Muleshoe is a city in Bailey County, Texas, United States. It was founded in 1913, when the Pecos and Northern Texas Railway built an 88-mile (142 km) line from Farwell, Texas, to Lubbock through northern Bailey County. In 1926, Muleshoe was incorporated. Its population was 5,158 at the 2010 census. The county seat of Bailey County, it is home to the National Mule Memorial.
The Muleshoe Heritage Center, located off the combined U.S. Routes 70 and 84, is a popular museum that commemorates the importance of ranching to West Texas. The complex has several unique buildings originally from Bailey County that display the living conditions of the area from the late 19th to the mid-20th centuries.
The Muleshoe National Wildlife Refuge is located some 20 mi (32 km) to the south on State Highway 214. Founded in 1935, the refuge is the oldest of its kind in Texas. It is a 5,000-acre (20 km) wintering area for migratory waterfowl flying from Canada to Mexico. It contains the largest number of sandhill cranes in North America.
| Name: | Muleshoe city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Texas |
| County: | Bailey County |
| Elevation: | 3,793 ft (1,156 m) |
| Total Area: | 3.43 sq mi (8.89 km²) |
| Land Area: | 3.43 sq mi (8.89 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km²) |
| Total Population: | 5,158 |
| Population Density: | 1,462.84/sq mi (564.81/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 79347 |
| Area code: | 806 |
| FIPS code: | 4849968 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1375067 |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Muleshoe location map. Where is Muleshoe city?
History
The name Muleshoe can be traced in the region to Henry Black, when he registered a brand on November 12, 1860. In 1877, Black purchased three houses on 40,000 acres (160 km) in Stephens County, naming it Muleshoe Ranch. Later, he built a large ranch house and a log schoolhouse, and established a small cemetery for family members. Muleshoe Ranch was supposedly named after the owner found a mule shoe in the soil.
On April 23, 1906, the Gulf, Santa Fe and Northwestern Railway Company and the Pecos and Northern Texas Railway Company merged (eventual successor BNSF Railway) and were chartered to construct a railway between Lubbock and Farwell on the New Mexico border. From 1901 to 1915, communities along the future railway contributed hundreds of thousands of dollars to its construction. Muleshoe was founded in 1913 when the Pecos and Northern Texas Railway laid rails across northern Bailey County; residents borrowed the name from the nearby Muleshoe Ranch.
Soon after the railroad passed through Muleshoe, the town expanded rapidly. In 1917, Muleshoe became the county seat after the county was organized, but it was not incorporated until 1926. Muleshoe continued to grow quickly, and by 1930, 800 residents were in the town. Three decades later, Muleshoe had tripled in population to 3,871. In 1970, Muleshoe reached its pinnacle at over 5,000 residents, 200 businesses, two hospitals, two banks, a library, a newspaper, and a radio station.
During the 1970s and 1980s the population stagnated, and by the 1990s Muleshoe’s population had begun to decrease. The population went from 5,048 in 1988 to 4,530 in 2000. The once lively and vibrant Main Street is now quiet, with many abandoned buildings. Many of the businesses that once called Main Street home are now on American Boulevard (US Highway 84/70).
During the early 1960s, Texas residents were eager to build a memorial to the mule for its strength and sparse eating habits, traits that endeared it to the pioneers. In war, the mule carried cannon; in peace, it hauled freight. Its small hooves allowed it to scale rocky areas. The Mule Memorial was first displayed on July 4, 1965, near the intersection of US 70/84. Muleshoe is the home of the world’s largest mule shoe, at the Muleshoe Heritage Center.
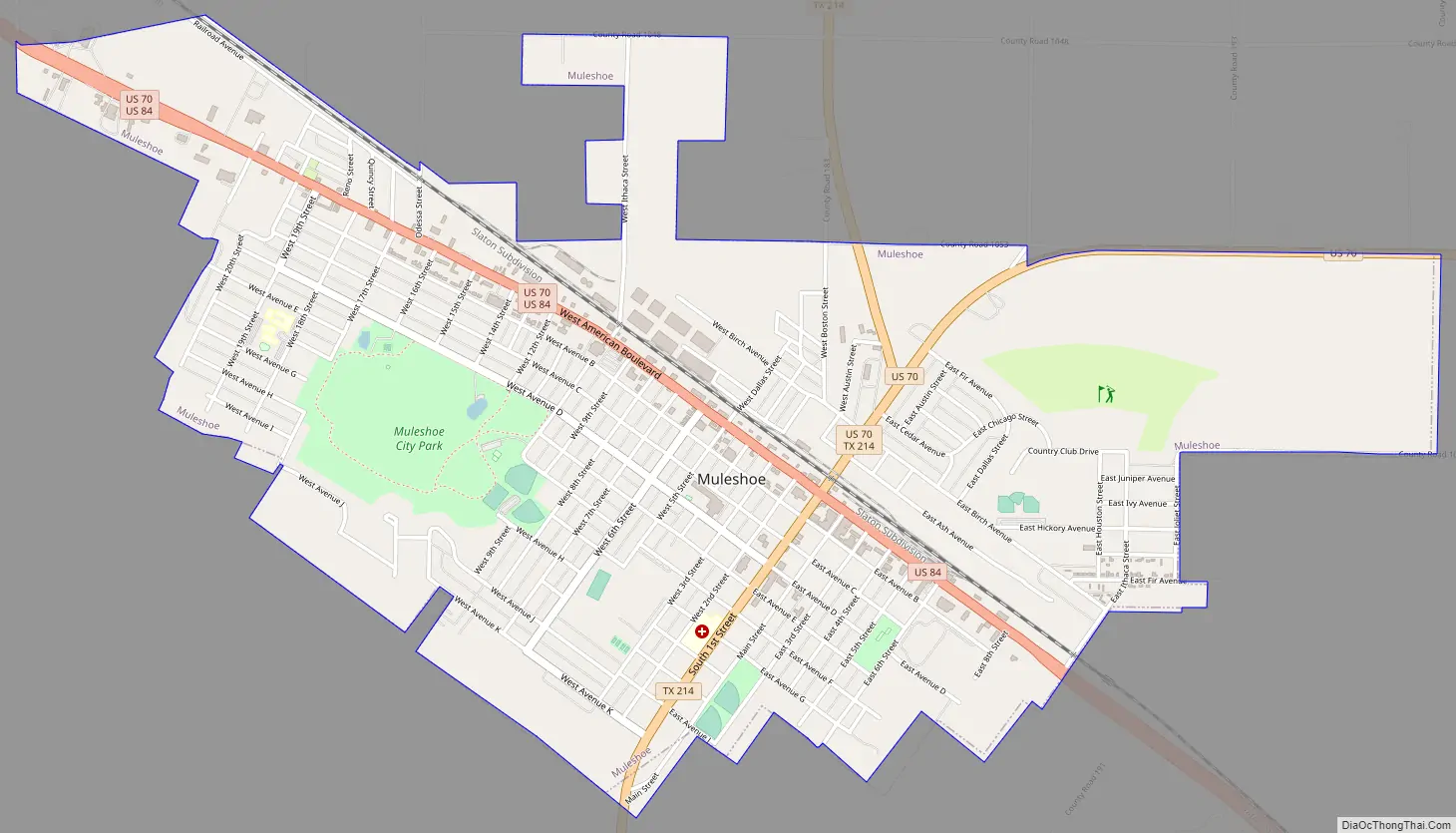
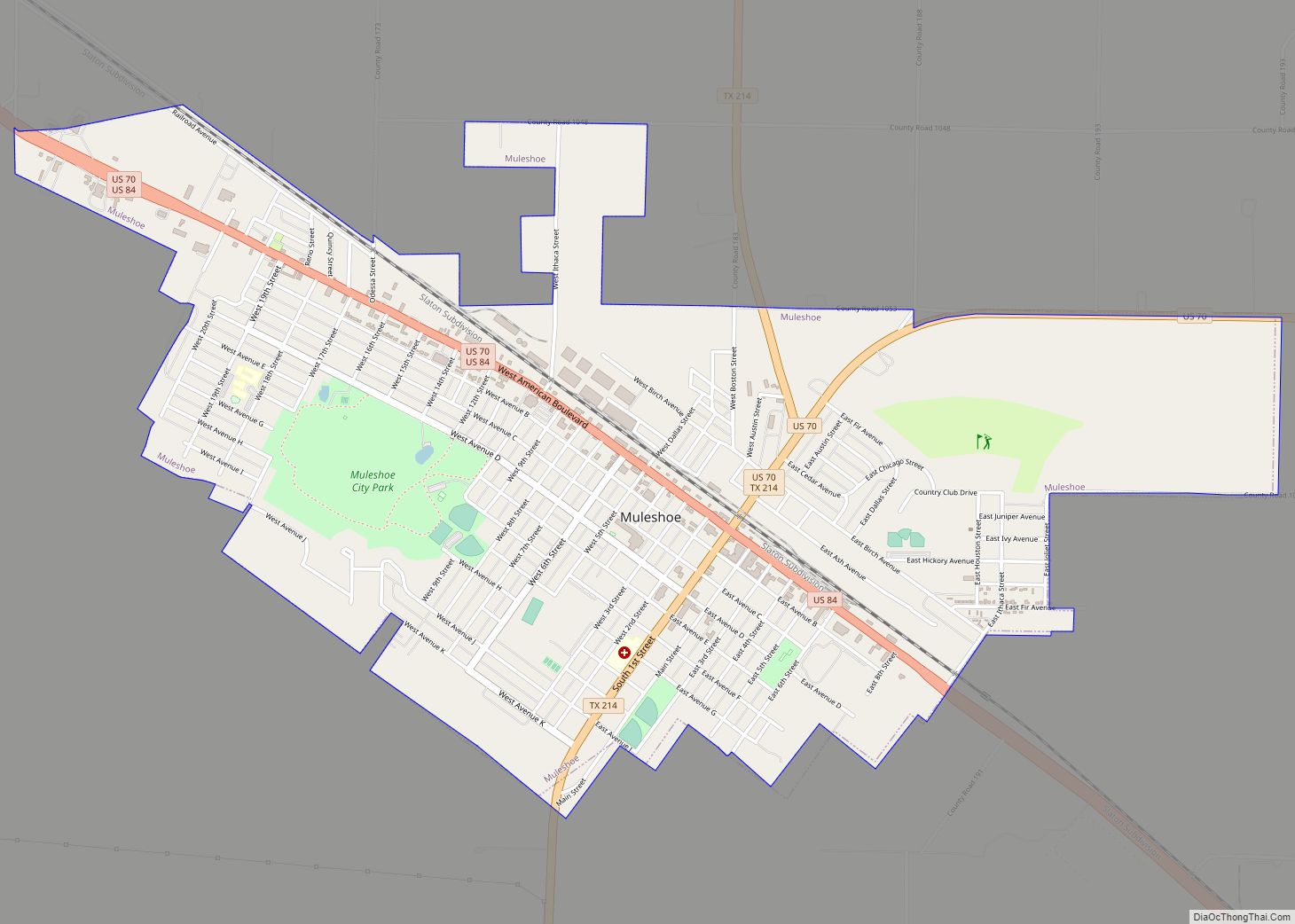
Muleshoe Road Map
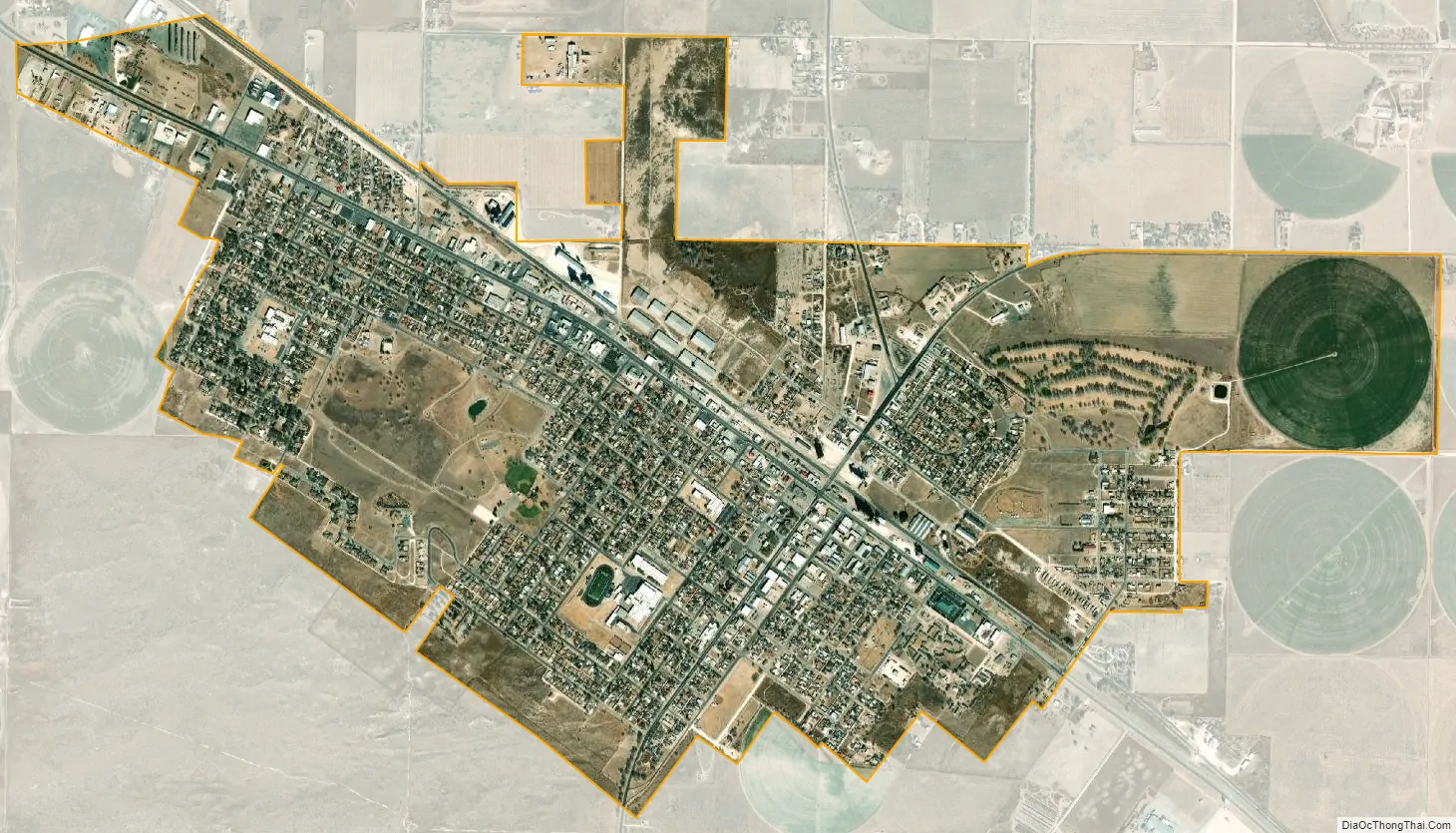
Muleshoe city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 3.4 square miles (8.8 km), all of it land. Muleshoe lies on the western extreme of the Central Time Zone, just 17 miles (27 km) east of the Mountain Time line.
Muleshoe is situated on the Great Plains in an area where the plains reach their highest altitude at the foot of the Rocky Mountains known as the High Plains; more specifically, it is located on the South Plains in a region known as the Llano Estacado. The area topology is gently rolling plains with a large number of playa lakes on top of a large plateau. Soil types vary from dark brown playa-lake silt to iron-rich clay to sandy soil; topsoil and subsoil layers vary, as well. Most of the area contains a layer of caliche; in some areas, no topsoil or subsoil reveals the layer of caliche, while other places have up to 4 ft of topsoil or subsoil combined.
Muleshoe lies over the largest aquifer in the United States, the Ogallala Aquifer. It provides all of the city’s water and is essential for the agriculture for the surrounding area. The aquifer is being depleted at an increasing rate over the years; this has triggered many changes in agriculture in efforts to preserve this natural resource.
The physical characteristics of the region make Muleshoe an ideal place for agriculture, except for water. Much of the natural habitat of grasslands and shrubs has been replaced by cash crops and livestock, but a few areas of native fauna (called Conservation Reserve Program) are preserved. About 20 miles (32 km) south of Muleshoe, a system of sink lakes is found at the Muleshoe National Wildlife Refuge. The refuge is a wintering area for large numbers of migratory waterfowl, such as sandhill cranes, and preserves much of the native wildlife.
Climate
Muleshoe is in an area considered part of the semiarid steppe climate zone that extends from areas of central Mexico to southern Alberta and Saskatchewan in Canada. The semiarid steppe classification identifies areas that are intermediate between desert zones and humid zones. This West Texas town experiences hot summer days and cool summer nights and cool to warm winter days and harsh, cold winter nights. Rainfall is low; the town and vicinity receive less than 18 inches (460 mm) of rainfall annually. High summer temperatures (average July temperature above 90 °F) precipitation moisture is rapidly lost to evaporation. Muleshoe experiences steady, and sometimes intense, winds from the north and west in the fall and winter, and winds from the south or west in the spring and summer. The winds add a considerable wind chill factor in the winter.
Shortgrass prairie, prickly pear cacti, and scrub vegetation are the most common flora to be seen around town. Agriculture in the forms of cattle ranching, dairy farming, and wheat and cotton farming are the most prevalent in the area.
See also
Map of Texas State and its subdivision:- Anderson
- Andrews
- Angelina
- Aransas
- Archer
- Armstrong
- Atascosa
- Austin
- Bailey
- Bandera
- Bastrop
- Baylor
- Bee
- Bell
- Bexar
- Blanco
- Borden
- Bosque
- Bowie
- Brazoria
- Brazos
- Brewster
- Briscoe
- Brooks
- Brown
- Burleson
- Burnet
- Caldwell
- Calhoun
- Callahan
- Cameron
- Camp
- Carson
- Cass
- Castro
- Chambers
- Cherokee
- Childress
- Clay
- Cochran
- Coke
- Coleman
- Collin
- Collingsworth
- Colorado
- Comal
- Comanche
- Concho
- Cooke
- Coryell
- Cottle
- Crane
- Crockett
- Crosby
- Culberson
- Dallam
- Dallas
- Dawson
- Deaf Smith
- Delta
- Denton
- Dewitt
- Dickens
- Dimmit
- Donley
- Duval
- Eastland
- Ector
- Edwards
- El Paso
- Ellis
- Erath
- Falls
- Fannin
- Fayette
- Fisher
- Floyd
- Foard
- Fort Bend
- Franklin
- Freestone
- Frio
- Gaines
- Galveston
- Garza
- Gillespie
- Glasscock
- Goliad
- Gonzales
- Gray
- Grayson
- Gregg
- Grimes
- Guadalupe
- Hale
- Hall
- Hamilton
- Hansford
- Hardeman
- Hardin
- Harris
- Harrison
- Hartley
- Haskell
- Hays
- Hemphill
- Henderson
- Hidalgo
- Hill
- Hockley
- Hood
- Hopkins
- Houston
- Howard
- Hudspeth
- Hunt
- Hutchinson
- Irion
- Jack
- Jackson
- Jasper
- Jeff Davis
- Jefferson
- Jim Hogg
- Jim Wells
- Johnson
- Jones
- Karnes
- Kaufman
- Kendall
- Kenedy
- Kent
- Kerr
- Kimble
- King
- Kinney
- Kleberg
- Knox
- La Salle
- Lamar
- Lamb
- Lampasas
- Lavaca
- Lee
- Leon
- Liberty
- Limestone
- Lipscomb
- Live Oak
- Llano
- Loving
- Lubbock
- Lynn
- Madison
- Marion
- Martin
- Mason
- Matagorda
- Maverick
- McCulloch
- McLennan
- McMullen
- Medina
- Menard
- Midland
- Milam
- Mills
- Mitchell
- Montague
- Montgomery
- Moore
- Morris
- Motley
- Nacogdoches
- Navarro
- Newton
- Nolan
- Nueces
- Ochiltree
- Oldham
- Orange
- Palo Pinto
- Panola
- Parker
- Parmer
- Pecos
- Polk
- Potter
- Presidio
- Rains
- Randall
- Reagan
- Real
- Red River
- Reeves
- Refugio
- Roberts
- Robertson
- Rockwall
- Runnels
- Rusk
- Sabine
- San Augustine
- San Jacinto
- San Patricio
- San Saba
- Schleicher
- Scurry
- Shackelford
- Shelby
- Sherman
- Smith
- Somervell
- Starr
- Stephens
- Sterling
- Stonewall
- Sutton
- Swisher
- Tarrant
- Taylor
- Terrell
- Terry
- Throckmorton
- Titus
- Tom Green
- Travis
- Trinity
- Tyler
- Upshur
- Upton
- Uvalde
- Val Verde
- Van Zandt
- Victoria
- Walker
- Waller
- Ward
- Washington
- Webb
- Wharton
- Wheeler
- Wichita
- Wilbarger
- Willacy
- Williamson
- Wilson
- Winkler
- Wise
- Wood
- Yoakum
- Young
- Zapata
- Zavala
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming