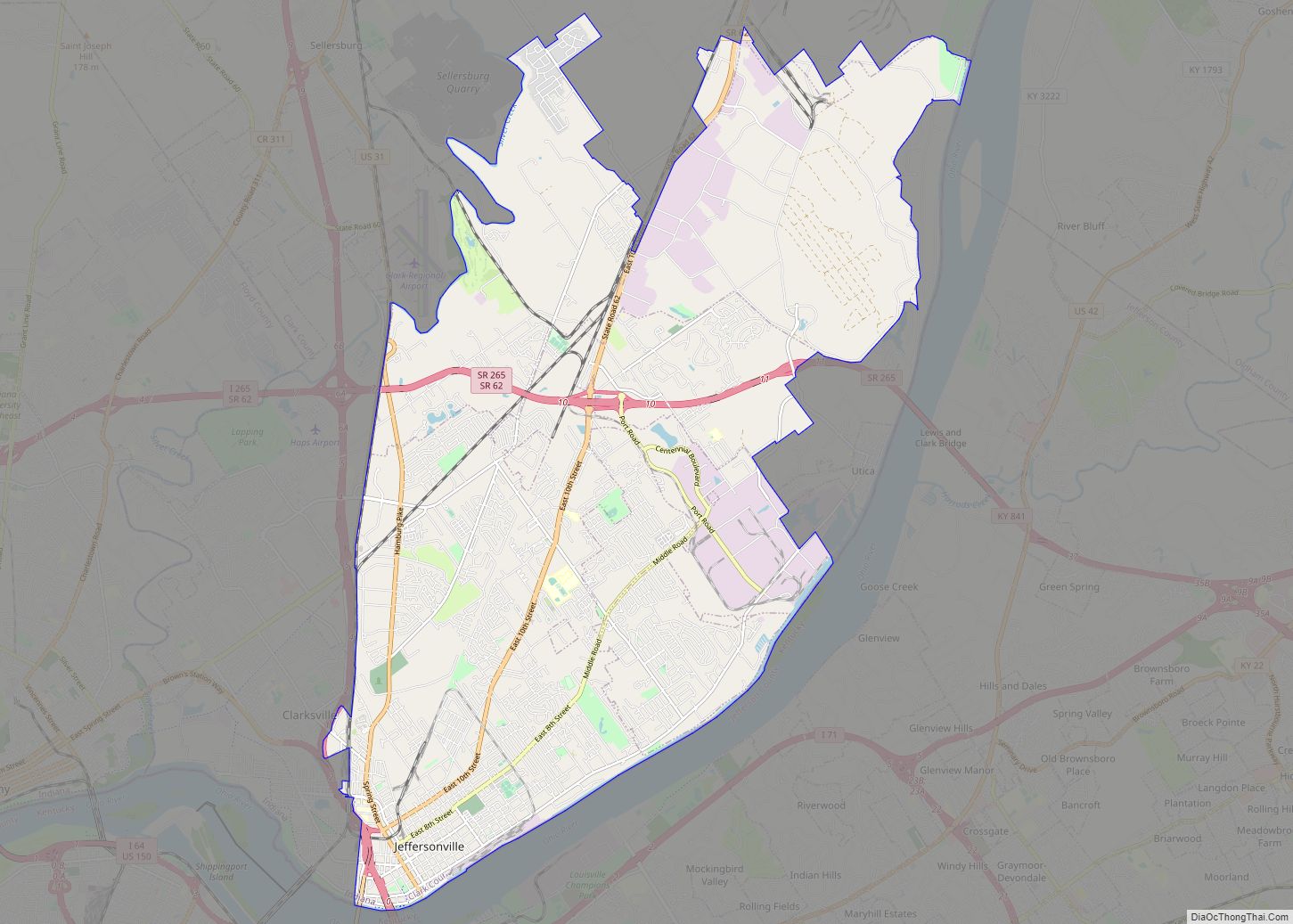
Jeffersonville is a city and the county seat of Clark County, Indiana, United States, situated along the Ohio River. Locally, the city is often referred to by the abbreviated name Jeff. It lies directly across the Ohio River to the north of Louisville, Kentucky, along I-65. The population was 49,447 at the 2020 census.
