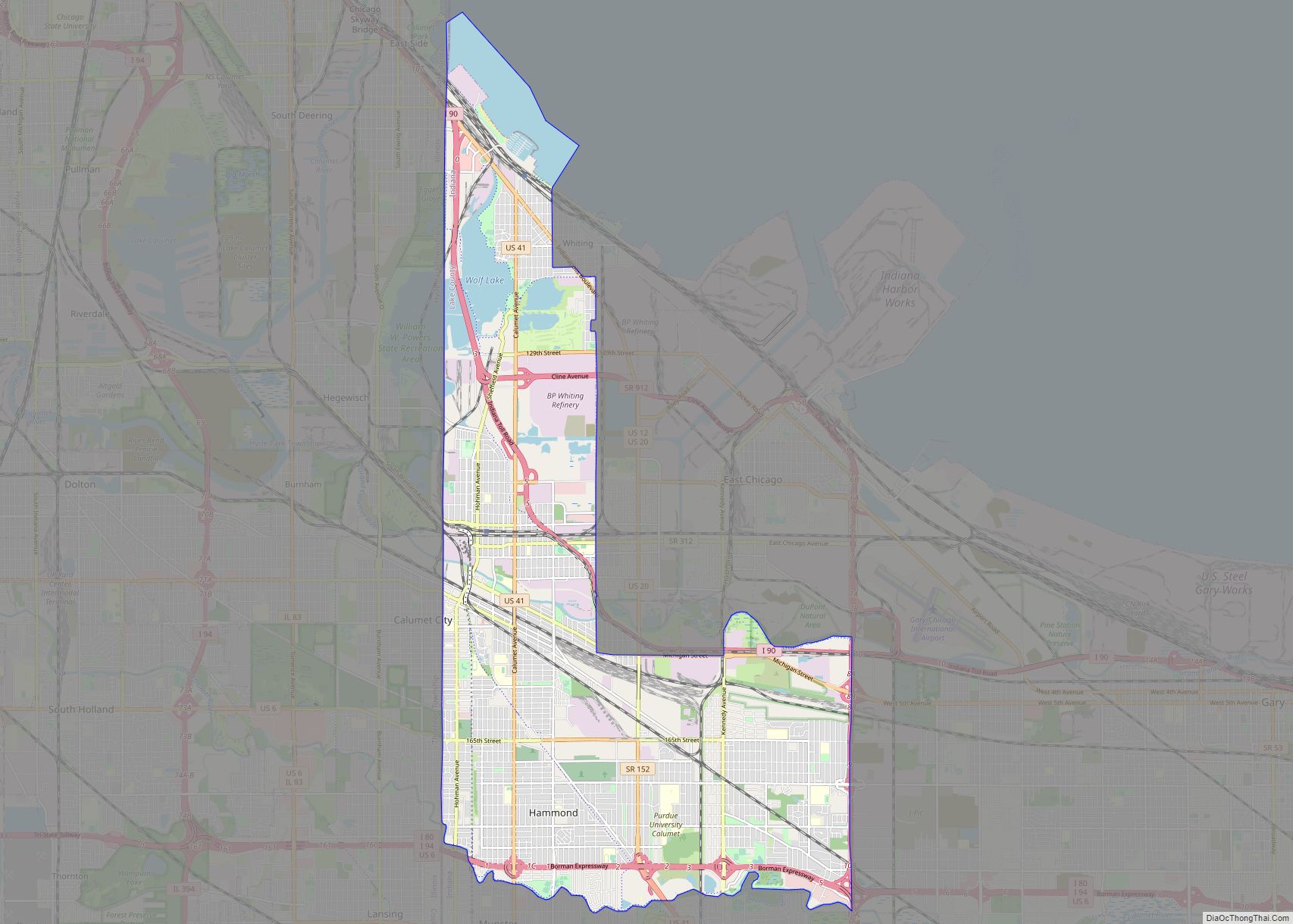
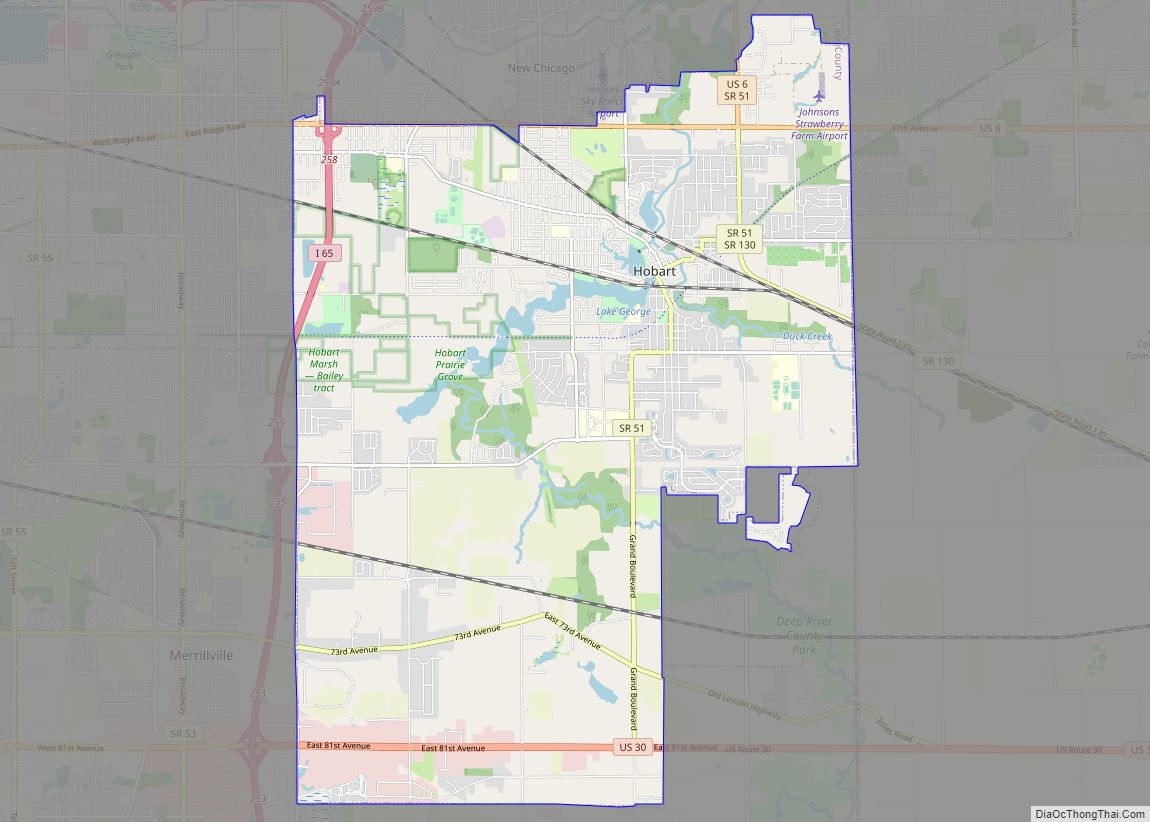
Hammond (/ˈhæmənd/ HAM-ənd) is a city in Lake County, Indiana, United States. It is part of the Chicago metropolitan area, and the only city in Indiana to border Chicago. First settled in the mid-19th century, it is one of the oldest cities of northern Lake County. As of the 2020 United States census, it is also the largest in population. The 2020 population was 77,879, replacing Gary as the most populous city in Lake County. From north to south, Hammond runs from Lake Michigan down to the Little Calumet River; from east to west along its southern border, it runs from the Illinois state line to Cline Avenue. The city is traversed by numerous railroads and expressways, including the South Shore Line, Borman Expressway, and Indiana Toll Road. Notable local landmarks include the parkland around Wolf Lake and the Horseshoe Hammond riverboat casino. Part of the Rust Belt, Hammond has been industrial almost from its inception, but is also home to a Purdue University campus and numerous historic districts that showcase the residential and commercial architecture of the early 20th century.
