The Arctic, a vast and enigmatic region at the northernmost part of our planet, has long captivated explorers, scientists, and nature enthusiasts alike. At its heart lies the Geographic North Pole, where the Earth’s axis of rotation intersects with its surface, located in the Arctic Ocean. Unlike Antarctica, which is on land, the Arctic is covered year-round by drifting sea ice, creating a unique and challenging environment. This frozen realm is not just a single point on the map, but a complex ecosystem spanning multiple countries and encompassing distinctive geographical, climatic, and biological features. The harsh climate makes it extremely difficult to build permanent research stations, yet the Arctic has attracted numerous expeditions throughout history, with the first successful conquest by hot air balloon in 1926.
From the mesmerizing Northern Lights to its crucial role in global climate regulation, the Arctic is a place of wonder and scientific importance. This article delves into the geography, characteristics, and significance of the Arctic region, exploring its definition, the differences between the geographic and magnetic North Poles, and the fascinating phenomena that make this icy wilderness one of Earth’s most extraordinary environments.
However, it’s important to distinguish between the Geographic North Pole and the Earth’s Magnetic North Pole.
Geographic North Pole
- Is the northernmost point of Earth.
- Located in the Arctic Ocean.
- Is an imaginary point, with no physical location.
- Determined by Earth’s axis of rotation.
Magnetic North Pole
- Is where Earth’s magnetic field points straight down.
- Located on Bathurst Island, Canada.
- Is a real point with specific coordinates. (82.7°N 114.4°W)
- Moves over time.
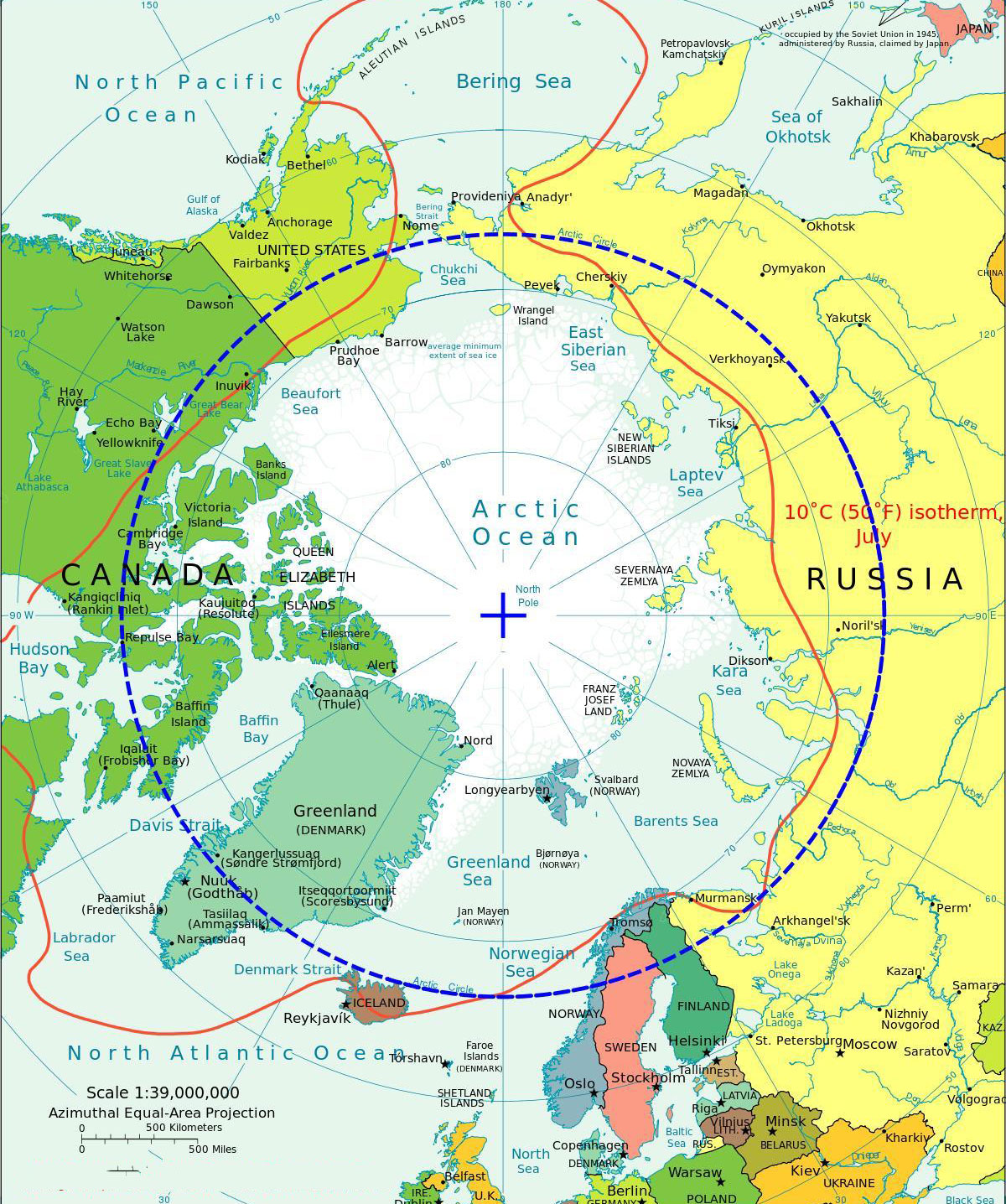
Above, we’ve discussed the North Pole of Earth, but in everyday communication, when we mention “the Arctic,” we usually understand it as the region near the North Pole of Earth rather than a single coordinate point. To determine which area can be called the Arctic region, we’ll explore a term called the Arctic Circle.
The Arctic Circle is defined by the latitude 66° 33′ 39″ (or 66.56083°) north of the equator. The area north of this circle is called the Arctic region. Within the Arctic region, there will be at least one day in the year when daylight lasts for 24 continuous hours, and similarly for night. The closer to the pole, the longer these periods of continuous daylight and night can be, not just 24 hours but even many days or months. This is due to the Earth’s axial tilt, which remains constant as the Earth orbits the Sun; thus, during summer, the North Pole always receives sunlight.
Looking at the map, we can see that the Arctic region includes the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Alaska (USA), northern Canada, Greenland, Denmark, Russia, Iceland, Norway, Sweden, and Finland.
The Arctic region is considered the world’s second-largest desert by area after Antarctica. The land in the Arctic region has snow and ice cover that changes seasonally, with permafrost (permanently frozen subsoil) containing resources. The Arctic Ocean contains seasonal sea ice in many places.
The Arctic is much warmer than Antarctica because it is at sea level in the middle of an ocean (which acts as a heat reservoir), rather than at a high altitude on a continent. This allows the Arctic region to have a rich ecosystem, including ice-living organisms, plankton, fish and marine mammals, birds, land animals, plants, and even human settlements.
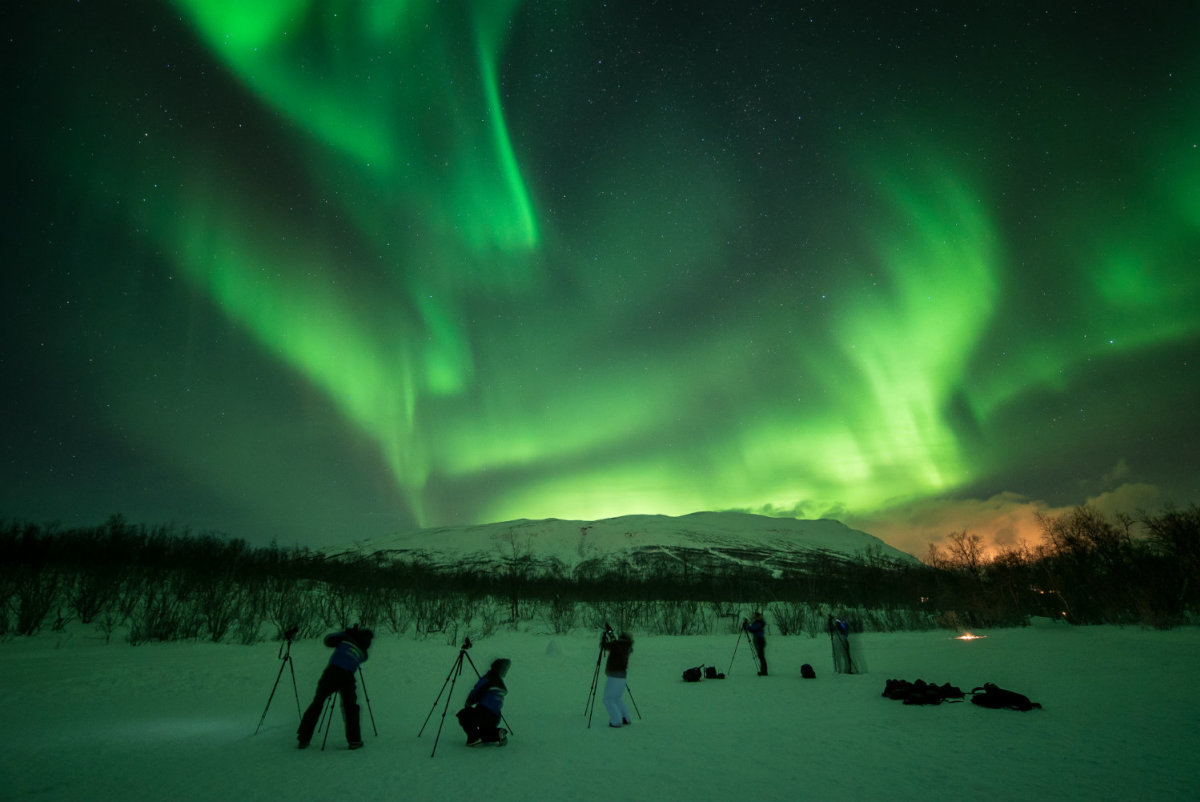
People living in the Arctic region can observe beautiful auroras. Auroras are arc-shaped clusters of light that constantly move with many colors against the night sky. The aurora phenomenon occurs due to the collision of particles in the solar wind with gases in the atmosphere.
Some famous places to view auroras:
- Iceland: Kirkjufell mountain peak, outskirts of Reykjavík, Grotta lighthouse, …
- Sweden: Kiruna town
- Finland: Rovaniemi town, Lapland region, …
- Norway: Tromsø urban area, Lyngen Alps mountain range, Lofoten archipelago, …
- Alaska, USA: Fairbanks city
- Canada: Prosperous Lake, Yellowknife city
See more
- Saint Kitts & Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Samoa
- San Marino
- São Tomé & Príncipe
- Saudi Arabia
- Senegal
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Singapore
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Solomon Islands
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Korea
- South Sudan
- Spain
- Sri Lanka
- Saint Vincent & the Grenadines
- Sudan
- Suriname
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Syria
- Saint Helena
- Saint Barthélemy
- Saint Martin
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Somaliland