Jeffersonville began its existence as a settlement around Fort Finney after 1786 and was named after Thomas Jefferson in 1801, the year he took office.
| Name: | Jeffersonville city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Indiana |
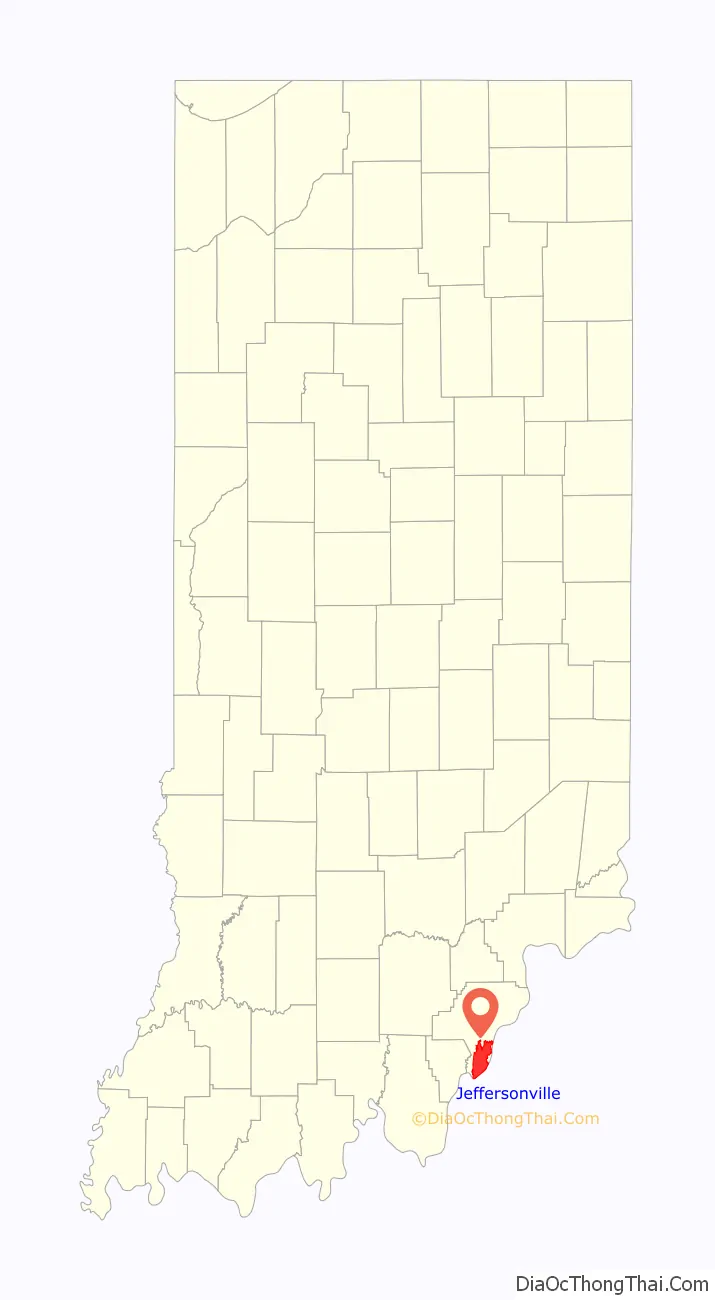
| County: | Clark County |
| Elevation: | 446 ft (136 m) |
| Total Area: | 34.35 sq mi (88.97 km²) |
| Land Area: | 34.08 sq mi (88.26 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.28 sq mi (0.71 km²) |
| Total Population: | 49,447 |
| Population Density: | 1,451.04/sq mi (560.26/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 47130, 47131, and 47199 |
| Area code: | 812 & 930 |
| FIPS code: | 1838358 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0436979 |
| Website: | cityofjeff.net |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Jeffersonville location map. Where is Jeffersonville city?
History
18th century
The foundation for what would become Jeffersonville began in 1786 when Fort Finney was established near where the Kennedy Bridge is today. U.S. Army planners chose the location for its view of a nearby bend in the Ohio River, which offered a strategic advantage in the protection of settlers from Native Americans. Overtime, a settlement grew. In 1791 the fort was renamed to Fort Steuben in honor of Baron von Steuben. Then in 1793 the fort was abandoned.
19th century
Precisely when the settlement became known as Jeffersonville is unclear, but it was probably around 1801, the year in which President Thomas Jefferson took office. In 1802 local residents used a grid pattern designed by Thomas Jefferson for the formation of a city. On September 13, 1803, a post office was established in the city. In 1808 Indiana’s second federal land sale office was established in Jeffersonville, which initiated a growth in settling in Indiana that was further spurred by the end of the War of 1812.
In 1802, Jeffersonville replaced Springville as the county seat of Clark County. Charlestown was named the county seat in 1812 but it returned to Jeffersonville in 1878, where it remains.
In 1813 and 1814 Jeffersonville was briefly the de facto capital of the Indiana Territory, as then-governor Thomas Posey disliked then-capital Corydon and decided to live in Jeffersonville to be closer to his personal physician in Louisville. The territorial legislature remained in Corydon and communicated with Posey by messenger.
In 1819 the first shipbuilding took place in Jeffersonville, and steamboats would become key to Jeffersonville’s economy. In 1834, James Howard built his first steamboat, named the Hyperion, in Jeffersonville. He established his ship building company in Jeffersonville that year but moved his business to Madison, Indiana in 1836 and remained there until 1844. Howard returned his business to the Jeffersonville area to its final location in Port Fulton in 1849. There is an annual festival held in September called Steamboat Days that celebrates Jeffersonville’s heritage.
As a free state bordering the south, Indiana served as a crucial step along the Underground Railroad. By 1830, Jeffersonville was the first and largest route for fugitives crossing the Ohio River at Louisville. Hundreds of freedom seekers made their way north to Canada through Clark County.
During the Civil War Jeffersonville was one of the principal gateways to the South. This was largely due to its location directly opposite Louisville. Three railroads (including the Jeffersonville Railroad and the Ohio and Mississippi Railway) served Jeffersonville from the north, as well as the waterway of the Ohio River. Operating in the South, the Louisville and Nashville Railroad furnished the connecting link between Louisville and the rest of the South. These factors made the city a good location to house supplies and troops for the Union Army.
In 1862, two area regiments established the first military camp in the city. The location was christened Camp Joe Holt, and the name was retained when the camp was converted to a hospital called Joe Holt Hospital.
In September and October 1862, two Confederate armies led by Generals Braxton Bragg and E. Kirby Smith closed in on Louisville, a key strategic prize. General William “Bull” Nelson ordered women and children to evacuate. So many fled across the river to Jeffersonville that the city’s hotels and rooming houses were filled to capacity. On September 24, General Don Carlos Buell and his men managed to reach Louisville barely ahead of the Confederates. The force of 100,000 Union soldiers successfully defended Louisville and forestalled any invasion.
Between 1864 and 1866 Port Fulton (now within Jeffersonville) was home to Jefferson General Hospital, the third largest hospital in the country at that time. The institution was built to replace Joe Holt Hospital and occupied land obtained from U.S. Senator Jesse D. Bright, a Confederate sympathizer. The land stretched down to the Ohio River, facilitating patient transfer from riverboats to the hospital. The facility contained 24 wards each radiating out like spokes on a wheel and all connected by a corridor one-half mile in circumference. Each ward was 150 feet long and 22 feet wide and could accommodate 60 patients. Female nurses and matrons were quartered separately from the men. During its nearly three year existence the institution cared for more than 16,000 patients and served more than 2,500,000 meals.
The Jeffersonville Quartermaster Depot had its first beginnings in the early days of the Civil War as a storage depot for the Union Quartermaster Department. As the war came to a close all military supply depots along the Ohio Valley were shut down (except Jeffersonville’s), and their supplies were stored at the Jeffersonville location. In 1871, the U.S. Army began consolidating operations in the city into four square blocks. Throughout the rest of the 19th century, the Quartermaster Depot continued supplying troops engaged in frontier wars with Native Americans.
20th and 21st century
On December 17, 1900, Jeffersonville officially opened a new Jeffersonville Township Public Library in a room above the Citizens National Bank. 1400 books formed the initial collection. Soon, the Carnegie Foundation donated $16,000 for the construction of a new library building – a beaux arts, copper-domed landmark. The building was designed by Jeffersonville architect Arthur Loomis. Masonic officials laid the building’s cornerstone on September 19, 1903, in Warder Park. When the Carnegie Library opened in 1905, it contained 3,869 volumes. Whereas in later years grants from the Carnegie Foundation were scaled back to prevent the construction of lavish libraries, the library in Warder Park was relatively ornate.