| Name: | Hammond city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Indiana |
| County: | Lake County |
| Elevation: | 577–610 ft (176–186 m) |
| Total Area: | 23.81 sq mi (61.68 km²) |
| Land Area: | 22.73 sq mi (58.86 km²) |
| Water Area: | 1.09 sq mi (2.81 km²) |
| Total Population: | 77,879 |
| Population Density: | 3,426.72/sq mi (1,323.04/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 46320, 46323-25, 46327 |
| Area code: | 219 |
| FIPS code: | 1831000 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0435658 |
| Website: | www.gohammond.com |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
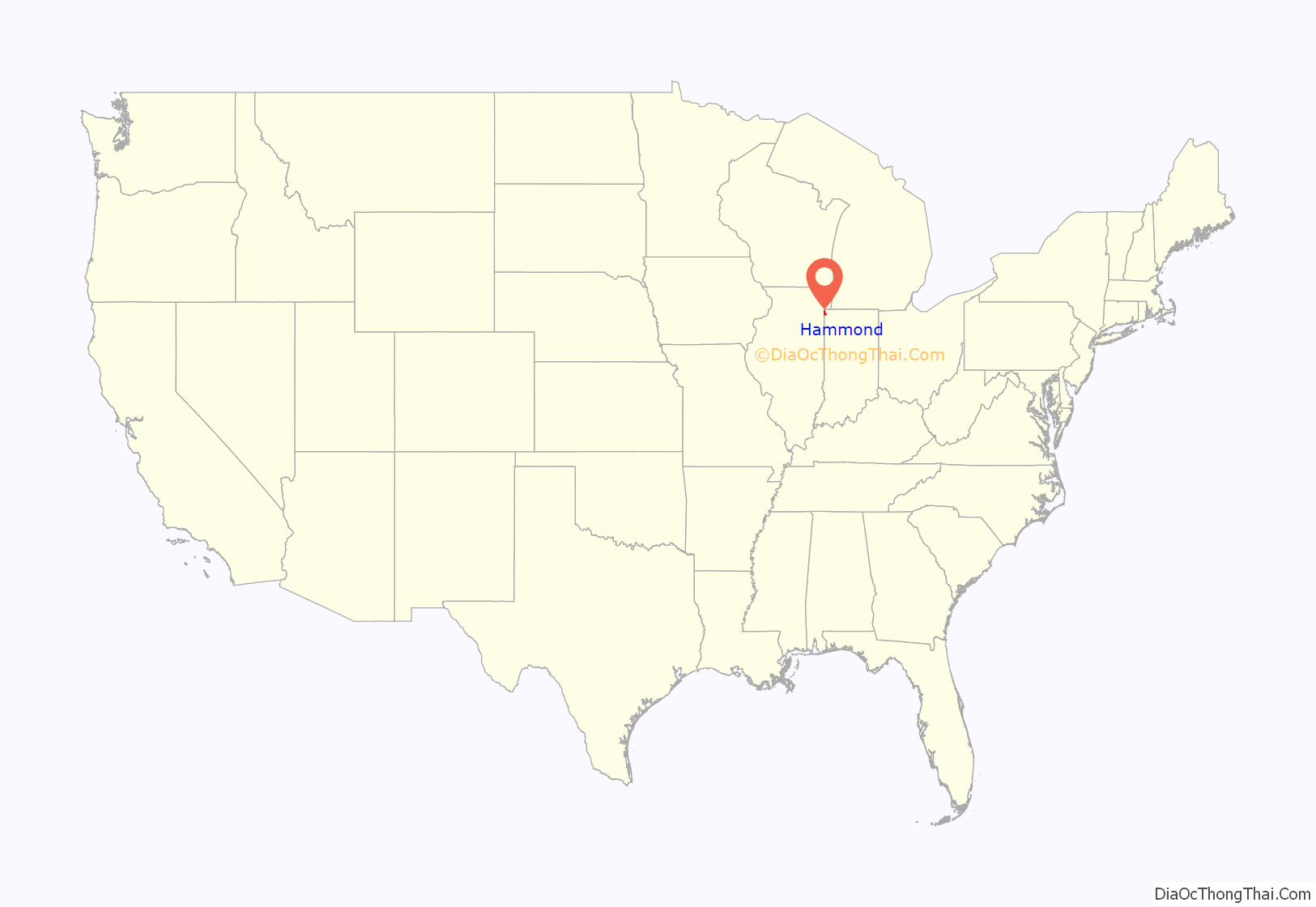
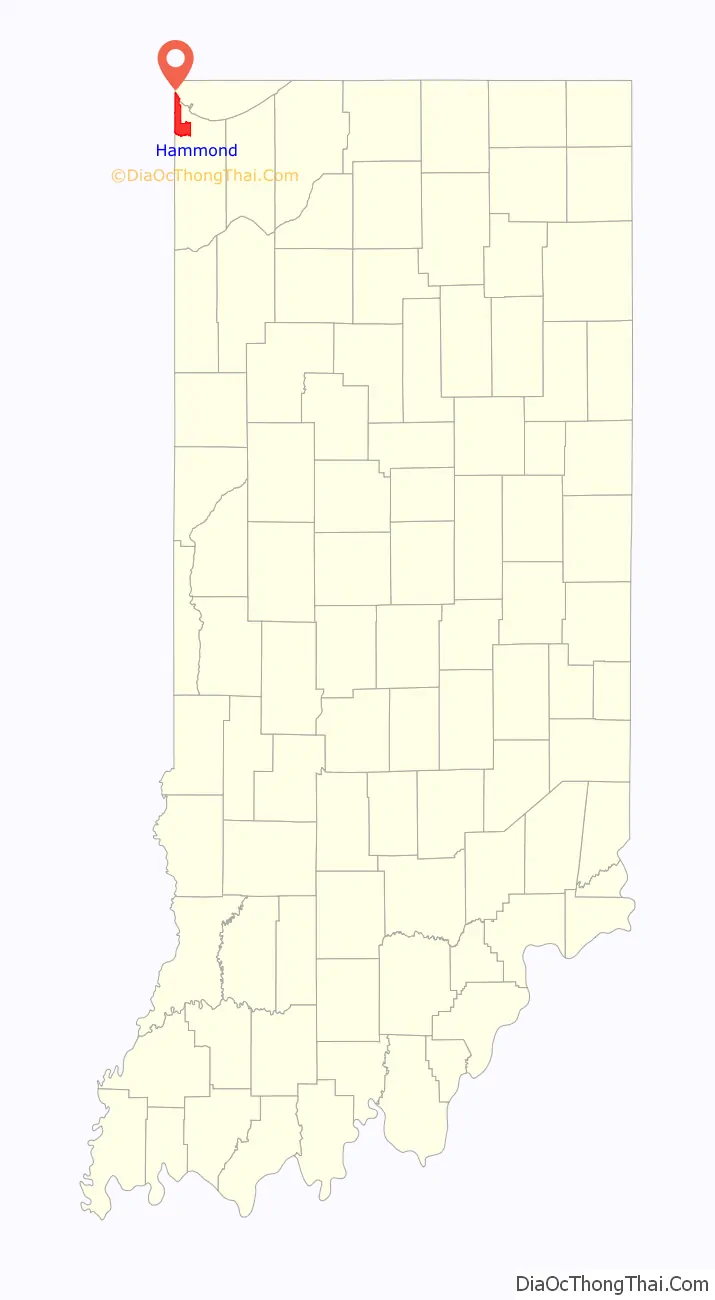
Hammond location map. Where is Hammond city?
History
The first permanent residents arrived around 1847 to settle on land between the Grand and Little Calumet Rivers, on the south end of Lake Michigan. Those first residents were German farmers newly arrived from Europe looking for land and opportunity. Before that time, the area was a crossroad for Indian tribes, explorers, stagecoach lines and supply lines to the West. Convenient location and abundant fresh water from Lake Michigan led to the beginning of Hammond’s industrialization in 1869 with the George H. Hammond Company meat-packing plant following merchants and farmers to the area. Hammond was incorporated on April 21, 1884, and was named after the Detroit butcher.
Hammond is one of the oldest cities in Lake County, with Crown Point being the oldest, established in 1834. According to the Encyclopedia of Chicago, George Henry Hammond, a pioneer in the use of refrigerated railcars for the transport of fresh meat, first used this method with his small packing company in Detroit, Michigan. In 1868, Hammond received a patent for a refrigerator car design. In the early 1870s, he built a new plant in northern Indiana along the tracks of the Michigan Central Railroad. By 1873, the George H. Hammond Co. was selling $1 million worth of meat a year; by 1875, sales were nearly $2 million. The company’s large packing house in Hammond rivaled those located at the Union Stock Yard in Chicago. By the middle of the 1880s, when it built a new plant in Omaha, Nebraska, Hammond was slaughtering over 100,000 cattle a year and owned a fleet of 800 refrigerator cars. After Hammond died in 1886, the company became less important and no longer challenged the giant Chicago packers, who acquired Hammond at the turn of the century and merged it into their National Packing Co.
The Hammond Whiting & East Chicago Electric Railway Company trolley service ran from 1893 to 1940.
On June 22, 1918, the Hammond circus train wreck occurred about 5.5 miles (8.9 km) east of the city, killing 86 and injuring 127 persons.
The downtown Hammond shopping district along State Street and Hohman Avenue included major chains such as Sears and J. C. Penney. The largest stores in downtown were the Goldblatt’s and E.C. Minas department stores. The E.C. Minas store was constructed in 1894 and was in business until August 1984. The building which housed the Goldblatt’s store had been purchased by the Chicago-based retailer in 1931 and operated until 1982 when it closed due to bankruptcy.
The Pullman Standard Car Company built M4 Sherman tanks in Hammond during World War II.
Architect Victor Gruen designed the Woodmar Mall in the Woodmar neighborhood. The mall opened in 1954 and was anchored by a Carson Pirie Scott and Co. store.
According to the 1960 United States Census Hammond’s population reached a record high of 111,698 residents. Hammond, like other industrial cities in the Rust Belt, went into decline during the 1970s and 1980s, with the city’s population plunging to 94,000 in 1980, and 83,000 in 2000. However, Hammond’s economy was more diversified than neighboring Gary, Indiana, East Chicago, Indiana, and the south side of Chicago, which all relied on heavy industry (primarily steel production). Hammond’s economy, on the other hand, depended on light manufacturing, transportation & warehousing, retail, banking & insurance, healthcare, hospitality & food service, and construction. In 1981, a toxic flood in Gary led Hammond to erect a barrier on 165th Street, one of several roads connecting the two cities, which led to lasting tensions with Gary.
Prominent manufacturing companies in Hammond include Unilever’s soap factory, Atlas Tube, Cargill food processing, Munster Steel, Lear Seating Corporation, Jupiter Aluminum, Tri-State Automation, and Dover Chemical. Warehousing and storage is also prominent, with ExxonMobil and Marathon Petroleum having large oil storage facilities, and FedEx has a distribution center. Large railroad marshalling yards are also present in the city, with the Indiana Harbor Belt Railroad’s headquarters in the city. The State Line Generating Plant operated on the Indiana-Illinois state line from 1929 to 2012, and was demolished in 2014.
The Empress Casino opened in Hammond in June 1996 and was replaced with the Horseshoe Hammond casino in 2001.
In February 2006, the decision was made to demolish Woodmar Mall except for the Carson’s store. The Hammond Redevelopment Commission announced plans in June 2016 for a $12 million sports complex to be built on the site of the former mall. The Carson’s store closed in 2018, and was demolished in 2019, as part of its parent company’s liquidation.
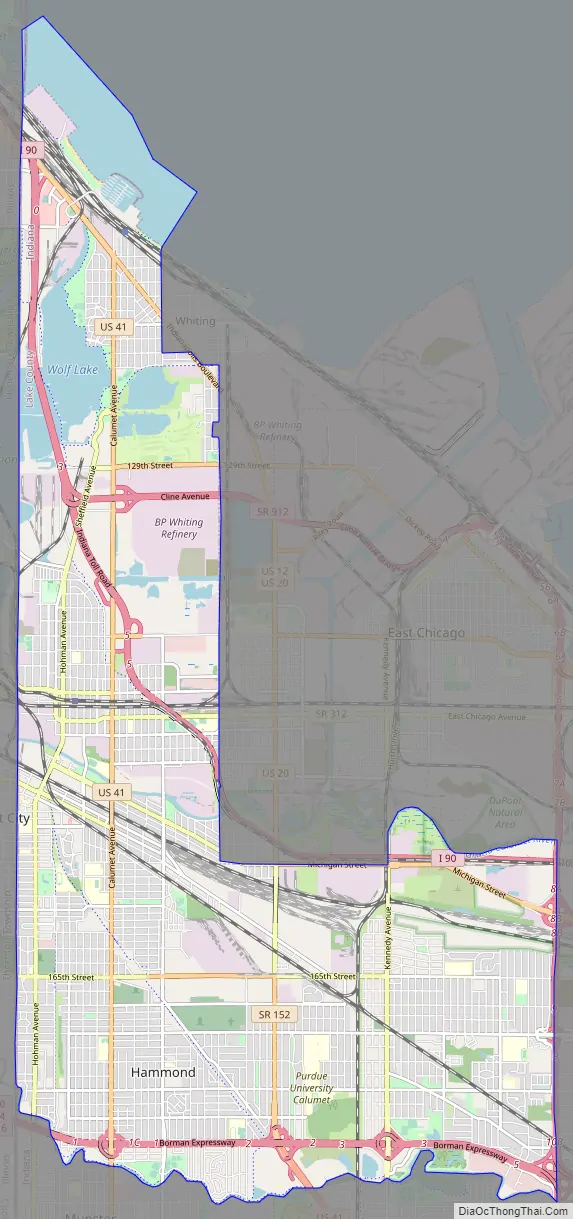
Hammond Road Map
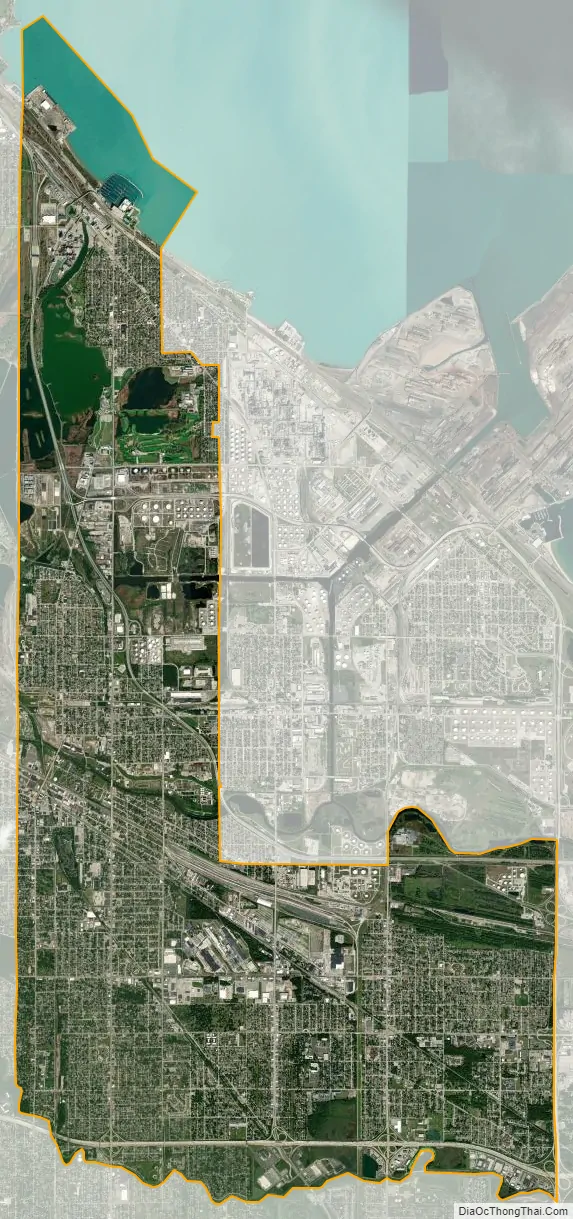
Hammond city Satellite Map
Geography
The city sits within the boundaries of the former Lake Chicago, and much of its land area consists of former dune and swale terrain that was subsequently leveled. Most of the city is on sandy soil with a layer of black topsoil that varies from non-existent to several feet (a meter or more) thick. Much of the exposed sand was removed for purposes such as industrial use to make concrete and glass. According to the 2010 census, Hammond has a total area of 24.886 square miles (64.45 km), of which 22.78 square miles (59.00 km) (or 91.54%) is land and 2.106 square miles (5.45 km) (or 8.46%) is water.
Neighborhoods
- Lakefront
- Marina District
- Five Points
- Robertsdale
- Water Gardens
- North Hammond
- Pulaski Park
- Downtown Hammond
- Central Hammond
- South Hammond
- Woodmar
- Schleicher
- Hessville
Lakes and rivers
- Grand Calumet River (partial)
- Lake George
- Lake Michigan (partial)
- Little Calumet River (partial)
- Oxbow Lake
- Wolf Lake (partial)
Adjacent cities, towns and villages
- Burnham
- Calumet City
- Chicago
- Lansing
- East Chicago
- Gary
- Griffith
- Highland
- Munster
- Whiting
See also
Map of Indiana State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Allen
- Bartholomew
- Benton
- Blackford
- Boone
- Brown
- Carroll
- Cass
- Clark
- Clay
- Clinton
- Crawford
- Daviess
- De Kalb
- Dearborn
- Decatur
- Delaware
- Dubois
- Elkhart
- Fayette
- Floyd
- Fountain
- Franklin
- Fulton
- Gibson
- Grant
- Greene
- Hamilton
- Hancock
- Harrison
- Hendricks
- Henry
- Howard
- Huntington
- Jackson
- Jasper
- Jay
- Jefferson
- Jennings
- Johnson
- Knox
- Kosciusko
- LaGrange
- Lake
- Lake Michigan
- LaPorte
- Lawrence
- Madison
- Marion
- Marshall
- Martin
- Miami
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Morgan
- Newton
- Noble
- Ohio
- Orange
- Owen
- Parke
- Perry
- Pike
- Porter
- Posey
- Pulaski
- Putnam
- Randolph
- Ripley
- Rush
- Saint Joseph
- Scott
- Shelby
- Spencer
- Starke
- Steuben
- Sullivan
- Switzerland
- Tippecanoe
- Tipton
- Union
- Vanderburgh
- Vermillion
- Vigo
- Wabash
- Warren
- Warrick
- Washington
- Wayne
- Wells
- White
- Whitley
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming