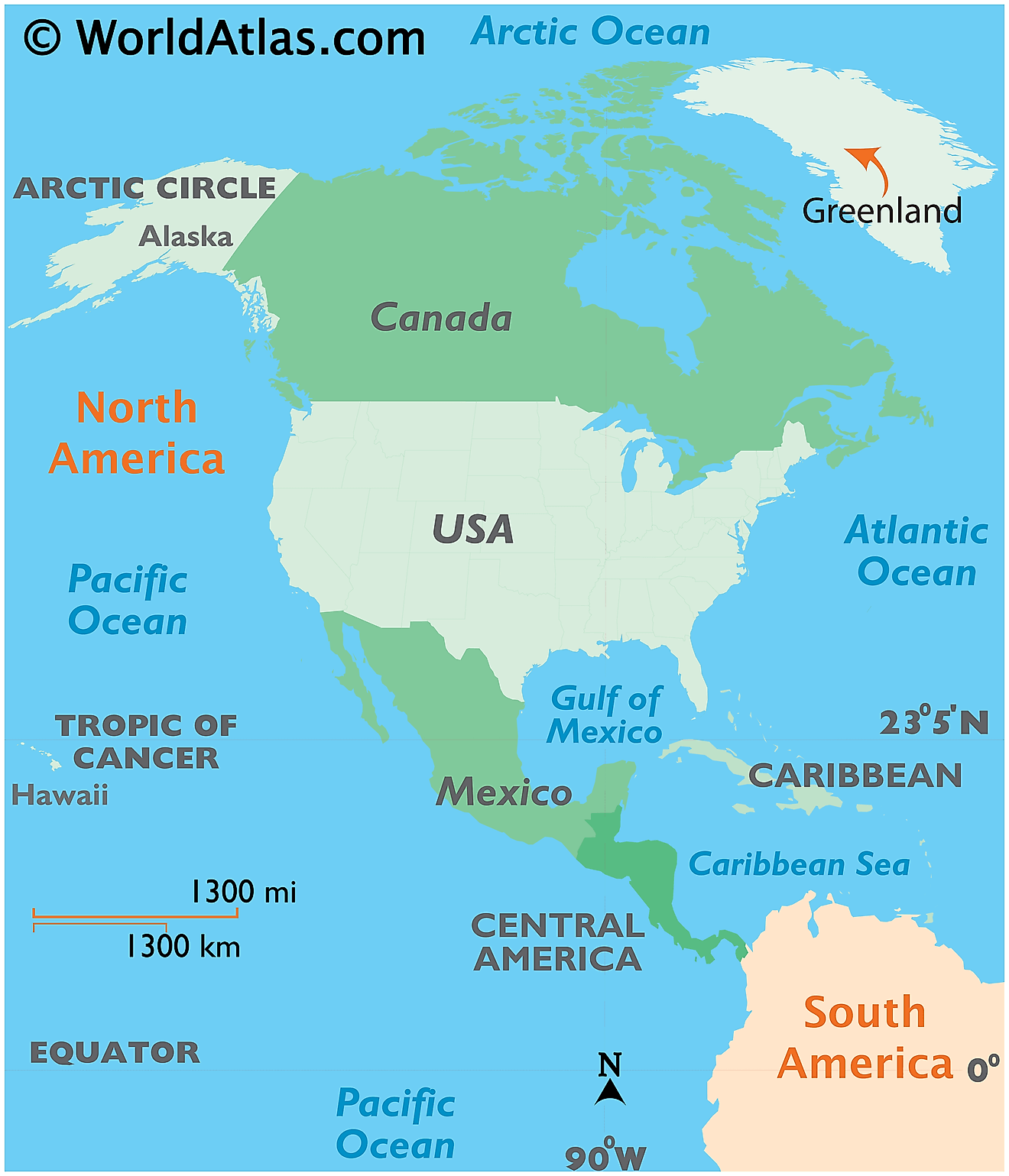
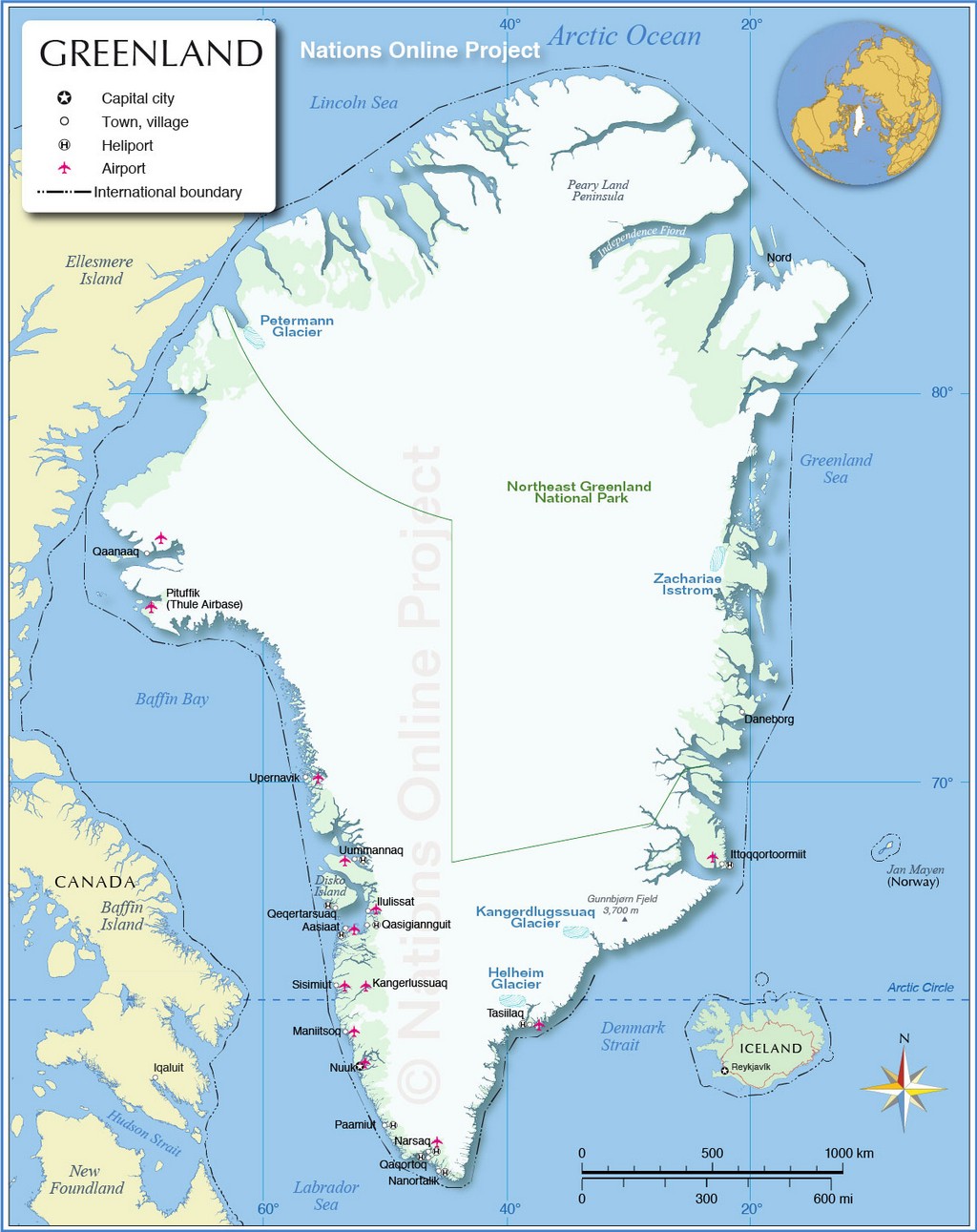
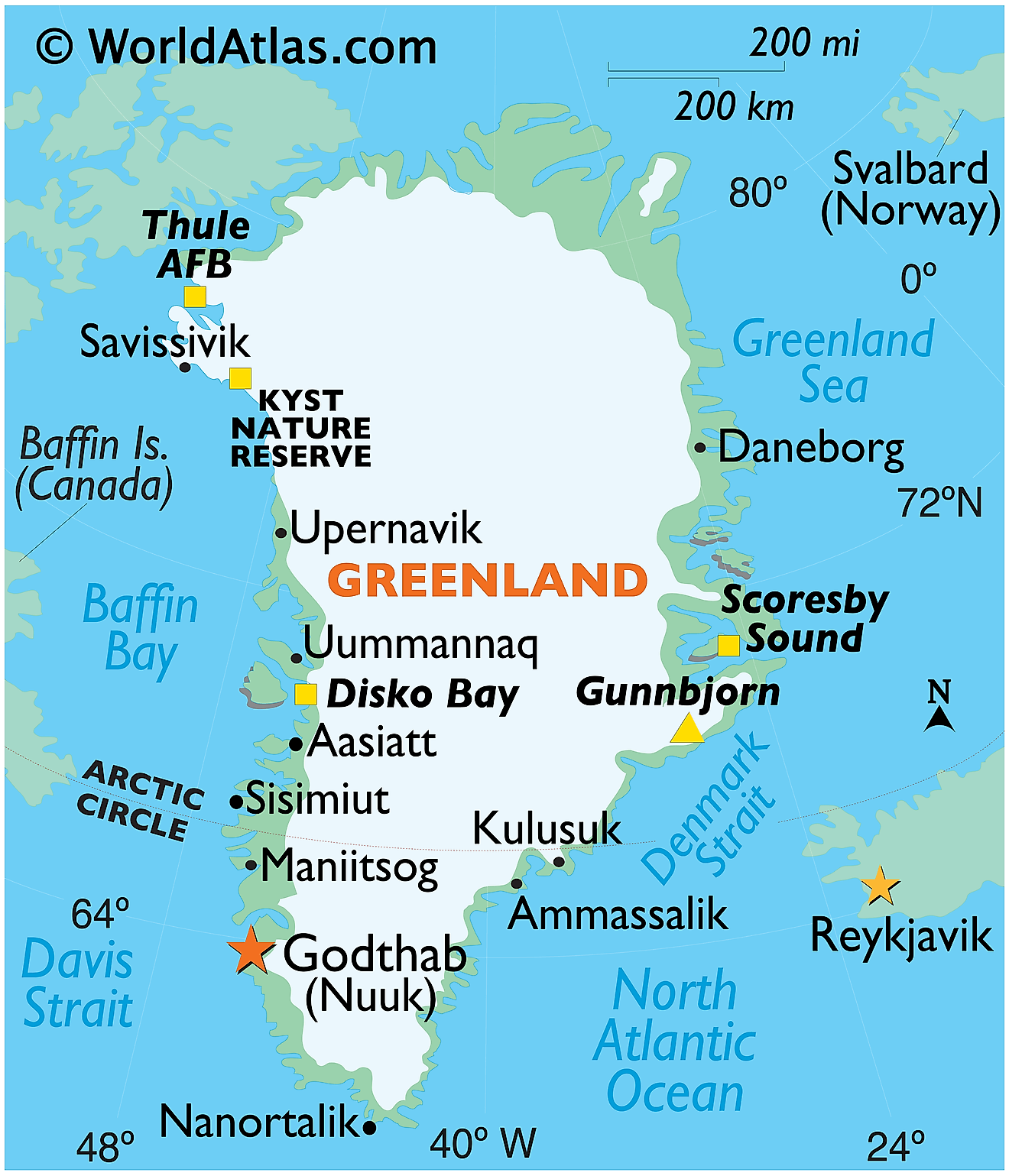
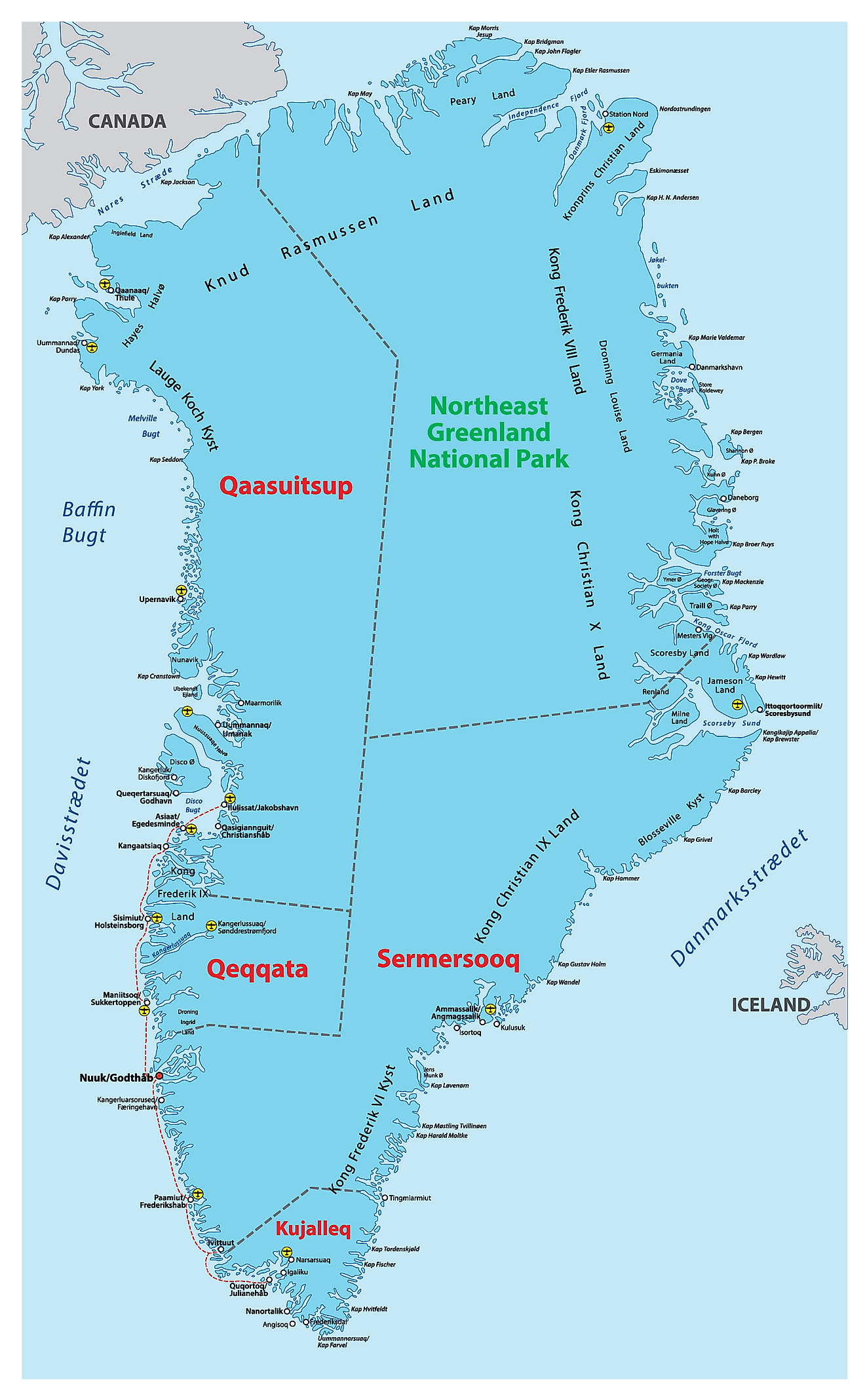
Covering an area of 2,166,086 sq. km (836,330 sq mi), Greenland (about 80% of which is ice-covered) is the world’s largest (non-continent) island, located between the Atlantic and Arctic Oceans.
As observed on the physical map of Greenland above, the coastline is rugged, mountainous, and for the most part, barren. The land then rises to a sloping icecap that covers (81%) most of the island. In places that ice has been measured at more than 11,000ft (3,350m) thick, countless (mostly small) rocky islands ring the coastline central to south, and much like Norway, fjords are plentiful.
Some scientists have claimed that the Greenland ice sheet may actually conceal three large separate island land masses that have been bridged by glaciers since the last ice age. In 2002, as the ice in the far north began to melt, it left a small island exposed to daylight. Additional islands are expected to be discovered if that melting trend continues.
There are nearly 40 glaciers covering the Greenland landmass, and one of the largest is the Peterman. Recently, a chunk of ice broke off the Peterman; an area of ice 100 sq. miles and 600ft thick. It is now drifting in a remote area called the Nares Strait between Greenland and Canada.
Mountain ranges, either partly or totally buried by ice, fringe the toothy-edged coast. Greenland’s highest mountains are the massive ice-covered peaks and exposed cliffs of the Watkins Range that run along it’s eastern coastline. The island’s highest point is located there: Gunnbjorn’s Fjeld at 3,700m (12,139 ft). A yellow triangle marks its position on the map.
Believe it, or not, hot springs are a common natural phenomenon in Greenland. In the far south on Uunartoq Island, they’re warm enough to swim in. On Disko Island in the far-west, there are thousands of small hot springs.
There are about 20 rivers in Greenland. All ring the coastline and all are small melt water outflows from a nearby glacier on the Greenland ice sheet. There are scattered small (summer lakes) across Greenland, all the result of glacier melt. These lakes drain away quickly, or freeze solid in the winter months.
| Legal Name: | Greenland |
|---|---|
| Capital Value: | Nuuk (Godthaab) |
| Official languages: | Greenlandic
|
| Demonym(s): |
|
| Government: | Devolved government within a parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
| Legislature: | Inatsisartut |
| Total Area: | 2,166,086 km² |
| Land Area: | 2,166,086 km² |
| Population: | 56,225 |
| Density: | 0.028/km (0.1/sq mi) |
| GDP: | $3.05 Billion |
| GDP Per Capita: | $54,470.96 |
| Currency Value: | Danish kroner (DKK) |
| Driving side: | right |
| Calling code: | +299 |
| Internet TLD: | .gl |
Location Maps
Where is Greenland?
High Definition Political Map of Greenland
History
Early Paleo-Inuit cultures
In prehistoric times, Greenland was home to several successive Paleo-Inuit cultures known today primarily through archaeological finds. The earliest entry of the Paleo-Inuit into Greenland is thought to have occurred about 2500 BC. From about 2500 BC to 800 BC, southern and western Greenland was inhabited by the Saqqaq culture. Most finds of remains from that period have been around Disko Bay, including the site of Saqqaq, for which the culture is named.
From 2400 BC to 1300 BC, the Independence I culture existed in northern Greenland. It was a part of the Arctic small-tool tradition. Towns, including Deltaterrasserne, appeared. About 800 BC, the Saqqaq culture disappeared and the Early Dorset culture emerged in western Greenland and the Independence II culture in northern Greenland. The Dorset culture was the first culture to extend throughout the Greenlandic coastal areas, in the west and the east. It lasted until the total onset of the Thule culture, in AD 1500. The people of the Dorset culture lived mainly by hunting whales and reindeer.
Norse settlement
From 986, the west coast was settled by Icelanders and Norwegians, through a contingent of 14 boats led by Erik the Red. They formed three settlements—the Eastern Settlement, the Western Settlement, and the Middle Settlement—on fjords near the southwestern tip of the island. They shared the island with the late Dorset culture inhabitants, who occupied the northern and western parts, and later with those or the Thule culture, who entered from the north. Norse Greenlanders submitted to Norwegian rule in 1261 under the Kingdom of Norway. The Kingdom of Norway entered a personal union with Denmark in 1380, and from 1397 was a part of the Kalmar Union.
The Norse settlements, such as Brattahlíð, thrived for centuries, before disappearing in the 15th century, perhaps at the onset of the Little Ice Age. Except some runic inscriptions, the only contemporary records or historiography that survives from the Norse settlements is of their contact with Iceland or Norway. Medieval Norwegian sagas and historical works mention Greenland’s economy, the bishops of Gardar, and the collection of tithes. A chapter in the Konungs skuggsjá (The King’s Mirror) describes Norse Greenland’s exports, imports, and grain cultivation.
Icelandic saga accounts of life in Greenland were composed in the 13th century and later, and are not primary sources for the history of early Norse Greenland. Those accounts are closer to primary for more contemporaneous accounts of late Norse Greenland. Modern understanding therefore mostly depends on the physical data from archeological sites. Interpretation of ice-core and clam-shell data suggests that between AD 800 and 1300 the regions around the fjords of southern Greenland had a relatively mild climate, several degrees Celsius warmer than usual in the North Atlantic with trees and herbaceous plants growing and livestock being farmed. Barley was grown as a crop up to the 70th parallel. The ice cores show that Greenland has had dramatic temperature shifts many times in the past 100,000 years. Similarly the Icelandic Book of Settlements records famines during the winters, in which “the old and helpless were killed and thrown over cliffs”.
These Icelandic settlements vanished during the 14th and early 15th centuries. The demise of the Western Settlement coincides with a decrease in summer and winter temperatures. A study of North Atlantic seasonal temperature variability during the Little Ice Age showed a significant decrease in maximum summer temperatures beginning about the turn of the 14th century—as much as 6 to 8 °C (11 to 14 °F) lower than modern summer temperatures. The study also found that the lowest winter temperatures of the last 2,000 years occurred in the late 14th century and early 15th century. The Eastern Settlement was probably abandoned in the early to mid-15th century, during this cold period.
Theories drawn from archeological excavations at Herjolfsnes in the 1920s suggest that the condition of human bones from this period indicates that the Norse population was malnourished, possibly because of soil erosion resulting from the Norsemen’s destruction of natural vegetation in the course of farming, turf-cutting, and wood-cutting. Malnutrition may also have resulted from widespread deaths from pandemic plague; the decline in temperatures during the Little Ice Age; and armed conflicts with the Skrælings (Norse word for Inuit, meaning “wretches”). Recent archeological studies somewhat challenge the general assumption that the Norse colonization had a dramatic negative environmental effect on the vegetation. Data support traces of a possible Norse soil amendment strategy. More recent evidence suggests that the Norse, who never numbered more than about 2,500, gradually abandoned the Greenland settlements over the 15th century as walrus ivory, the most valuable export from Greenland, decreased in price because of competition with other sources of higher-quality ivory, and that there was actually little evidence of starvation or difficulties.
Other explanations of the disappearance of the Norse settlements have been proposed:
- Lack of support from the homeland.
- Ship-borne marauders (such as Basque, English, or German pirates) rather than Skrælings, could have plundered and displaced the Greenlanders.
- They were “the victims of hidebound thinking and of a hierarchical society dominated by the Church and the biggest land owners. In their reluctance to see themselves as anything but Europeans, the Greenlanders failed to adopt the kind of apparel that the Inuit employed as protection against the cold and damp or to borrow any of the Inuit hunting gear.”
- That portion of the Greenlander population willing to adopt Inuit ways and means intermarried with and assimilated into the Inuit community. Vilhjalmur Stefansson, Unsolved Mysteries of the Arctic, 1938, chapter 1. Much of the Greenland population today is mixed Inuit and European ancestry. It was impossible in 1938 when Stefansson wrote his book to distinguish between intermarriage before the European loss of contact and after the contact was restored.
- “Norse society’s structure created a conflict between the short-term interests of those in power, and the long-term interests of the society as a whole.”
Thule culture (1300–present)
The Thule people are the ancestors of the current Greenlandic population. No genes from the Paleo-Inuit have been found in the present population of Greenland. The Thule culture migrated eastward from what is now known as Alaska around 1000 AD, reaching Greenland around 1300. The Thule culture was the first to introduce to Greenland such technological innovations as dog sleds and toggling harpoons.
There is an account of contact and conflict with the Norse population, as told by the Inuit. It is republished in The Norse Atlantic Sagas, by Gwyn Jones. Jones reports that there is also an account of perhaps the same incident, of more doubtful provenance, told by the Norse side.
1500–1814
In 1500, King Manuel I of Portugal sent Gaspar Corte-Real to Greenland in search of a Northwest Passage to Asia which, according to the Treaty of Tordesillas, was part of Portugal’s sphere of influence. In 1501, Corte-Real returned with his brother, Miguel Corte-Real. Finding the sea frozen, they headed south and arrived in Labrador and Newfoundland. Upon the brothers’ return to Portugal, the cartographic information supplied by Corte-Real was incorporated into a new map of the world which was presented to Ercole I d’Este, Duke of Ferrara, by Alberto Cantino in 1502. The Cantino planisphere, made in Lisbon, accurately depicts the southern coastline of Greenland.
In 1605–1607, King Christian IV of Denmark and Norway sent a series of expeditions to Greenland and Arctic waterways to locate the lost eastern Norse settlement and assert Danish-norwegian sovereignty over Greenland. The expeditions were mostly unsuccessful, partly due to leaders who lacked experience with the difficult Arctic ice and weather conditions, and partly because the expedition leaders were given instructions to search for the Eastern Settlement on the east coast of Greenland just north of Cape Farewell, which is almost inaccessible due to southward drifting ice. The pilot on all three trips was English explorer James Hall.
After the Norse settlements died off, Greenland came under the de facto control of various Inuit groups, but the Dano-Norwegian government never forgot or relinquished the claims to Greenland that it had inherited from the Norse. When it re-established contact with Greenland in the early 17th century, Denmark-Norway asserted its sovereignty over the island. In 1721, a joint mercantile and clerical expedition led by Dano-Norwegian missionary Hans Egede was sent to Greenland, not knowing whether a Norse civilization remained there. This expedition is part of the Dano-Norwegian colonization of the Americas. After 15 years in Greenland, Hans Egede left his son Paul Egede in charge of the mission there and returned to Denmark, where he established a Greenland Seminary. This new colony was centred at Godthåb (“Good Hope”) on the southwest coast. Gradually, Greenland was opened up to Danish merchants, but closed to those from other countries.
Treaty of Kiel to World War II
When the union between the crowns of Denmark and Norway was dissolved in 1814, the Treaty of Kiel severed Norway’s former colonies and left them under the control of the Danish monarch. Norway occupied then-uninhabited eastern Greenland as Erik the Red’s Land in July 1931, claiming that it constituted terra nullius. Norway and Denmark agreed to submit the matter in 1933 to the Permanent Court of International Justice, which decided against Norway.
Greenland’s connection to Denmark was severed on 9 April 1940, early in World War II, after Denmark was occupied by Nazi Germany. On 8 April 1941, the United States occupied Greenland to defend it against a possible invasion by Germany. The United States occupation of Greenland continued until 1945. Greenland was able to buy goods from the United States and Canada by selling cryolite from the mine at Ivittuut. The major air bases were Bluie West-1 at Narsarsuaq and Bluie West-8 at Søndre Strømfjord (Kangerlussuaq), both of which are still used as Greenland’s major international airports. Bluie was the military code name for Greenland.
During this war, the system of government changed: Governor Eske Brun ruled the island under a law of 1925 that allowed governors to take control under extreme circumstances; Governor Aksel Svane was transferred to the United States to lead the commission to supply Greenland. The Danish Sirius Patrol guarded the northeastern shores of Greenland in 1942 using dog sleds. They detected several German weather stations and alerted American troops, who destroyed the facilities. After the collapse of the Third Reich, Albert Speer briefly considered escaping in a small aeroplane to hide out in Greenland, but changed his mind and decided to surrender to the United States Armed Forces.
Greenland had been a protected and very isolated society until 1940. The Danish government had maintained a strict monopoly of Greenlandic trade, allowing no more than small scale barter trading with British whalers. In wartime Greenland developed a sense of self-reliance through self-government and independent communication with the outside world. Despite this change, in 1946 a commission including the highest Greenlandic council, the Landsrådene, recommended patience and no radical reform of the system. Two years later, the first step towards a change of government was initiated when a grand commission was established. A final report (G-50) was presented in 1950, which recommended the introduction of a modern welfare state with Denmark’s development as sponsor and model. In 1953, Greenland was made an equal part of the Danish Kingdom. Home rule was granted in 1979.
Home rule and self-rule
In 1867, United States Secretary of State William H. Seward worked with former senator Robert J. Walker to explore the possibility of buying Greenland and, perhaps, Iceland. Opposition in Congress ended this project. Following World War II, the United States developed a geopolitical interest in Greenland, and in 1946 the United States offered to buy the island from Denmark for $100,000,000. Denmark refused to sell it. In the 21st century, the United States remains interested in investing in the resource base of Greenland and in tapping hydrocarbons off the Greenlandic coast. In August 2019, the US again proposed to buy the country, prompting premier Kim Kielsen to issue the statement, “Greenland is not for sale and cannot be sold, but Greenland is open for trade and cooperation with other countries — including the United States.”
In 1950, Denmark agreed to allow the US to regain the use of Thule Air Base; it was greatly expanded between 1951 and 1953 as part of a unified NATO Cold War defence strategy. The local population of three nearby villages was moved more than 100 km (62 miles) away in the winter. The United States tried to construct a subterranean network of secret nuclear missile launch sites in the Greenlandic ice cap, named Project Iceworm. According to documents declassified in 1996, this project was managed from Camp Century from 1960 to 1966 before abandonment as unworkable. The missiles were never fielded, and necessary consent from the Danish Government to do so was never sought. The Danish government did not become aware of the programme’s mission until 1997, when they discovered it while looking, in the declassified documents, for records related to the crash of a nuclear equipped B-52 bomber at Thule in 1968.
With the 1953 Danish constitution, Greenland’s colonial status ended as the island was incorporated into the Danish realm as an amt (county). Danish citizenship was extended to Greenlanders. Danish policies toward Greenland consisted of a strategy of cultural assimilation — or de-Greenlandification. During this period, the Danish government promoted the exclusive use of the Danish language in official matters, and required Greenlanders to go to Denmark for their post-secondary education. Many Greenlandic children grew up in boarding schools in southern Denmark, and a number lost their cultural ties to Greenland. While the policies “succeeded” in the sense of shifting Greenlanders from being primarily subsistence hunters into being urbanized wage earners, the Greenlandic elite began to reassert a Greenlandic cultural identity. A movement developed in favour of independence, reaching its peak in the 1970s. As a consequence of political complications in relation to Denmark’s entry into the European Common Market in 1972, Denmark began to seek a different status for Greenland, resulting in the Home Rule Act of 1979.
This gave Greenland limited autonomy with its own legislature taking control of some internal policies, while the Parliament of Denmark maintained full control of external policies, security, and natural resources. The law came into effect on 1 May 1979. The Queen of Denmark, Margrethe II, remains Greenland’s head of state. In 1985, Greenland left the European Economic Community (EEC) upon achieving self-rule, as it did not agree with the EEC’s commercial fishing regulations and an EEC ban on seal skin products. Greenland voters approved a referendum on greater autonomy on 25 November 2008. According to one study, the 2008 vote created what “can be seen as a system between home rule and full independence”.
On 21 June 2009, Greenland gained self-rule with provisions for assuming responsibility for self-government of judicial affairs, policing, and natural resources. Also, Greenlanders were recognized as a separate people under international law. Denmark maintains control of foreign affairs and defence matters. Denmark upholds the annual block grant of 3.2 billion Danish kroner, but as Greenland begins to collect revenues of its natural resources, the grant will gradually be diminished. This is generally considered to be a step toward eventual full independence from Denmark. Greenlandic was declared the sole official language of Greenland at the historic ceremony.