Due to the Ohio River Flood of 1937, the library suffered a near total loss of its collection. However, it reopened in November 1937 thanks to months of work and donations of money and books.
During World War I, Jeffersonville contributed to the war effort largely through its production capabilities. On the eve of war, the Quartermaster Depot began producing a wide range in items, including saddles, harnesses, stoves, and kitchen utensils. Most famously, though, the depot produced 700,000 shirts per month, earning it the nickname “America’s largest shirt factory.” Meanwhile, the American Car and Foundry Company’s local plant manufactured a variety of products ranging from components for over 228,000 artillery shells to 18,156 cake turners.
Shortly after the war ended in 1918, civilian employment at the Quartermaster Depot fell to 445, and military presence dropped to just ten officers and two enlisted.
For a brief period in the mid-1920s and early 1930s, Roy E. Davis, a founding member of the 1915 Ku Klux Klan, hosted a series of religious revivals in Jeffersonville. He also moved his First Pentecostal Baptist Church there, and held revivals in neighboring states. Meanwhile, he routinely challenged the Jeffersonville Evening News for its depiction of his church, eventually starting a new publication called The Banner of Truth to publicize his services and aid recruitment. Much of his popularity stemmed from his vocal opposition of prohibition.
In 1934, a fire destroyed Davis’s First Pentecostal Baptist Church. After years of legal trouble, Davis was denied a permit to rebuild. He left Jeffersonville, and William Branham – formerly a ministering elder in Davis’s church – became pastor of the congregation. Branham moved the group to a new building, eventually naming it Branham Tabernacle, as it is known today.
Between January 9 and 23 the Ohio Valley was inundated with record rainfall, swelling the Ohio River and flooding surrounding communities. In Jeffersonville, where 90% of the city was flooded, electricity was lost, all roads leading into the city were covered, and a levee failed. By January 21 the Indiana National Guard arrived in the area to help those displaced, distribute much-needed emergency supplies, inoculate residents for typhoid fever, and purify drinking water. Finally, on January 26 the water began to recede, leaving an estimated $250 million worth of damage throughout the Ohio Valley.
In the 1930s and 1940s, gambling was instrumental in Jeffersonville’s recovery from the Great Depression and the Flood of 1937. This earned the town the nickname “Little Las Vegas“. During this time, Jeffersonville attracted the likes of Clark Gable, John Dillinger, Al Capone, and others. After Clarence Amster, a New Albany resident was gunned down on July 2, 1937, public sentiment turned against gambling and the mobsters it brought. In 1938, James L. Bottorff was elected judge and announced that gambling would not be tolerated. The Club Greyhound, a major dog racing track known for fixing races, was raided and closed within a year, with others soon following.
Having acquired the Howard Shipyards in 1925, the U.S. Navy awarded the Jeffersonville Boat & Machine Company (later known as Jeffboat) a contract to build boats during World War II. Jeffboat built landing vessels such as the LST, and swelled in number of employees from 200 to 13,000 people. After the war ended, the Navy sold the Howard Shipyard to Jeffboat.
Also during World War II, the Quartermaster Depot, in conjunction with Fort Knox, Kentucky, housed German prisoners of war until 1945.
Jeffersonville ended segregation in its public schools in 1952, two years before the Supreme Court case Brown v. Board of Education ruled that segregation was unconstitutional. Prior to this, Jeffersonville High School was reserved for white high school students. Meanwhile, black students in grades one through twelve were sent to Taylor High School. While the New York Times held up Jeffersonville as a model for all “southern-minded” cities, integration came at a cost. Though black students were allowed to attend the newly integrated Jeffersonville High School, black instructors previously employed at Taylor High School were terminated.
On February 5, 2008 the city of Jeffersonville officially annexed four out of six planned annex zones. The proposed annexation of the other two zones was postponed due to lawsuits. One of the two areas remaining to be annexed was Oak Park, Indiana an area of about 5,000 more citizens. The areas annexed added about 5,500 acres (22 km) to the city and about 4,500 citizens, raising the population to an estimated 33,100. The total area planned to be annexed was 7,800 acres (32 km). The areas received planning and zoning, building permits and drainage issues services immediately, with new in-city sewer rates. Other services were phased in, such as police and fire, and worked jointly with the pre-existing non-city services until they were available.
The Clark County Courts dismissed the lawsuits against the city on February 25, 2008. This dismissal brought the remaining Oak Park area into the city. The population of the city grew to nearly 50,000 citizens, making it the largest annexation in Jeffersonville’s history.
Conceived in the 1990s and completed in 2014, the Big Four Bridge was converted to a pedestrian bridge in a joint effort between Kentucky and Indiana governments. An average of 1.5 million pedestrians and bicycles cross the roughly-1/2 mile bridge each year. 1/4 mile ramps complete the bridge on each end. The bridge is also decorated with a colorful LED lighting system that operates from twilight to 1 am. The lights can be customized by request.
On the Jeffersonville side of the bridge the city constructed Big Four Station, a plaza and park. The park features green space, fountains, a farmers market on Saturdays, a restroom, a bike-sharing station, a pavilion, a playground, and easy access to downtown shops and restaurants. Big Four Station is also the home of the annual Abbey Road on the River, the largest Beatles-inspired music festival in the world, as well as other annual celebrations.
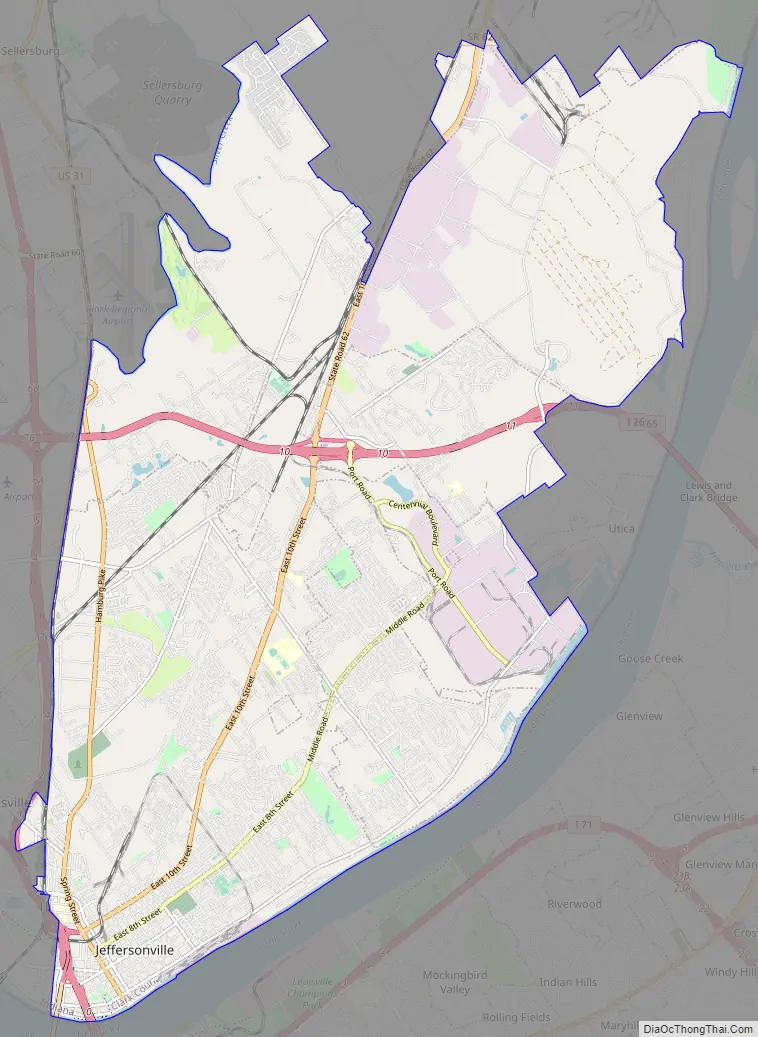
Jeffersonville Road Map
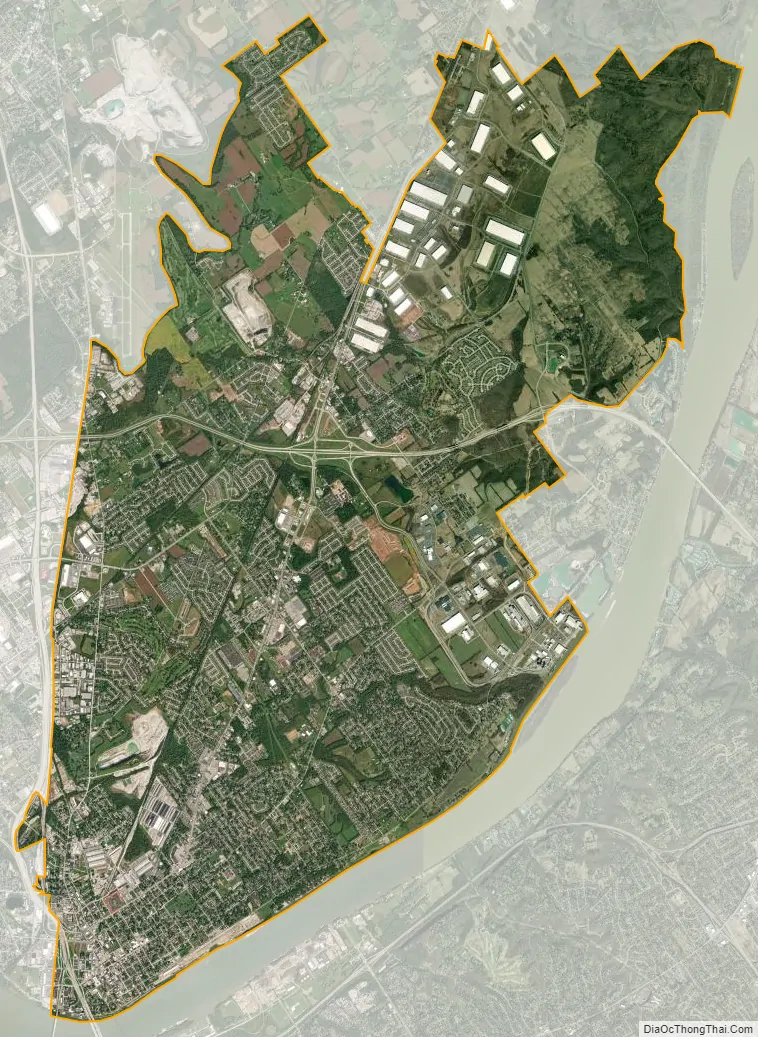
Jeffersonville city Satellite Map
Geography
Jeffersonville is located at 38°17′44″N 85°43′53″W / 38.29556°N 85.73139°W / 38.29556; -85.73139 (38.295669, -85.731485).
According to the 2010 census, Jeffersonville has a total area of 34.354 square miles (88.98 km), of which 34.06 square miles (88.21 km) (or 99.14%) is land and 0.294 square miles (0.76 km) (or 0.86%) is water.
See also
Map of Indiana State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Allen
- Bartholomew
- Benton
- Blackford
- Boone
- Brown
- Carroll
- Cass
- Clark
- Clay
- Clinton
- Crawford
- Daviess
- De Kalb
- Dearborn
- Decatur
- Delaware
- Dubois
- Elkhart
- Fayette
- Floyd
- Fountain
- Franklin
- Fulton
- Gibson
- Grant
- Greene
- Hamilton
- Hancock
- Harrison
- Hendricks
- Henry
- Howard
- Huntington
- Jackson
- Jasper
- Jay
- Jefferson
- Jennings
- Johnson
- Knox
- Kosciusko
- LaGrange
- Lake
- Lake Michigan
- LaPorte
- Lawrence
- Madison
- Marion
- Marshall
- Martin
- Miami
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Morgan
- Newton
- Noble
- Ohio
- Orange
- Owen
- Parke
- Perry
- Pike
- Porter
- Posey
- Pulaski
- Putnam
- Randolph
- Ripley
- Rush
- Saint Joseph
- Scott
- Shelby
- Spencer
- Starke
- Steuben
- Sullivan
- Switzerland
- Tippecanoe
- Tipton
- Union
- Vanderburgh
- Vermillion
- Vigo
- Wabash
- Warren
- Warrick
- Washington
- Wayne
- Wells
- White
- Whitley
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming