Grand Prairie is a city in Dallas, Tarrant, and Ellis counties of Texas, in the United States. It is part of the Mid-Cities region in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex. It had a population of 175,396 according to the 2010 census, making it the fifteenth most populous city in the state. Remaining the 15th-most populous city in Texas, the 2020 census reported a population of 196,100.
| Name: | Grand Prairie city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Texas |
| County: | Dallas County, Ellis County, Tarrant County |
| Elevation: | 515 ft (157 m) |
| Land Area: | 72.57 sq mi (187.95 km²) |
| Water Area: | 8.90 sq mi (23.05 km²) |
| Population Density: | 2,680.91/sq mi (1,035.10/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 75050-75054 |
| Area code: | 682,817, 214, 469, 945, 972 |
| FIPS code: | 4830464 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1336802 |
| Website: | www.gptx.org |
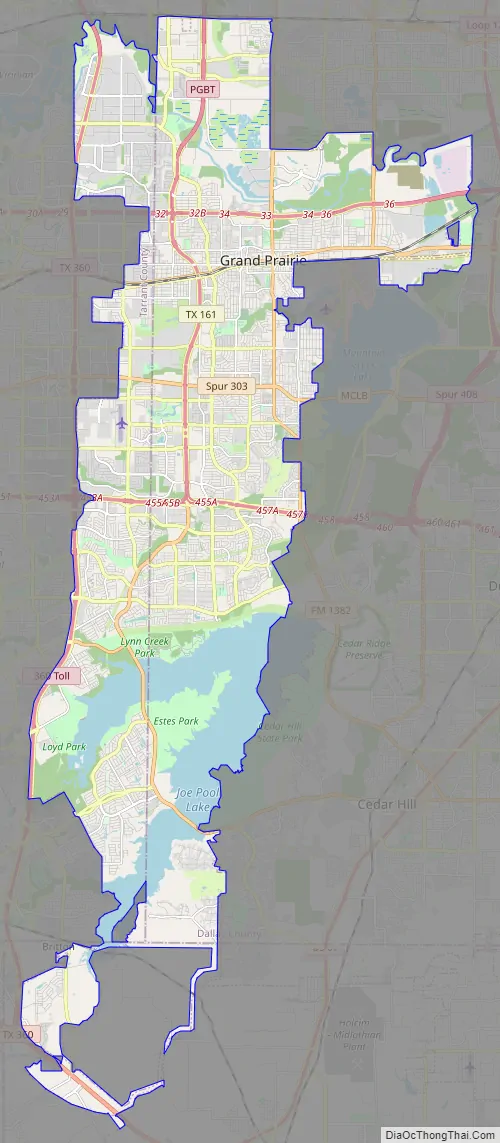
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
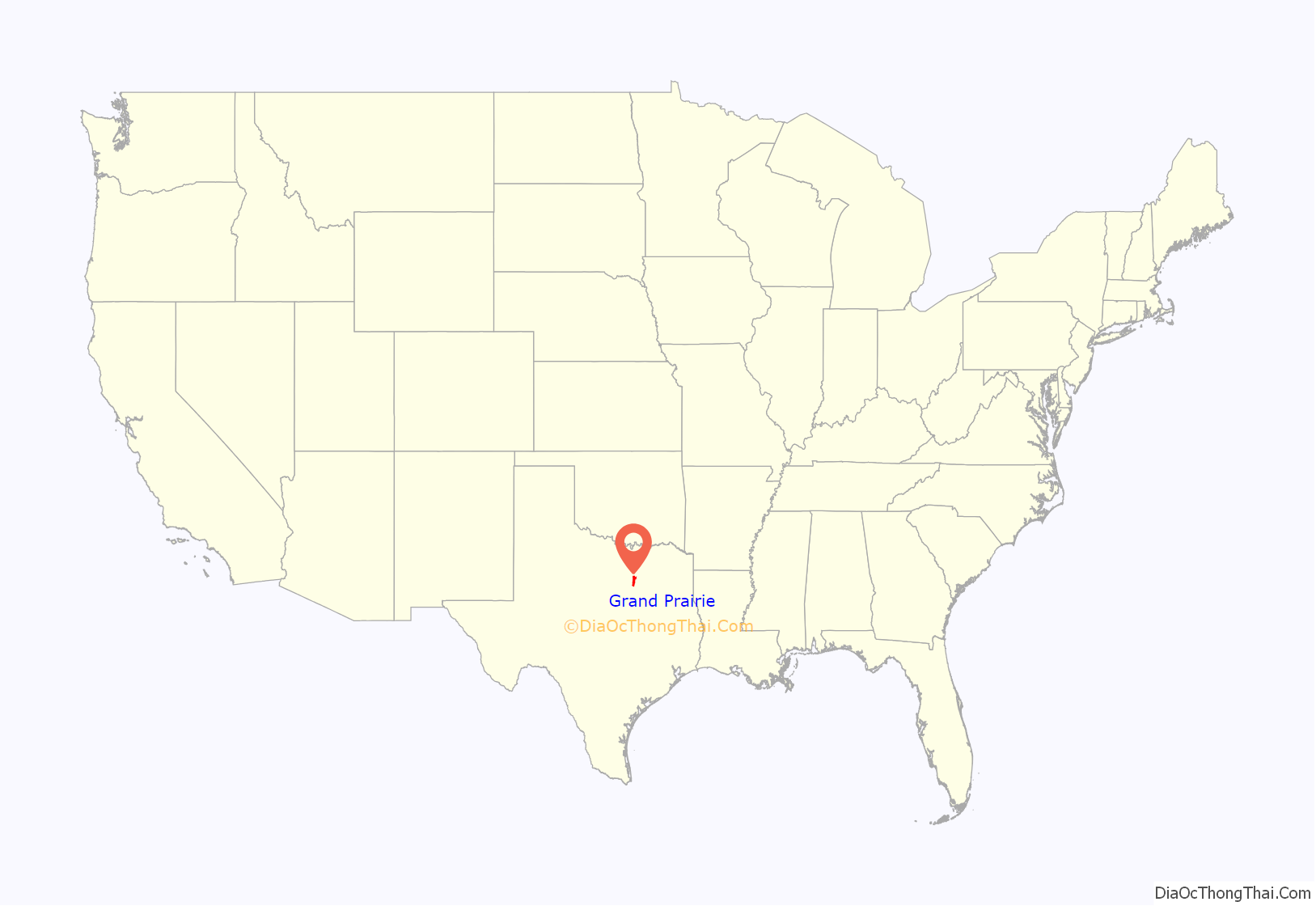
Grand Prairie location map. Where is Grand Prairie city?
History
The city of Grand Prairie was first established as Dechman by Alexander McRae Dechman in 1863. He based the name of the town on Big Prairie, Ohio. Prior to then, he resided in Young County near Fort Belknap. The 1860 U.S. Federal Census—Slave Schedules shows an A McR Dechman as having 4 slaves, ages 50, 25, 37 and 10. Dechman learned that he could trade his oxen and wagons for land in Dallas County. In 1863, Dechman bought 239.5 acres (96.9 ha) of land on the eastern side of the Trinity River and 100 acres (40 ha) of timber land on the west side of the river for a broken-down wagon, oxen team and US$200 in Confederate money. He tried to establish a home on the property, but ran into difficulties, so he returned to his family in Birdville before joining in the Civil War. In 1867 he filed a town plat with Dallas County, consisting of 50 acres (20 ha).
After the war, he returned to Birdville for two years before selling that farm in 1867 and moving to Houston, where yellow fever broke out, causing the family to settle in Bryan. In 1876, Dechman traded half his “prairie” property to the T&P Railroad to ensure the railroad came through the town. The railroad named the depot “Dechman”, prompting its namesake to relocate his home from Bryan to Dechman. His son Alexander had been living in Dechman and operating a trading post and farm. The first church in the area was the Good Hope Cumberland Sabbath School, established in 1870 by Rev. Andrew Hayter. The church was later renamed West Fork United Presbyterian Church and remains an active church.
