Anahuac (/ˈænəwæk/ AN-ə-wak) is a city in the U.S. state of Texas on the coast of Trinity Bay. The population of the city was 1,980 at the 2020 census. Anahuac is the seat of Chambers County and is situated in Southeast Texas. The Texas Legislature designated the city as the “Alligator Capital of Texas” in 1989. Anahuac hosts an annual alligator festival.
| Name: | Anahuac city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Texas |
| County: | Chambers County |
| Elevation: | 30 ft (9 m) |
| Total Area: | 2.13 sq mi (5.51 km²) |
| Land Area: | 2.13 sq mi (5.51 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km²) |
| Total Population: | 1,980 |
| Population Density: | 1,100.19/sq mi (424.72/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 77514 |
| Area code: | 409 |
| FIPS code: | 4803144 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1329510 |
| Website: | www.anahuac.us |
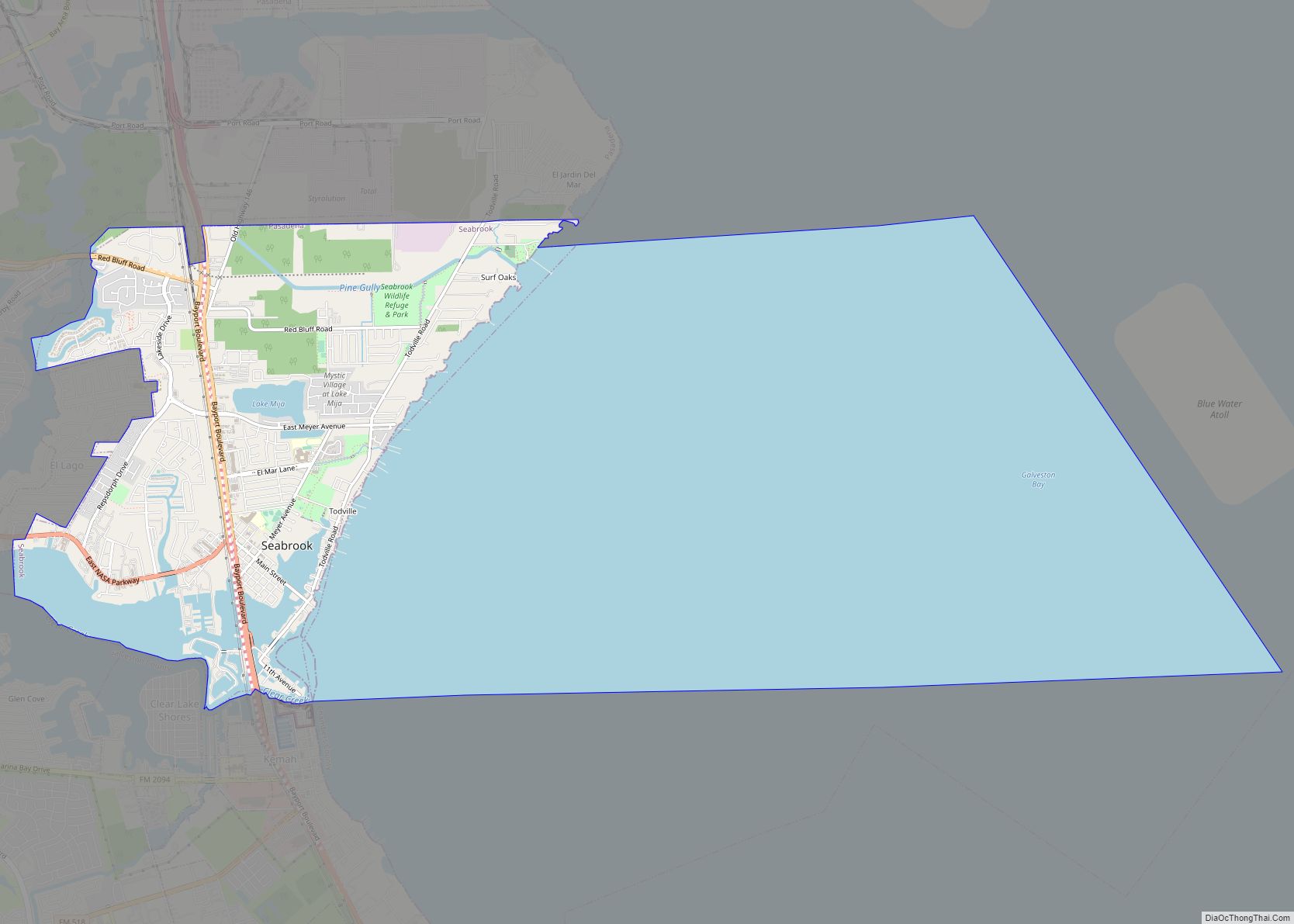
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
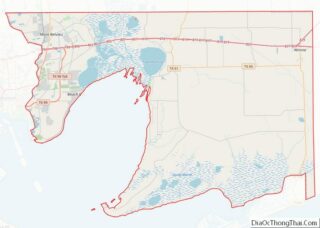
Anahuac location map. Where is Anahuac city?
History
The Mexican term Anahuac comes from Nahuatl, the language of the Aztecs. The name has various meanings, including “center”, “world”, and “city”, but it also means “capital”. Anáhuac is the pre-Columbian name of the Valley of Mexico and its former lake basins around Mexico City, often including the Lerma and Pánuco river systems. Despite the name, neither the city of Anahuac, Texas, nor the immediate region were ever part of the Aztec Empire.
The first dwellers in this area were the Atakapan people as well as the Caddo. In 1721, Frenchman Jean Baptiste de La Harpe reached this area. In the 19th century the area became known as “Perry’s Point”, after Colonel Harry Perry, who erected a military post here in 1816.
Two major events in 1832 and 1835, known as the Anahuac Disturbances (caused mainly by rogue bandits termed “Texians” from the Brazos Valley area), helped to precipitate the Texas Revolution that led to the separation of Texas from Mexico. One of these events was the jailing by Mexican authorities of William Travis for illegal slave importation, and the other was unfair taxation and duties on river traffic to the settlers by the Mexican authorities.
In October 1830, Mexican Colonel Juan Davis Bradburn established a customs post atop the same 30-foot (9.1 m) bluff where Perry had camped. Bradburn’s orders specified that the new post be named Fort Anahuac. The soldiers erected two large kilns to produce bricks to build a more permanent fort. Fort Anahuac would still be intact today had it not been for the locals using the bricks for their own home construction soon after the Texas Revolution; virtually all bricks were taken and none remain to this day. By March 1831, Anahuac comprised 20 houses and seven stores. The town grew quickly. Soldiers were given 25 cents per day to use for food and other supplies, and they spent the money locally. By June 1, the town comprised over 300 civilians and 170 military personnel.
In 1862, a small Confederate outpost was established nearby.
The 1935 discovery of the Anahuac Oil Field and the Monroe City area oil field brought a period of economic development. The Anahuac National Wildlife Refuge was established 16 miles (26 km) southeast of the city in 1963 by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service. In 1989, the local chamber of commerce organized the first Gatorfest, which attracted 14,000 people into the Fort Anahuac Park, and it has been held annually since then. The festival has expanded every year since, and in 2010 hosted the largest festival, with more than 30,000 people attending.
In 2019, Atlas Air Flight 3591, a cargo flight operating for Amazon Air, crashed in the Trinity Bay, near Anahuac, while flying from Miami to Houston.
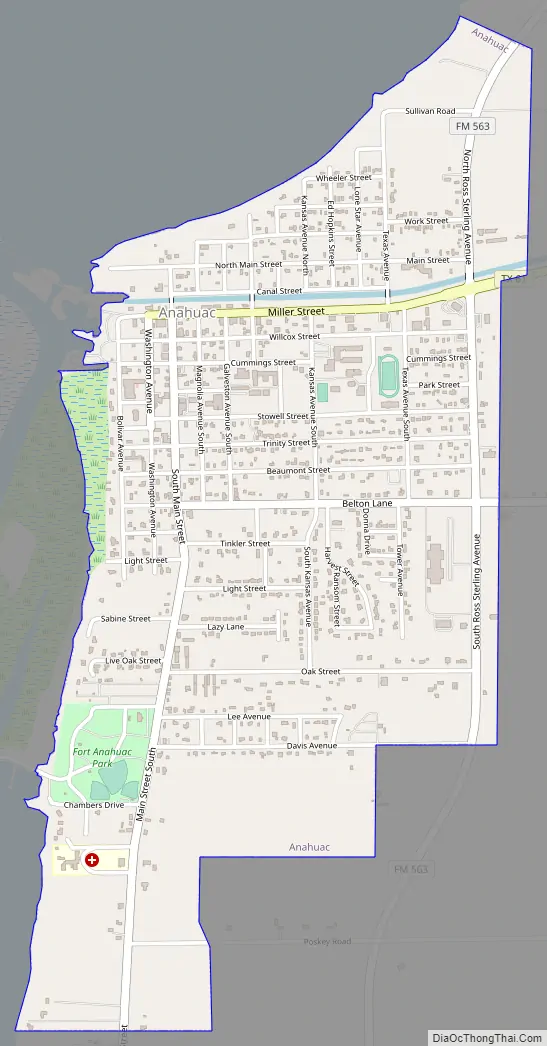
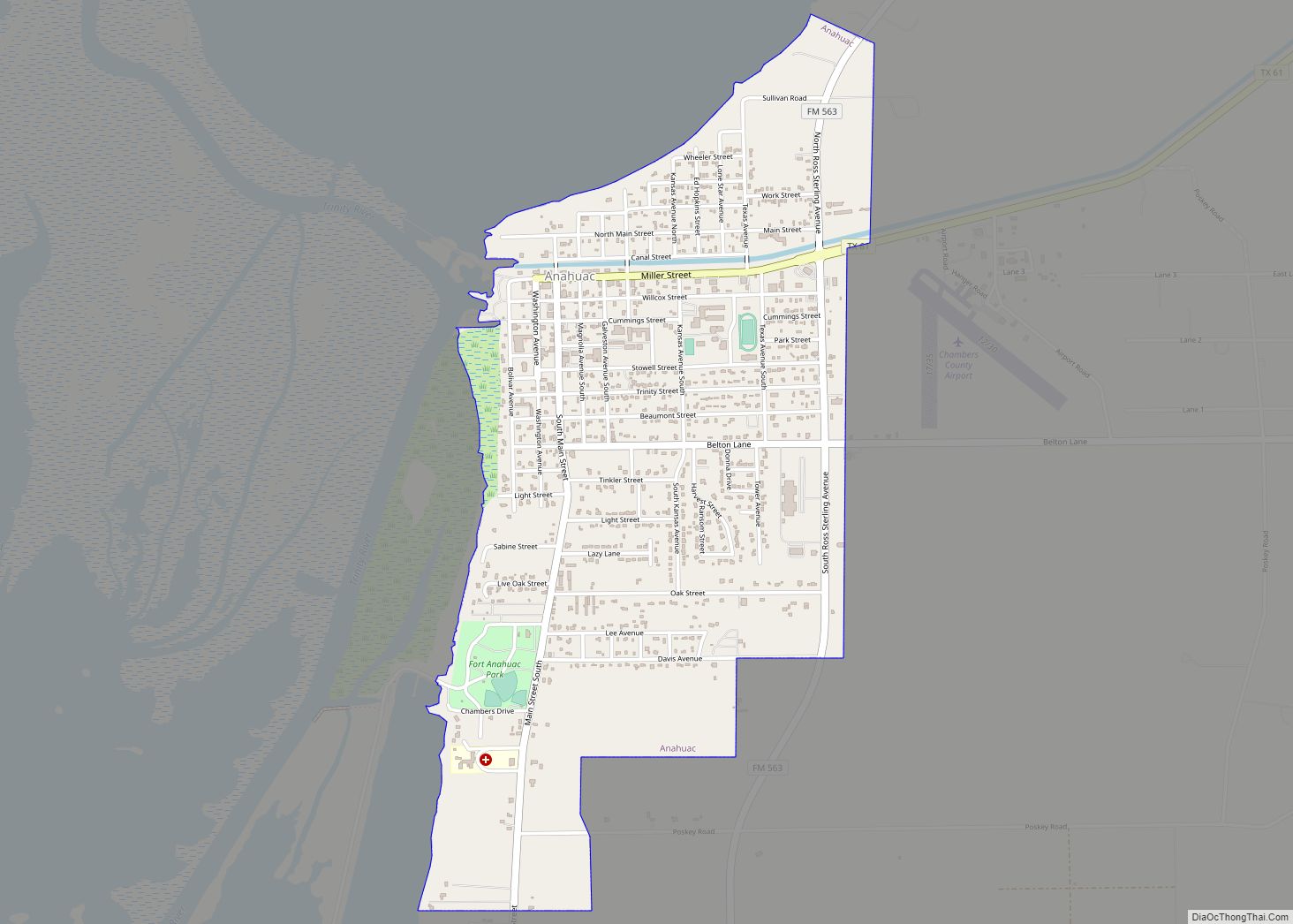
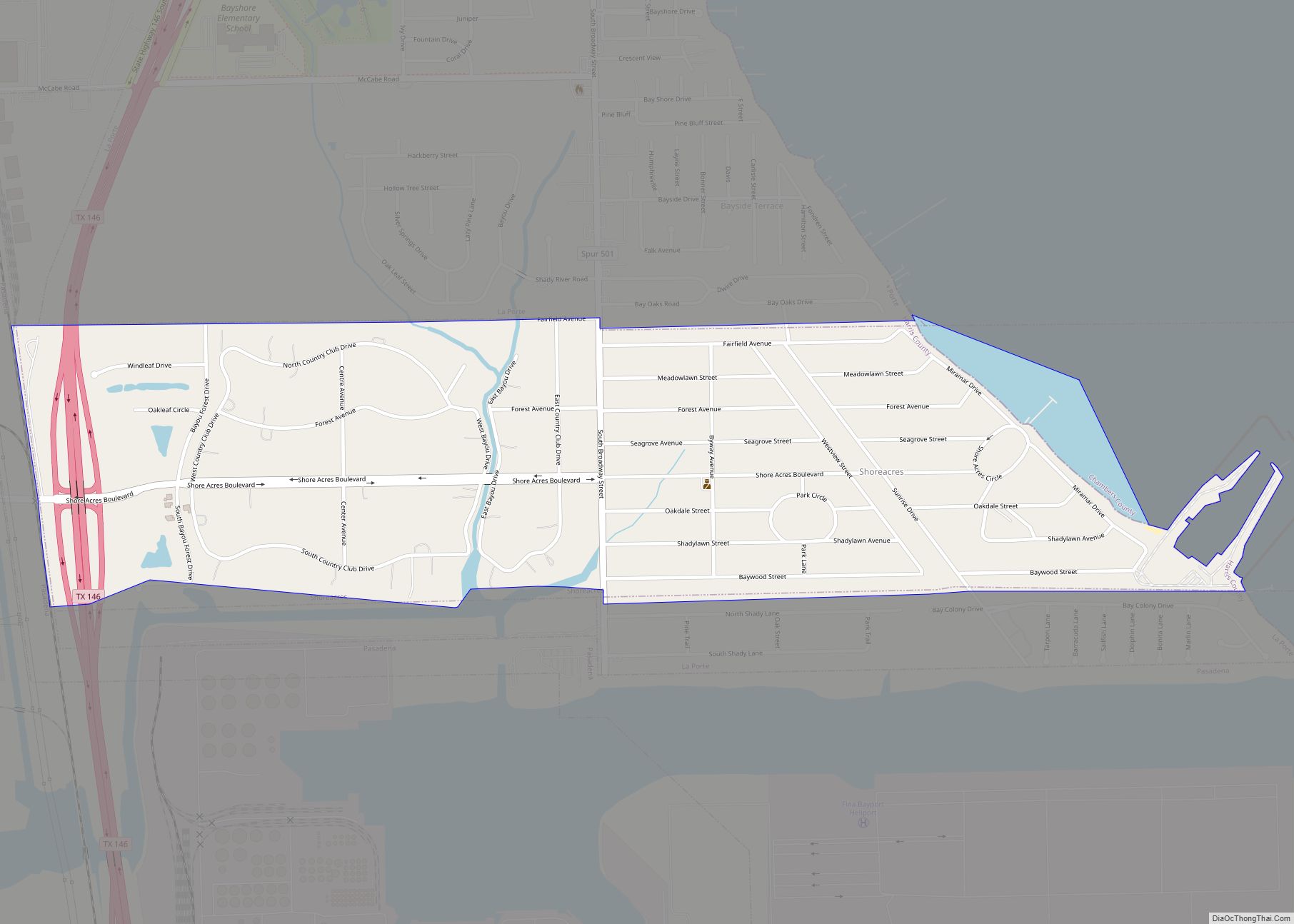
Anahuac Road Map
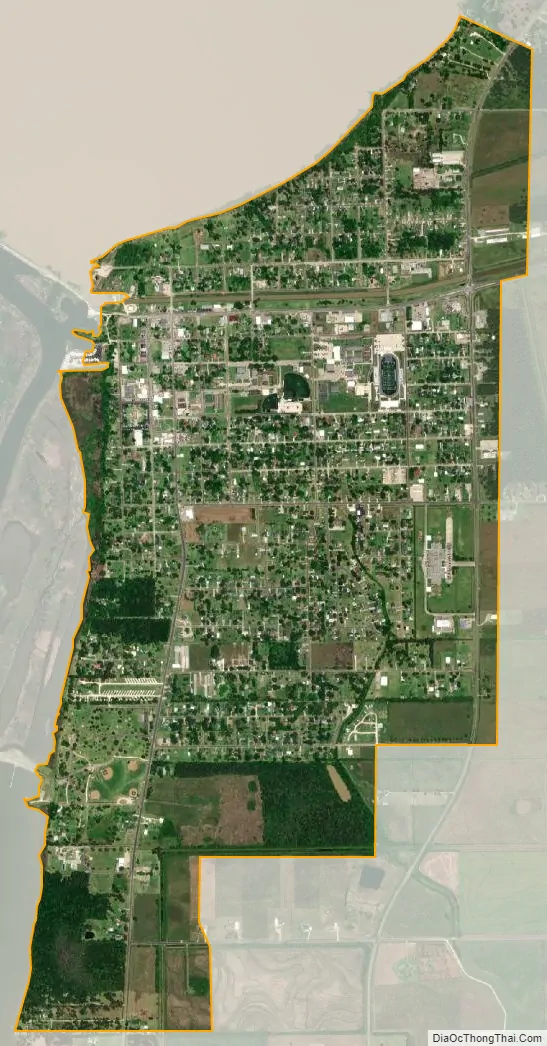
Anahuac city Satellite Map
Geography
Anahuac is located near the center of Chambers County at 29°46′7″N 94°40′45″W / 29.76861°N 94.67917°W / 29.76861; -94.67917 (29.768622, –94.679067), at the northeast end of Trinity Bay and the south end of Lake Anahuac. The mouth of the Trinity River into Trinity Bay is just west of the city. Lake Anahuac is approximately 33,348 acre-feet it was constructed by the Burkhalter family in 1953.
Texas State Highway 61 follows Washington Avenue and Miller Street in Anahuac and leads east and north 12 miles (19 km) to Interstate 10 at a point 43 miles (69 km) east of Houston and 40 miles (64 km) southwest of Beaumont.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city of Anahuac has a total area of 2.1 square miles (5.5 km), all of it land.
With the City of Houston’s annex of the I-10 corridor through Bayton and Mt Belvieu to the Trinity River in Chambers County and possible further expansion to Wallisville Texas, The City of Anahuac is considering annexing and expanding its City Limits on Highway 563 to Wallisville which would possibly bring the Houston Annex to Anahuac as well. Anahuac is also initiating a $50M School Expansion Bond due to influx of many homes and families around the area and expectation of 1000 additional school aged individuals over the next five years alone.
See also
Map of Texas State and its subdivision:- Anderson
- Andrews
- Angelina
- Aransas
- Archer
- Armstrong
- Atascosa
- Austin
- Bailey
- Bandera
- Bastrop
- Baylor
- Bee
- Bell
- Bexar
- Blanco
- Borden
- Bosque
- Bowie
- Brazoria
- Brazos
- Brewster
- Briscoe
- Brooks
- Brown
- Burleson
- Burnet
- Caldwell
- Calhoun
- Callahan
- Cameron
- Camp
- Carson
- Cass
- Castro
- Chambers
- Cherokee
- Childress
- Clay
- Cochran
- Coke
- Coleman
- Collin
- Collingsworth
- Colorado
- Comal
- Comanche
- Concho
- Cooke
- Coryell
- Cottle
- Crane
- Crockett
- Crosby
- Culberson
- Dallam
- Dallas
- Dawson
- Deaf Smith
- Delta
- Denton
- Dewitt
- Dickens
- Dimmit
- Donley
- Duval
- Eastland
- Ector
- Edwards
- El Paso
- Ellis
- Erath
- Falls
- Fannin
- Fayette
- Fisher
- Floyd
- Foard
- Fort Bend
- Franklin
- Freestone
- Frio
- Gaines
- Galveston
- Garza
- Gillespie
- Glasscock
- Goliad
- Gonzales
- Gray
- Grayson
- Gregg
- Grimes
- Guadalupe
- Hale
- Hall
- Hamilton
- Hansford
- Hardeman
- Hardin
- Harris
- Harrison
- Hartley
- Haskell
- Hays
- Hemphill
- Henderson
- Hidalgo
- Hill
- Hockley
- Hood
- Hopkins
- Houston
- Howard
- Hudspeth
- Hunt
- Hutchinson
- Irion
- Jack
- Jackson
- Jasper
- Jeff Davis
- Jefferson
- Jim Hogg
- Jim Wells
- Johnson
- Jones
- Karnes
- Kaufman
- Kendall
- Kenedy
- Kent
- Kerr
- Kimble
- King
- Kinney
- Kleberg
- Knox
- La Salle
- Lamar
- Lamb
- Lampasas
- Lavaca
- Lee
- Leon
- Liberty
- Limestone
- Lipscomb
- Live Oak
- Llano
- Loving
- Lubbock
- Lynn
- Madison
- Marion
- Martin
- Mason
- Matagorda
- Maverick
- McCulloch
- McLennan
- McMullen
- Medina
- Menard
- Midland
- Milam
- Mills
- Mitchell
- Montague
- Montgomery
- Moore
- Morris
- Motley
- Nacogdoches
- Navarro
- Newton
- Nolan
- Nueces
- Ochiltree
- Oldham
- Orange
- Palo Pinto
- Panola
- Parker
- Parmer
- Pecos
- Polk
- Potter
- Presidio
- Rains
- Randall
- Reagan
- Real
- Red River
- Reeves
- Refugio
- Roberts
- Robertson
- Rockwall
- Runnels
- Rusk
- Sabine
- San Augustine
- San Jacinto
- San Patricio
- San Saba
- Schleicher
- Scurry
- Shackelford
- Shelby
- Sherman
- Smith
- Somervell
- Starr
- Stephens
- Sterling
- Stonewall
- Sutton
- Swisher
- Tarrant
- Taylor
- Terrell
- Terry
- Throckmorton
- Titus
- Tom Green
- Travis
- Trinity
- Tyler
- Upshur
- Upton
- Uvalde
- Val Verde
- Van Zandt
- Victoria
- Walker
- Waller
- Ward
- Washington
- Webb
- Wharton
- Wheeler
- Wichita
- Wilbarger
- Willacy
- Williamson
- Wilson
- Winkler
- Wise
- Wood
- Yoakum
- Young
- Zapata
- Zavala
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming