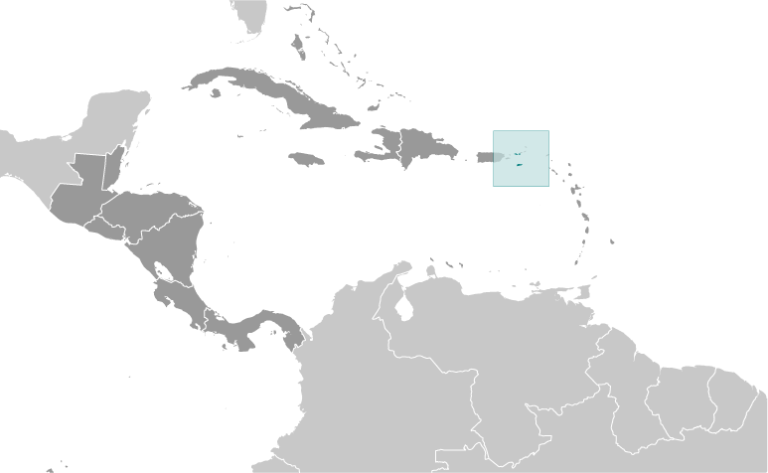
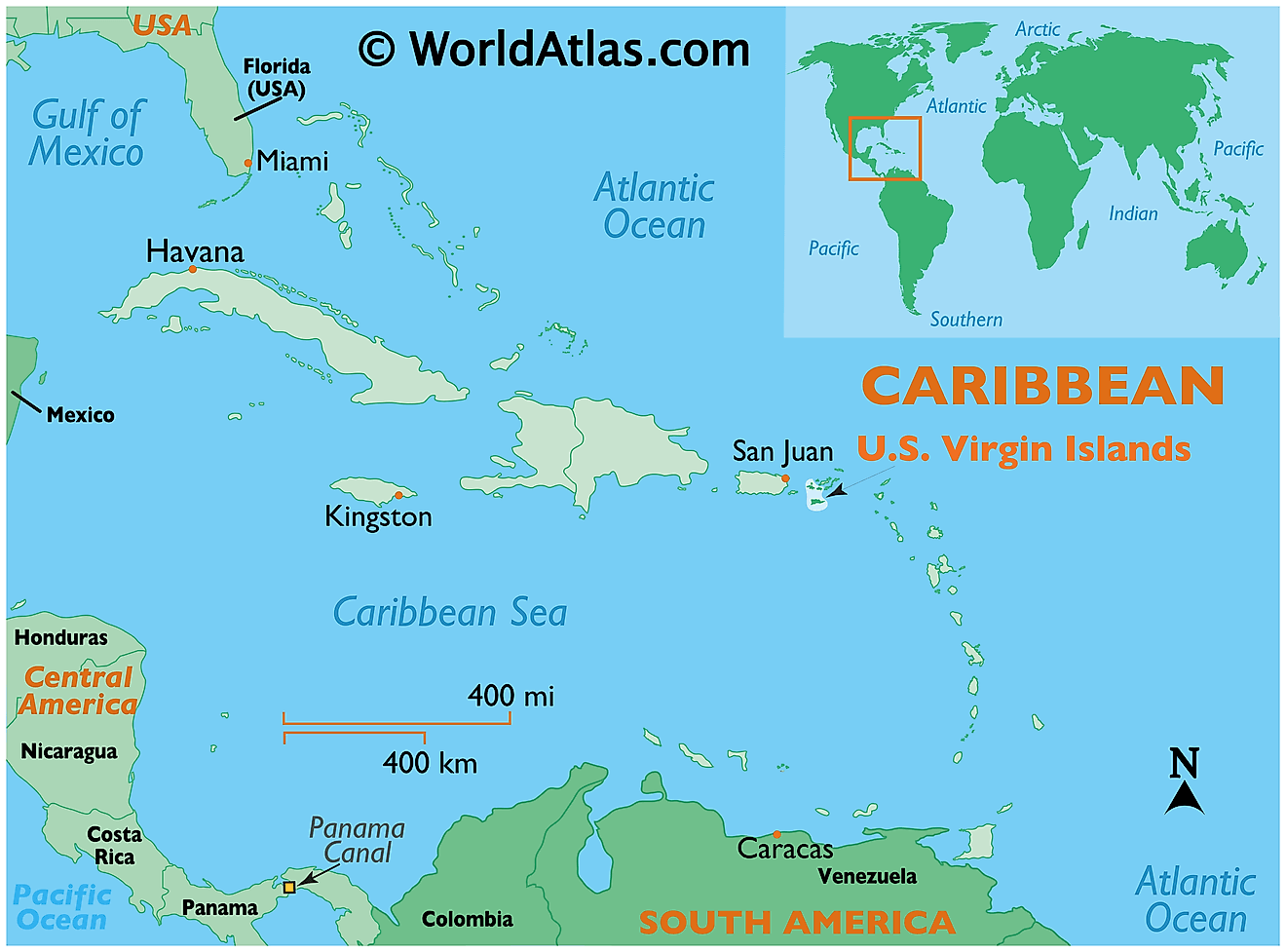
The U.S. Virgin Islands is an organized and unincorporated island territory of the United States of America, located between the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea.
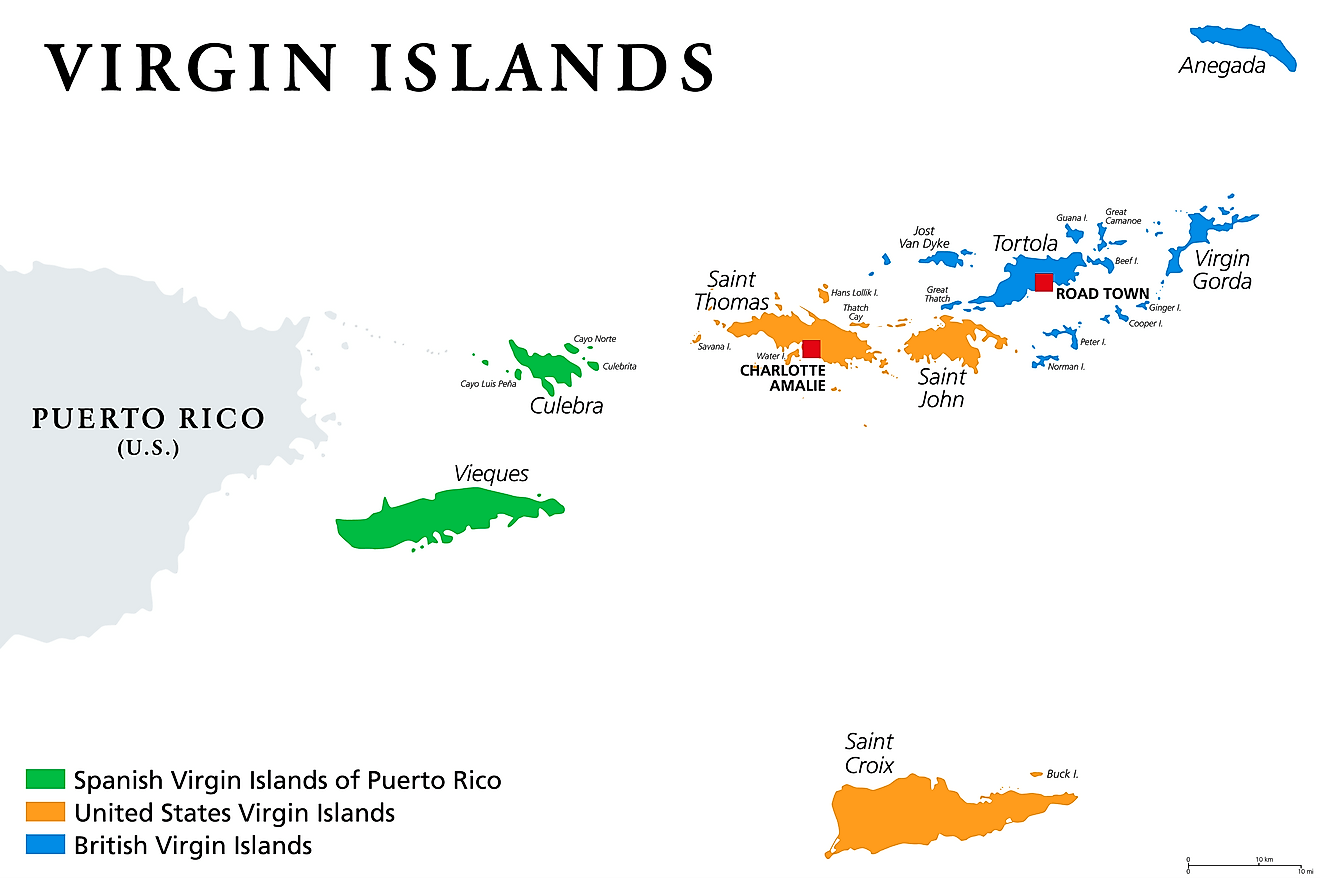
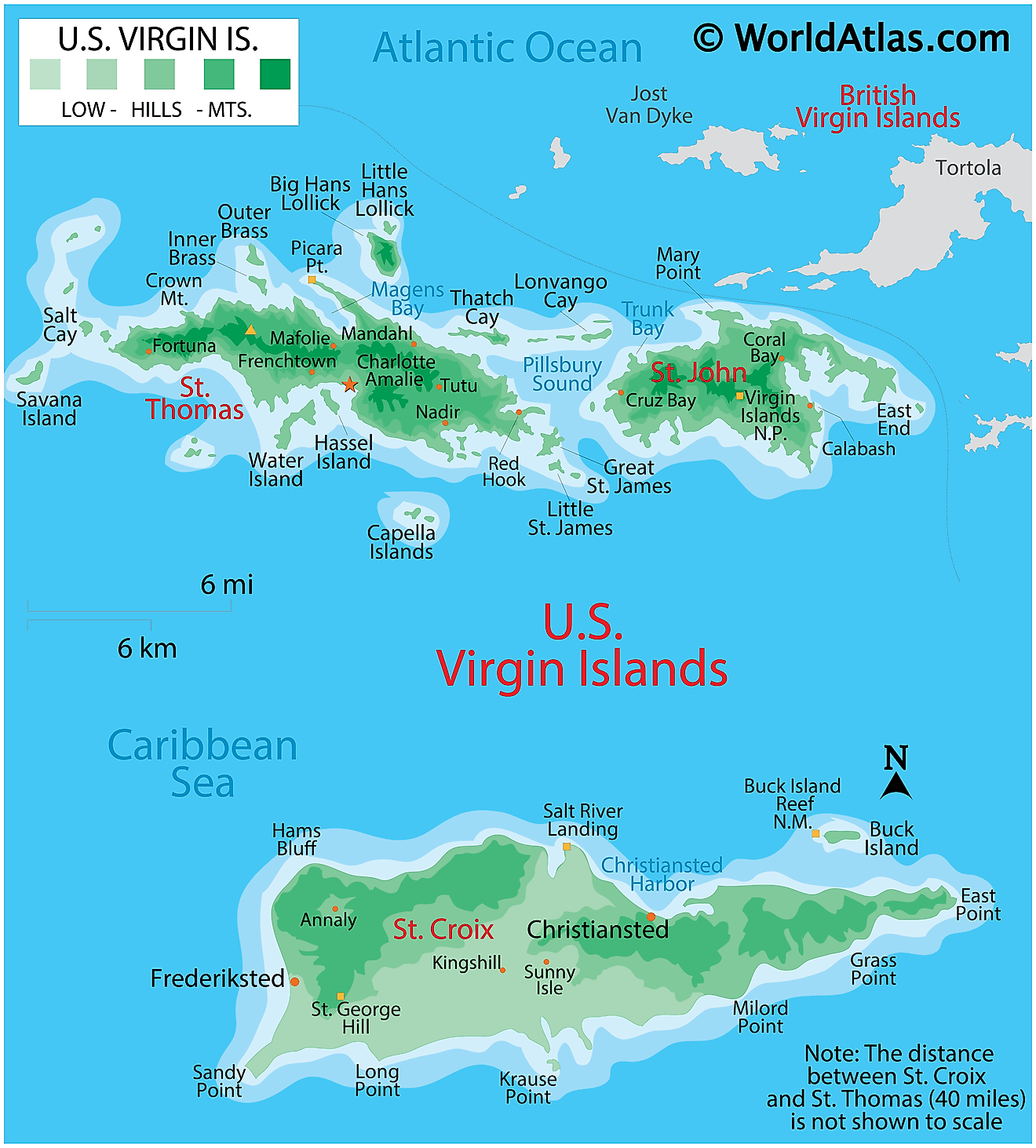
Covering a total land area of 346.36 sq. km. As observed on the physical map of the US Virgin Islands above, the territory consists of three main islands: Saint Thomas, Saint John, Saint Croix, as well as several dozen smaller islands.
Most of the islands are volcanic in origin and as observed on the map, the islands of Saint Thomas and Saint John are quite hilly. Saint Croix is the largest of the US Virgin Islands and comparatively has a much flatter terrain.
The highest point is Crown Mountain on Saint Thomas at 1,555 ft. (474 m). The lowest point is at the sea level.
Scattered streams help to drain the islands, while white sand beaches and coral reefs are common.
Online Interactive Political Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
There are no first-order administrative divisions of the US Virgin Islands as defined by the US Government, but there are 3 islands at the second order; Saint Croix, Saint John, Saint Thomas.
Location Maps
Where is U.S. Virgin Islands?
High Definition Political Map of U.S. Virgin Islands
History
The Virgin Islands were originally inhabited by the Arawak and Carib, many of whom are thought to have perished during the colonial period due to enslavement, foreign disease, and war brought about by European colonists.
European colonists later settled here and established sugar plantations, at least one tobacco plantation, and purchased people for slavery taken from Africa. The descendants of the enslaved people remain the bulk of the population, sharing a common African-Caribbean heritage with the rest of the English-speaking Caribbean.
Like mainland Puerto Rico, the Virgin Islands that belonged to Spain were ceded to the United States in 1898. The United States took possession of the islands after the signing of the armistice that put an end to military operations in the Spanish–American War.
A 1916 treaty between the United States and Denmark (not ratified by the United States until 1917) resulted in Denmark selling the Danish Virgin Islands to the United States for $25 million in gold.
Historical affiliations
The Virgin Islands have been under the sovereignty of several nations and groups throughout history. Below is a table which represents the affiliation of the various islands:
*Largely under control of pirates
**Coexisting claim
***Leased/shared territory