The first U.S. post office opened in 1877 under the name “Deckman” rather than “Dechman”, because the U.S. Postal Service couldn’t read the writing on the form completed to open the post office. Later that same year, after the Postal Service had adopted the “Deckman” name, confusion resulted from the T&P Railroad designation “Grand Prairie”. This name was based on maps drawn from around 1850 through 1858 that labeled the area between Dallas and Fort Worth “the grand prairie of Texas”. In order to alleviate the confusion, the Postal Service named the post office “Grand Prairie”.
The town of Grand Prairie was eventually incorporated as a city in 1909. During World War I and since, Grand Prairie has had a long history with the defense and aviation industry. While the present-day Vought plant on Jefferson Avenue is part of a small strip within the Dallas city limits, it was originally in Grand Prairie. During World War II the North American Aviation Plant B produced the Consolidated B-24 Liberator and the P-51C and K Mustang variants. After the war, Vought Aircraft took over the plant. This later became Ling Temco Vought (LTV) and then eventually returned to the Vought moniker. The plant was the production site for the F-8 Crusader and the A-7 Corsair II aircraft of the 1950–1989 time period. The LTV Missile and Space division produced missiles such as the Scout and MLRS. This division was eventually sold to Lockheed Martin, which continues to operate in Grand Prairie. Grand Prairie was also the North American headquarters for Aérospatiale Helicopter. This company eventually became Airbus Helicopters, Inc., the U.S. subsidiary of Airbus Helicopters.
In 1953, the mayor and city council of Grand Prairie attempted to annex nearly 70 square miles (180 km) of then-unincorporated and largely undeveloped land in southern Dallas and Tarrant counties. Vehement debate ensued, and the legal pressure from cities like Arlington, Duncanville and Irving wound up overturning part of the annexation attempt.
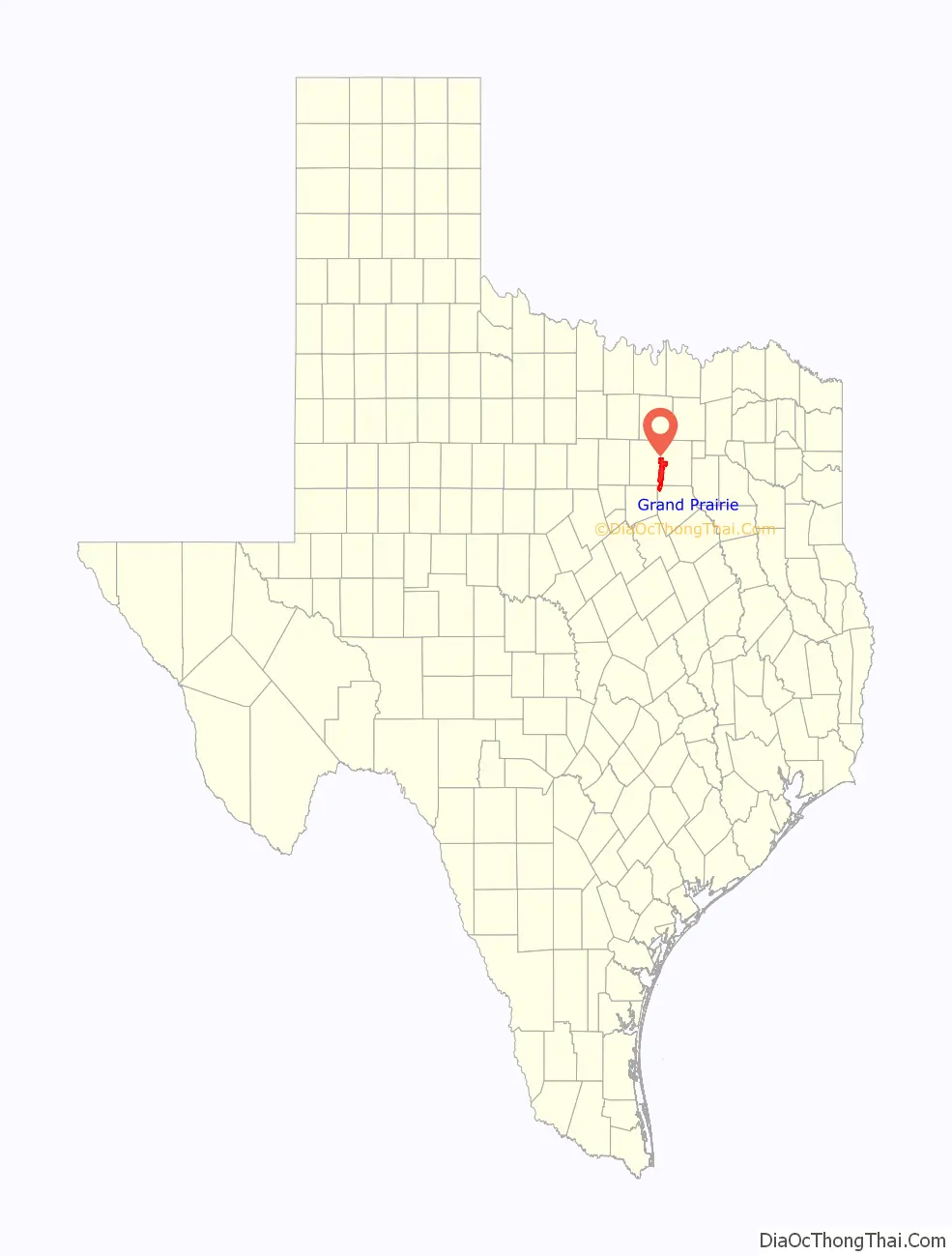
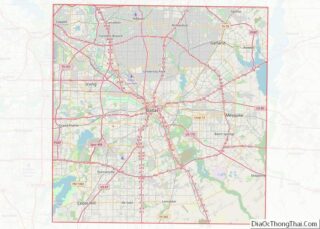
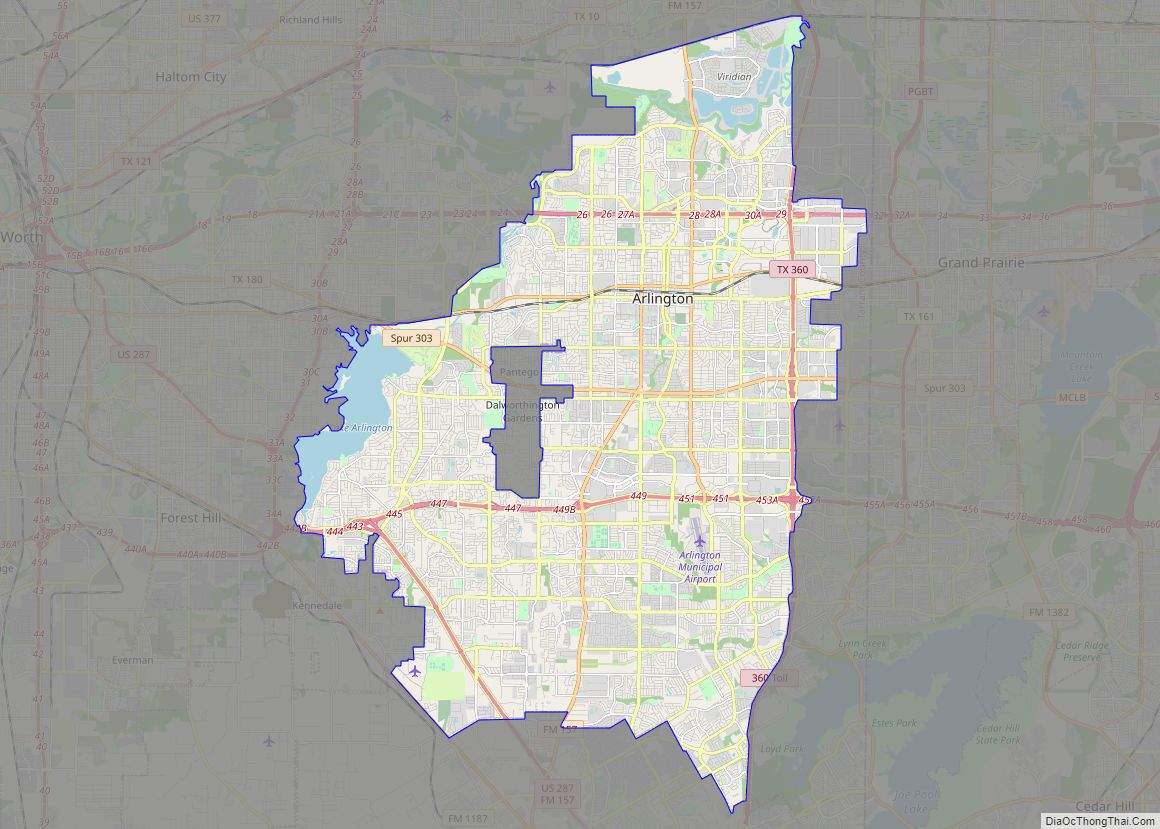
Grand Prairie Road Map
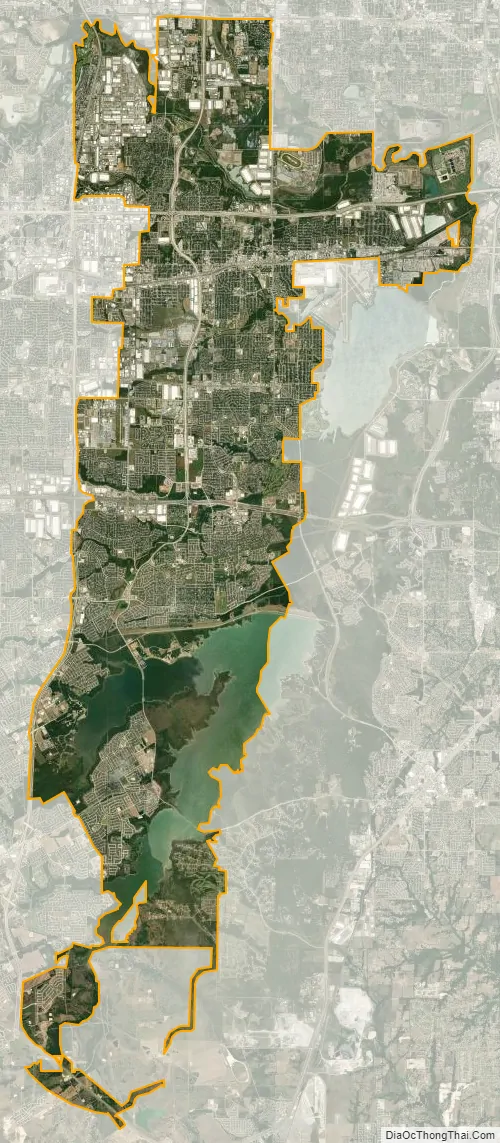
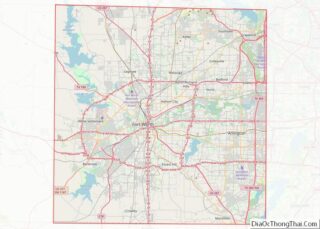
Grand Prairie city Satellite Map
Geography
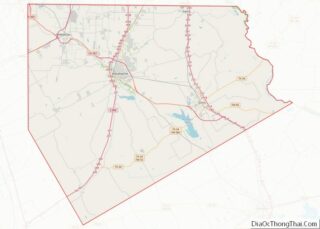
Grand Prairie is located along the border between Tarrant and Dallas counties, with a small portion extending south into Ellis County. The city is bordered by Dallas to the east, Cedar Hill and Midlothian to the southeast, Mansfield to the southwest, Arlington to the west, Fort Worth to the northwest, and Irving to the north.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 81.1 square miles (210.0 km), of which 72.1 square miles (186.8 km) is land and 9.0 square miles (23.3 km), or 11.08%, is water.
The West Fork of the Trinity River and a major tributary, Johnson Creek, flow through Grand Prairie.
Grand Prairie has a long history of flooding from Johnson Creek. In the 1980s, a major Army Corps of Engineers project was begun to straighten the channel, which has reduced the damage of flooding.
Climate
Grand Prairie is part of the humid subtropical region.
See also
Map of Texas State and its subdivision:- Anderson
- Andrews
- Angelina
- Aransas
- Archer
- Armstrong
- Atascosa
- Austin
- Bailey
- Bandera
- Bastrop
- Baylor
- Bee
- Bell
- Bexar
- Blanco
- Borden
- Bosque
- Bowie
- Brazoria
- Brazos
- Brewster
- Briscoe
- Brooks
- Brown
- Burleson
- Burnet
- Caldwell
- Calhoun
- Callahan
- Cameron
- Camp
- Carson
- Cass
- Castro
- Chambers
- Cherokee
- Childress
- Clay
- Cochran
- Coke
- Coleman
- Collin
- Collingsworth
- Colorado
- Comal
- Comanche
- Concho
- Cooke
- Coryell
- Cottle
- Crane
- Crockett
- Crosby
- Culberson
- Dallam
- Dallas
- Dawson
- Deaf Smith
- Delta
- Denton
- Dewitt
- Dickens
- Dimmit
- Donley
- Duval
- Eastland
- Ector
- Edwards
- El Paso
- Ellis
- Erath
- Falls
- Fannin
- Fayette
- Fisher
- Floyd
- Foard
- Fort Bend
- Franklin
- Freestone
- Frio
- Gaines
- Galveston
- Garza
- Gillespie
- Glasscock
- Goliad
- Gonzales
- Gray
- Grayson
- Gregg
- Grimes
- Guadalupe
- Hale
- Hall
- Hamilton
- Hansford
- Hardeman
- Hardin
- Harris
- Harrison
- Hartley
- Haskell
- Hays
- Hemphill
- Henderson
- Hidalgo
- Hill
- Hockley
- Hood
- Hopkins
- Houston
- Howard
- Hudspeth
- Hunt
- Hutchinson
- Irion
- Jack
- Jackson
- Jasper
- Jeff Davis
- Jefferson
- Jim Hogg
- Jim Wells
- Johnson
- Jones
- Karnes
- Kaufman
- Kendall
- Kenedy
- Kent
- Kerr
- Kimble
- King
- Kinney
- Kleberg
- Knox
- La Salle
- Lamar
- Lamb
- Lampasas
- Lavaca
- Lee
- Leon
- Liberty
- Limestone
- Lipscomb
- Live Oak
- Llano
- Loving
- Lubbock
- Lynn
- Madison
- Marion
- Martin
- Mason
- Matagorda
- Maverick
- McCulloch
- McLennan
- McMullen
- Medina
- Menard
- Midland
- Milam
- Mills
- Mitchell
- Montague
- Montgomery
- Moore
- Morris
- Motley
- Nacogdoches
- Navarro
- Newton
- Nolan
- Nueces
- Ochiltree
- Oldham
- Orange
- Palo Pinto
- Panola
- Parker
- Parmer
- Pecos
- Polk
- Potter
- Presidio
- Rains
- Randall
- Reagan
- Real
- Red River
- Reeves
- Refugio
- Roberts
- Robertson
- Rockwall
- Runnels
- Rusk
- Sabine
- San Augustine
- San Jacinto
- San Patricio
- San Saba
- Schleicher
- Scurry
- Shackelford
- Shelby
- Sherman
- Smith
- Somervell
- Starr
- Stephens
- Sterling
- Stonewall
- Sutton
- Swisher
- Tarrant
- Taylor
- Terrell
- Terry
- Throckmorton
- Titus
- Tom Green
- Travis
- Trinity
- Tyler
- Upshur
- Upton
- Uvalde
- Val Verde
- Van Zandt
- Victoria
- Walker
- Waller
- Ward
- Washington
- Webb
- Wharton
- Wheeler
- Wichita
- Wilbarger
- Willacy
- Williamson
- Wilson
- Winkler
- Wise
- Wood
- Yoakum
- Young
- Zapata
- Zavala
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming